Peds Orthopedics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Scoliosis
A spinal deformity in which there is a lateral curvature and rotation of the vertebrate in the spine greater than 10 degrees.
if greater then 10 degrees on screen => referal
Congenital Scoliosis
condition of birth with a lateral curvature of the spine
anomolous vertebral development
Infantile Scoliosis
onset of scoliosis before 3yrs old
Juvenile scoliosis
Detected between ages 3-10
neuromuscular scoliosis
associated with neurological or muscular diseases
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
• Present in 2 to 4 percent of children between 10 to 16 yrs. old
• Possible genetic link because it is often seen in multiple family members.
• most common form, More common in girls
• Of adolescents diagnosed with AIS, only 10% have curve progression requiring medical attention.
Curve Progression
•Double curves progress more than single curves
•Larger curves (30-40°) progress more than smaller curves (20-30°)
•Females progress more than males
•Increase risk of curve progression during Peak Height Velocity during adolescent growth spurt (girls Tanner 2-3, boys Tanner 3-5)
Scoliosis S/Sx
•One shoulder higher than other
•One shoulder blade sticks out more than other
•One side of rib cage appears larger than the other
•One hip higher and more prominent
•Waist appears uneven
•Body tilts to one side
•One leg appears shorter than other
•Head not centered over body
•PAIN ON SPINE IS NOT A TYPICAL SYMPTOM

Scoliosis Screening
Females screened twice (age 10 and 12)
Males screened once (age 13 or 14)
should not just be just in school
Scoliosis Hx Questions
•Primarily diagnosis of exclusion
•Family history of scoliosis or other musculoskeletal disorders
•Menstrual onset
•Development of secondary sexual characteristics and recent growth patterns
•Presence of pain and neurologic changes including bowel and bladder dysfunction because this is atypical for AIS
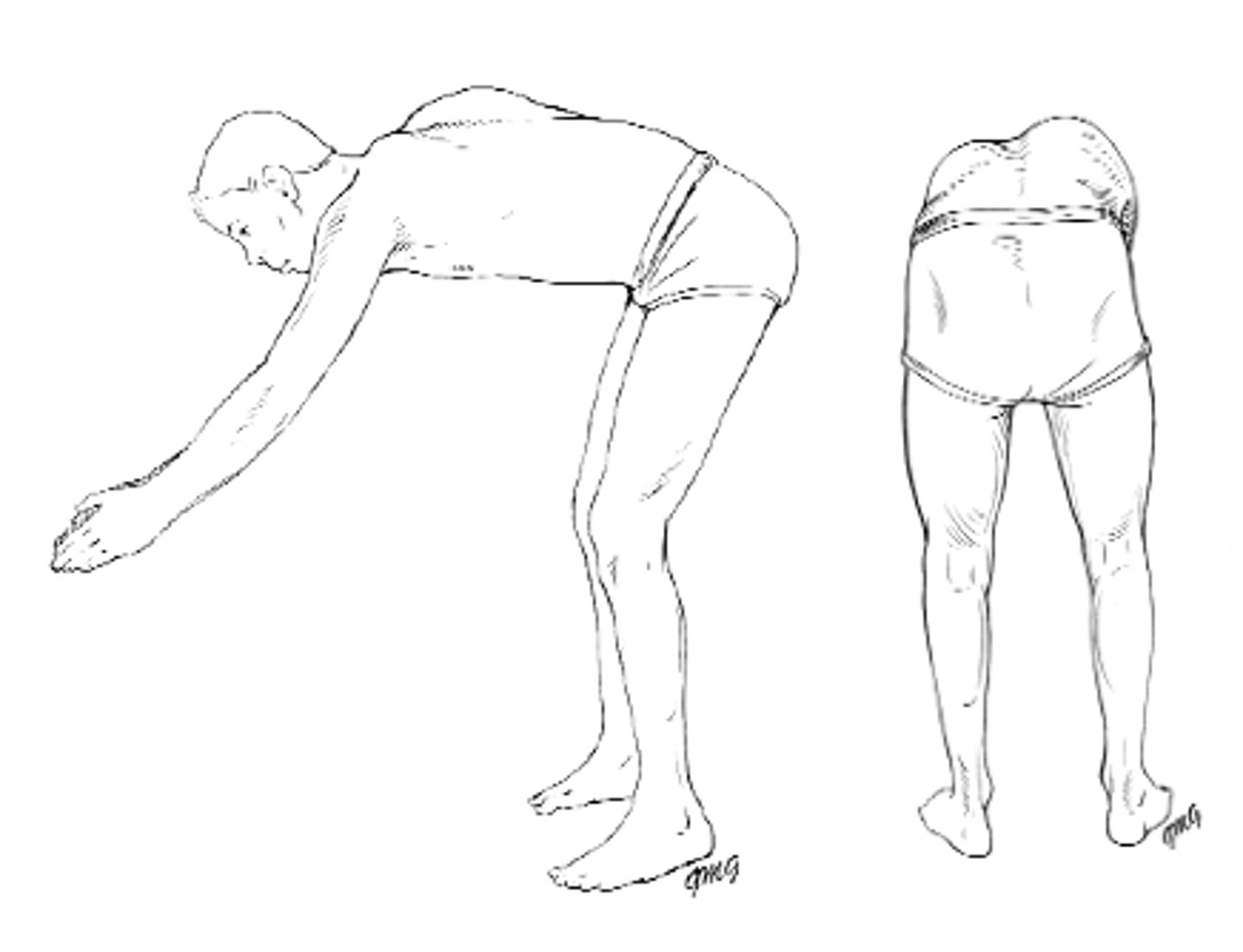
Adams bend forward test
Bend forward at waist until spine becomes parallel to the floor while holding palms together with arms extended.
Examine child from behind and side looking for asymmetry in the contour of the back (rib hump)
Flexibility should also be evaluated by stabilizing the spine and asking the child to twist to both sides
