FINAL Flashcards CP Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/163
Last updated 9:08 PM on 1/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
What is a macromolecule?
A large, complex assembly of molecules. **Made up of monomers.**
2
New cards
What is matter?
Anything–from which objects are made up of atoms–that has a mass (weight), and occupies space (volume).
3
New cards
What is an atom?
The basic building blocks of everything around you (that you can not see).
4
New cards
What is a molecule?
A group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound.
5
New cards
What are the six elements found in all living things?
1. Carbon
2. Hydrogen
3. Nitrogen
4. Oxygen
5. Phosphorus
6. Sulfur
6
New cards
What is meant by “You are what you eat”?
The macronutrients that you take in each day determine how well your body works and supports itself.
7
New cards
What happens in a chemical reaction?
Chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products.
8
New cards
Monomer
A single form of a macromolecule
9
New cards
Polymer
Multiple monomers bonded together
10
New cards
What is the function of carbohydrates?
Used as an immediate energy source in living organisms. When it is not used it’s stored in fat cells.
11
New cards
Monosaccharide
The monomer of carbohydrates.
12
New cards
What is the function of lipids?
Essential for the health of cell membranes and long term energy storage.
13
New cards
Fatty acids
The monomer of lipids.
14
New cards
Fat (lipids) is used for _________ in animals, otherwise known as _______.
insulation; blubber
15
New cards
What is the function of proteins?
Proteins help repair cells and make new ones. Proteins are also important for development and function.
16
New cards
Amino acids
The monomer of protein.
17
New cards
What is the function of nucleic acids?
Store information, include instructions for life, and coding for proteins (DNA).
18
New cards
Nucleotides
The monomer of nucleic acids.
19
New cards
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA (double stranded) and RNA (single stranded).
20
New cards
Where does the mass of a tree come from?
The mass of a tree comes from the carbon in the air.
21
New cards
What are autotrophs?
Organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis.
22
New cards
What are heterotrophs?
Organisms that cannot make their own foods and must eat other organisms to obtain energy.
23
New cards
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
One, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Two, energy can be transformed from one form to another.
24
New cards
What is an example of energy transfer?
Potential → kinetic energy.
25
New cards
What are the two main chemical reactions that allow for life on Earth?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
26
New cards
Energy is needed to ____ bonds and released when bonds are ______.
form; broken
27
New cards
What is ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate: a portable form of energy.
28
New cards
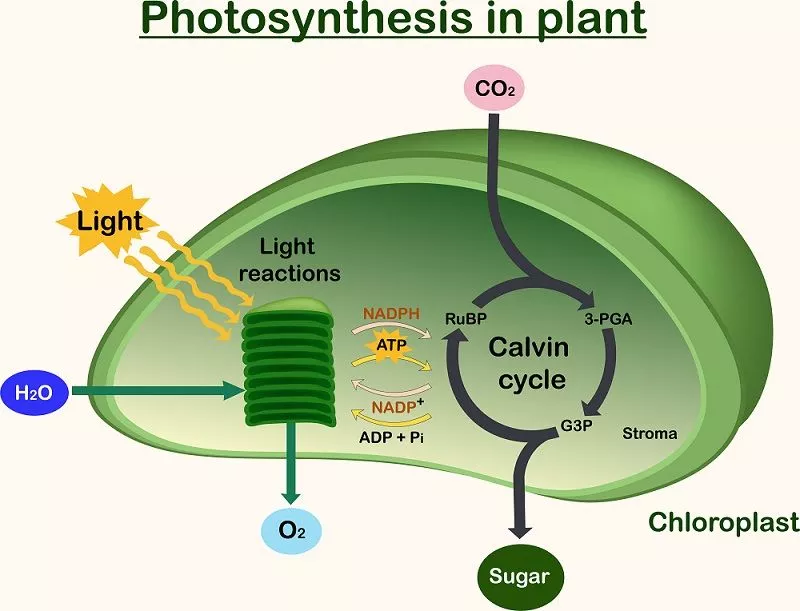
What is photosynthesis?
Process by which plants convert solar energy into glucose. It takes place in chloroplasts of plant cells.
29
New cards
Photosynthesis has how many stages?
Two stages called the light and dark reaction.
30
New cards
Photosynthesis reaction:
The reactants: *Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight*
The products: *Glucose and oxygen*
The products: *Glucose and oxygen*
31
New cards
What are the inputs and outputs of the light reaction (step 1)?
Input: *Water (H20) and sunlight*
Output: *ATP, NADPH (go to Calvin Cycle)*
**Byproduct:** *Oxygen*
Output: *ATP, NADPH (go to Calvin Cycle)*
**Byproduct:** *Oxygen*
32
New cards
What are the inputs and outputs of the Calvin cycle (dark reaction)?
Input: *ATP, NADPH, CO2*
Output: *Glucose (C6H12O6)*
Output: *Glucose (C6H12O6)*
33
New cards
The dark reaction is a __________ cycle.
