Respiratory Physiology and Anatomy: Air Pressure, Breathing Mechanics, and Lung Structure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is air pressure defined as?
The sum of the forces of collision divided by the area of the container.
What are the four types of pressures in the respiratory system?
Atmospheric pressure, alveolar pressure, pleural pressure, and abdominal pressure.
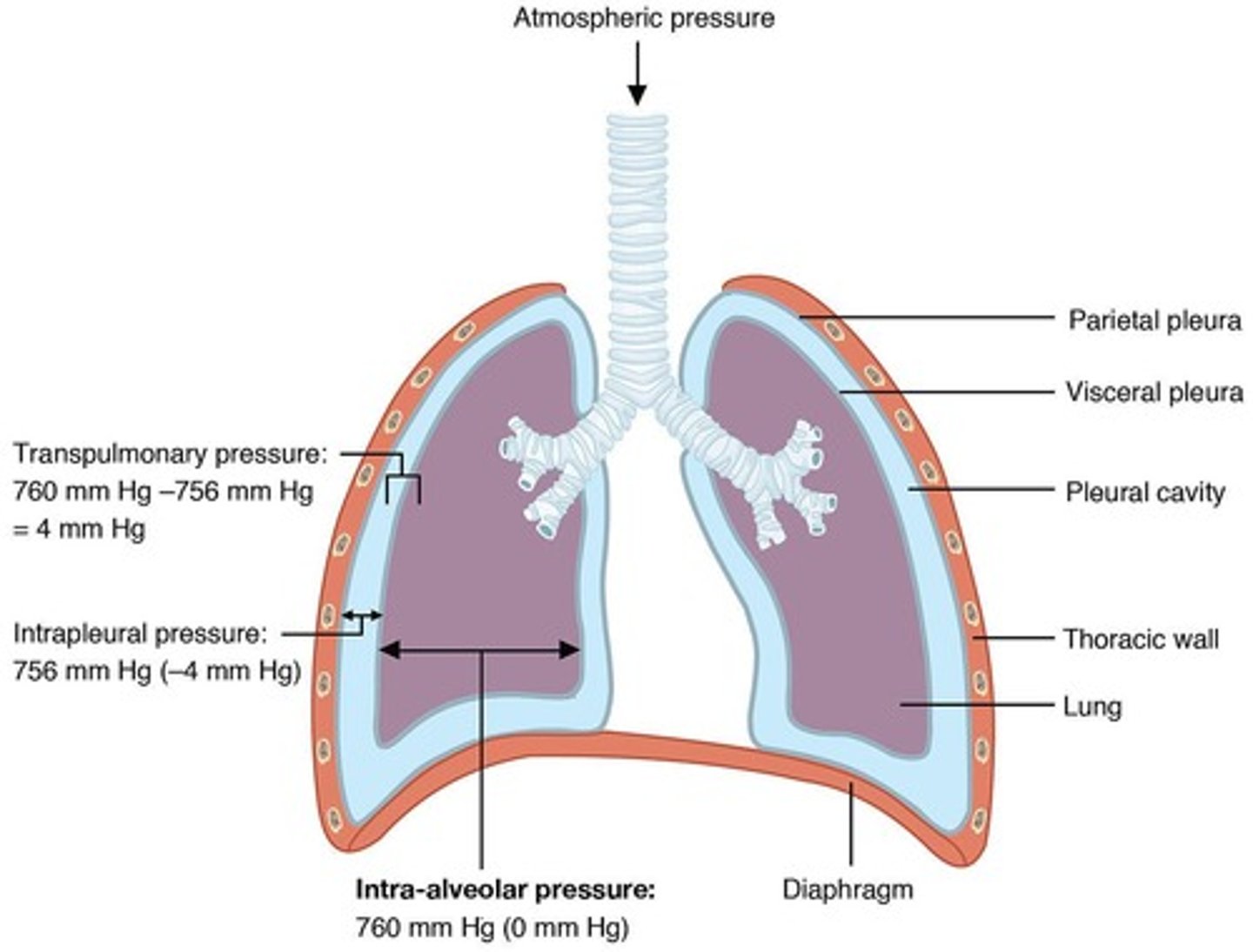
What is a pressure differential?
The change in pressure across containers.
How is atmospheric pressure defined in respiratory physiology?
It is given a value of 0.
What is the difference between negative and positive pressure?
Negative pressure is less than atmospheric pressure, while positive pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
What drives airflow during respiration?
The pressure difference between the atmosphere and the lungs.
