22. Bonus Class >> Neuro
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
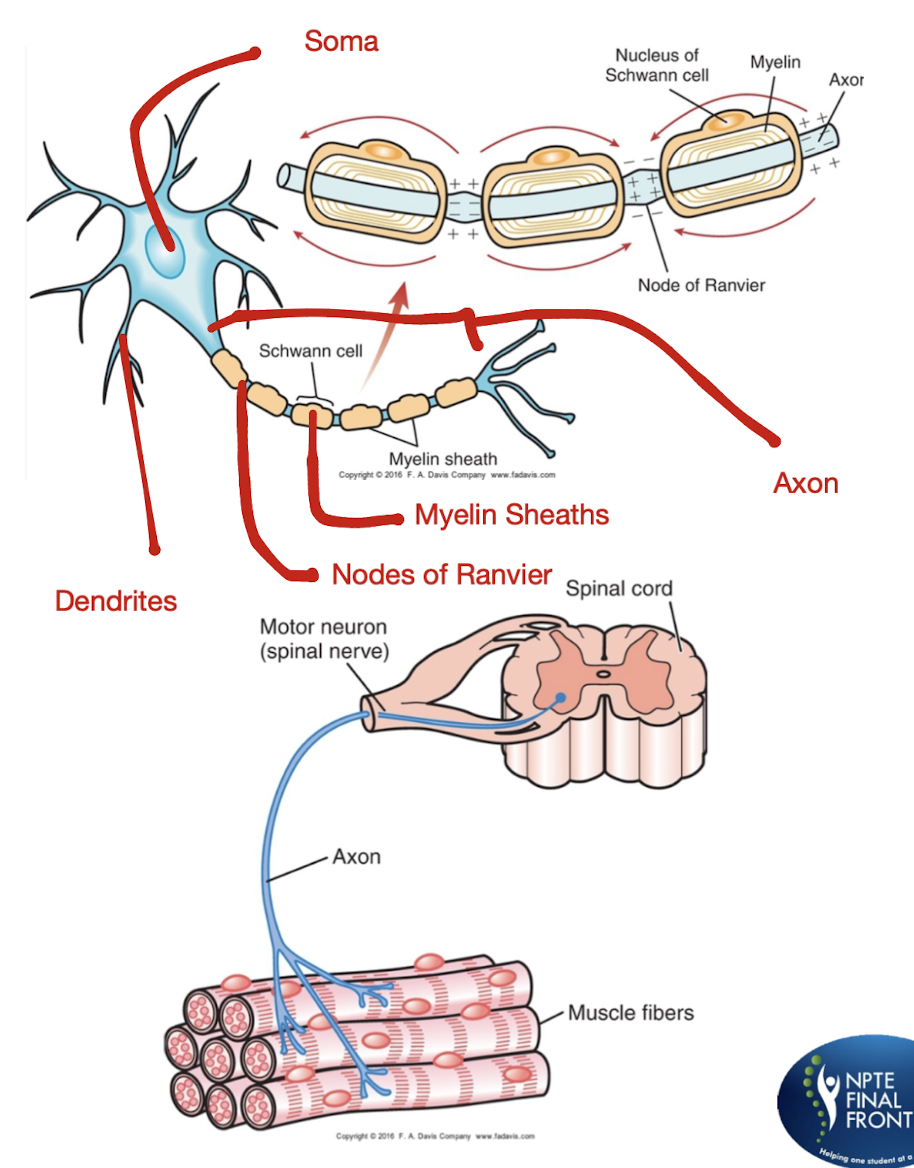
Neuro Anatomy and Background:
What is a Motor Unit?
A Motor Unit consists of what 6 structures?
Any disruption of the neuron or motor unit can cause what 2 things?
Motor Unit:
Functional unit of the peripheral neuromuscular system
Consists:
Anterior Horn Cell
Nerve Root
Plexus
Individual Nerve Fiber
NMJ
Muscle Fibers Innervated by that Axon
Cause:
Disruption in the flow of Information
Impairment in the neuromuscular system
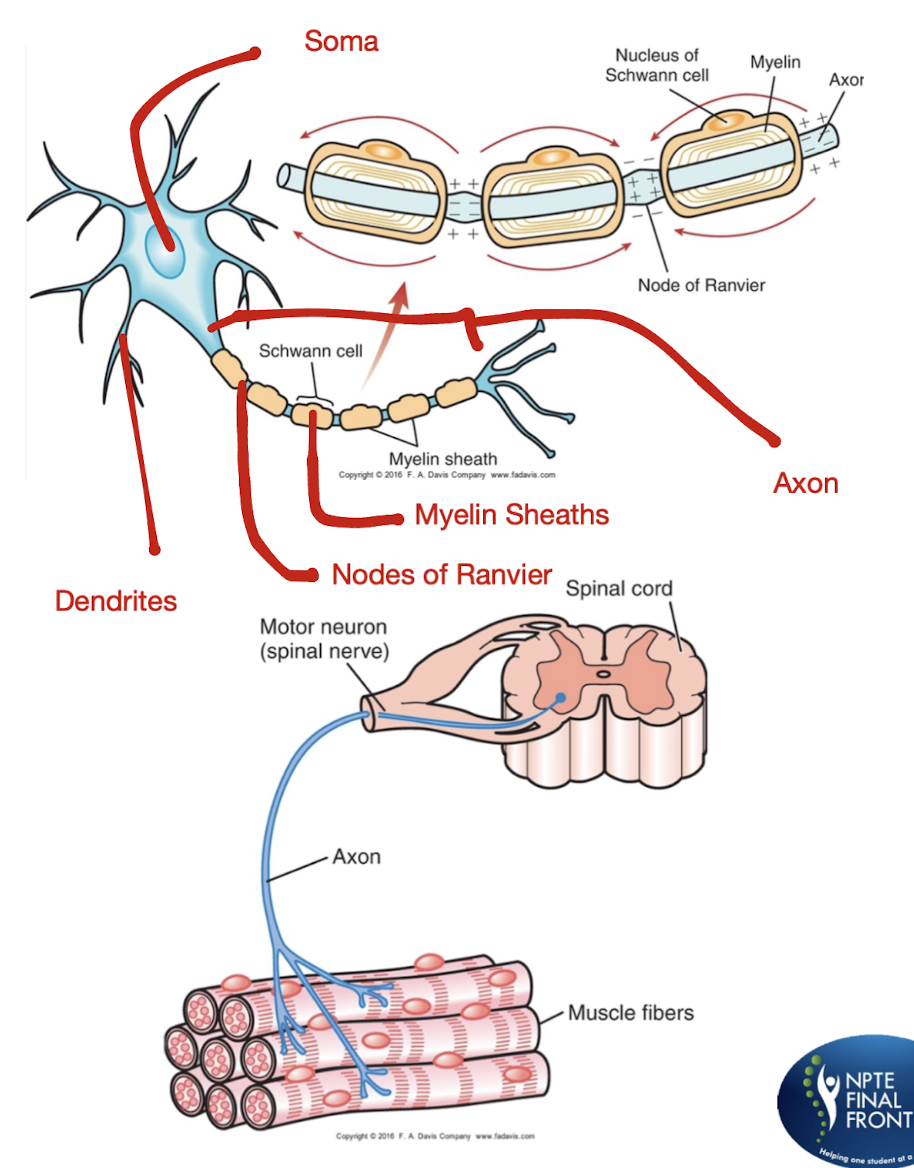
Practice Q 1:
Which of the following are periodic interruptions of myelin along the nerve axon that have relatively decreased resistance to ionic exchange, thus more easily permitting depolarization?
