Unit 3 - Biomolecules
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A1.1, D2.3, A1.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Water
Medium for life
Most biochemical processes happens in water
Water is a solvent in which these reactions can happen
Main component for many fluids such as the cytoplasm, blood, etc.

Cohesion
The ability of like molecules to stick together
Water is very cohesive (forms hydrogen bonds)
Surface tension of water
Water molecules stick close together due to cohesive force
The tension must be broken in order for something to enter the water
The surface of the water is a habitat for animals
Xylem transportation
Water in plants move through the xylem
Because of cohesive force, there is tension which pulls the water up the xylem from the roots
Transpiration - water evaporates from the leaves
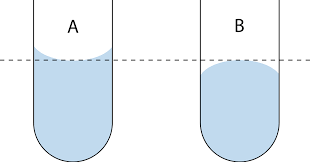
Water adhesion
The ability for dissimilar molecules to stick together
Water will form intermolecular associations with polar and charged molecules
Water can form menicuses and capillary action
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid (DNA)
De-oxygenated
Codes forinformation
Makes RNA during transcription
RiboNucleic Acid (RNA)
Codes for proteins during translation
Multiple versions (3) - tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
Virus
Are not cells - lack the properties required to be considered a “living” cell
Have RNA or DNA as genetic material
Nucleotide (RNA & DNA)
Components:
5 carbon pentose sugar - ribose or deoxyribose
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous base connects to 1’carbon of the sugar
Phosphate base attached to 5’ carbon of the sugar
When connecting two nucleotides, a covalent bonds forms from a condensation reaction - 5’carbon on one molecule to the 3’ carbon of another (sugar phosphate backbone)
Purines (larger)
Adenine, Guanine
Pyrimidines (smaller)
Cytosine , Thymine(+Uracil)
Nulceosome structure
Negatively charged DNA strand binds to the positively charged histone proteins
DNA strand is wrapped around 8 histones, one secures the form
4 different types of histones in each nucleosome
Nucleosomes are connected together by linker DNA
Supercoiling
Wrapping around of histones protects DNA
Histones also assist in the supercoiling of DNA (mitosis & meisosis)
DNA cannot be read when it is supercoiled
Hershey-Chase experiment
Bacteriophages grew in 2 different conditions - radioactive phosphorus & sulfur
DNA doesn’t contain sulfur
Bacteriophages infected bacteria - those injected with sulfur did not have any left - those injected with phosphorus were found to still contain phosphor
Genetic information was deemed to have been made of DNA
Chargaff’s rule
DNA contains the same number of adenine as thymine (or any other base pairing)
Capillary action
Ability of water to flow in narrow spaces, even against gravity
Due to cohesion and adhesion
In soil
Adhesion - water adheres to soil particles
Cohesion - water molecules stick together, bringing each other up through tiny pores of the soil
In xylem
Water in xylem can adhere to the sides - adhesion
Water molecules pull each other up - cohesion
Solvent properties of water
Hydrophilic particles dissolve in water - (polar, positive or negative - amino acids, some proteins, or substances that adhere to water)
Hydrophobic molecules do not dissolve in water - (lipids - oils, fats)
Physical properties of water
Buoyancy
Viscosity
Thermal conductivity
Heat capacity
Origin of water theory
Most water on Earth exists in two forms:
Water
Heavy water (H+ with a neutron) - deuterium
Ratio of water & deuterium is similar to that on asteroids
Theory that water came from asteroids bringing minerals, releasing water - as early Earth only had magma on the surface
Goldilocks zone
The certain distance between the sun and a planet in a solar system in order to have water - with correct temperature and gravity to retain water
Earth also has an atmosphere and magnetic field to protect against harmful radiation
Water potential - Ψ
Measures the potential energy per unit volume in water
Main factor for the movement of water in living organisms
Measurements are compared to pure water as a reference point (at room temperature & atmospheric pressure)
Kilopascals (kPa) or megapascal (mPa)
Solute potential + pressure potential = water potential
High Ψ → low Ψ
Water movement in plants
Ψ decreases from root to tip - from soil (high Ψ) → to roots (low Ψ)
Water also moves from low solute concentration → to high solute concentration (in cells) - osmosis
Transpiration, water loss - makes pressure potential drop
Pressure potential dropping → more water moves up
Water potential in plant tissue
Hypertonic solution - less solute conc. inside cell
Higher Ψ in the roots - higher solute potential outside of the cell
Ψ goes from high to low - water moves out of the roots
Plant will wilt as pressure potential drops - flaccid cell?
Hypotonic solution - higher solute conc. inside the cell
Roots have a lower Ψ - solute potential is higher inside of the cell ??
Water moves into the root
Pressure potential will increase until its high enough to stop inward movement
Polar covalent bond
Oxygen and two hydrogens unequally share electrons
Oxygen becomes slightly negative, hydrogen becomes slightly positive
Carbon
Atom that can form up to 4 covalent bonds with other atoms
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds, consisting of one(monosaccharide) or more(di- polysaccharide) simple sugars
Glucose - Monosaccharide
Form of sugar - hexose
Fuels respiration
Base unit for many polymers
Fructose - Monosaccharide
Pentose sugar
Found in fruits, honey
Sweetest natural occurring carbohydrate
Polysaccharides
Cellulose - plants
Amylose - plants
Amylopectin - plants - branched
Glycogen - animals - branched
Lipids
Water insoluable organic molecules
Glycoproteins
Polypeptide with an attached carbohydrate
Part of the plasma membrane - cell to cell recognition
Nucleotide
Consists of:
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous gas
Pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
Amino acid
Consists of:
Central carbon
Amine group
Carboxyl group
Variable group (R-group) - what gives amino acids different properties (polar, charge)
Hydrolosis
When organic molecules break apart
Water is needed to break the bond
Is done because smaller molecules are easier to absorb
Enzymes control the process
Condensation reaction
When organic molecules join together
Water is formed as a byproduct
Used to build up & store large molecules
Ribose - Pentose
Sugar in RNA
Has 5 carbons
Deoxyribose - Hexose
Sugar in DNA
Has 6 carbons