biochem quiz 4 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:35 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
pH optimum
the pH that results in the maximal activity of an enzyme
2
New cards
step 1 acid-base catalysis: chymotrypsin
a group can take on a H+ at a low pH when H+ from the solution diffuses into the active site. if the group already has a H+, catalysis wont happen
3
New cards
step 2 acid-base catalysis: chymotrypsin
a group can give up an H+ at a high pH because some base from the solution can diffuse into the active site. if the H+ was already given up, catalysis won't happen
4
New cards
what causes differences in the pH optimum?
amino acid sequence, structure, how they catalyze
5
New cards
pH optimum graph
up - take on a proton (increase in enzyme activity)
down- release a proton (decrease in enzyme activity)
down- release a proton (decrease in enzyme activity)
6
New cards
serine proteases
hydrolyze bonds by using water to break them into 2 pieces
7
New cards
chymotrypsin
hydrolyzes peptide bonds adjacent to aromatic acids (specific) with Asp 102, His 57, and Ser 195
8
New cards
difference between catalysis of enzymes and non enzymes
non enzymes are not specific but enzymes are specific
9
New cards
what type of reaction is the ser protease mechanism?
ping pong double displacement
10
New cards
step 1 of the two step reaction process
-OH Ser side chain of the enzyme covalently binds to part of the substrate producing the leaving group (XH) and the acyl-enzyme
11
New cards
step 2 of the two step reaction process
h2o displaced the leaving group (XH) and the enzyme binds to the substrate through deacylation
12
New cards
convergent evolution
2 things do not have a common ancestor, but have evolved similar in function
13
New cards
convergent evolution in chymotrypsin and substilisin
they both cleave peptide bonds in other proteins and use Ser, Asp, and His.
His is the closest to the N terminal (lowest number)
Ser is closest to the C terminal (highest number)
His is the closest to the N terminal (lowest number)
Ser is closest to the C terminal (highest number)
14
New cards
site directed mutagensis
generate a polypeptide chain that is identical except Ser-221 is replaced with Ala
15
New cards
findings of site directed mutagensis
the Ala replacement had a lower kcat (ES = E + P) which shows the Ser-221 is important
the Km is unchanged which means the Ala is only good for E + S = ES, not for ES = E + P
the Km is unchanged which means the Ala is only good for E + S = ES, not for ES = E + P
16
New cards
enzyme regulation: maintenance of ordered state
thermodynamically unfavorable because the lower change in entropy, but some enzymes increase the change in entropy and make it favorable
17
New cards
enzyme regulation: conservation of energy
enzymes catalyze unfavorable reactions and use energy and if we don't need them, they are stopped
18
New cards
enzyme regulation: responsiveness to environmental changes
warm vs. cold has different internal changes for each
19
New cards
genetic control
change in regulation of transcription and translation = change in the amount of proteins produced
20
New cards
covalent modification
after enzyme is made in translation, another enzyme uses it as a substrate and covalently changes the polypeptide chain. PHOSPHORYLATION
21
New cards
allosteric regulation
something binds to the enzyme non-covalently and changes the ability to bind and catalyze
22
New cards
compartmentalization
enzyme is one part of the cell and substrate is in the another and regulation moves them to the same part
23
New cards
kinases
group of enzymes that transfer phosphate between molecules and use ATP as the phosphate donor
24
New cards
phosphatases
unphosphorylates an amino acid by dding water
25
New cards
phosphorylation
the -OH of a protein turns ATP to ADP and a phosphate is added
26
New cards
net result of phosphorylation
ATP hydrolysis
27
New cards
what process are proteases involved in?
clotting because they are active when bleeding and inactive when not bleeding (improper: stroke)
28
New cards
chymotrysinogen
inactive form of chymotrypsin which prevents degrading of proteins nearby and only secreted when needed
29
New cards
trypsin
breaks peptide bond in chymotrysinogen and makes pi-chymotrypsin which is more active
30
New cards
alpha chymotrypsin
fully active version of chymotrypsin
31
New cards
types of covalent modification
phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, and nucleotidylation
32
New cards
proenzymes/zymogens
protein made as an inactive enzyme (ex: chymotrypsinogen)
33
New cards
what do covalent modifications in enzyme structure cause?