“continuous”
34
New cards
What is G3P?
An end product of photosynthesis: It can be used to make GLUCOSE, OR Fatty Acids, OR Amino Acids.
35
New cards
Why is photosynthesis and autotrophs important to life on Earth?
Autotrophs take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the atmosphere. This oxygen is what we need to breathe and survive.
36
New cards
Why are phytoplankton important?
They produce half of the oxygen we breath and take in large amounts of CO2.
37
New cards
What affects the rate of photosynthesis?
1) Light intensity/color
2) Temperature
3) Water
4) Health of soil/environment
2) Temperature
3) Water
4) Health of soil/environment
38
New cards
Why is the mitochondria important for cellular respiration?
The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell that provides energy throughout the cell.
39
New cards
Who goes through cellular respiration?
Every living organism.
40
New cards
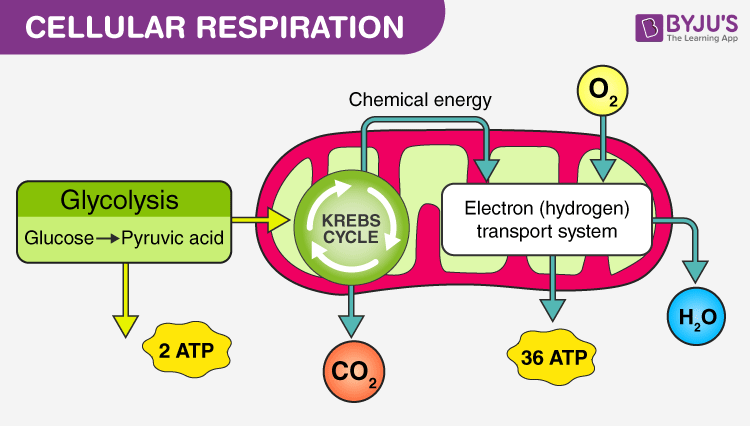
What is cellular respiration?
The process of **releasing** energy stored in the bonds of glucose.
41
New cards
Why is cellular respiration important?
It provides our cells with energy so that they might function and run our system properly.
42
New cards
Which macromolecules are enzymes?
Proteins.
43
New cards
What is the importance of enzymes?
They save energy in our body by using less energy over time, and speed up chemical reactions.
44
New cards
What are the stages of cellular respiration?
Aerobic (Oxidative respiration) and Anaerobic (Glycolysis).
45
New cards
What is the aerobic stage of cellular respiration?
Presence of oxygen. Breaks down glucose with oxygen to release ATP (and CO2 and H2O)
46
New cards
What is the anaerobic stage of cellular respiration?
The stage with an absence of oxygen.
47
New cards
What happens in Glycolysis (stage 1)?
Glucose is broken down to be sent to the next stage, it takes place in the cytoplast, and 2 ATP of stored energy is released in this process.
48
New cards
Where does stage 2 (Oxidative respiration) occur?
In the mitochondria.
49
New cards
What are the two reactions that occur in Aerobic Oxidative Respiration?
Kreb Cycle and ETC.
50
New cards
What should I know about the Kreb Cycle?
**Byproduct:** CO2
**Found in:** Mitochondria
**Energy produced:** 2 ATP
**Found in:** Mitochondria
**Energy produced:** 2 ATP
51
New cards
What should I know about ETC (Electron Transport Chain)?
**Byproduct:** Water
**Found in:** Mitochondria
**Energy produced:** 34 ATP
**Found in:** Mitochondria
**Energy produced:** 34 ATP
52
New cards
How much energy is produced in total by cellular respiration?
38 ATP.
53
New cards
Fermentation occurs after glycolysis when:
Oxygen is not present or the organism has no mitochondria.
54
New cards
What are the types of fermentation?
Lactic acid and alcoholic (ethanol).
55
New cards
Where does lactic acid fermentation occur and how much energy does it produce?
It occurs in the muscles, and it produces 2 ATP.
56
New cards
Where does alcoholic fermentation occur and how much energy does it produce?
It occurs in yeast, some bacteria, and plants, and it produces 2 ATP.
57
New cards
Why is aerobic respiration preferred over fermentation?
Aerobic respiration is preferred because it produces more ATP.
58
New cards
Why is Earth called a “closed system”?
The elements used on the planet do not leave the system, they just cycle through in various forms.
59
New cards
What is the biosphere?
This sphere contains all living organisms.
60
New cards
What is the hydrosphere?
This sphere contains all water sources.
61
New cards
What is the atmosphere?
This sphere contains gasses like carbon dioxide and oxygen, etc.
62
New cards
What is the geosphere?
This sphere contains rocks, land/dirt, and clay.
63
New cards
What is combustion?
The process of burning things, especially fossil fuels.
64
New cards
What is a system?
A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or an interconnecting network.
65
New cards
What are the parts of system?
Components, boundaries, inputs, and outputs.