A. Schwann cells
B. Nodes of Ranvier
C. Anterior horn cells
D. Motor units
B. Nodes of Ranvier
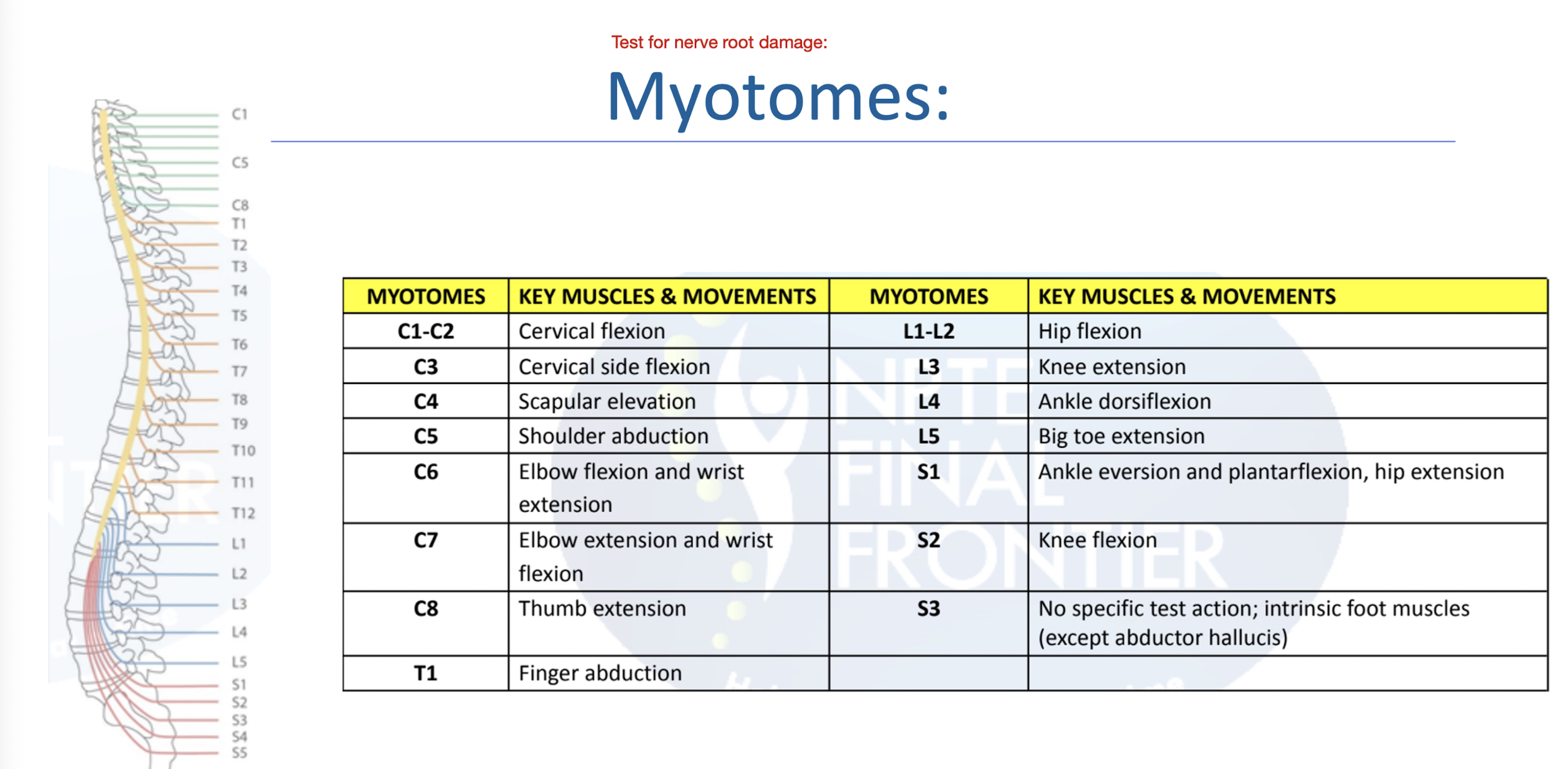
UE and LE Myotomes:
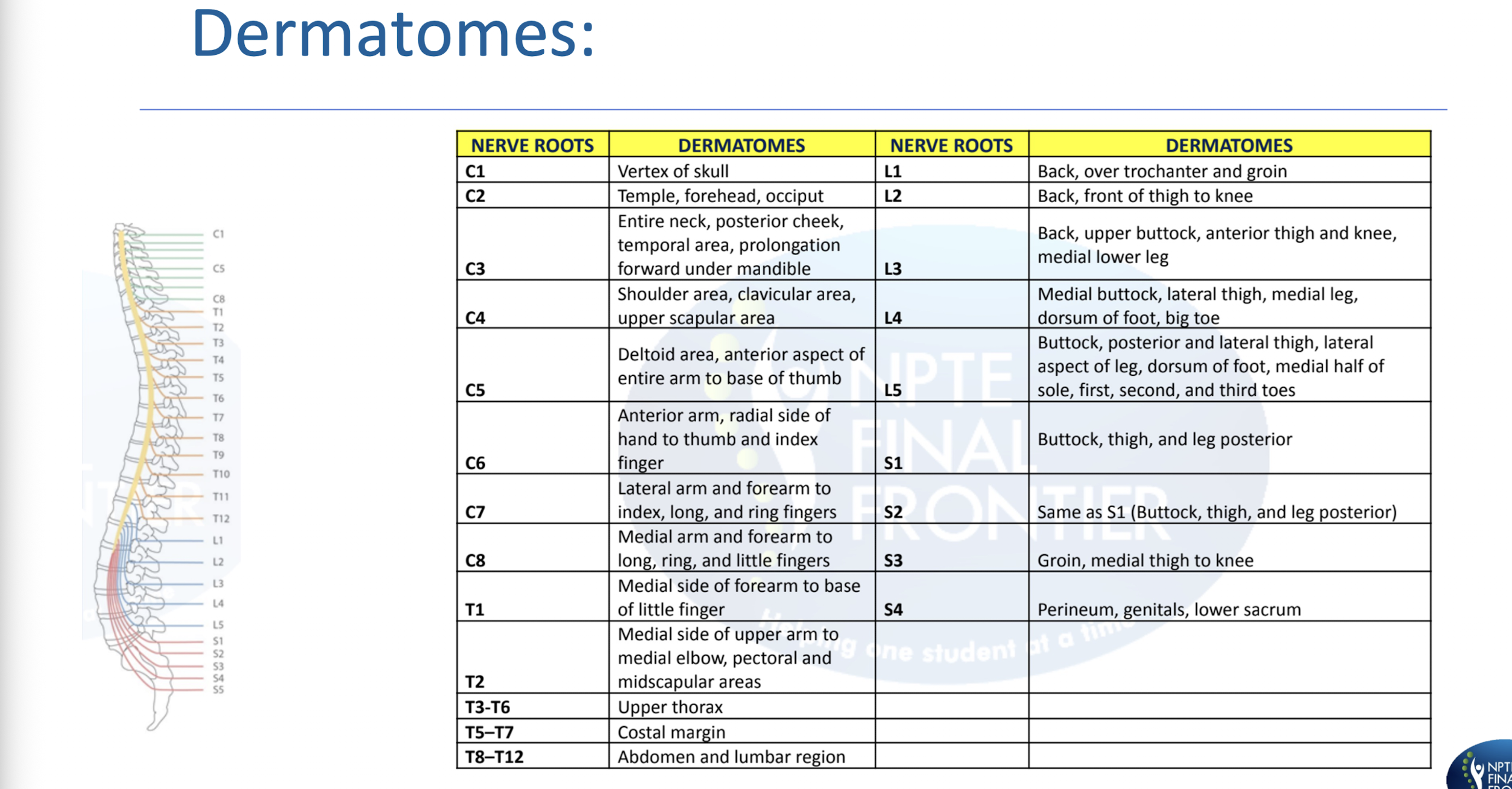
UE and LE Dermatomes:
Practice Q 2:
Patient presents with weak knee extension on right lower extremity, and decreased sensation over upper buttock, anterior thigh and knee. Which of the following would be an appropriate diagnosis for this patient?
A. Femoral nerve entrapment
B. L3 nerve root compression
C. Obturator nerve lesion
D. Lateral stenosis compressing L4 nerve root
B. L3 nerve root compression