changes in function
34
New cards
serpins
proteins that inhibit Ser proteases through covalent interactions
35
New cards
how do serpins inhibit Ser proteases
protease catalyzes the first part of the reaction to become the acyl-enzyme intermediate and the serpin undergoes a conformational change that forces the protease to undergo a conformational change
36
New cards
trypsin and serpins
after the cut, the serpin conformationally changes and the loop becomes a beta sheet and pulls our of trypsin's active site so it cannot catalyze the second step of the reaction and release Ser from the serpin
37
New cards
proteases and drug targets
regulate blood vessel constriction, so inhibition allows relaxation which causes a drop in blood pressure
HIV has a protease needed for replication so stopping the replication prevents HIV from turning to AIDS
COVID has a protease
HIV has a protease needed for replication so stopping the replication prevents HIV from turning to AIDS
COVID has a protease
38
New cards
the anabolic process in glycogen synthesis
the glycogen is made from glucose monomers
39
New cards
steps of glycogen synthesis
activate the glucose, add the activated molecule to the glycogen chain, branches are created through isomerization
40
New cards
glycogensis
the synthesis of glycogen when glucose is stored (after a meal because high concentration of glucose)
41
New cards
synthesis of glucose-1-phosphate
reaction one of glycogenesis (preparatory); made from G6P with the phosphoglucomutase
42
New cards
synthesis of UDP-glucose
reaction two of glycogenesis (preparatory); made from G1P by the UDP-glucose phosphorylase
43
New cards
what energy source is used to make G6P and G1P?
ATP
44
New cards
what energy source is used to make UDP-glucose?
UTP and PPi is made and gives more energy because it is hydrolyzed
45
New cards
where does the energy of ATP come from?
phosphates
46
New cards
synthesis of glycogen from UDP-glucose
reaction three of glycogenesis (chain elongation and isomerization); requires glycogen synthase for growth and amylo-alpha(1,4-->1,6) glucosyl transferase for alpha(1,6) linkages for branching
47
New cards
why does UDP release energy?
beta-phosphate has more resonance in products than reactants and a proton is generated
48
New cards
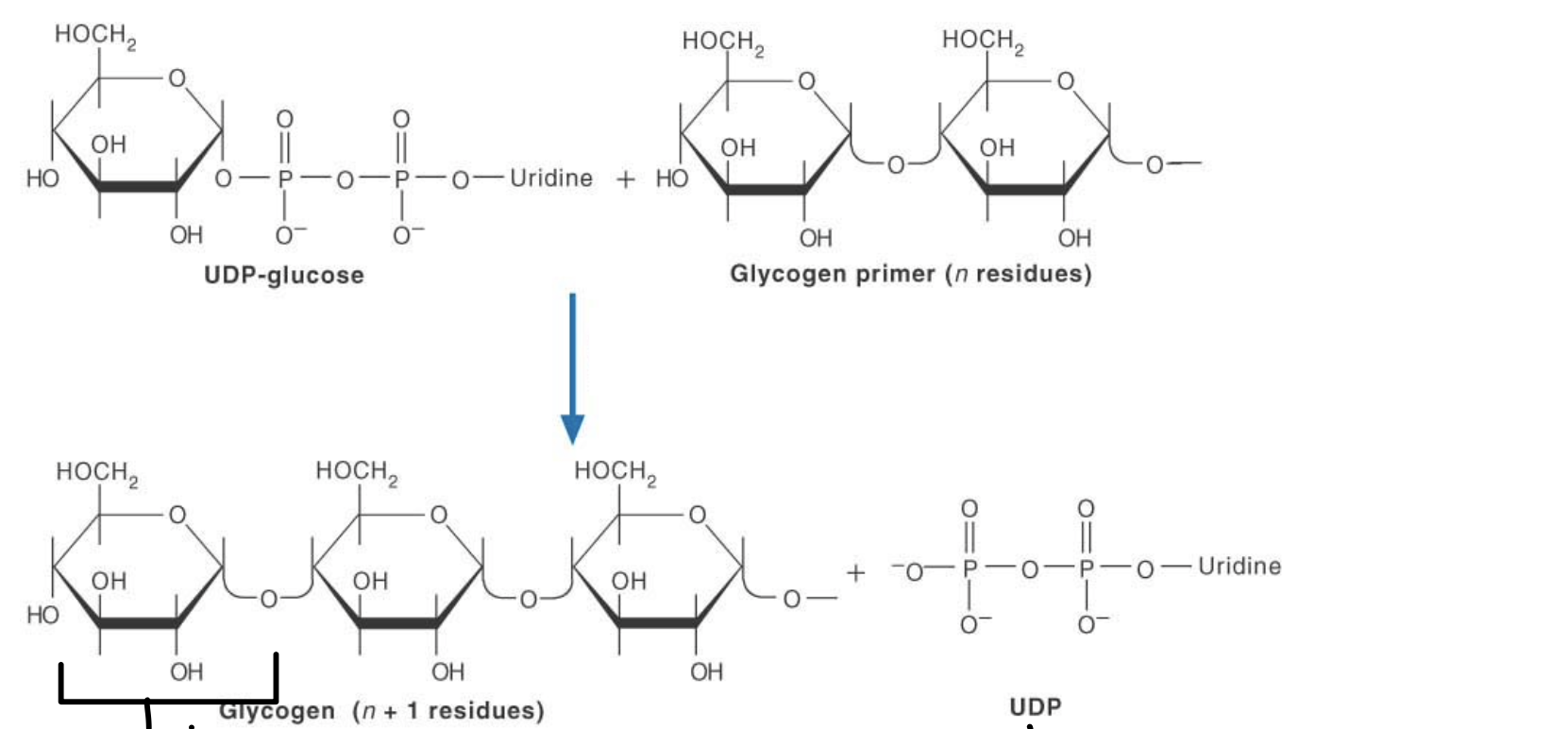
what is happening here?
glycogen is being formed from UDP-glucose
49
New cards
what is happening here?
addition of branching enzyme forms branching in the glycogen
50
New cards
glycogenolysis
glycogen degradation
51
New cards