Ninety percent of curves are to the right, left thoracic concerning
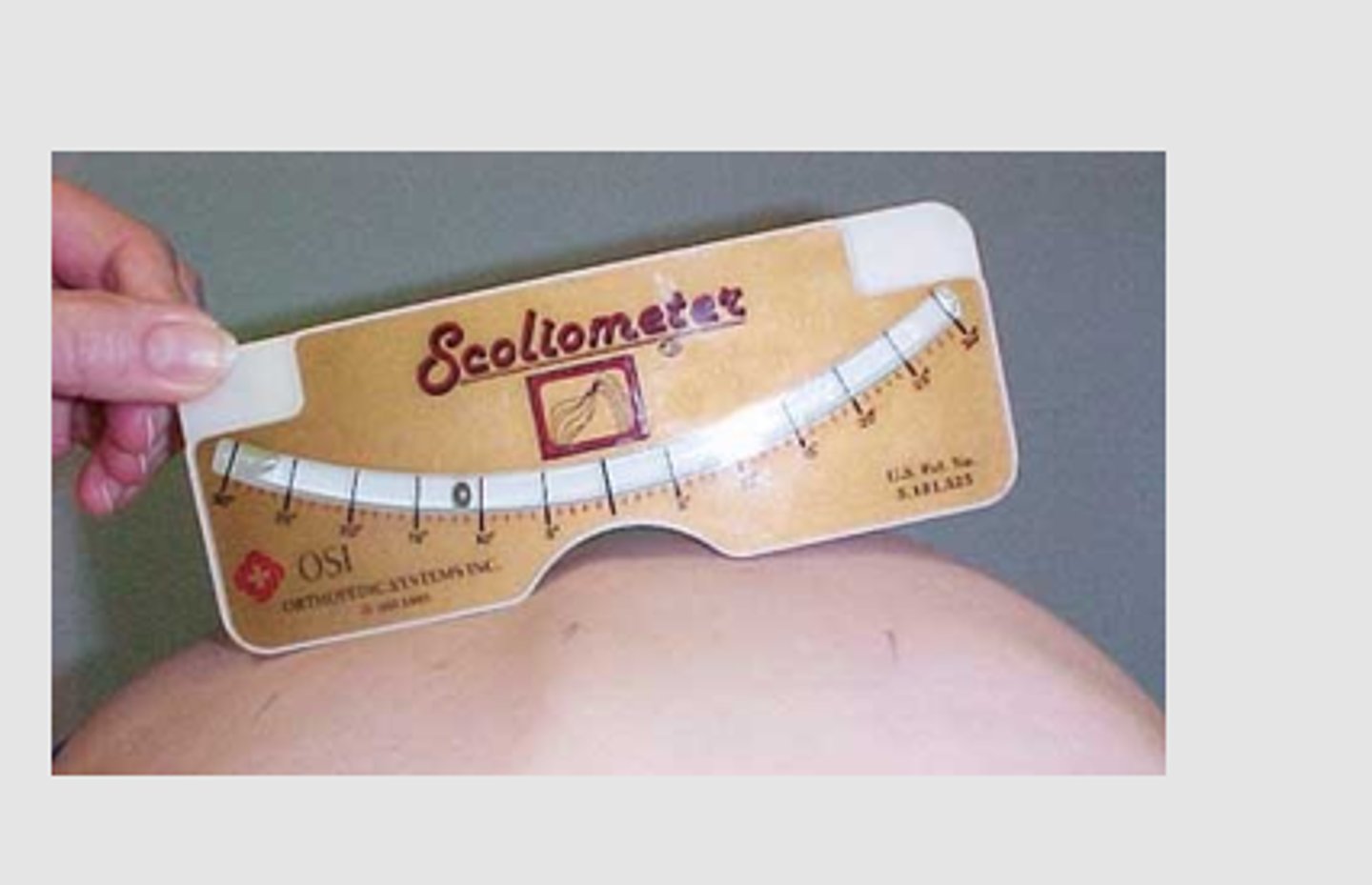
Scoliometer
Measuring device that may be used to obtain a measurement of the number of degrees that the spine is deviated in scoliosis.
7-10: just monitor
>10: needs referal
Screening tool
Scoliosis Diagnosis Primary concerns
Primary concerns: possible underlying cause and curve progression
Determinants of progression: gender, future growth potential and curve magnitude at time of diagnosis.
What is evaluated for potential growth of scoliosis curve
•Tanner Stage assessment
•Risser scale-evaluates skeletal maturity
•Bone Age
•Cobb Angle
Risser scale-evaluates skeletal maturity
the further along the growth plate has closed on the hip the less growth there is left
higher the number the less curve progression risk
Bone age
A measure of physical maturation based on x-ray examination of bones, typically the wrist and hand growth plates
determines closer of the growth plate
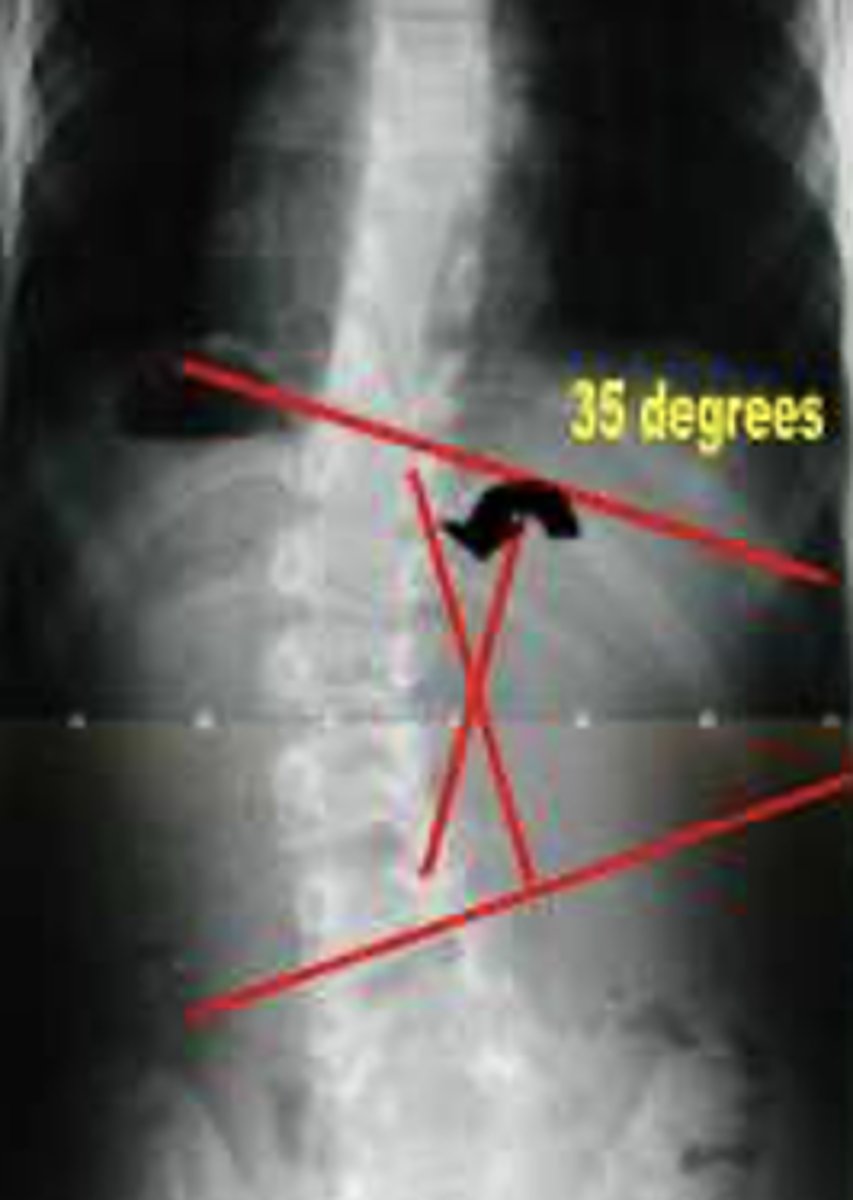
Cobb Angle
Measured to define scoliosis. > 10° is needed for dx.
