Genetics - Lecture 2: Mendelian Genetics, Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Preformation
the entire organism was in a miniaturized version within a sperm or egg
Blended inheritance
offspring merge information from both parents,
resulting in a unique blend
Why were pea plants a good choice?
- short generation time
- small and easy to grow
- mating produces many seeds
- can self-fertilize or corss-fertilize
Pea flowers have both male and female parts called:
anthers(male) and ovules(female)
Mendel allowed his original 34 strains of pea plants to...
self-fertilize for many generations to ensure genetic purity meaning they were heavily inbred
Inbred pea plants
every member of the inbred strain is genetically identical
True-breeding
Organisms that, when reproducing, create offspring of all the same variety.
Qualitative traits
traits that differ from one another by discrete qualities
Quantitative traits
traits that show continuous variation (most traits, i.e.: height, intelligence, athleticism)
Which traits did Mendel work with?
Qualitative traits
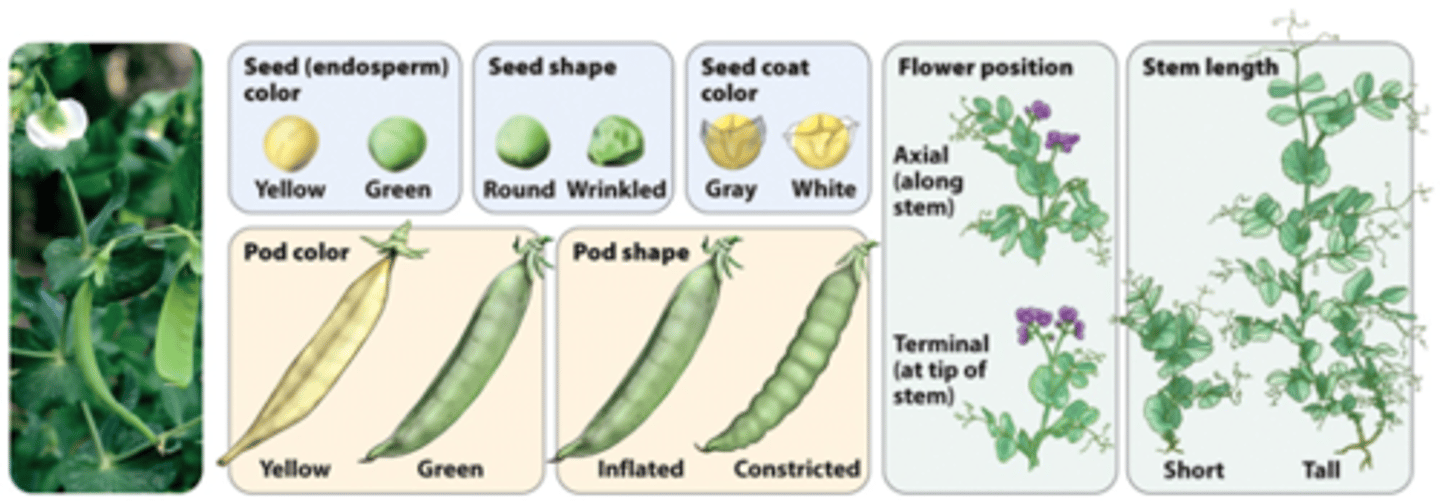
Mendel's 7 traits
seed color (Yellow/green)
seed shape (Round/wrinkled)
seed coat (Gray/white)
pod color (Green/yellow)
pod shape (Smooth/constricted)
flower position (Axial/terminal)
plant height (Tall/short)
Why did Mendel succeed?