reaction 1 of glycogenolysis
removal of glucose from nonreducing ends (glycogen phosphorylase) within 4 glucose of branch point
52
New cards
reaction 2 of glycogenolysis
transfer 3 remaining glucoses to another location on the glycogen molecule via the debranching enzyme; the glycogen phosphorylase cannot act on glucoses 4 away from branch point so they have to be moved
53
New cards
reaction 3 of glycogenolysis
last glucose unit is removed from the glycogen via hydrolysis with the debranching enzyme and the glucose can end up in the bloodstream or glycolysis
54
New cards
glycogen phosphorylase
work on different part of the molecule because of branching which allows for faster G1P production and makes the release of glucose from glycogen more efficient
55
New cards
draw glycogenesis
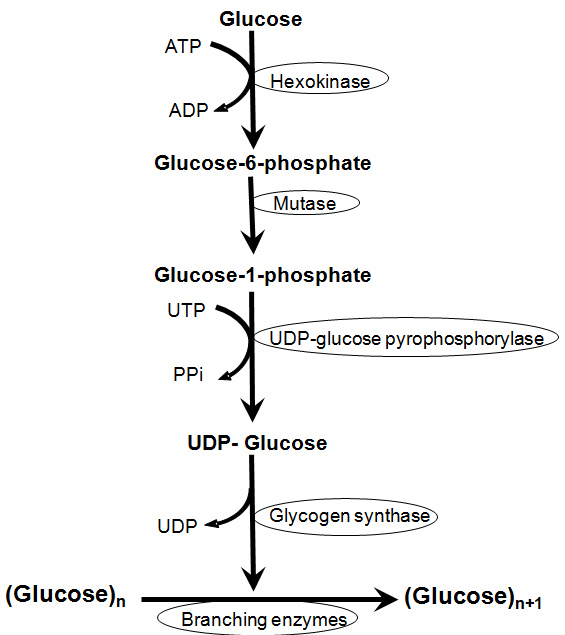
56
New cards
draw glycogenolysis
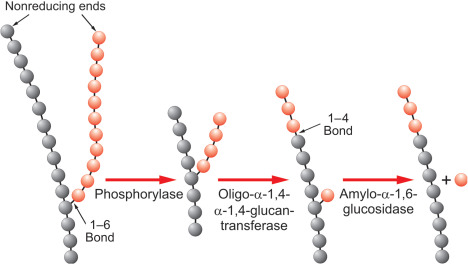
57
New cards
glucagon
activates glycogenolysis
58
New cards
insulin
inhibits glycogenolysis and activates glycogenesis
59
New cards
epinephrine
inhibits glycogenesis and activates glycogenolysis
60
New cards
futile cycle
when glycogenesis and glycogenolysis occur at the same time
61
New cards
protein kinase
enzyme that uses ATP to add phosphate to a protein and regulates the glycogen phosphorylase via the cascase
62
New cards
active form of glycogen phosphorylase
phosphorylated
63
New cards
active form of glycogen synthase
unphosphorylated
64
New cards
draw the glycogen complex
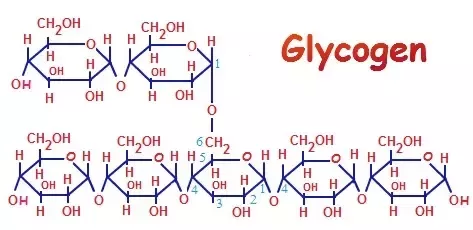
65
New cards
t form of glycogen phosphorylase
unphosphorylated and minimizes glycogen bonding
66
New cards
r form of glycogen phosphorylase
phosphorylated and maximizes glycogen bonding
67
New cards
muscle cells negative allosteric regulators
ATP and G6P
68
New cards
muscle cells positive allosteric regulators
AMP
69
New cards
liver cells negative allosteric regulators
glucose
70
New cards
liver cells
doesn't cycle through ATP quickly and maintain blood sugar levels, so it is responsive to [glucose]
71
New cards
muscle cells
store glucose for themselves and degrade glycogen when running low on ATP
72
New cards
feedback inhibition
due to regulation of a direct product or a product further down stream of the enzyme (G6P and hexokinase)
73
New cards
draw feedback inhibition chart
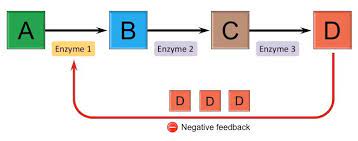
74
New cards
glycogen phosphorylase active site in the r state
lys and arg in the active site allow for higher affinity for phosphate and orient themselves for acid base catalysis (decreased Km)
75