According to Boyle's Law, how are volume and pressure related?
Volume is inversely proportional to pressure.
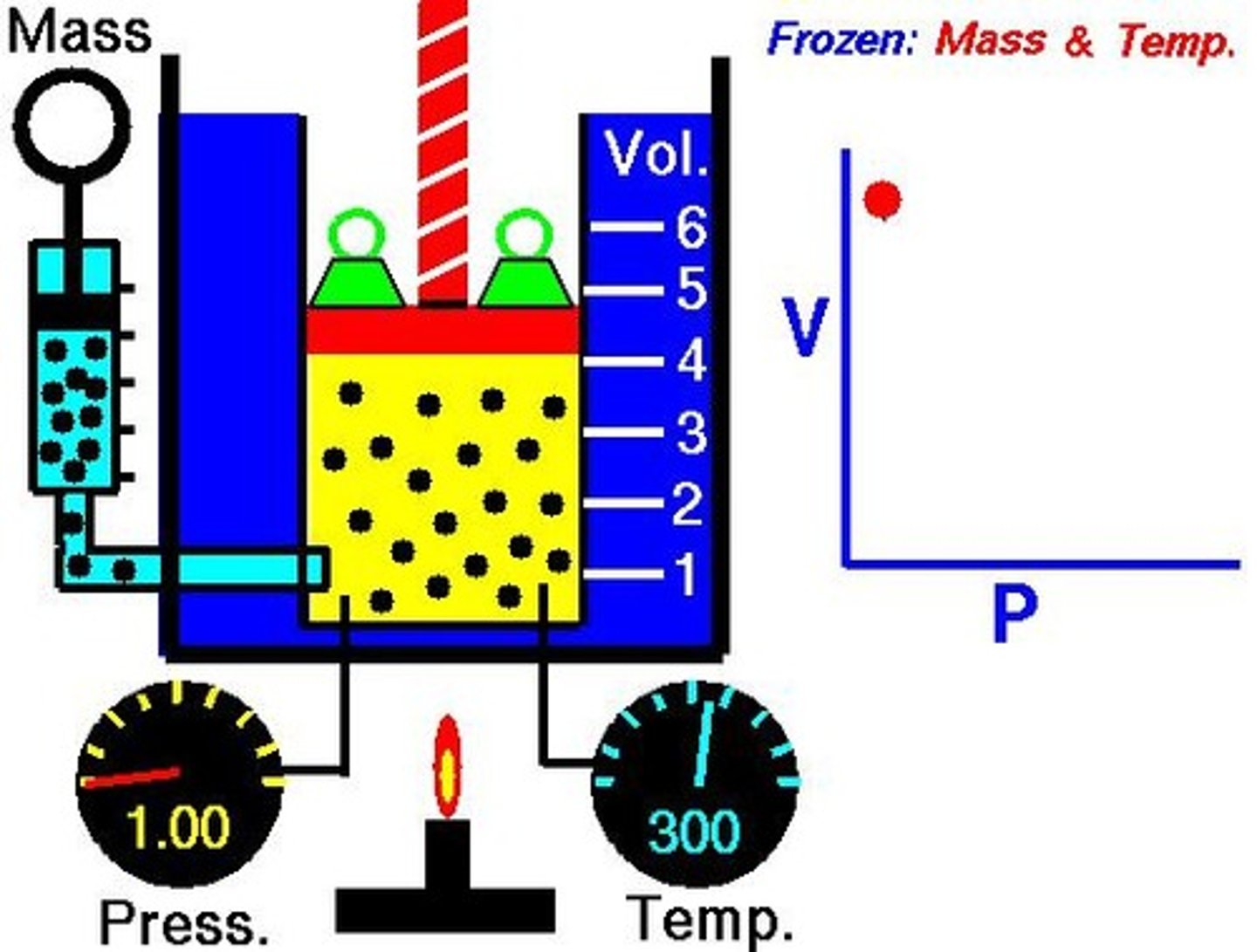
What happens to pressure when the volume of a container decreases?
The pressure increases.
What is the process of inhalation/inspiration?
Air flows from the atmosphere into the lungs.