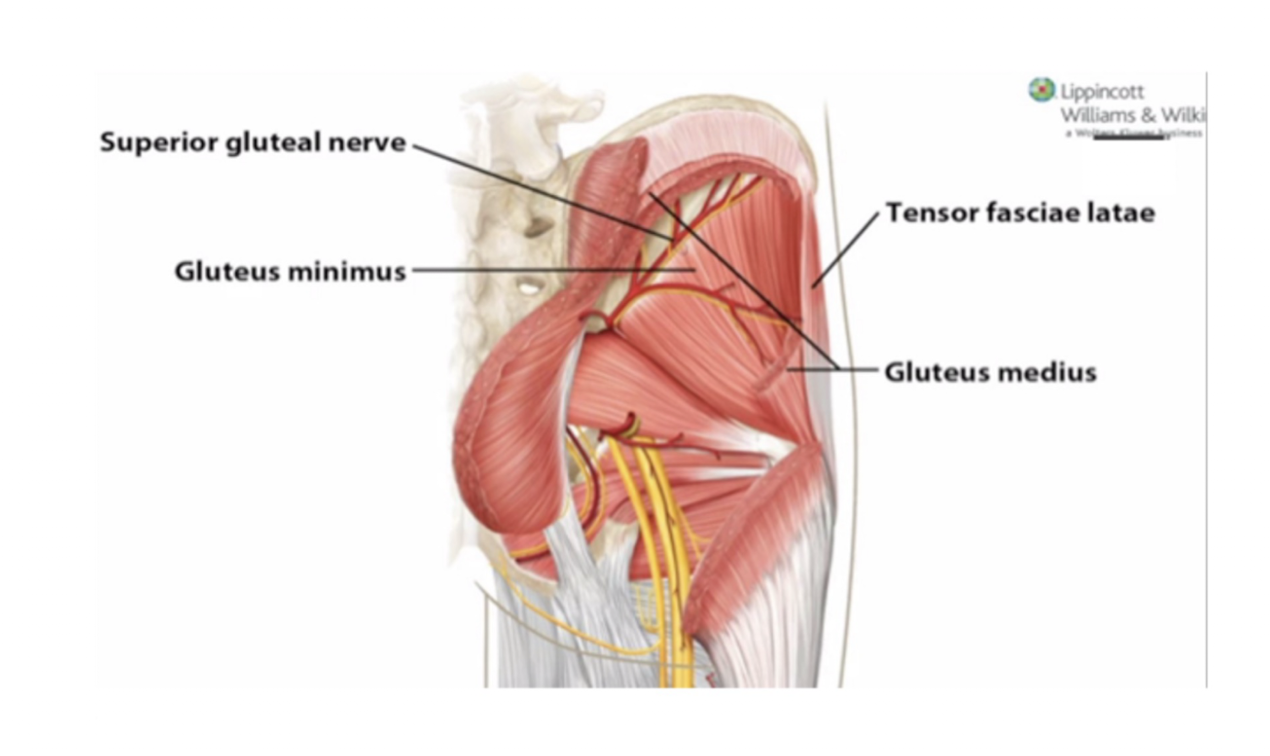
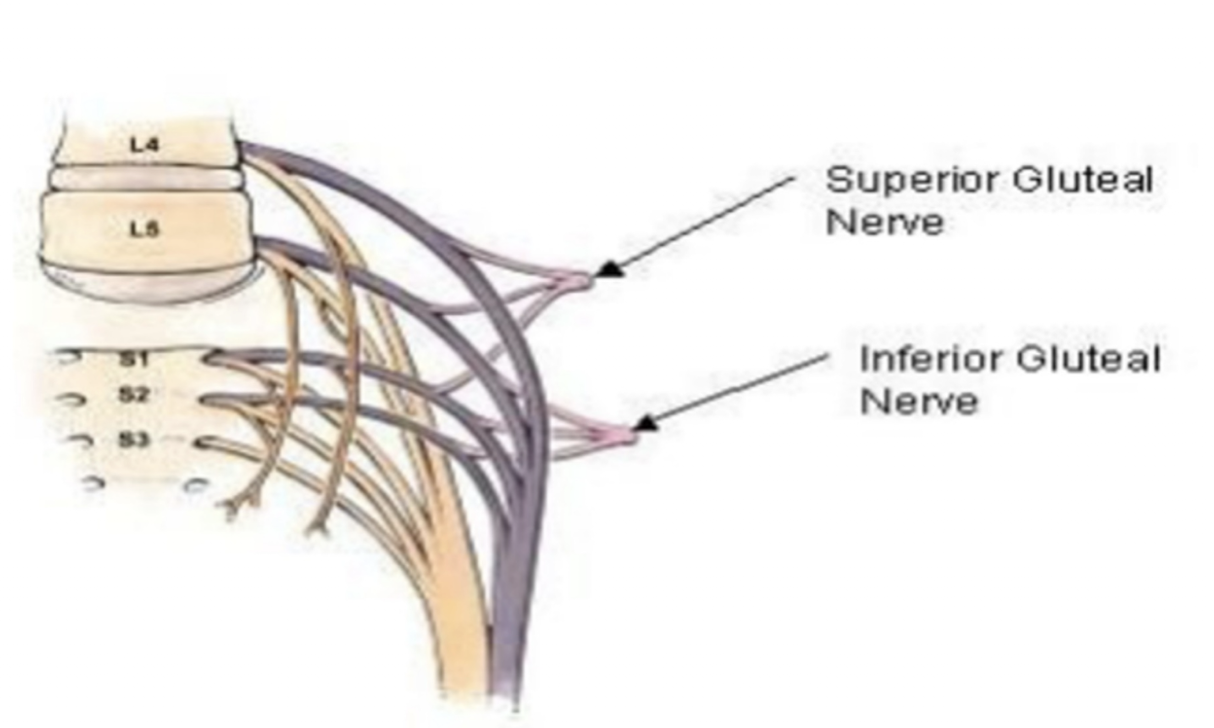
Superior Gluteal Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
Muscles Affected: (3)
Movement Impaired: (3)
Gait Pattern:
L4-S1
Muscles:
Glute Med
Glute Min
TFL
Movements:
Hip Abd
Hip Flex
Medial Rotation (IR)
Gait:
Trendelenberg Gait
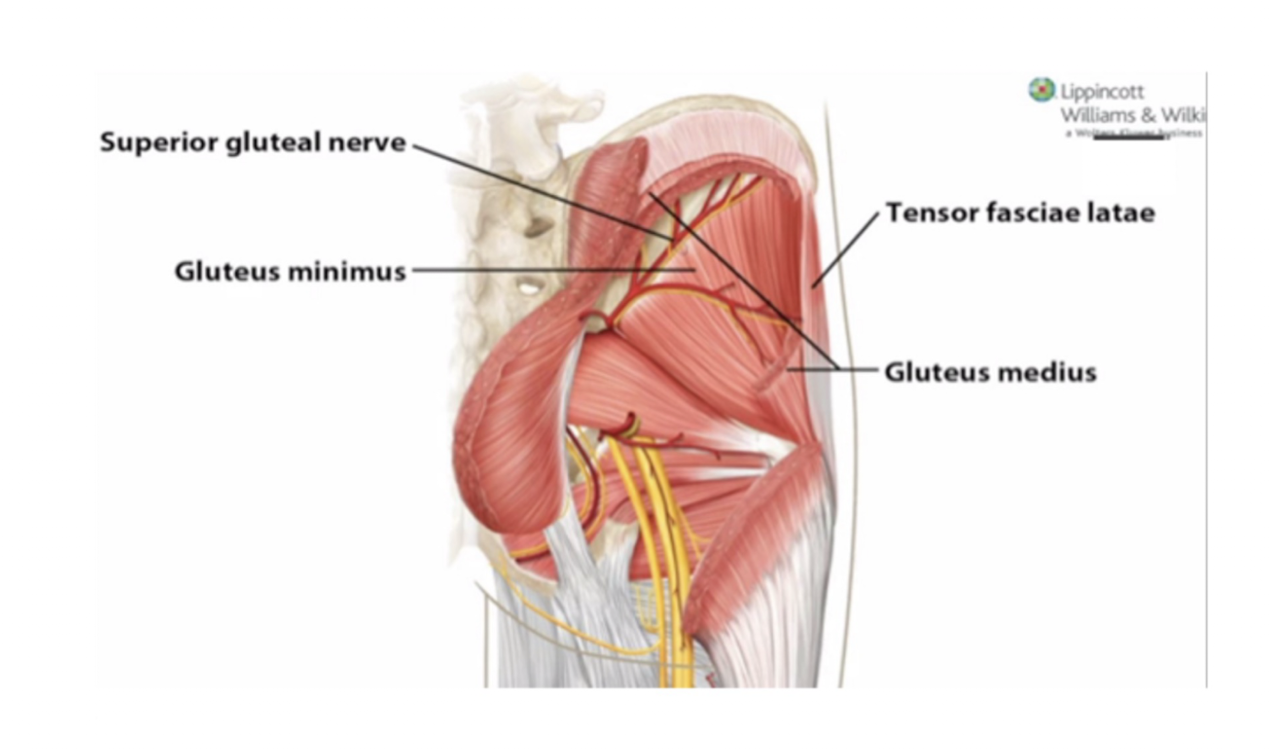
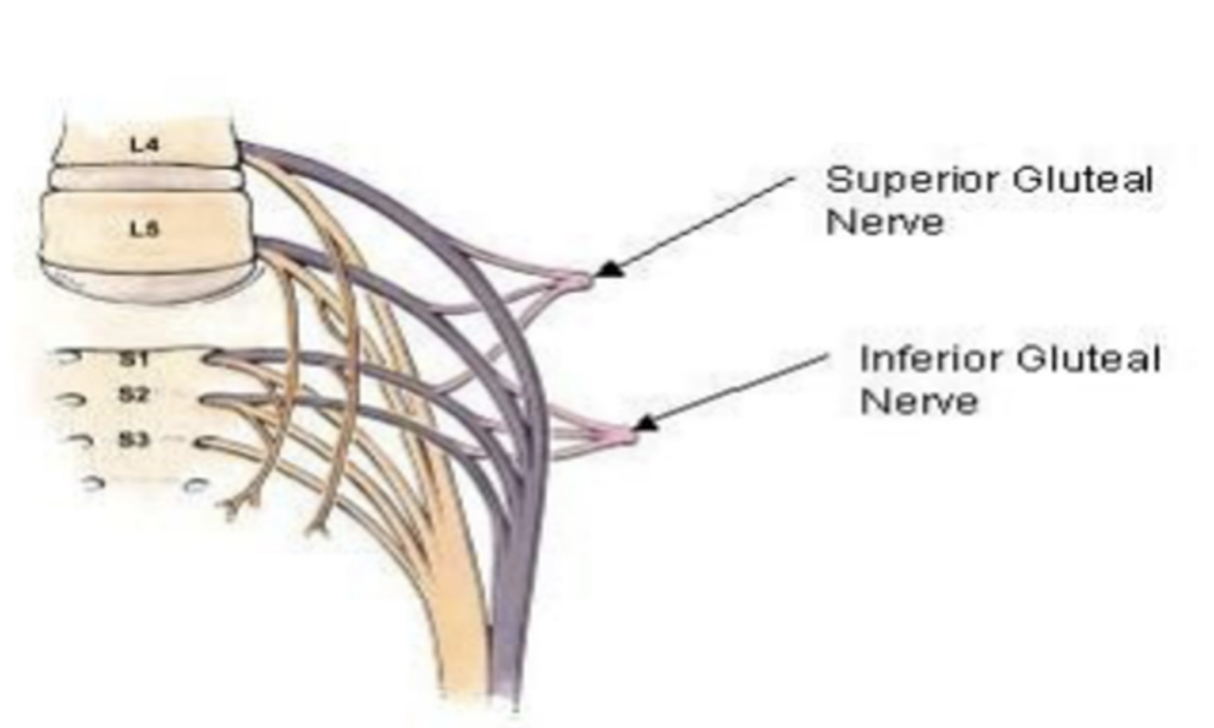
Inferior Gluteal Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
Muscle Affected:
Movement Impaired: (2)
L5-S2
Muscles:
Glute Max
Movement:
Hip Extension
ER
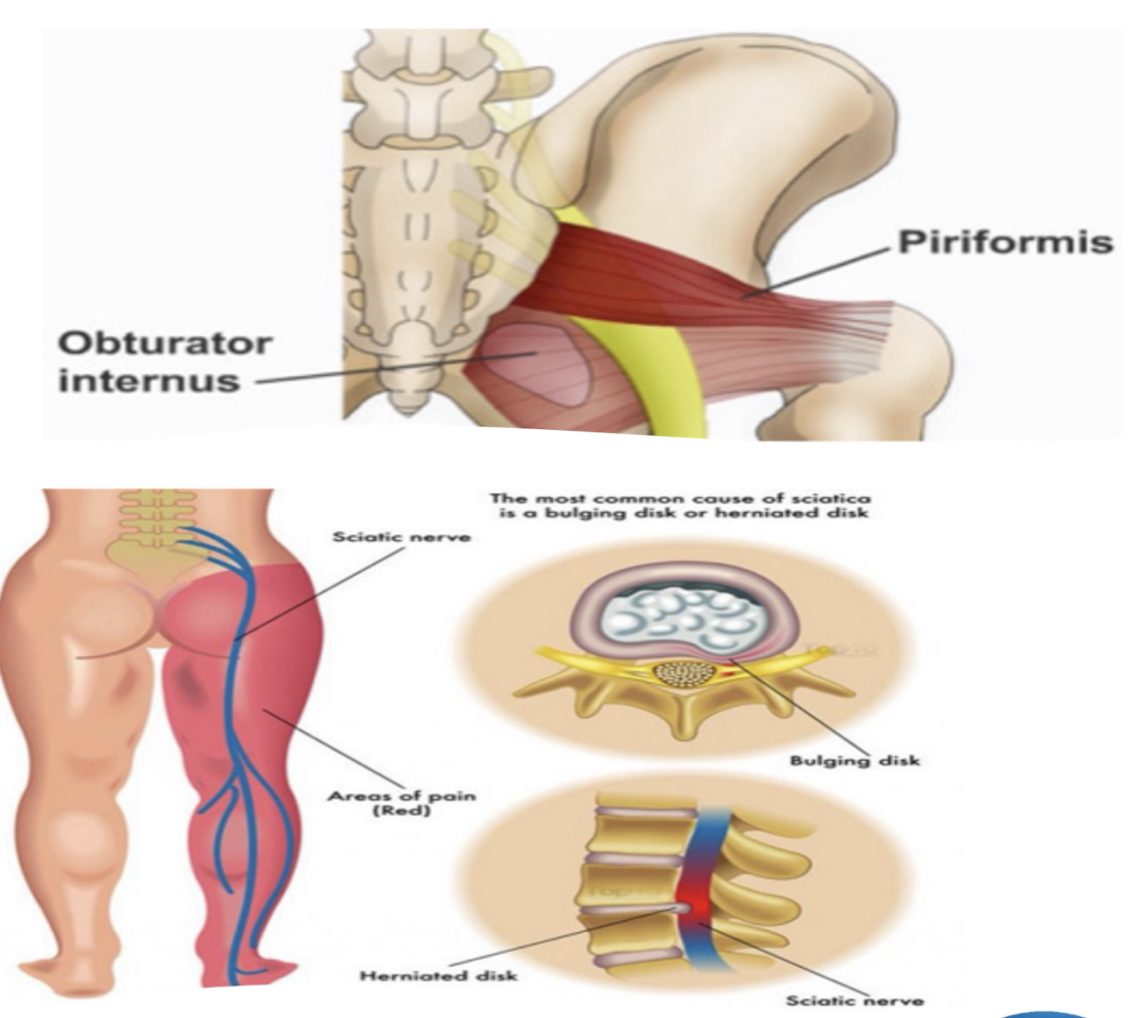
Sciatic Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
Originates and Crosses where?