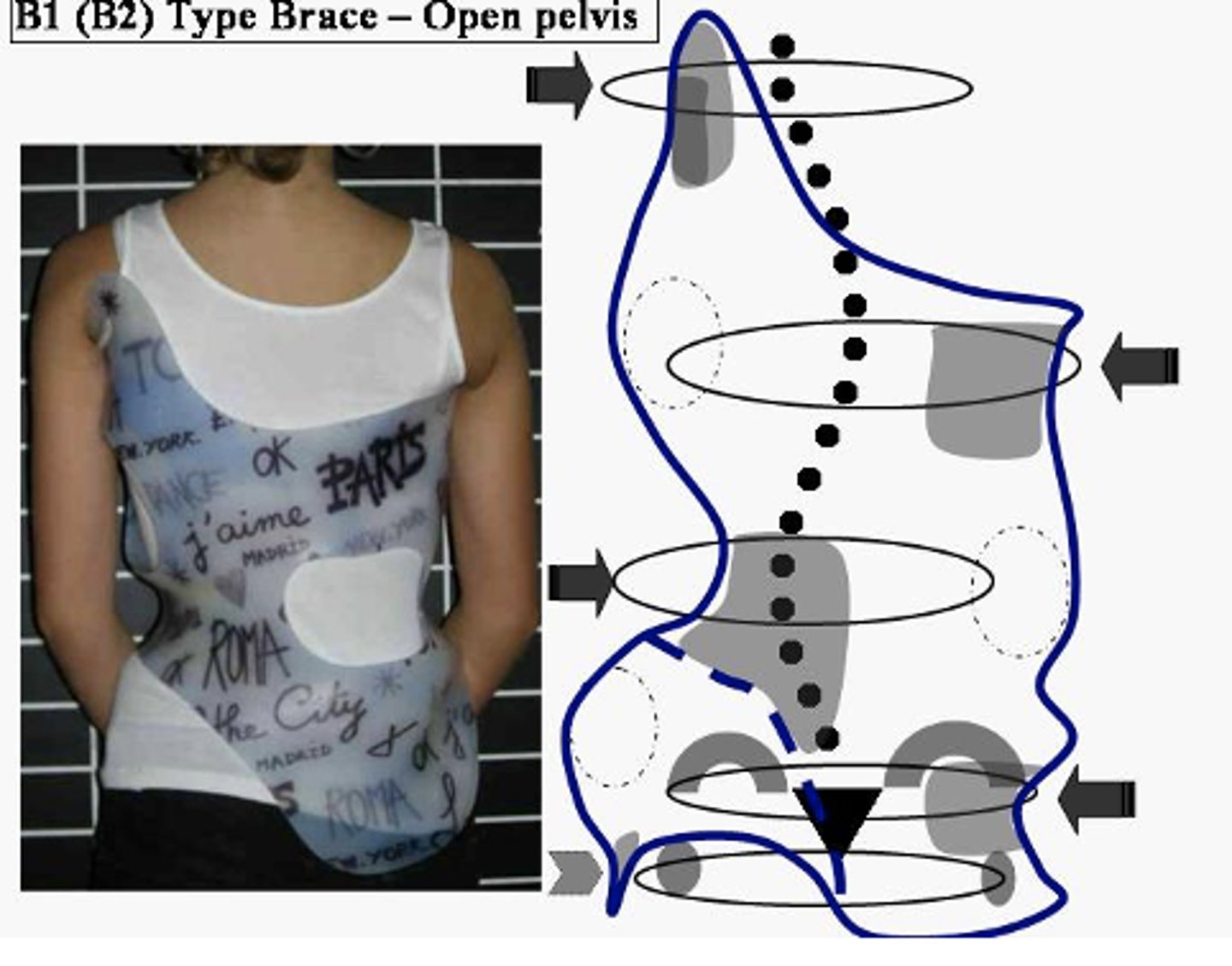
Bracing Treatment
•Skeletally immature child
•Curve > 30° Or
•Curve which increased from 10°- >25°
•Goal: prevent curve progression or until curve progression can't be controlled
•Worn 18 - 23 hours/day
•Part time or night time bracing may be effective for curves <35°
•Should be continued until growth stopped
•Compliance a cause for poor results
Spinecor Brace
research has shown to NOT be effective!