He chose his model system wisely and quantified his results
Mendel's imaginative and creative model
1. There is a gene responsible for each trait
2. Each gene comes in version - "alleles"
3. Each individual has 2 alleles, one from each parent
4. Some alleles can mask (dominant) other recessive alleles
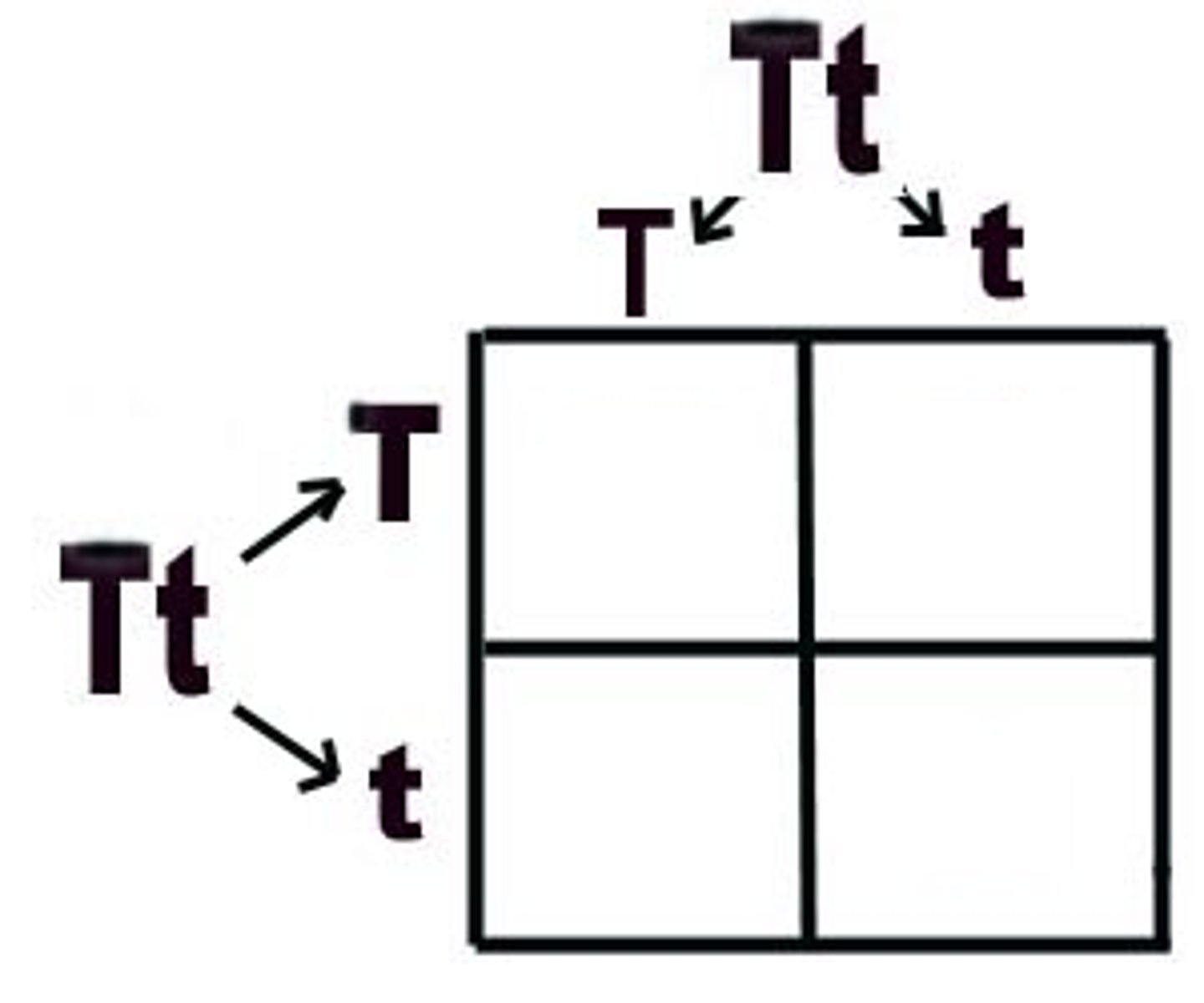