Piriformis Syndrome » due to…
L4-S3
Originates from SACRAL PLEXUS and Crosses through GREATER SCIATIC FORAMEN in Pelvis
Piriformis:
Abnormal shortening of the muscle » compression and causing irritation at nerve site
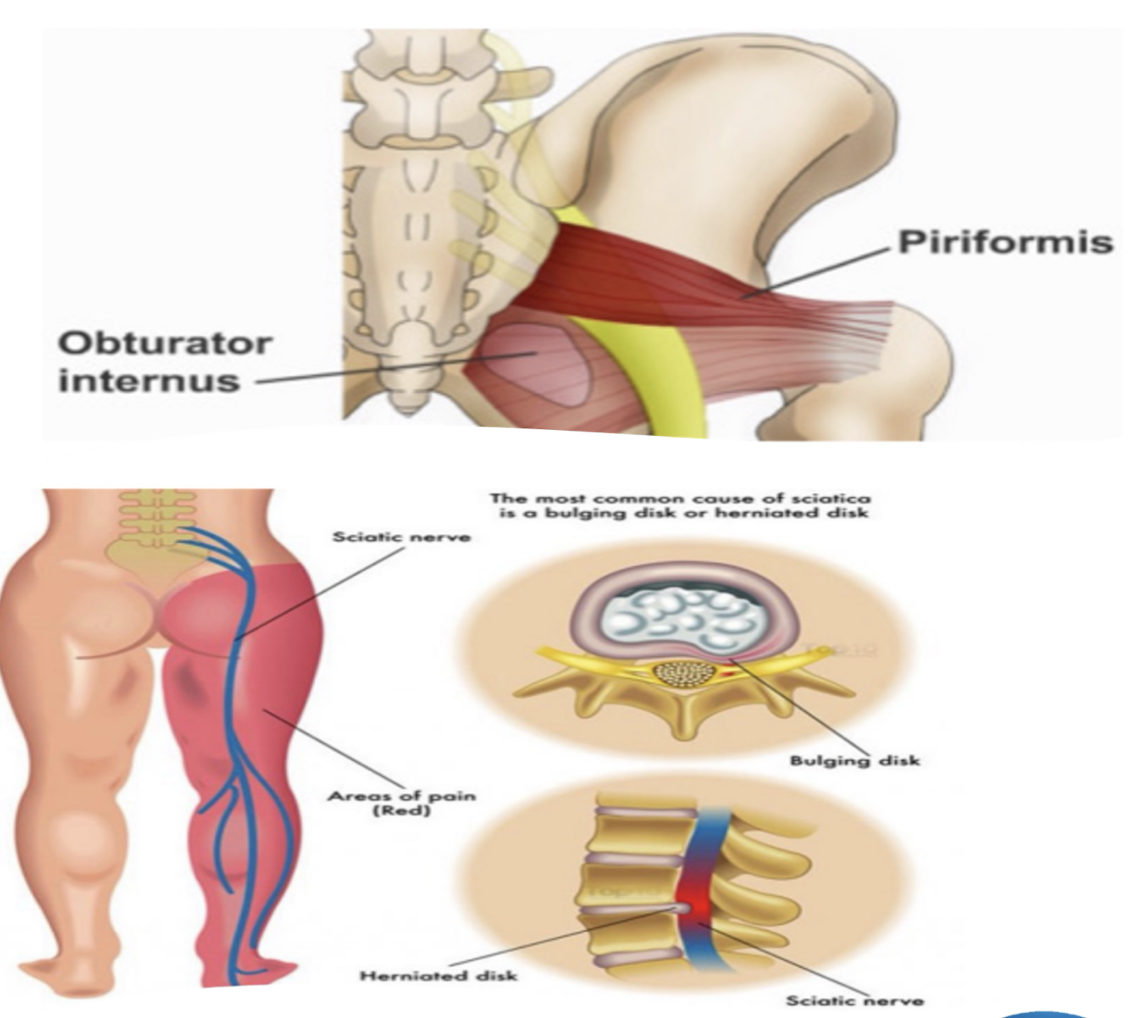
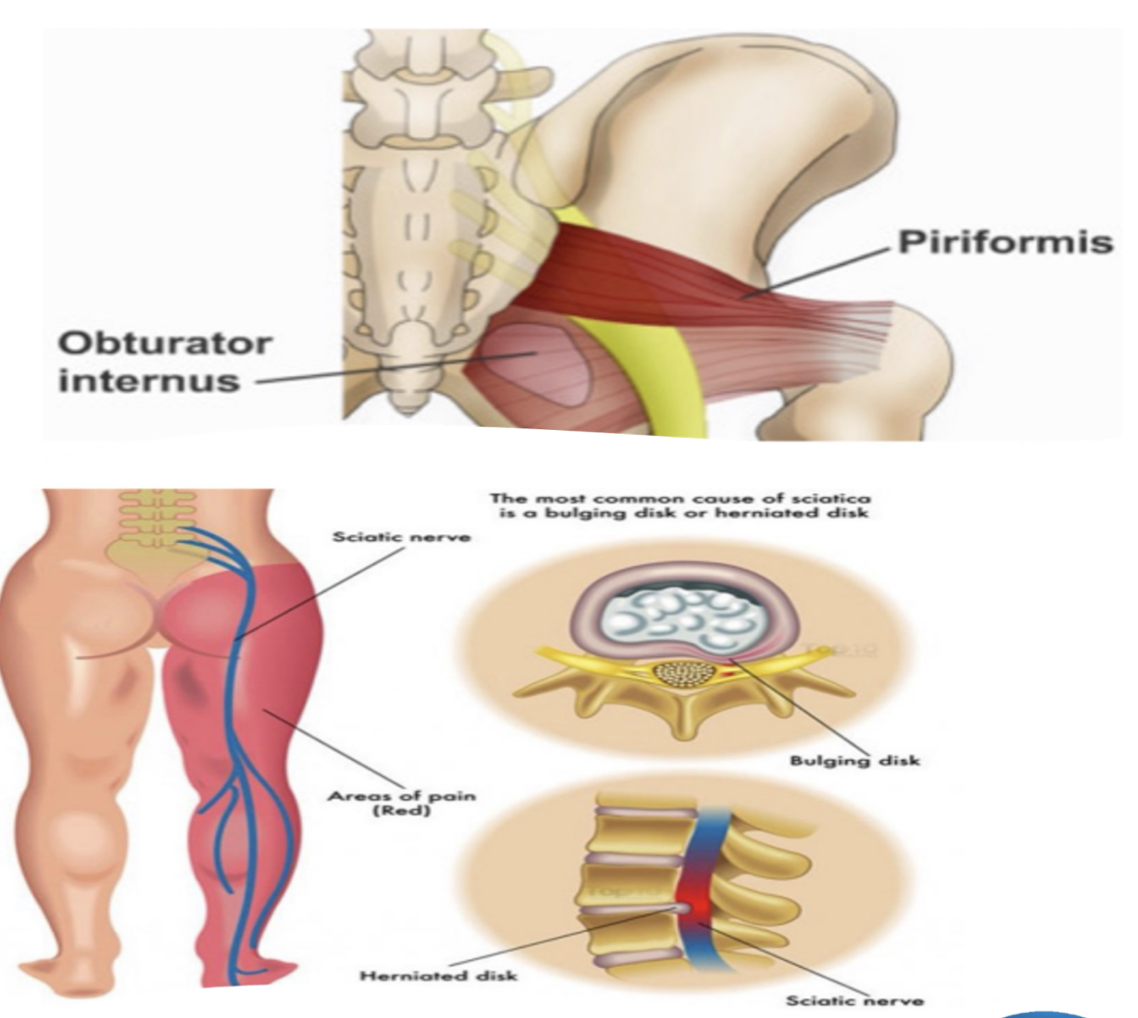
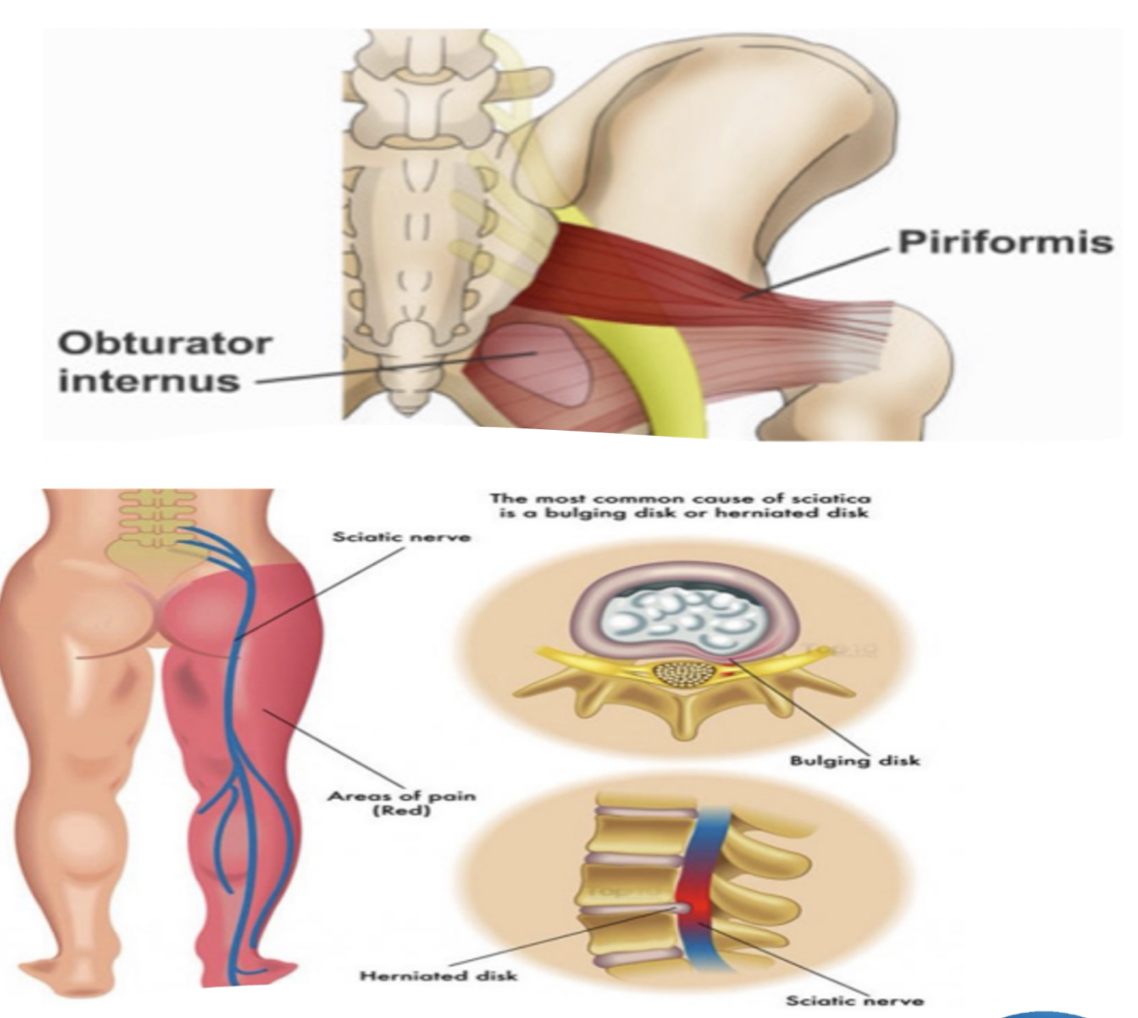
Sciatic Nerve:
Sciatica » due to…
Muscles Affected: (4)
Sciatica:
Herniated Disc OR Bone Spur that cormpresses Sciatic Nerve and causes radiating pain
Muscles: (BASS)
Biceps Femoris
Adductor Magnus
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
Practice Q 3:
Pt presents with left hip drop while performing gait training on an even surface and no assistive device. Which of the following findings would be expected while examining the patient?
