AAH practice test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Last updated 6:10 PM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
The T Wave represents
ventricular re-polarization
2
New cards
If the heart is in a state of asystole
There is no contraction
3
New cards
What are the bipolar leads
I, II, and III
4
New cards
The most common type of supraventricular Tachycardia is
AV nodal Reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
5
New cards
In 2:1 AV block, the PR interval
Lengthens
6
New cards
In sinus arrhythmia, a gradual decreasing of the heart rate is usually associated with:
Expiration
7
New cards
When the cardiac muscle cell is stimulated, the cell is said to:
Depolarize
8
New cards
Leads, II,III AVF view which portion of the heart
Inferior
9
New cards
A regular rhythm with a rate of 100-250 beats per minute would most likely be
Atrial Tachycardia
10
New cards
Artifact can be cause by
Alternating currents, Patient movements, poorly applied or dirty sensors
11
New cards
When you have more than one premature beat that are of a different kind they are called
Multifocal
12
New cards
What is the rate range for junctional tachycardia?
100-180
13
New cards
Another name for the S-A node is
Pacemaker
14
New cards
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome is associated with
Short P-R interval, delta wave, wide QRS complex
15
New cards
How are frequent PAC's usually managed?
Correcting the underlying cause
16
New cards
The term for three or more PVC's occurring in a row at a rate of more than 100 beats per min is?
A run of ventricular Tachycardia
17
New cards
How do you determine whether the atrial rhythm on an ECG tracing is regular or Irregular ?
Compare to P to P Intervals
18
New cards
Tall, Peaked T waves observed on the ECG are most commonly seen in patients with.
Hyperkalemia
19
New cards
Leads V3 and V4 view which portion of the heart?
Anterior
20
New cards
A normal rhythm with a normal rate is a
Normal Sinus Rhythm
21
New cards
Defibrillation is a
Shock to the heart to stop the heart and shock to the heart to change rhythms
22
New cards
Which of the following small waves sometimes appears between the T wave and P wave?
U wave
23
New cards
What structure maintains the control of the control of blood flowing through the heart?
Valves
24
New cards
Sinus rhythm at a rate of 48 would be considered
Bradycardia
25
New cards
The function of the AV node is to
Delay the electrical signal to the Purkinje Fibers
26
New cards
The inherent rate for the AV Junction is
40-60 bpm
27
New cards
The term for three or more PVC's occurring in a row at a rate of more than 100 beats
A run of ventricular tachycardia
28
New cards
The usual rate of nonparoxymal junction tachycardia is
101-140 bpm
29
New cards
When the cardiac muscle cell is simulated , the cell is said to
Depolarize
30
New cards
Leads V1 and V2 view which portion of the heart?
Septal
31
New cards
In atrial Tachycardia, the atrial rate can be as low as
100-150
32
New cards
A QRS measurement of less than ________ seconds indicates a supraventricular
0.12
33
New cards
A straight line on the ECG strip produced by the stylus when the EKG isn't connected to a patient is called
Isoelectric line
34
New cards
The atrial rate in atrial fibrillation is
More than 350 bpm
35
New cards
Normally a complete ECG consists of __________ leads
12
36
New cards
The anterior surface of the heart consists primarily of the :
Right ventricle
37
New cards
The ________ supplies the right atrium and ventricle with blood
Right coronary Artery
38
New cards
The inherent rate of the AV Junction is
40-60 bpm
39
New cards
The segment representing the time fro the end of the P wave to the onset of the QRS complex is the
P-R segment
40
New cards
Impulses from the AV node go through the ____________ tot the right an left branches
Bundle of His
41
New cards
The single most important thing you can do to prevent the spread of infection is
Wash your hands
42
New cards
When the atria and ventricles are seen to be beating independently is called
Third- degree heart block
43
New cards
Wenckebach is characterized by increasingly PRI's followed _________a P wave
Blocked
44
New cards
A rhythm with regular P-P and R-R intervals, a normal P wave before each QRS complex, and a rate below 60 beats premature would most likely be
Sinus Bradycardia
45
New cards
When you have more than one premature beat that appears identical, they are called
Unifocal
46
New cards
The atrial rate in atrial fibrillation is
More than 350 bpm
47
New cards
The QRS measurement for a PAC should be
Less than 0.12 seconds
48
New cards
When a site speeds up/takes over as the pacemaker it is referred to as?