RSC Brace
in conjunction with exercises can correct lateral and rotational curves
Schroth Method
PT approach to scoliosis treatment based on exercises tailored to each pt's spine curvature
lots of lengthening and stretching
*includes use of RSC brace when not stretching
*exercises MUST be done every day to be effective
surgery for scoliosis objectives
Indication: Cobb angle >45°
Objectives of surgery
1. Arrest progression
2. Achieve maximum permanent correction
3. Improve appearance
4. Keep short & long term complications to a minimum
short & long term complications of scoliosis
- nerve damage
- organ damage from compression
Surgery for scoliosis method
•Fusing the vertebrae along the curve
•Supporting fused bones with instrumentation attached to spine
•Bone grafts fuse the vertebrae together
•Many surgical variation exist using different instruments, procedures and surgical approaches.
•Cause of scoliosis usually determines type of procedure
Complications of scoliosis Surgery
•Bleeding
•Postoperative pain
•Infection
•Nerve damage
•Pseudoarthrosis
•Disk degeneration and low back pain
•Complications that involve lungs and circulation
•Flat back syndrome with Harrington rod.
•function takes a long (no sports for a year)
•no NSAIDS
Clubfoot
•Involves bone deformities & malposition with soft tissue contractures
•Talipes Equinovarus (TEV) most frequently occurring clubfoot (95%)
•Early evaluation & treatment for optimum correction
Talipes Equinovarus (TEV)
Complex deformity of the ankle & foot
- forefoot adduction: toes point in
- midfoot supination: turns upward
- hindfoot varus-heel: turns inward
- ankle equinus-toes: point downward
Clubfoot Incidence
•1-2/1,000 live births
•Affects boys nearly twice as often as girls
•Bilateral in 50% of the cases
•A positive family history is associated with an increased incidence
Etiology of Clubfoot
Exact cause is unknown:
* intrauterine positioning
* neuromuscular or muscle abnormality
* genetic predisposition
* arrested fetal development of skeletal and soft tissue
* amniotic banding
* oligohydramnios, a decreased amount of amniotic fluid
* breech delivery
categories of clubfoot
positional, syndromic, congenital
positional clubfoot
Occurs primarily from intrauterine crowding (twins, LFGA)
Responds to simple stretching and casting
Syndromic (tetralogic) clubfoot
associated with other congenital abnormalities (spina bifida)
More severe form, often requires surgery
congenital (idiopathic) clubfoot
occur in otherwise healthy infants
It is the most common form.
