Semester Exam Revision
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
What is an infectious disease?
Diseases that are contagious and are caused by a pathogen.
What is a disease?
Human disease: any change that impairs the function of an individual in some way; it causes harm to the individual.
What is a non-infectious disease?
Non-infectious diseases cannot be spread from one person to another; they are not contagious
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that causes disease
What are the types of pathogens?
Cellular and non-cellular pathogens
What are cellular pathogens?
A microorganism made of cells, such as bacteria and protozoa.
What are non-cellular pathogens?
Pathogens not made up of cells that can't survive on their own without a host, such as prions and viruses.
What are the modes of transmission?
Direct contact, through vectors, contaminated objects and contaminated water.
What is direct contact?
When diseases are spread through contact with another person, and pathogens are directly transferred.
What are vectors?
Organisms that carry disease causing pathogens between organisms without being affected by the disease themselves. For example, mosquitoes and houseflies.
What is the difference between cellular and non-cellular pathogens?
One is made up of cells and can survive on it's own, the other has no cell structure and cannot survive on it's own.
What are contaminated objects?
An object that has a pathogen on or in it.
What is contaminated water?
Water that has many pathogenic organisms living and being carried about in it.
What is a host?
A host is the organism that a parasite lives on or in.
What is a primary host?
The primary host is the organism used for the adult stage.
What is a intermediate host?
Intermediate or secondary host is the host used for the larval stage.
What is the difference between a host and a vector?
Vectors transmit diseases, but don't get infected themselves, and hosts do get infected.
Examples of cellular pathogens?
Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and parasites such as worms
What are parasites living inside the host's body called?
Endoparasites
What are parasites living outside the hosts body called?
Ectoparasites
Are all bacteria bad?
No, their are many good bacteria that live on and in our bodies, and are known as the microbiome.
What is the spherical bacterium called?
Coccus
What is the rod shaped bacterium called?
Bacillus
What is the spiral shaped bacterium called?
Spirochaete
Why do we need the microbiome?
To survive. They play a role in defending us from attack from outside invaders.
What are prions?
They are abnormal and infectious proteins that can convert your normal protein into prion protein.
How do prions spread?
When cells containing prions burst, more of these infectious proteins are released to infect other cells.
What are diseases caused by prions?
Mad cow disease, creutzfeld- Jakob
What is a viruses life cycle.
It enters a host cell, then multiplies inside the host cell, and then bursts out of the cell when it's ready.
What are the major features of a virus?
RNA or DNA, and a protein coat or capsid.
What are protozoans?
Single-celled cellular pathogens.
Where are protozoa commonly found?
In water and tropical regions.
Diseases caused by protozoa?
Head lice and malaria
What are antigens?
Molecules that sit on surface of cells. They are all unique, and allow the body to recognise cells as self or non-self.
How do antigens trigger an immune response?
Antibodies test to bind to antigens, and if it binds B cells activate and neutralise.
What is the first line of defence?
The first line of defence is non-specific, and is designed to prevent the entry of invading pathogens using physical and chemical barriers.
What are examples of physical barriers?
Intact skin, cilia and nasal hairs
What does non-specific mean?
They fight the same way for all infections, regardless of whether they have encountered them before.
What are examples of chemical barriers?
Body fluids such as saliva, tears, and stomach acid.
What is the second line of defence?
The second line of defence is non-specific, and involves immune cells and proteins nonspecifically recognising and eliminating any pathogen that enters the body.
Why is redness and swelling triggered in the second line of defence?
It's caused by an increase in blood flow to the infected area, which occurs because histamine has been released.
What are phagocytes?
Special types of white blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens and other foreign material. This action of engulfing and destroying material is called phagocytosis.
How does phagocytosis work?
When the phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens and other foreign material after antibodies clump them.
What is the role of the lymphatic system in the third line of defence?
Transports the immune cells around
What is the third line of defence?
A highly specific form of defence that has the ability to remember pathogens.
How do B lymphocytes work to destroy pathogens?
B lymphocytes divide into plasma cells, which produce chemicals called antibodies that are specific to the invader's antigens. These antibodies assist in the destruction of the invading pathogen.
What do antibodies do?
Antibodies can bind to antigens, causing pathogens to clump together. This clumping makes it easier for the phagocytes to engulf them.
How do T lymphocytes work to destroy pathogens?
They not only attack foreign invading cells, but may also attack your own cells that have been invaded.
What do T lymphocytes do by destroying invaded self cells?
They also destroy the cause of infection and reduce the chance that it will be spread to other cells.
What are the 4 types of T lymphocytes?
Killer T cells, cytotoxic T cells, regulatory T cells and helper T cells.
What do killer T cells do?
Can kill infected body cells by releasing toxins
What do cytotoxic T cells do?
Produce toxic agents to kill their targets
What do helper T cells do?
Stimulate B and T cells to become active
What do regulatory T cells do?
Stop attacks once virus is killed
How are memory cells made?
Lymphocytes form them.
How are memory cells vital in protecting the body?
They remember diseases so next time you're infected you heal faster and sometimes don't even get symptoms.