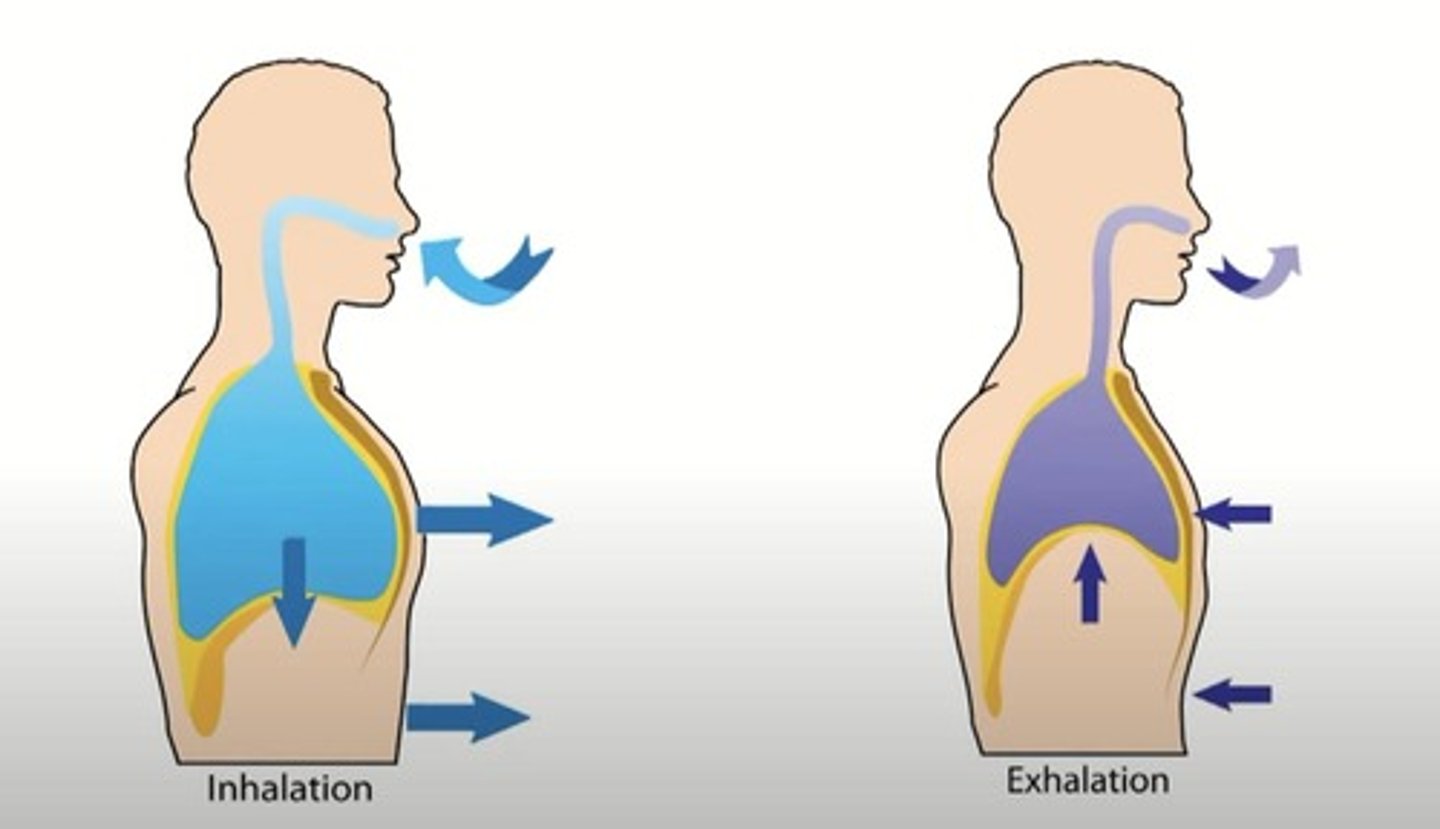
What is the process of exhalation/expiration?
Air flows from the lungs to the atmosphere.
What characterizes inspiration in terms of muscular effort?
Inspiration is an active process that requires muscular effort.
What characterizes expiration in terms of muscular effort?
Expiration is a passive process that does not require muscular effort.
What happens to the lungs during expiration?
The lungs compress and contract due to their elastic nature.
What is the role of the diaphragm during inspiration?
The diaphragm contracts and descends, expanding the thoracic cavity.
What happens to the diaphragm during expiration?
The diaphragm rises and the intercostal muscles relax, shrinking the thoracic cavity.
What are the main components of the respiratory passages?
Nasal/oral cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, and lungs.