other symptoms of clubfoot
•Small foot
•Shortened Achilles tendon
•Underdeveloped calf muscle
•Empty heel bed
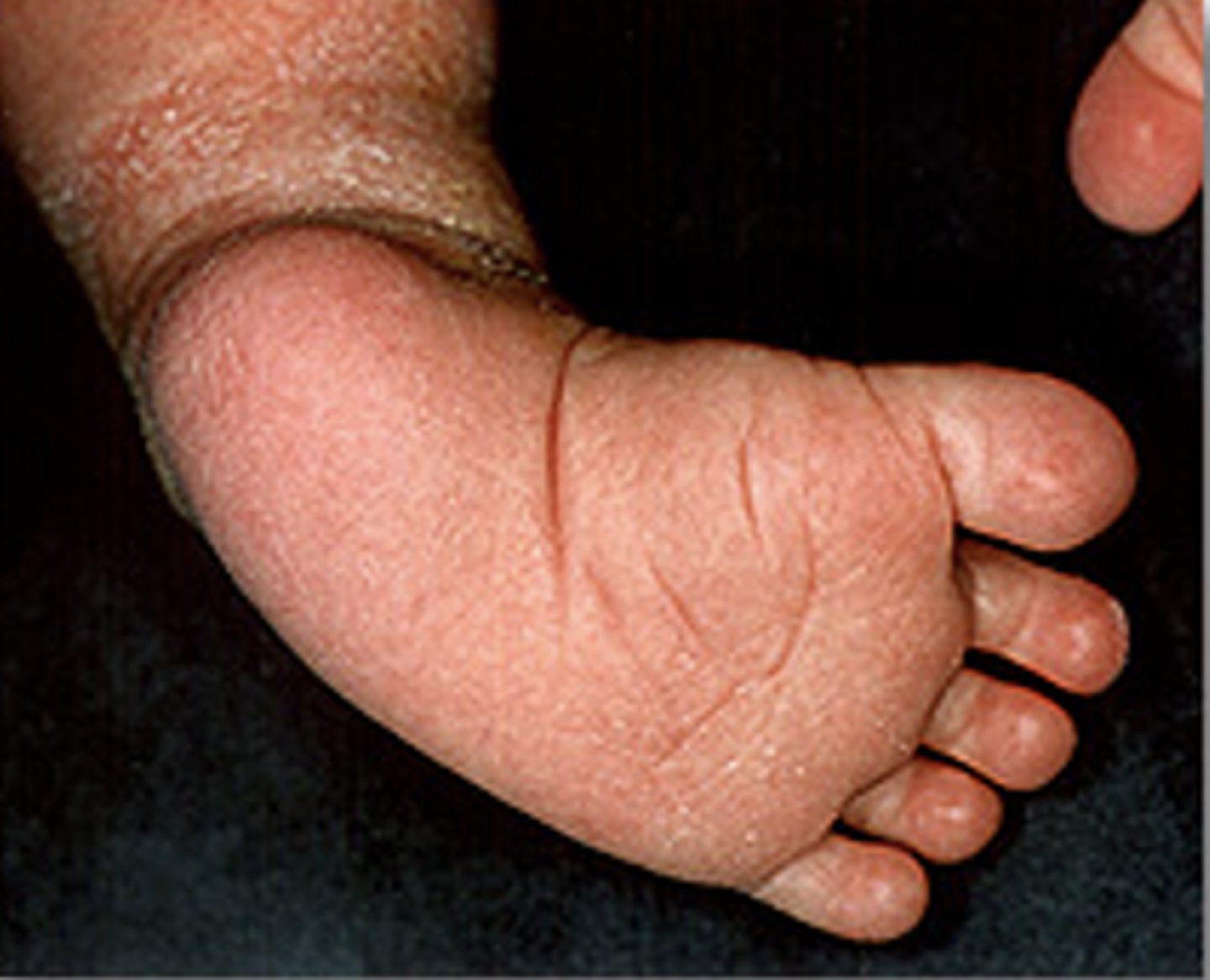
•Transverse plantar crease (image)
•Normal leg lengths
Diagnosis of clubfoot
•May be detected antenatally
•Diagnosis at birth - visual inspection
•Radiographs to confirm degree and severity of deformity
•MRI may also be used
Clubfoot Treatment
•Early treatment is essential to achieve successful correction and reduce chance of complications
•Serial casting is begun immediately or shortly after birth.
•Successive casting allows for gradual stretching of skin and tight structures on medial side of foot.
casting for clubfoot
•Every few day for first 1 to 2 weeks
•Then every 1 to 2 weeks until maximum correction is achieved.
•Avoid overcorrection can cause rocker bottom foot.
•If corrected, child wears splint (Denis Browne Splint) or corrective shoes.
•If deformity has not been corrected, surgical intervention is required between 3 - 12 months.