What is active immunity?
Your body makes antibodies to a specific antigen. Memory cells remember the antigen and make more identical antibodies very quickly.
What is passive immunity?
Receiving antibodies from an outside source.
Example of active immunity?
Vaccination and having disease
Example of passive immunity?
You could get passive immunity from your mother's milk.
How does vaccination help build your immune system?
Vaccination trains the immune response to fight a pathogen without being exposed to the dangers of the pathogen itself. Vaccination generates antibodies and forms memory of the pathogen, mimicking the primary infection without being infected
How does herd immunity work to protect the community?
It allows the protection of individuals who are unable to be vaccinated.
What are epidemics?
When many people in a particular area have the disease in a relatively short time
What are pandemics?
Diseases that occur worldwide
What are transverse waves?
When each point on the wave vibrates perpendicularly to the direction of the travel wave.
What are longitudinal waves?
When each point on the wave vibrates parallel to the direction of travel.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Transverse are used for electromagnetic waves, and longitudinal are for sound waves. The particles in each wave vibrate in different directions.
What are the features of a transverse wave?
Wavelength, frequency, period, crest, trough, and amplitude.
What is a trough?
The lowest point in the wave
What is a crest?
Highest point of a wave
What is a wavelength?
The distance between two crests or two troughs
What is frequency?
Frequency is the number of waves generated by the source per second, or the number of waves passing a certain point per second
What is period?
The period of a wave is the time taken for one complete cycle to pass a certain point.
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of a point in the wave from its resting position
What does high amplitude mean?
Large amplitude means the sound is loud or the light bright.
What does low amplitude mean?
A small amplitude means the sound is small or the light is dull.
When is the wave at its loudest or brightest?
At its largest amplitude
When is the wave at it's quietest or dullest?
At it's lowest amplitude
How is pitch affected by frequency?
The higher the frequency the higher the pitch
What does lower frequency mean?
Lower pitch
What does higher frequency mean?
Higher pitch
What are the features of a longitudinal wave?
Compression and rarefaction
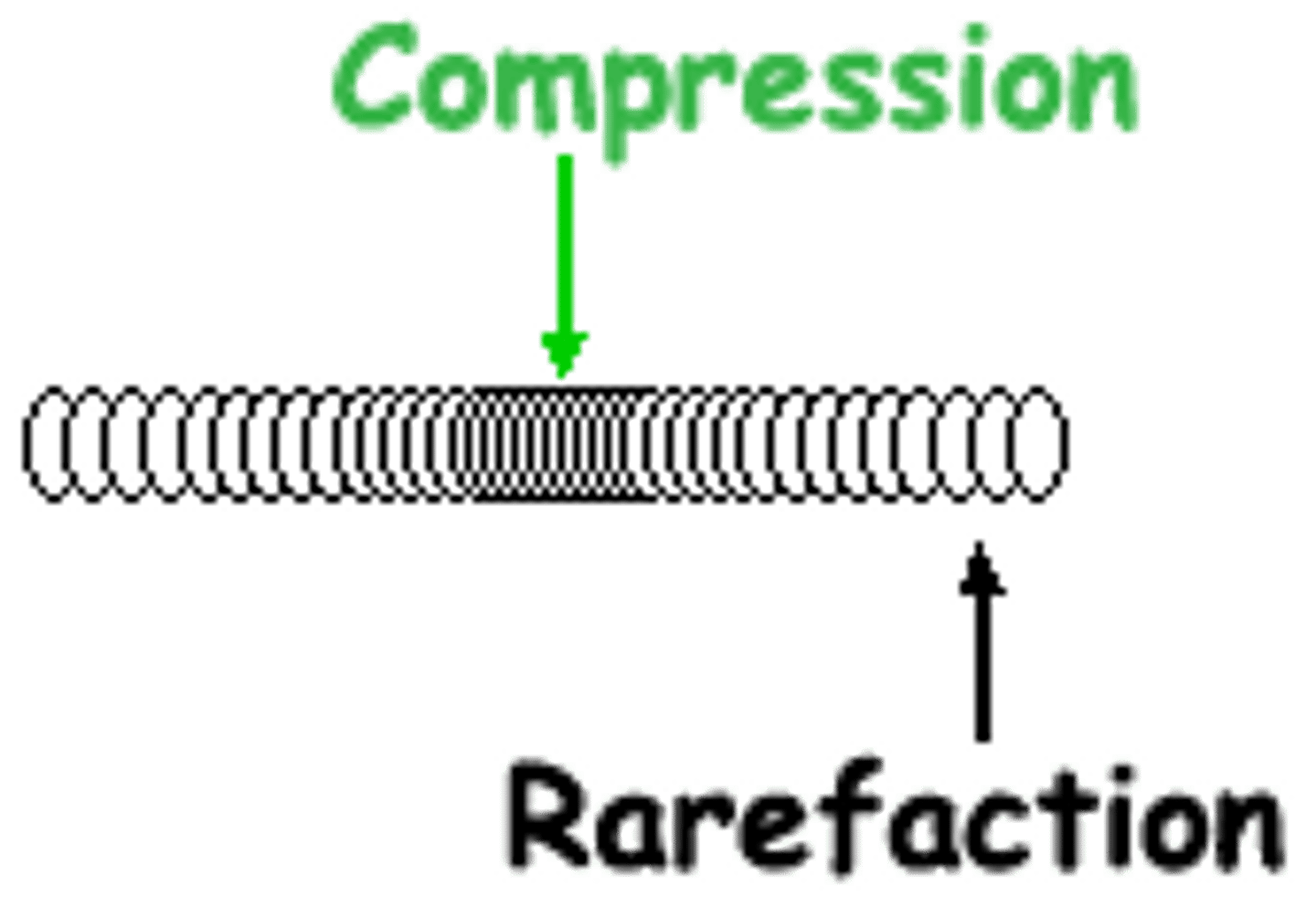
What is a compression?