A. A compensatory left trunk lean during stance on the right lower extremity
B. A posterior lean during stance phase on the right lower extremity
C. A compensatory right trunk lean during stance on the right lower extremity
D. A decrease in step length of the the right lower extremity
C. A compensatory right trunk lean during stance on the right lower extremity
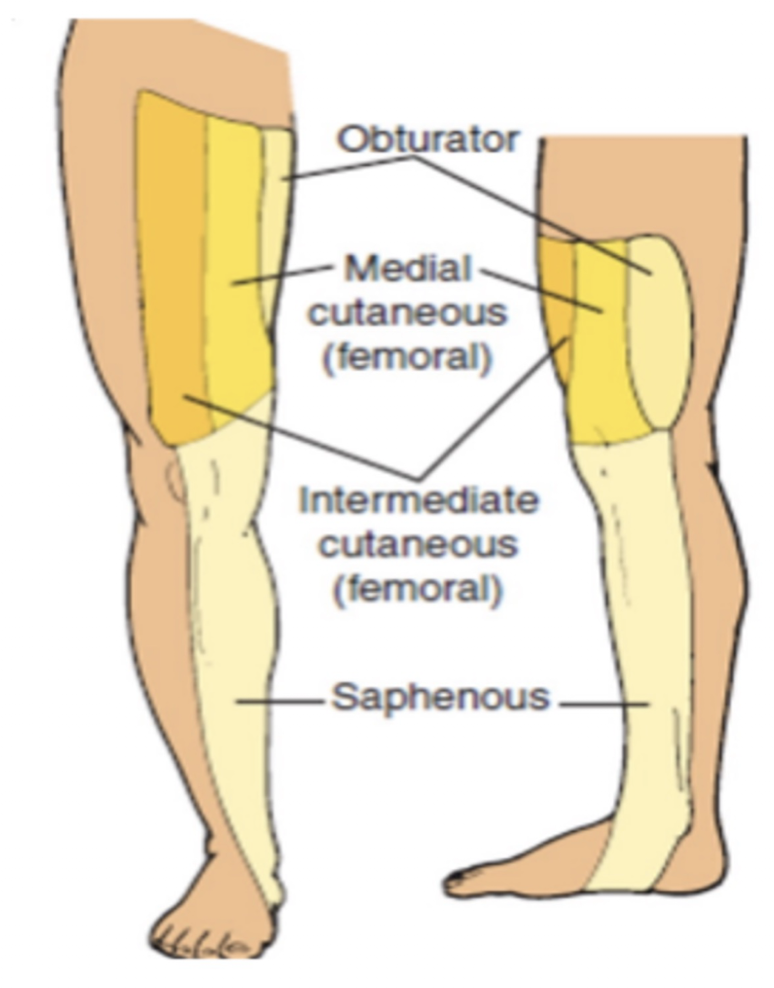
Femoral Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
Originated from where?
MOI: (3)
L2-L4
Originates from Lumbar Plexus
MOIS:
Upper femur or pelvis fx
Hip dislocation c reduction
Forceps pressure during labor
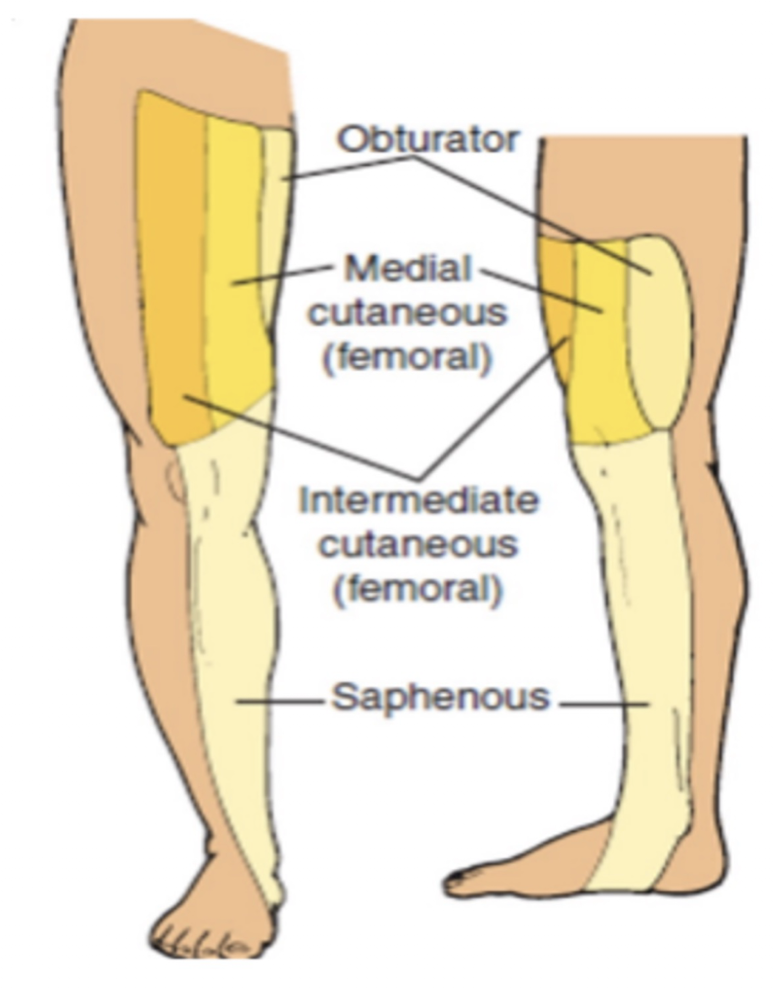
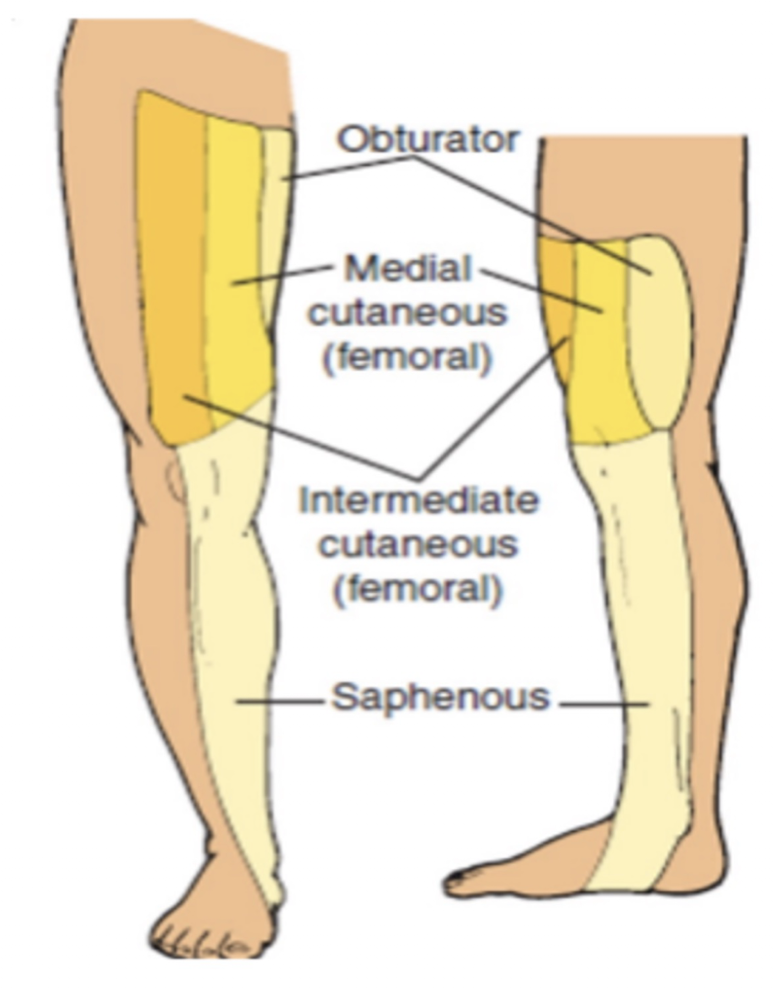
Femoral Nerve:
Muscle Affected: (3)
Sensory Impairments:
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Intermediate Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Medial Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Saphenous Nerve: (3)
NOTE: All these nerves are PURE SENSORY
Muscles:
Quads
Pectinius
Sartorius
Sensory Impairments:
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Lateral Thigh over ITB
Intermediate Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Anterior Thigh
Medial Femoral Cutaneous Nerve:
Anteromedial Thigh
Saphenous Nerve:
Medial Femoral Condyle