Clubfoot prognosis
•Parents should realize that outcomes are not always predictable and depend on severity of deformity, age of child at initial intervention, compliance with treatment, and development of bones, muscles & nerves
•Surgical intervention does not restore the ankle to an entirely normal state with the affected foot & leg remaining smaller & thinner than unaffected side.
•Most children after surgical repair are able to walk with out a limp and run or play.
•25% chance of reoccurrence
•With severe deformities, repeated surgeries.
Contusions Injuries
damage to soft tissue, subcutaneous structure & muscle
Sprains
severe trauma to a joint causing a ligament to be partially or completely torn.
Strains
injury to the muscle near the musculotendinous junction, as a result of a forceful contraction of the muscle.
Dislocation & Subluxation
dislocation and subluxation refer to the displacement of bones that form a joint.
These conditions affecting the joint most often result from trauma that causes adjoining bones to no longer align with each other. A partial or incomplete dislocation is called a subluxation
Therapeutic Management of injuries (contusion, sprain, etc)
RICE - NO HEAT
- 20 min of ice max with barrier
Immobilization
Fractures
•In children, they are result of increased mobility &/or immature motor & cognitive skills
•Infancy - RARE
•Traumatic musculoskeletal injuries most frequent
•Clavicle most frequent bone broken
•Epiphyseal injuries - Salter-Harris classifications
Stress Fractures
•Overuse injury
•Becoming more common in adolescents who limit intake of calories and calcium to remain lean for sports
Stress Fractures Symptoms
chronic pain that changes with intensity and focal tenderness in a singular site on the bone.
RDA - calcium
1500 mg/day for adolescents
Fracture Diagnosis
Symptoms
- pain or tenderness @ site
- immobility or decreased ROM
- deformity of extremity
- edema @ site, crepitis, ecchymosis or muscle spasms
X-rays - sometimes of both extremities
Cast Care Edu
nothing down cast
compartment syndrome sign
keep dry
keep elevated
Nursing of Fractures
Initial Assessment
- cause of fracture
- examine fracture site
- neurovascular evaluation
Asses & manage fat embolism
- after crush injury of long bones
- dyspnea, restless, fever over 103, petechie rash tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxia
Compartment Syndrome
•Results from swelling caused by trauma & immobilizing device
•Severe pain unrelieved by analgesics
•Pain more intense than what would be expected from fracture
•Pallor, paresthesia, lack of pulse distal to the trauma
•Pain with extending fingers or toes
Complications of Fractures
•Infection
•Neurovascular injury
•Vascular injury
•Mal-union or delayed
•Leg length discrepancy
Osteomyelitis
•Infection of bone
•Occurs in metaphyseal region of long bones
•Most frequent between 5 to 14 years
•Exogenous
•Hematogenous
exogenous Osteomyelitis
a bone infection caused by germs entering the bone directly from an external source, such as a deep wound, open fracture, or surgery
Hematogenous Osteomyelitis
a bone infection that occurs when pathogens from a distant infection in the body travel through the bloodstream to the bone
acute: within 2 weeks of infection
subacute: longer exposure
Why is Osteomyelitis more common in kids
their growing bones, particularly the metaphysis of long bones, have a rich blood supply that can carry bacteria from an infection in another part of the body
Organisms that cause Osteomyelitis kids
•Staphloccus aureus: most common over 5 years
•Haemophilus influenzae, Strep pneumonia,
•Salmonella & Staph aureus - Sickle Cell Disease
•E coli & B strep - most common in neonates
•Pseudomonas - puncture wounds over 6 years.
•Nisseria gonorrhea - sexually active adolescents
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis
Symptoms – vague & son-specific
- infant: fever, irritability, poor feeding
- older child: pain, warmth & tenderness over site of infection, fever, lethargy, decreased ROM
Diagnosis of Osteomyelitis (lab values and other tools)
Lab Data
- leukocytosis & elevated ESR
- blood cultures
- bone cultures
CT scan & MRI (actual diagnosis)
Therapeutic Management of Osteomyelitis
• Long term IV antibiotics
• monitor for side effects
• Complete bed rest
• Immobilization of affected limb
• May require surgical drainage
Nursing management of Osteomyelitis
• Positioning
• Careful & gentle moving of limb
• Pain control
• Monitor vital signs
• Antibiotic therapy
• May require isolation
• May require casting
• Nutrition
• Non-weight bearing
• Physical therapy