New cards
glycogen phosphorylase active site in the t state
loop acts as a lid and covers the binding site minimizing the glycogen binding
76
New cards
insulin receptor
in the membrane and sends a signal that there is insulin outside of the cell
77
New cards
bound insulin receptor
signal is transmitted into the cell through phosphorylating proteins and a kinase cascade occurs resulting in the glycogen phosphorylase being phosphorylated and becoming inactive
78
New cards
signal transduction
communication of information in biological systems
79
New cards
parts of signal transduction in insulin
insulin, insulin receptor, and protein kinase cascade
80
New cards
phosphoglucomutase
converts between G1P and G6P through isomerization
81
New cards
important fact about phosphoglucomutase
it does not move the phosphate from the molecule, it transfers the phosphate back to itself
82
New cards
which enters metabolic pathways: G1P or G6P
G6P
83
New cards
glycolysis stage 1
energy investment (uses ATP)
84
New cards
glycolysis step 1 stage 1
glucose is phosphorylated to G6P which is important because it keeps it from diffusing out of the membrane which is important because energy is put into making and taking it up (ATP USED)
85
New cards
draw phosphoglucomutase mechanism
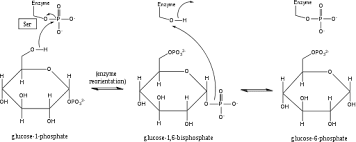
86
New cards
glycolysis step 2 stage 1
G6P is isomerized to F6P because a free -OH is needed
87
New cards
glycolysis step 3 stage 1
for symmetry another phosphate is added to an -OH of F6P forming F1,6BP which is a thermodynamic driving for (ATP USED)
88
New cards
glycolysis step 4 stage 1
F1,6BP is cleaved in to GAP and DHAP (which is later turned into GAP)
89
New cards
glycolysis stage 2
the energy production phase (2 rows)
90
New cards
glycolysis step 1 stage 2
GAP has a thermodynamically favorable oxidation and unfavorable phosphorylation to form G1,3,BP
91
New cards
glycolysis step 2 stage 2
high energy molecule that can phosphorylate ADP (ATP FORMED) and forms glycerate 3 phosphate
92
New cards
glycolysis step 3 stage 2
isomerization occurs to form glycerate 2 phosphate
93
New cards
glycolysis step 4 stage 2
dehydration occurs and phosphoenolpyruvate is formed
94
New cards
glycolysis step 5 stage 2
high energy molecule that can phosphorylate ADP (ATP FORMED) and forms pyruvate
95
New cards
net ATP of glycolysis
2 ATP (2 in energy investment and 4 in energy production)
96
New cards
hexokinase
catalyzes conversion of glucose and ATP into G6P, ADP, and a proton
97
New cards
what is the first reaction of glycolysis?