Posterior Medial Lower Leg
Medial Malleolus
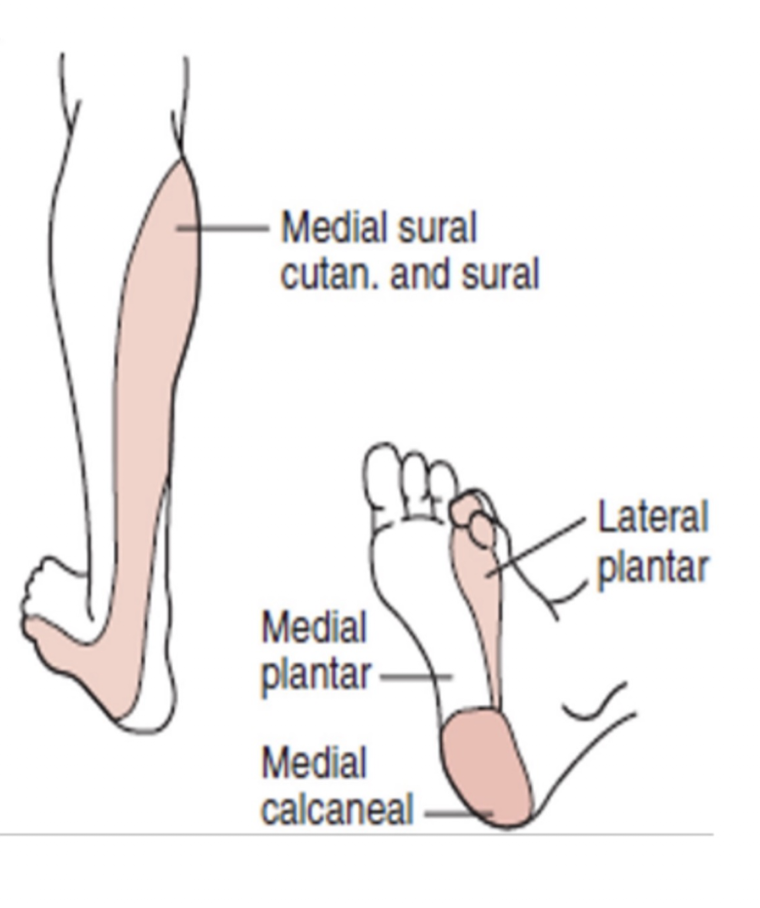
Tibial Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
Muscles: (7)
L4-S3
Muscles:
Gastroc
Soleus
Plantaris
Posterior Tib
Popliteus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
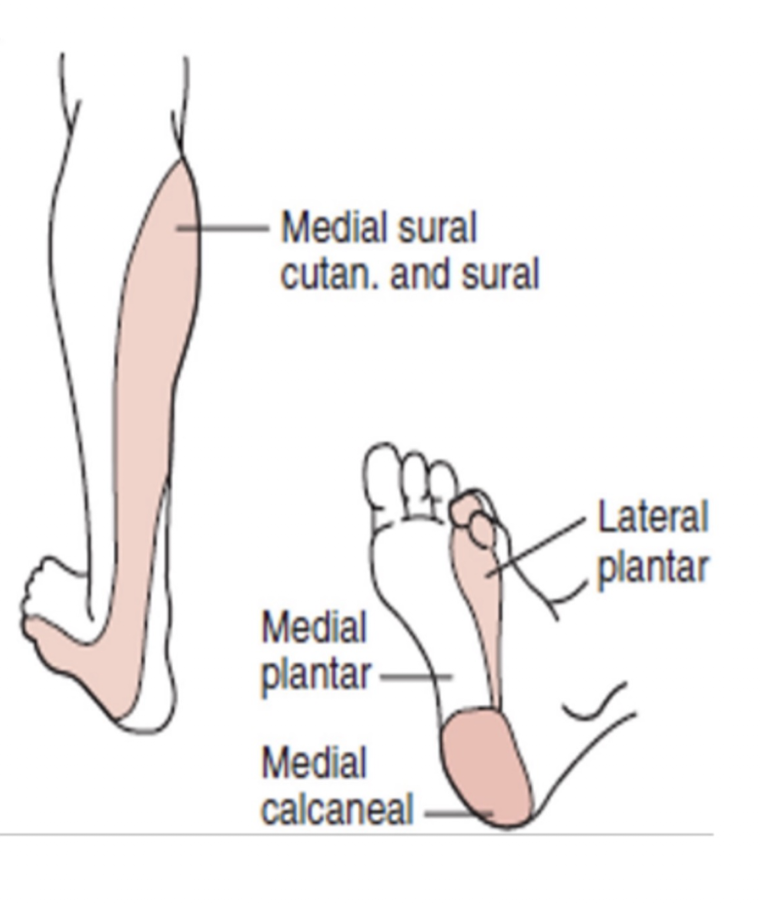
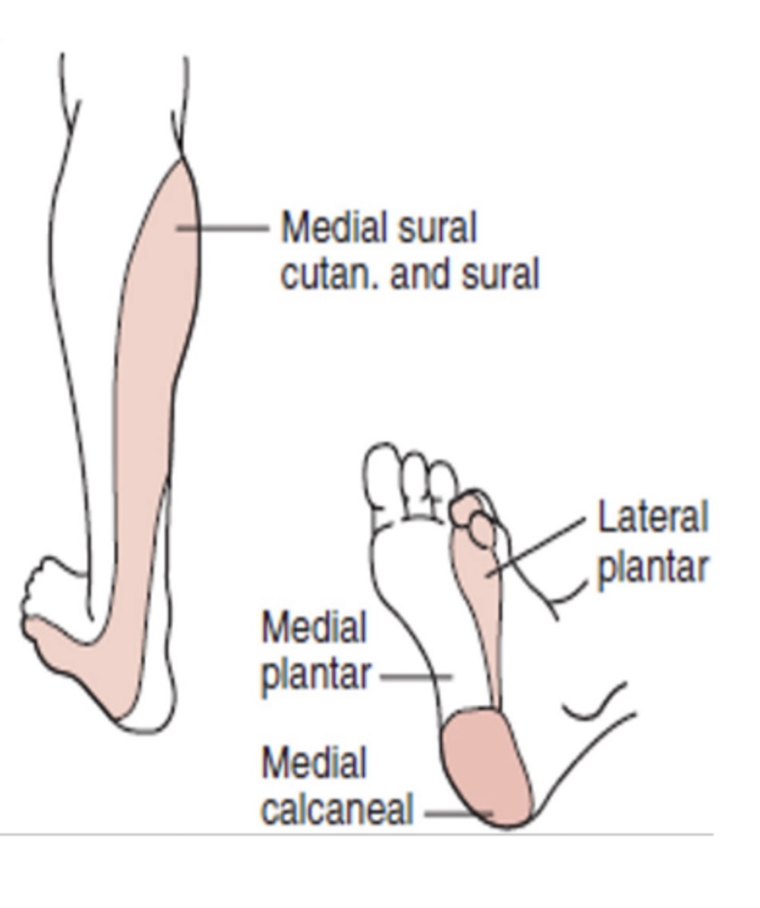
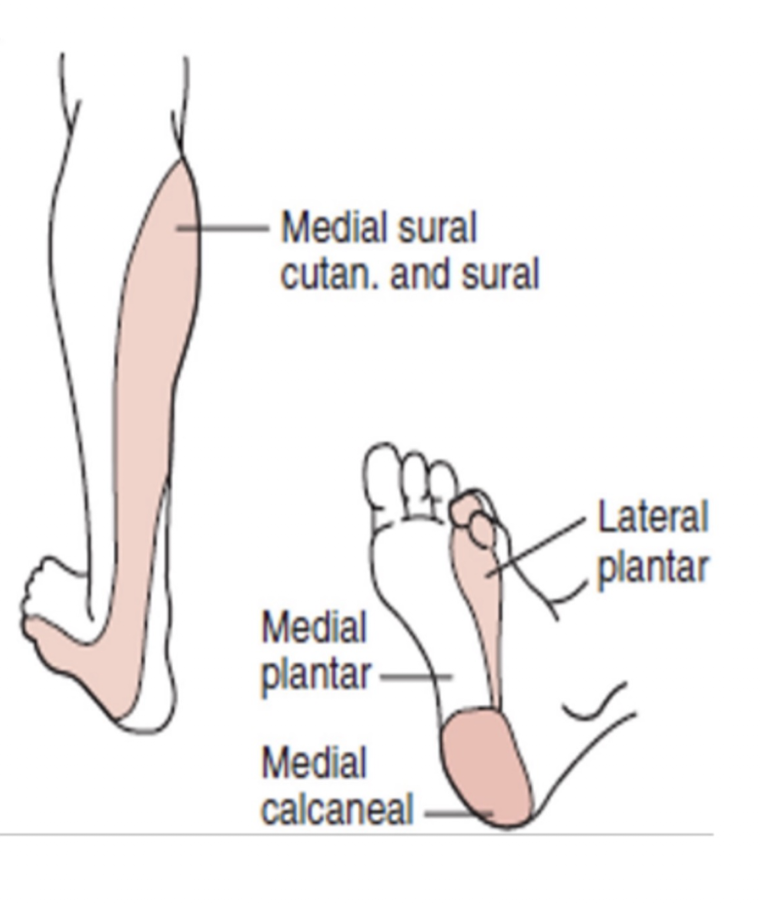
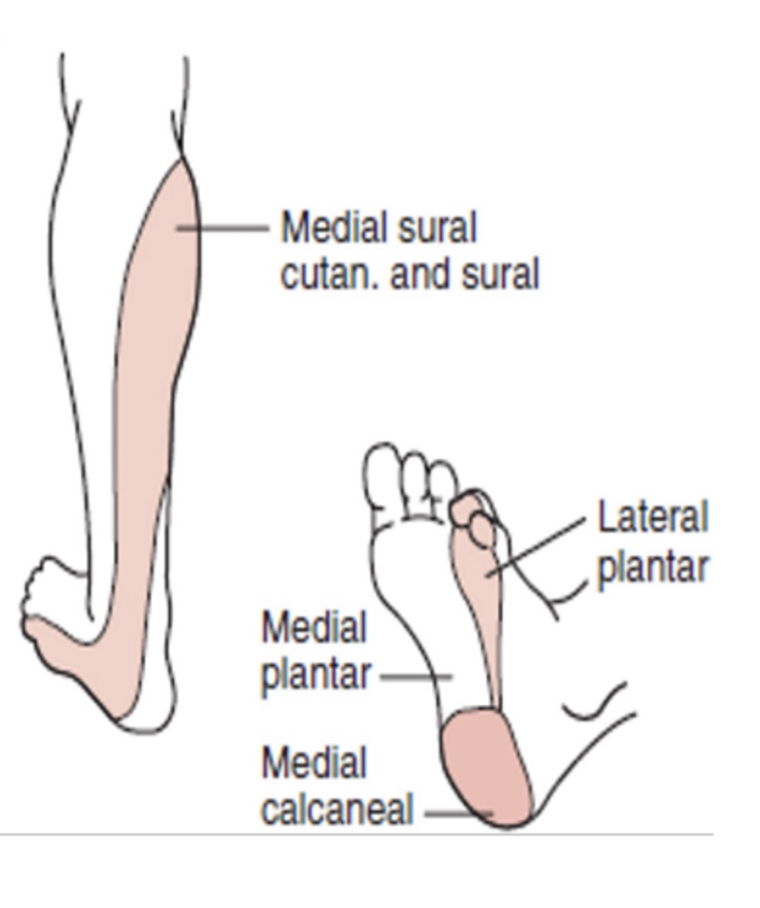
Tibial Nerve:
Sensory Branches:
Medial Plantar Nerve:
Lateral Plantar Nerve:
Medial Calcaneal Nerve:
Sural Nerve: (3)
NOTE: All these nerves are PURE SENSORY
Medial Plantar Nerve:
Medial foot » Sole over 1, 2, 3 and medial half of the 4 digit
Lateral Plantar Nerve:
Lateral foot » Sole over lateral half of 4 toe and entire 5 digit
Medial Calcaneal Nerve:
Medial heel
Sural Nerve:
Posteriolateral lower leg
Lateral border of the dorsum of the foot
Lateral heel
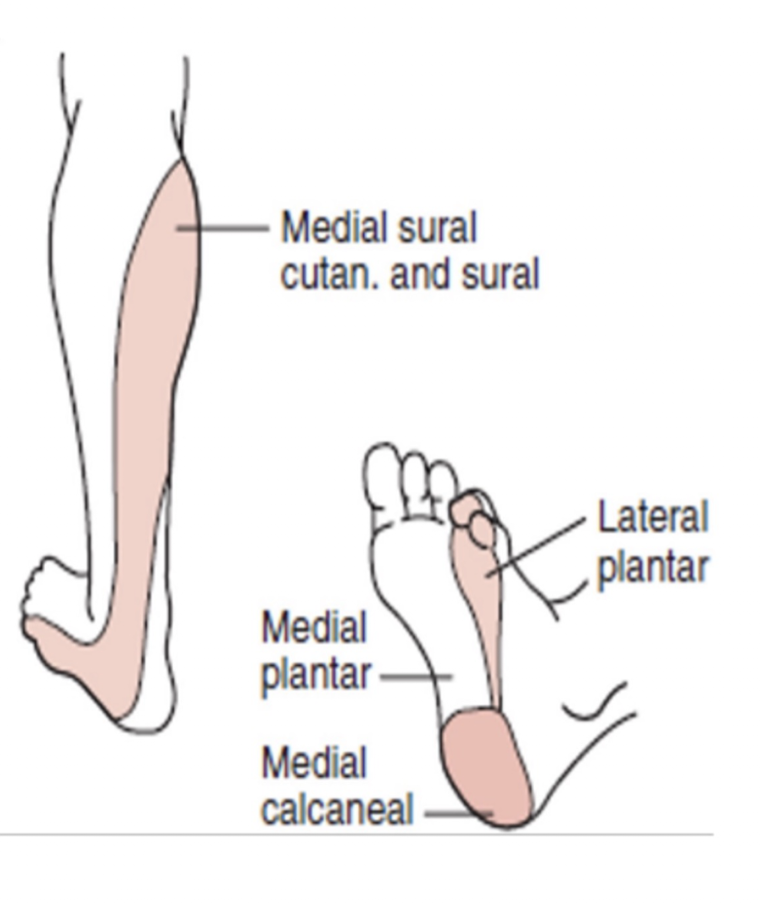
Tibial Nerve:
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome:
Describe:
S/S: (3)
Postural Foot Changes d/t Compression Injury:
Pes Cavus:
Pes Planus:
Claw Toes:
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome:
Describe:
Tibial Nerve entrapped under mefial foot through Adductor Hallucis
S/S: (3)
Postermedial Plantar Foot Pain
Painful Heel