Mendel's Law of Segregation
two alleles for each trait separate during meiosis
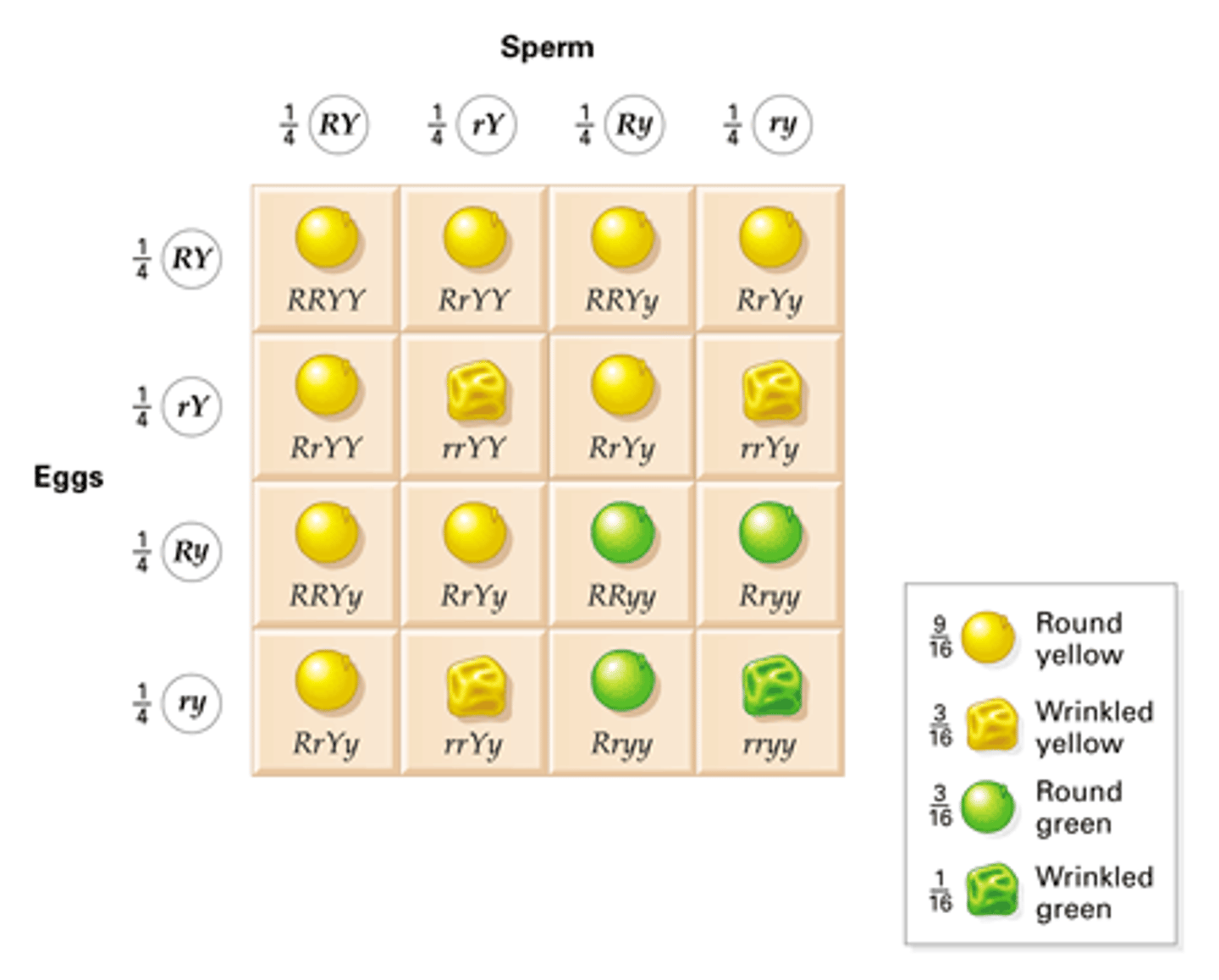
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
the inheritance of one character has no effect on the inheritance of another
Nucleoprotein complex
makes up eukaryotic chromosomes