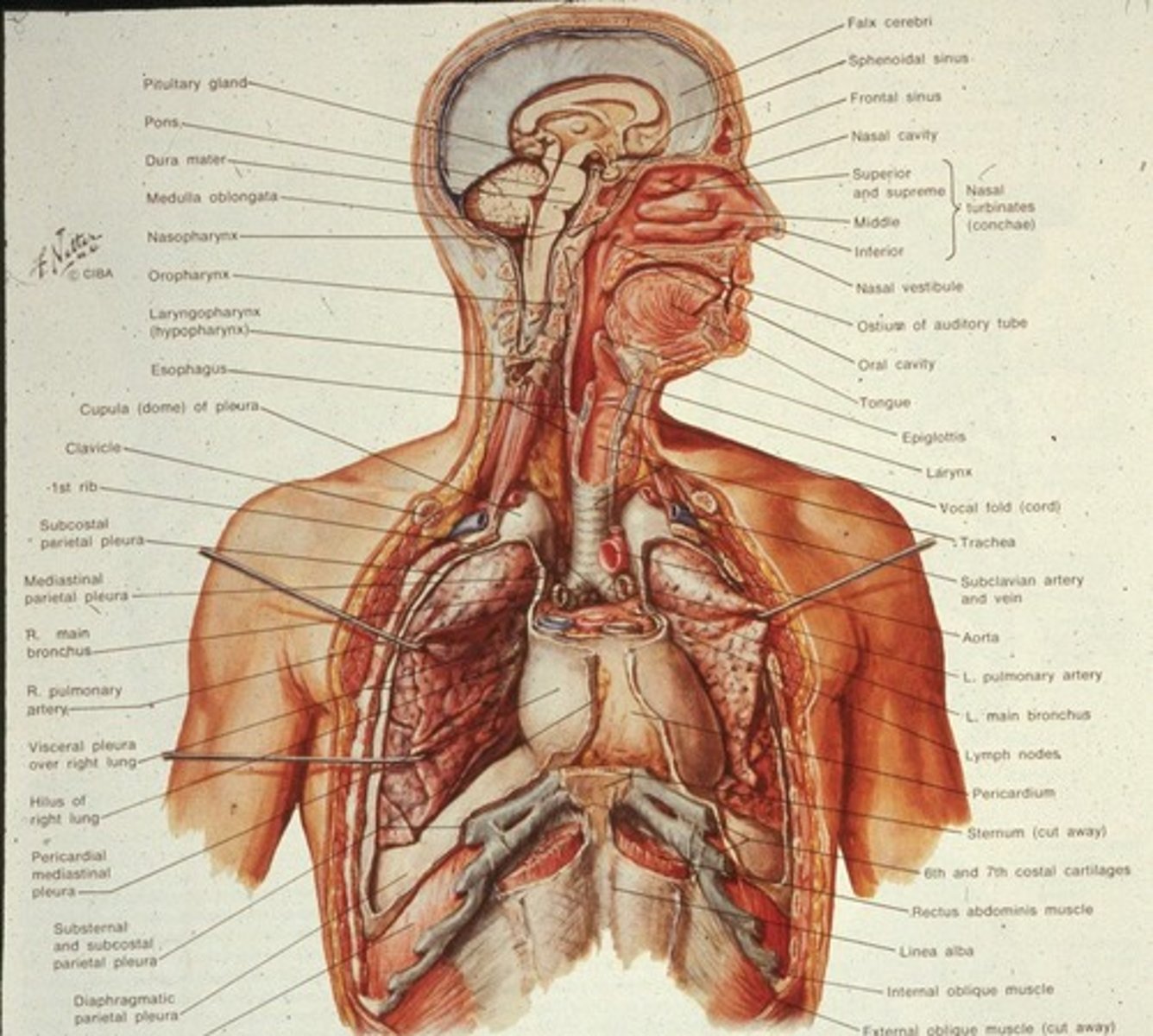
What is the structure of the trachea?
The trachea is 11-12 cm long, 2-2.5 cm in diameter, and has 16-20 horseshoe-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage.