Pes Cavus = Pain
Postural Foot Changes d/t Compression Injury:
Pes Cavus:
High Longitudinal Arch
Pes Planus:
Collapsed Medial Arch marked by flat feet when WB
Claw Toes:
MTP Ext, PIP/DIP Flex
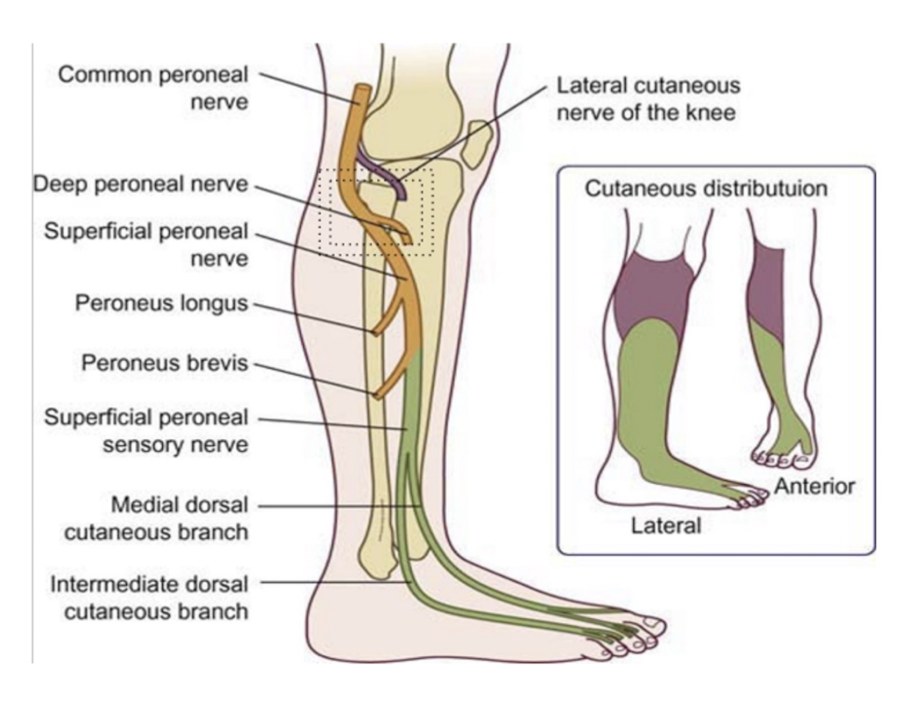
Common Peroneal Nerve:
Nerve Roots:
2 Branches:
L4-S2
2 Branches:
Superficial Peroneal
Deep Peroneal
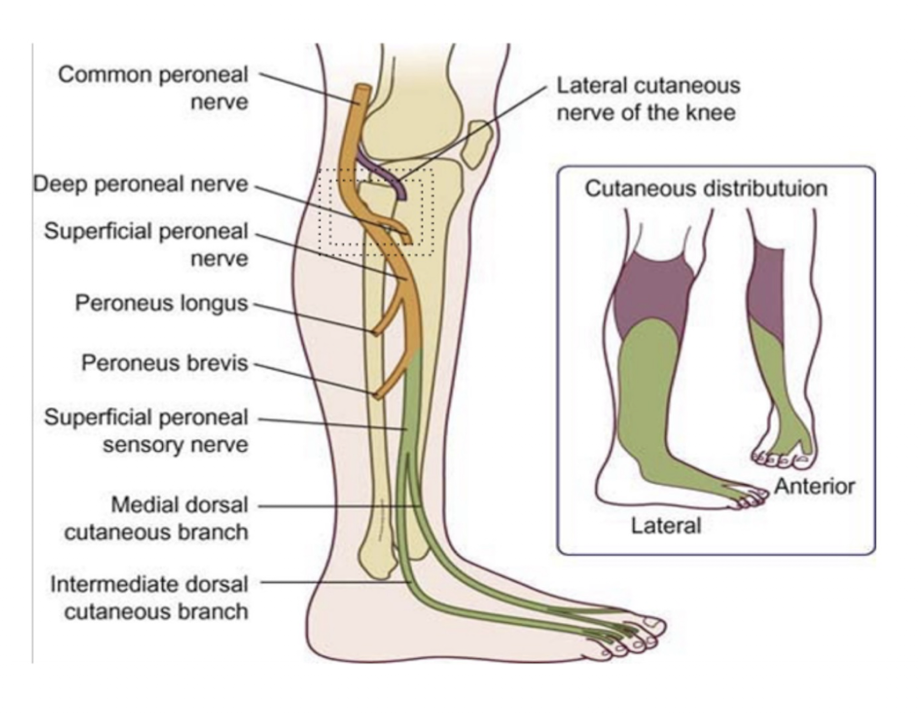
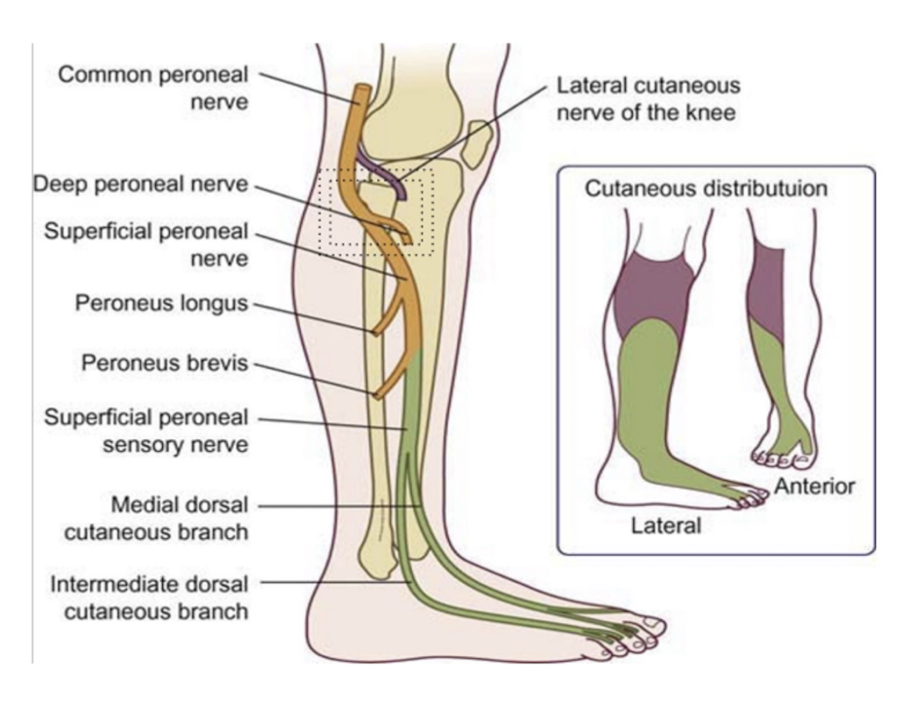
Common Peroneal » Superficial Peroneal:
Sensory = (2)
Muscles = (2)
Injury =
Sensory:
Anterolateral Lower Leg
Dorsum of the Foot
Muscles:
Peroneus Longus
Peroneus Brevis
Injury:
Decreased eversion strength
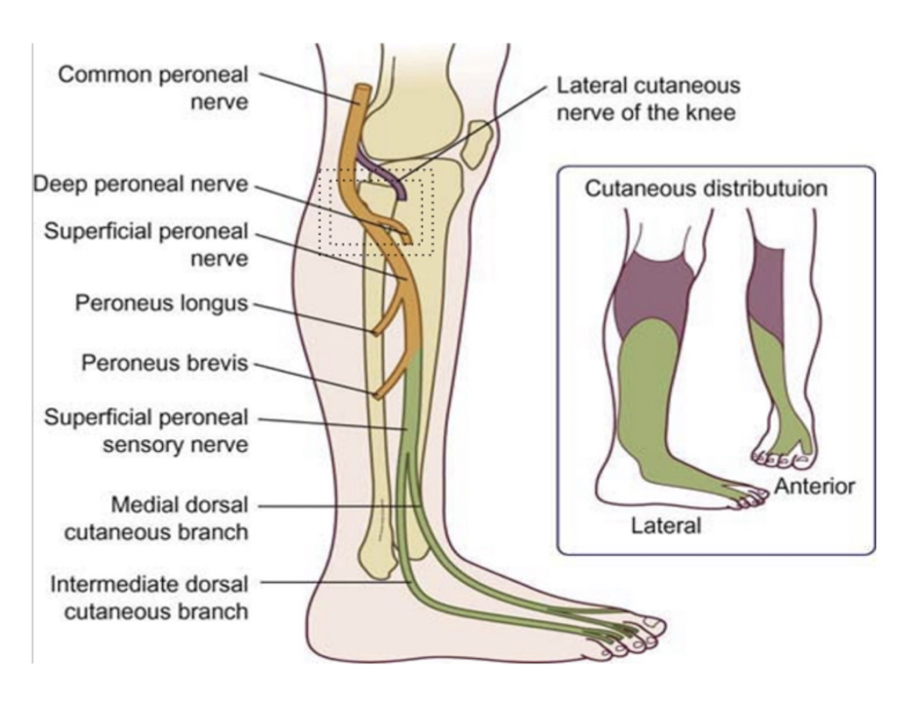
Common Peroneal » Deep Peroneal:
Sensory =
Paresthesia S/S = HALLMARK SIGN OF…
Muscles = (6)
Injury = (2)
Sensory:
Anterolateral Lower Leg
Dorsum of the Foot
Anterior Compartment Syndrome
Muscles:
Anterior Tib
Peroneus Tertius
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Extensor Hallucis Brevis
Extensor Digotorum Longus
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Injury:
Foot Drop
Unopposed Eversion
Practcie Q 4:
Patient reports chronic left lower extremity weakness. During examination pt noted to have genu recurvatum during stance on the left lower extremity. Which of the following be the cause of this impairment?