Ectopic pacemaker
49
New cards
A sinus rhythm at a rate of 48 would considered
Bradycardia
50
New cards
U wave are thought to represent
Repolarization of the Purkinje Fibers
51
New cards
Which of the following are chest leads
V1, V2,V3, V4, V5, V6
52
New cards
Sodium
NA+ 136-142 Essential in electrical activin electrical activity of neurons and muscle cells
53
New cards
Calcium
4.Ca++ 4.6-5.5 excitability of neurons and muscles cells cation
54
New cards
Potassium
K 3.5-5.0 The essential activity of neurons in a muscle cell
55
New cards
Myocardium infraction or MI
Heart attack; signs include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea
56
New cards
CHF (congestive heart failure)
condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to the rest of the body
57
New cards
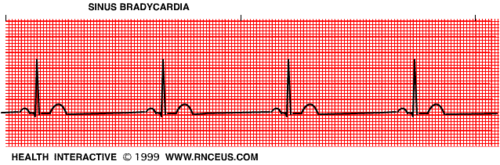
Bradycardia
slow heartbeat
58
New cards
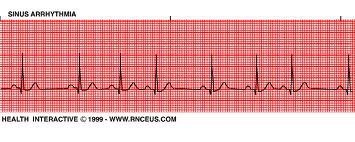
Arrythmia
Abnormal heart rhythm
59
New cards
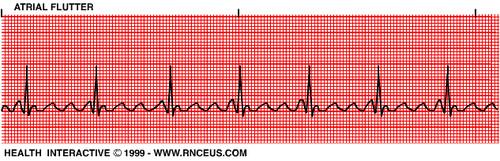
Atrial flutter
irregular beating of the atria; often described as "a-flutter with 2 to 1 block or 3 to 1 block"
60
New cards
coronary circulation
circulation of blood through the coronary blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle tissue
61
New cards
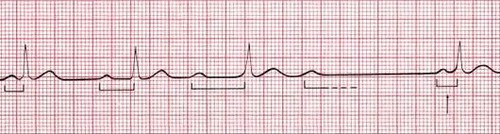
2nd degree block/Wenchebach
A disease process when there is a progressive prolongation of the PRI culminating in a non-conducted p Wave missing a QRS Complex. The PRI longest immediately before the dropped QRS
62
New cards
Premature Junctional Contraction (PJC)
- R-R irregular
- P wave may be inverted or absent
- Normal QRS
- P wave may be inverted or absent
- Normal QRS
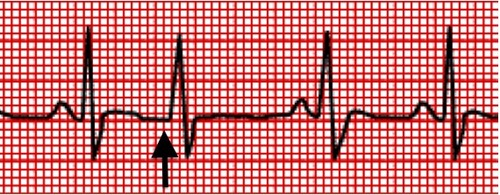
63
New cards
Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)
irregular heart rhythm characterized by atrial contractions occurring before the expected time
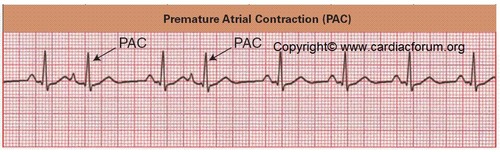
64
New cards
Dual Paced Rhythm
Spike before the P wave and a spike before the QRS
65
New cards
Ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart, and they pump blood out to the lungs and body.
66
New cards
atrium (atria)
The upper chamber of half the heart
67
New cards
Who invented the EKG?
Willem Einthoven 1895
68
New cards
Ventricle Pacemaker
Spike before the QRS
69
New cards
Atrial Pace
Spike before the P Wave
70
New cards
cyanosis
a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood.
71
New cards
plaque
A deposit of fatty material on the inner lining of an arterial wall
72
New cards
Arterioles
small vessels that receive blood from the arteries
73
New cards
epicardium
outer layer of the heart
74
New cards
Q-T interval
beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization
75
New cards
syncope
"Passing out", loss of consciousness or fainting
76
New cards
Sclerosis
abnormal hardening
77
New cards
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
78
New cards
ST segment
the time during which ventricles are contracting and emptying
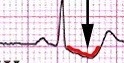
79
New cards
Venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
80
New cards
Capillaries
any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules.
81
New cards
aneurysm
an excessive localized enlargement of an artery caused by a weakening of the artery wall.
82
New cards
AIVR
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
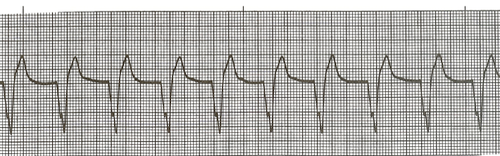
83
New cards
Pulmonary Circulation
flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
84
New cards
Pericardium
Double-layered membrane surrounding the heart.
85
New cards
Atrial Tachycardia
150 bpm
86
New cards
systemic circulation
flow of blood from body tissue to the heart and then from the heart back to body tissues
87
New cards
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
88
New cards
Aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
89
New cards
3rd degree AV block
P wave independent of QRS
90
New cards
Ventricular Flutter
250-350
- smooth sine-waves w/ similar amp
- can lead to deadly arryth
goes right into vfib
- smooth sine-waves w/ similar amp
- can lead to deadly arryth
goes right into vfib
91
New cards
VT
ventricular tachycardia
92
New cards
tricuspid valve
A valve that is situated at the opening of the right atrium of the heart into the right ventricle and that resembles the mitral valve in structure but consists of three triangular membranous flaps.
93
New cards
Ateries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
94
New cards
P-R interval
beginning of atrial excitation to beginning of ventricular excitation
95
New cards
R-R interval
Peak of R wave to peak of next R wave
96
New cards
Tachycardia
fast heart rate
97
New cards
Normal Sinus Rhythm
heart rhythm originating in the sinoatrial node with a rate in patients at rest of 60 to 100 beats per minute
98
New cards
PR segment
AV nodal delay
99
New cards
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
100
New cards
endocardium
Inner layer of the heart