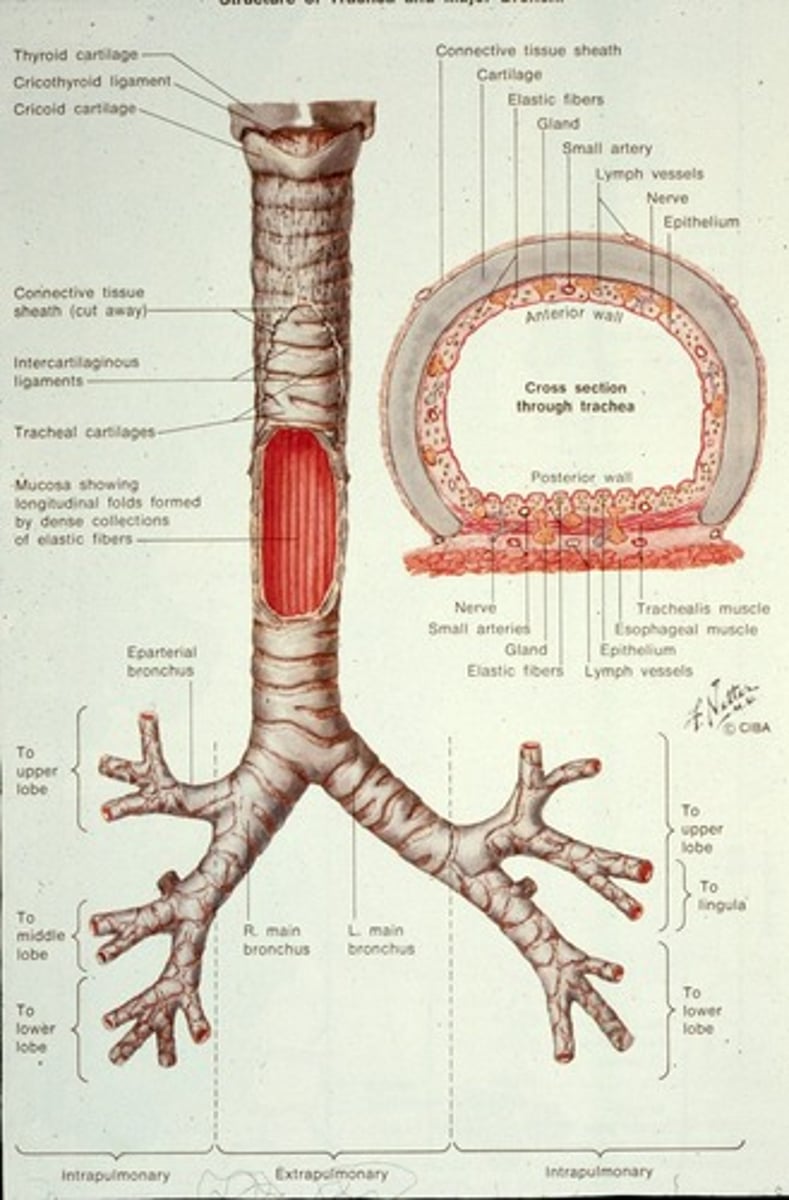
What is the function of the bronchi?
The bronchi carry air to the lungs, with primary bronchi serving each lung and secondary bronchi serving each lobe.
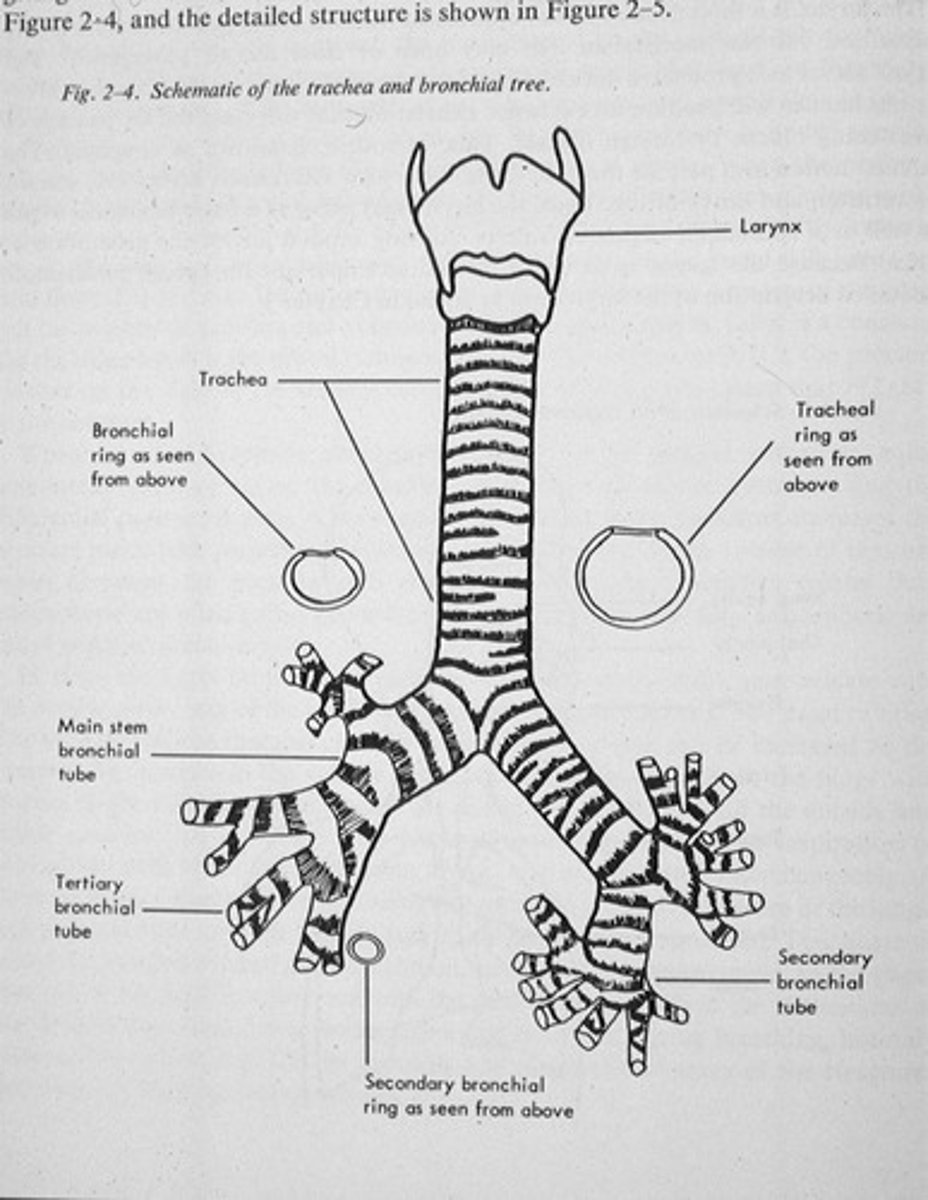