hexokinase
98
New cards
draw glycolysis mechanism
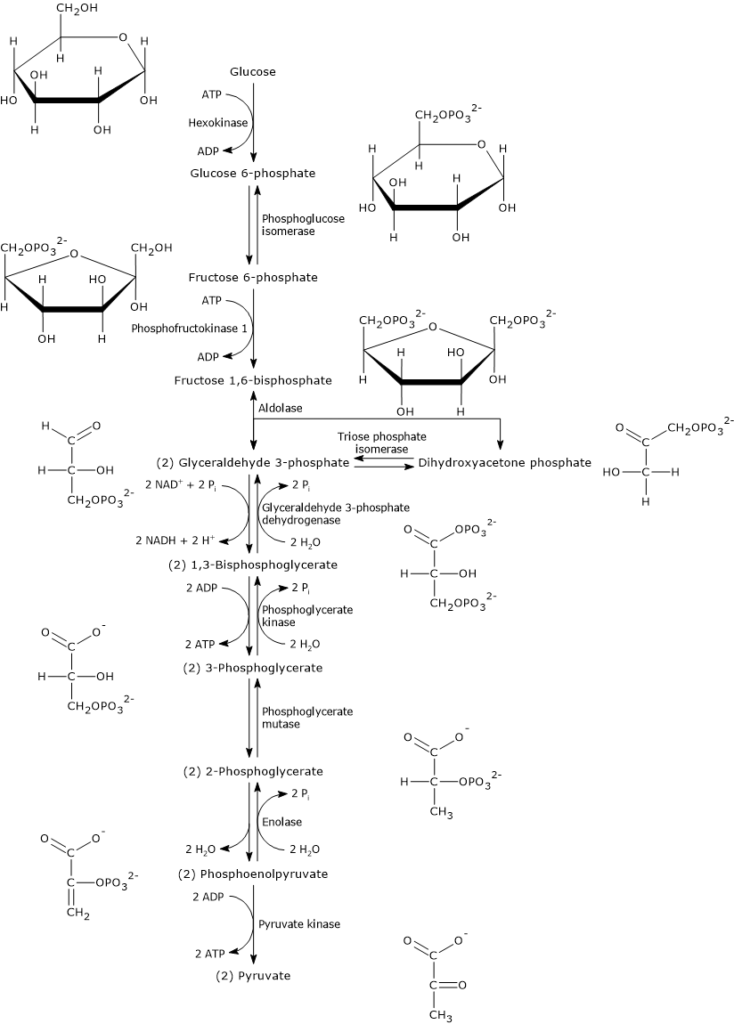
99
New cards
draw hexokinase mechanism
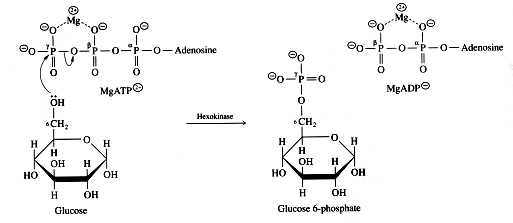
100
New cards
what are the 2 types of catalysis in the ser protease mechanisms?
acid-base and covalent