66
New cards
What is ecology?
The study of relations of organisms to one another and to their physical environment.
67
New cards
What is ecosystem?
A community of living organisms that live, feed, reproduce and interact in their physical environment
68
New cards
What are abiotic components?
The nonliving things inside an environment.
69
New cards
What are biotic components?
The living things inside an environment.
70
New cards
What is biodiversity?
The variety of life in the world or a particular habitat/ecosystem.
71
New cards
Why is biodiversity important?
All species are better able to adapt to change if there are lots of producers, consumers and decomposers.
72
New cards
What are producers?
Make or produce their own food (photosynthesis and chemosynthesis).
73
New cards
What are consumers?
Consume or eat other plants and animals to obtain their energy.
74
New cards
What are decomposers?
Consume dead plants and animals and break them down into nutrients that are released into the soil.
75
New cards
Herbivores eat _____*,*__ while carnivores eat *___*, and omnivores eat ___.
plants; meat; both
76
New cards
What is a community?
A group of organisms of different species growing or living together in a specified habitat.
77
New cards
A population is…
All the organisms of a given species that live in a particular area.
78
New cards
What is a food chain?
A hierarchical series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food.
79
New cards
What is a food web?
A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
80
New cards
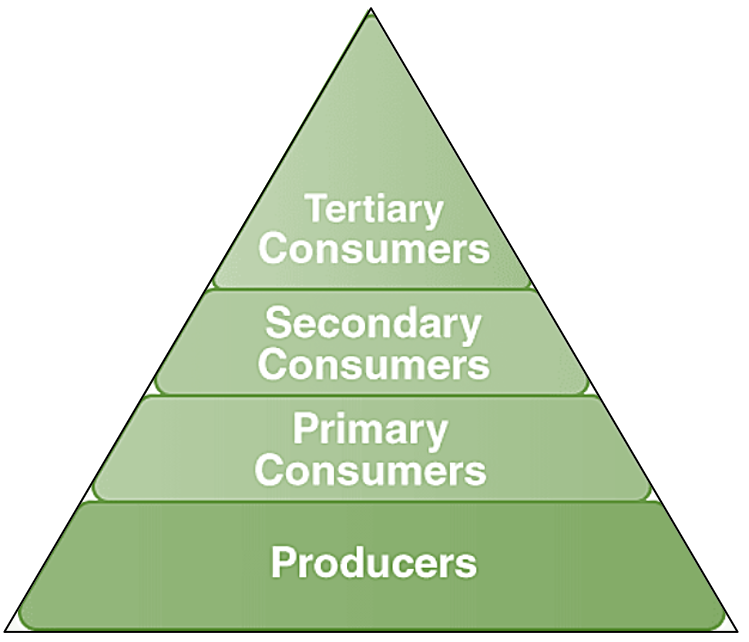
What is the purpose of an energy pyramid?
Showing the flow of energy at each trophic level of a food chain.
81
New cards
Where does the most energy come from?
The sun.
82
New cards
What is the 10% rule with energy?
As energy transfers up the pyramid, 10% of the energy is lost as heat with each trophic level.
83
New cards
What is a Trophic Cascade?
The addition/removal of a species which triggers a domino effect in an ecosystem.
84
New cards
What are Keystone Species?
Species on which other species in an ecosystem largely depend on.
85
New cards
What is Carrying Capacity?
The maximum number of individuals of a species in an environment that can support in the long term
86
New cards
What are limiting factors?
Anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing.
87
New cards
What is symbiosis?
An evolved interaction between two different species usually with benefits to one or both of the individuals.
88
New cards
Commensalism is…
An interaction between two organisms in which one benefits and the other receives no benefit nor harm.
89
New cards
Parasitism is…
A relationship between species, where one organisms lives on or in another organ and causes it harm or death.
90
New cards
Mutualism is…
A relationship between two different species of organisms where each gains benefits from the other species.
91
New cards
What are invasive species?
A non-native species that is introduced to and negatively alters its new environment.
92
New cards
What is homeostasis?
The state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by ANY living system. (Equilibrium)
93
New cards
What is the function of the heart/circulatory system?
Pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body.
94
New cards
What is the function of the kidneys/excretory system?
To cleanse the blood of toxins and transform the waste into urine.
95
New cards
What is the function of the lungs/respiratory system?
To move fresh air into the body and remove waste gas.
96
New cards
What is the function of the pancreas/digestive and endocrine system?
Controls blood sugar levels (releases insulin to lower, and glucagon to increase) and breaks down food.
97
New cards
What is an endotherm?
A warm blooded animal that can regulate its own body temperature.
98
New cards
What is an ectotherm?
A cold blooded animal that cannot regulate its own body temperature and uses the environment instead.
99
New cards
What are feedback loops?
Functions ordered by the brain to bring the body system back into homeostasis.
100
New cards
Positive feedback loops occur when…
A potential dangerous OR stressful process must be completed quickly before homeostasis can be restored.