What are the components of the tracheobronchial tree?
Trachea, primary bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles.
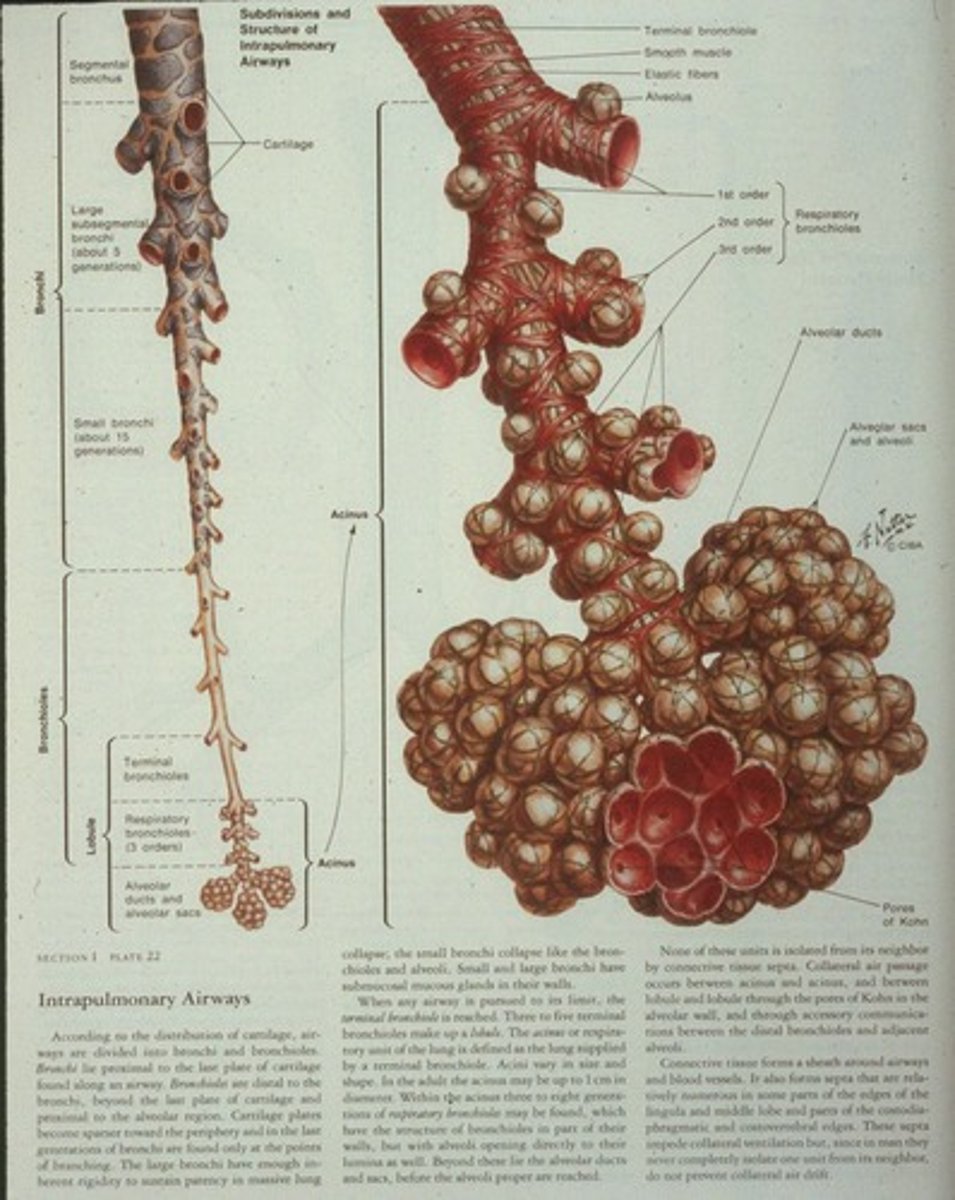
What is the function of alveoli?