The high pressure region in a longitudinal wave
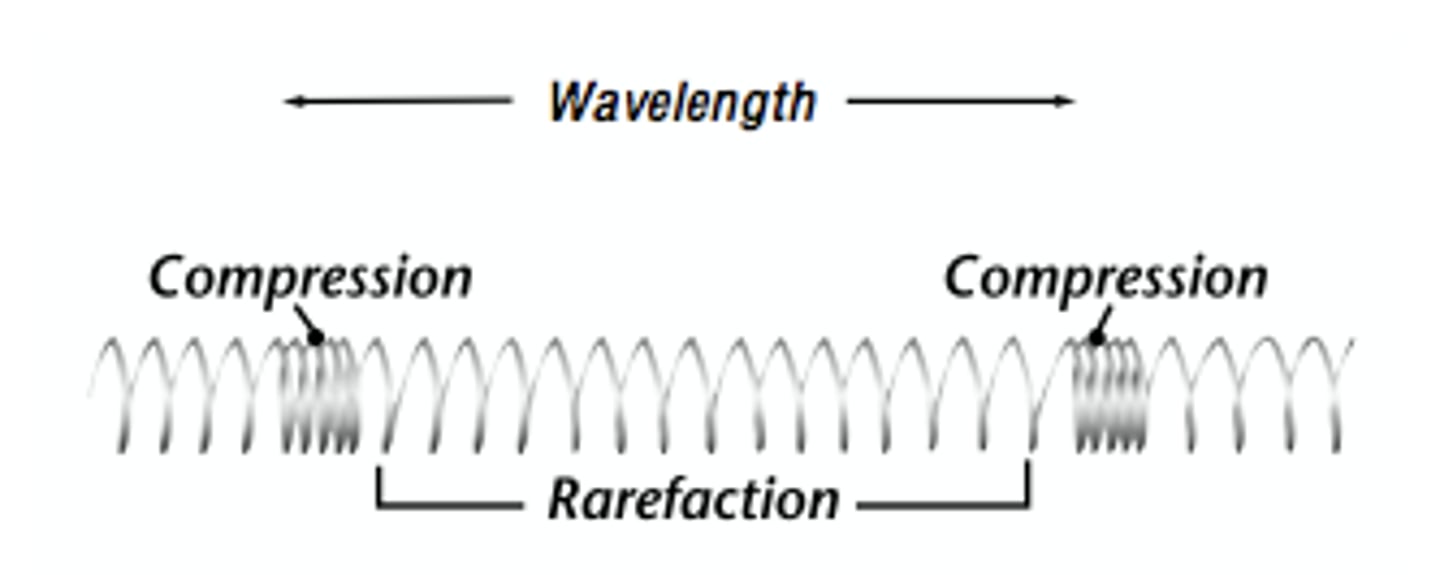
What is a rarefaction?
The low pressure region in a longitudinal wave
How does sound travel?
Sound needs a medium to travel through a series of compression and rarefaction.
Where does sound travel fastest?
Solids, then liquids, then gas. Particles are closer together and vibrate against each other faster. No sound in vacuum.
Where does light travel fastest?
In a vacuum, then gas, then liquids, then solids
What are radiowaves?
Part of EMR, the longest waves. They carry radio signals far.
What side of the EMR spectrum are radio-waves on?
Longer wavelength, to carry radio signals great distances.
What are microwaves?
Second longest wave in EMR. They are used in microwaves.
What side of the EMR spectrum are microwaves on?
The longer wavelength.
What do microwaves do?
Vibrate and therefore heat water molecules in food.
What is infared?
The light below red, just outside visible light.
What do infared rays do?
Cause body to feel warm. Not visible to the naked eyes, but humans can feel as heat.
What is visible light?
The part of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect
What is ultraviolet?
The light beyond violet, just outside the visible light.
What does ultraviolet radiation do?
Has a shorter wavelength, so it can damage skin.
What are x-rays?
Radiation at the short wavelength end of the EMR spectrum
What do x-rays do?
X-rays can penetrate flesh, but not bones or teeth, so can be used to "look" inside the body
What are gamma rays?
The shortest and most energetic part of the EMR