Alveoli are pitted with small depressions where O2-CO2 exchange occurs.
What is the quality of the lungs?
The lungs are spongy, elastic, and contain only a few smooth muscle fibers.
How many lobes do the right and left lungs have?
The right lung has 3 lobes, while the left lung has 2 lobes.
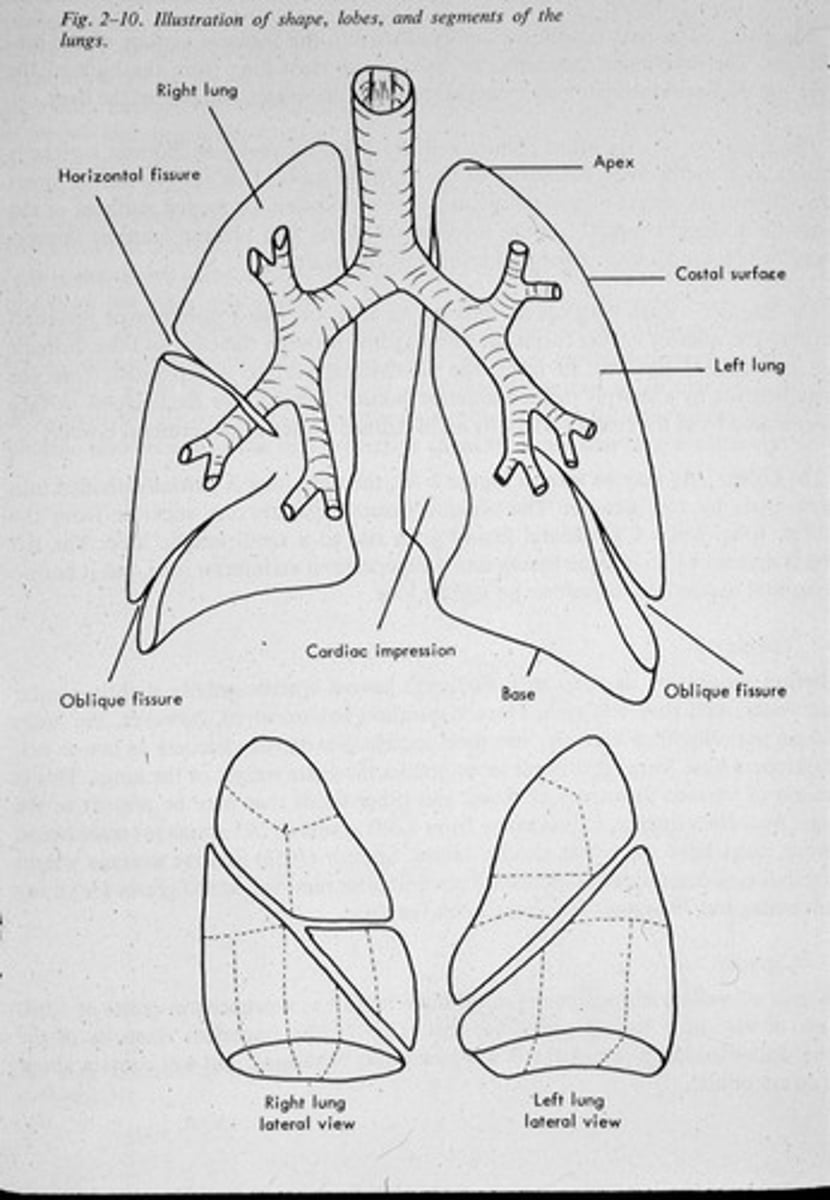
What is the function of the pleura?
The pleura is an airtight membrane that separates the two lungs.
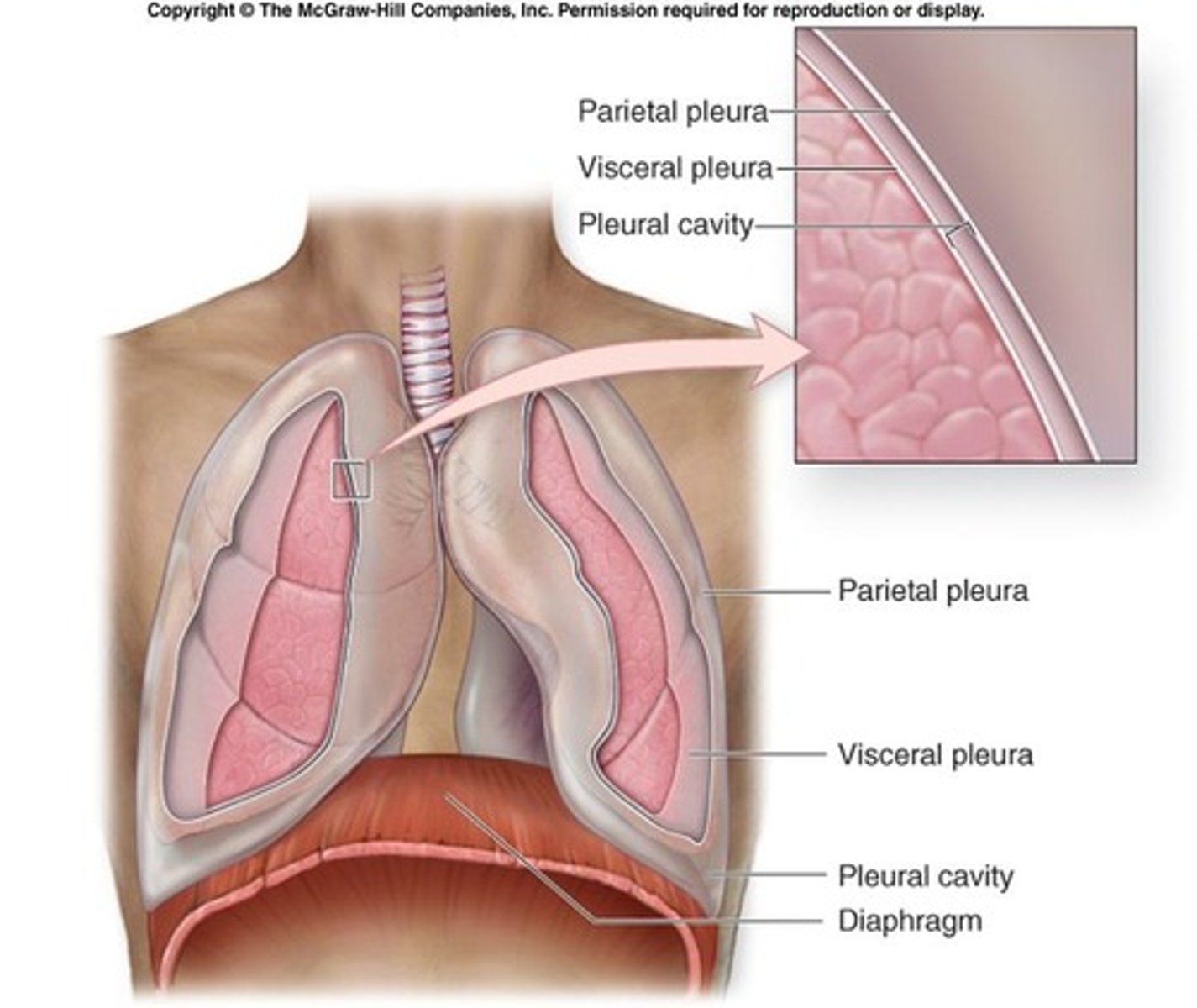
What are the two types of pleura?
Visceral (pulmonary) pleura, which houses the lungs, and parietal (costal) pleura, which adheres tightly to the rib cage.