A. Lesion to the femoral nerve
B. Lesion to the superior gluteal nerve
C. Lesion to the obturator nerve
D. Lesion to the sural nerve
A. Lesion to the femoral nerve
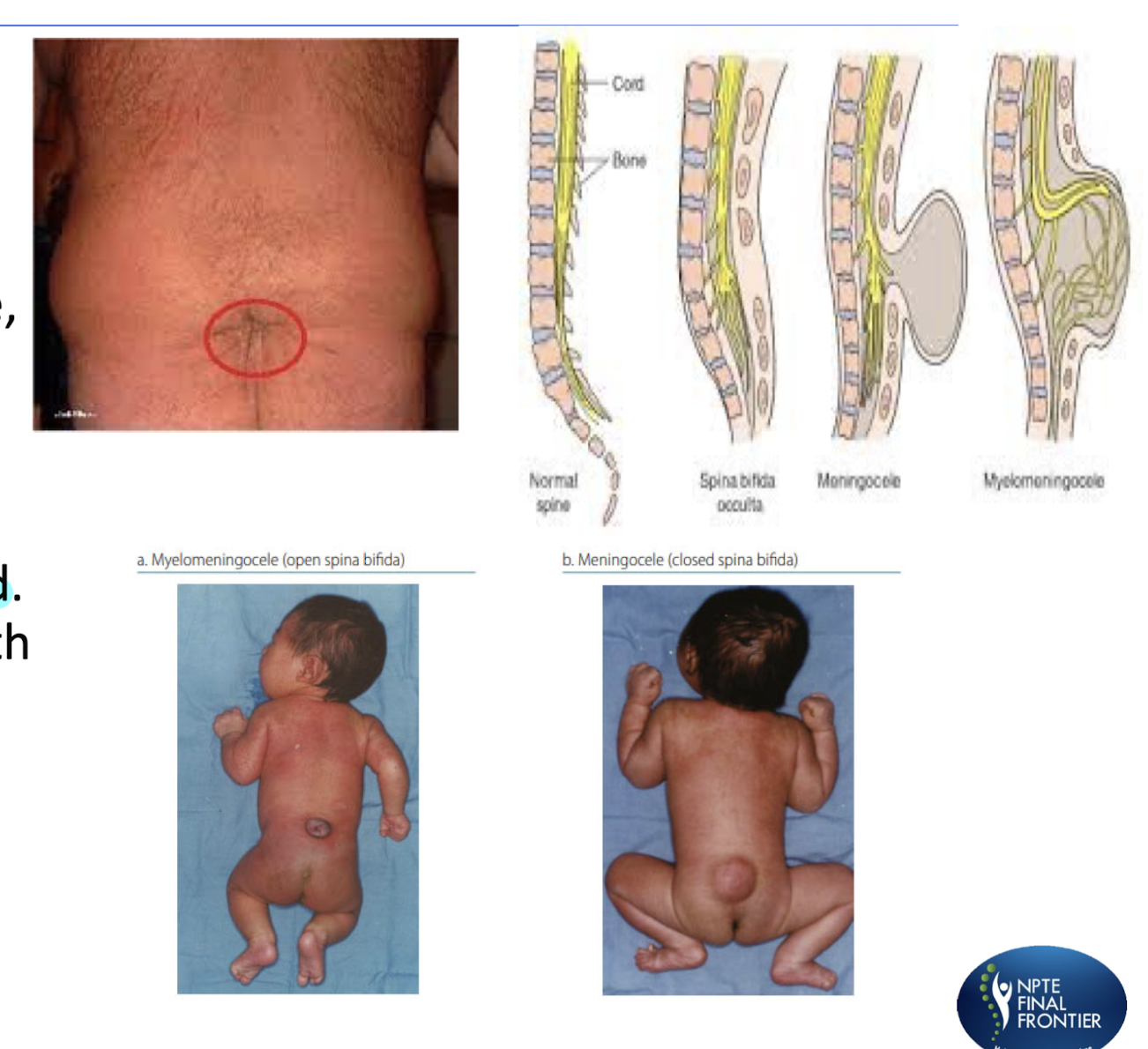
Spina Bifida:
What are the 3 types of Spina Bifida?
Most Severe/Worst Prognosis:
Least Severe:
Myelomeningiocele (MOST Severe)
Sac of fluid comes out through opening contains SC tissue, meninges, and CSF
Meningocele
Sac of fluid comes through an opening
SC is NOT INVOLVED
Covered by skin and associated c NAUR PARALYSIS
Occulta (LEAST Severe) » Means Hidden/Closed
Impariement and non fusion of the SP of the vertebra, SC, and nerves are usually normal
Spina Bifida Causes:
6 Causes:
Folic acid deficiency
Genetic factors
Excessive alcohol consumption
Anti-seizure medications
Recreational drugs
Higher than normal maternal temperature
Spina Bifida Causes;
What 2 tests are done by taking the mother’s blood to see if they have any factors that can cause Spina Bifida?
Maternal Serum Alpha Feto Protein (MSAFP) Test:
Checks Mom’s Alpha Fetoprotein (AFP) Levels
Triple Screen Blood Test:
AFO + Hyman Choronic Gonadotropin (hCG) + Estirol Levels
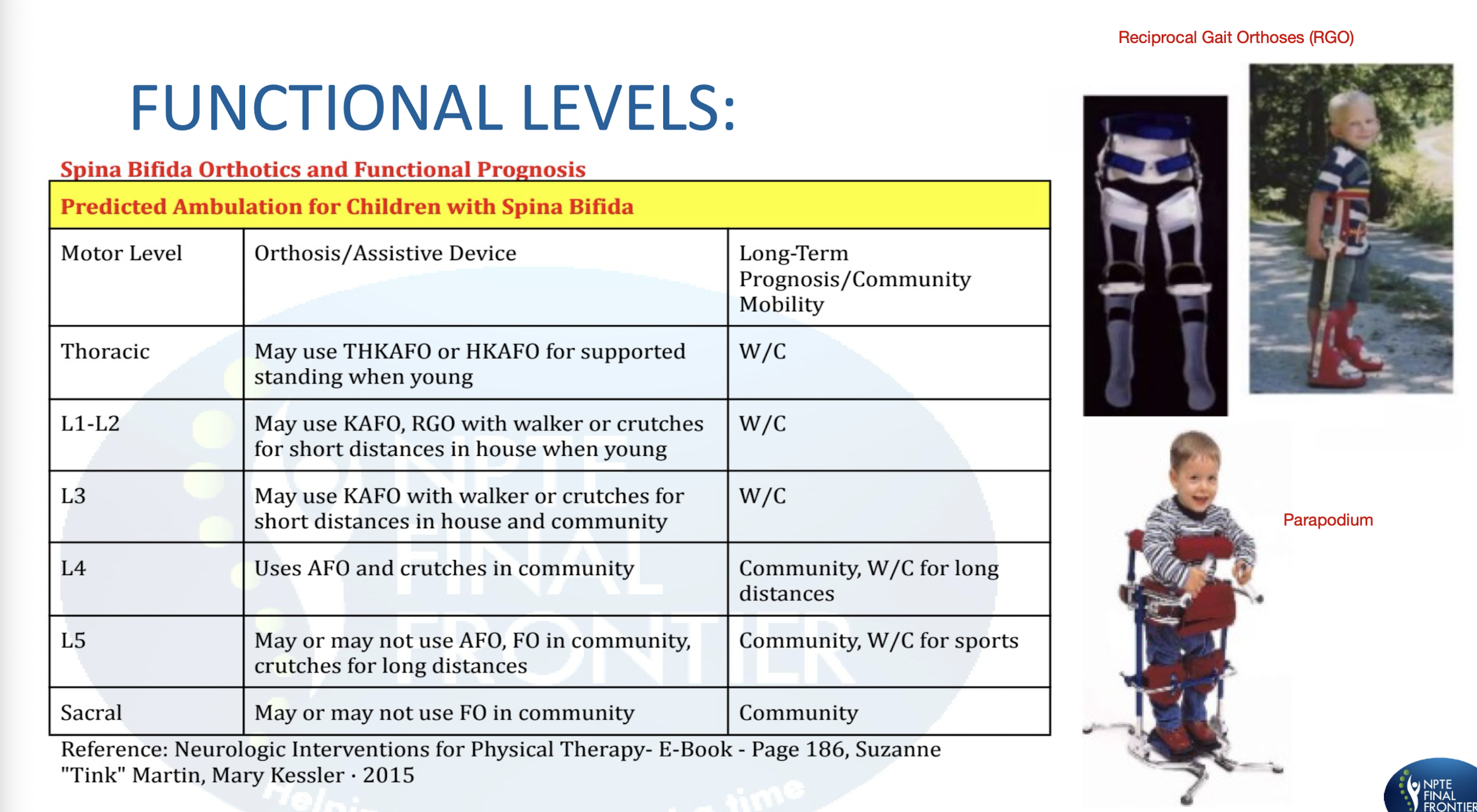
Spina Bifida Functional Levels:
Practics Q 5:
A clinician is treating a 2 y.o with L2 Spina Bifida myelomeningocele. The patient’s mother asks the clinician what is the long-term prognosis for walking. What is the BEST response from the clinician?
A)The patient will most likely require manual wheelchair for all functional mobility
B) The patient will most likely ambulate household distances with bilateral HKAFO’s and upper extremity support, manual wheelchair for all community mobility
C) The patient will most likely ambulate community distances with bilateral AFO’s
D)The patient will most likely ambulate household distances with bilateral KAFO and upper extremity support, manual wheelchair for all community mobility
D)The patient will most likely ambulate household distances with bilateral KAFO and upper extremity support, manual wheelchair for all community mobility
Balance Strategies: ANKLE
Perturbation/Force/Sway:
Muscle Activation:
Muscle Group Activation:
FWD Sway Ex:
Backward Sway Ex:
Perturbation/Force/Sway:
Small
Slow
Near Midline
Muscle Activation:
Distal to Proximal
Muscle Group Activation:
OPPOSITE
FWD Sway Ex:
Gastroc » HS » Paraspinals
Backward Sway Ex:
Ant Tib » Quads » Abs
Balance Strategies: HIP
Perturbation/Force/Sway:
Muscle Activation:
Muscle Group Activation:
FWD Sway Ex:
Backward Sway Ex:
Perturbation/Force/Sway:
Large
Muscle Activation:
Proximal to Distal
Muscle Group Activation:
SAME
FWD Sway Ex:
Abs » Quads » Ant Tib
Backward Sway Ex:
Paraspinals » HS » Gastroc
Balance Strategies » Protective:
Stepping Strategy:
Perturbations:
COM exceeds ___
Muscles activate to allow what?
Reaching/Grasping Strategy:
Use of…
Extend ___ to stabilize posture
Balance Strategy Order of Recruitement:
Stepping:
Perturbations: Fast and Large
BOS
Allow compensatory weight shift
Reaching:
UE
BOS
Order:
Ankle
Hip
Stepping
Reaching/Grasping
Practice Q 6:
While standing on a moving bus, a patient nearly falls when the bus suddenly stops. Which balance strategy is most likely used to recover stability in response to this quick, large perturbation?
A) Stepping Strategy
B) Ankle Strategy
C) Hip Strategy
D) Reaching Strategy
A) Stepping Strategy

Practice Q 7:
A physical therapist is treating a patient with a history of falls due to frequent tripping while walking. Examination reveals right foot flat initial contact during ambulation with decreased heel strike, patellar deep tendon reflex grading of 1+, and decreased sensation in the right lower extremity along the lateral thigh, medial leg, dorsum of foot, and big toe. The patient is demonstrating s/s that are MOST CONSISTENT with which of the following?
A)L MCA CVA
B) ASIA A SCI at T12
C) L4 radiculopathy
D)Tibial nerve neuropathy.
C) L4 radiculopathy

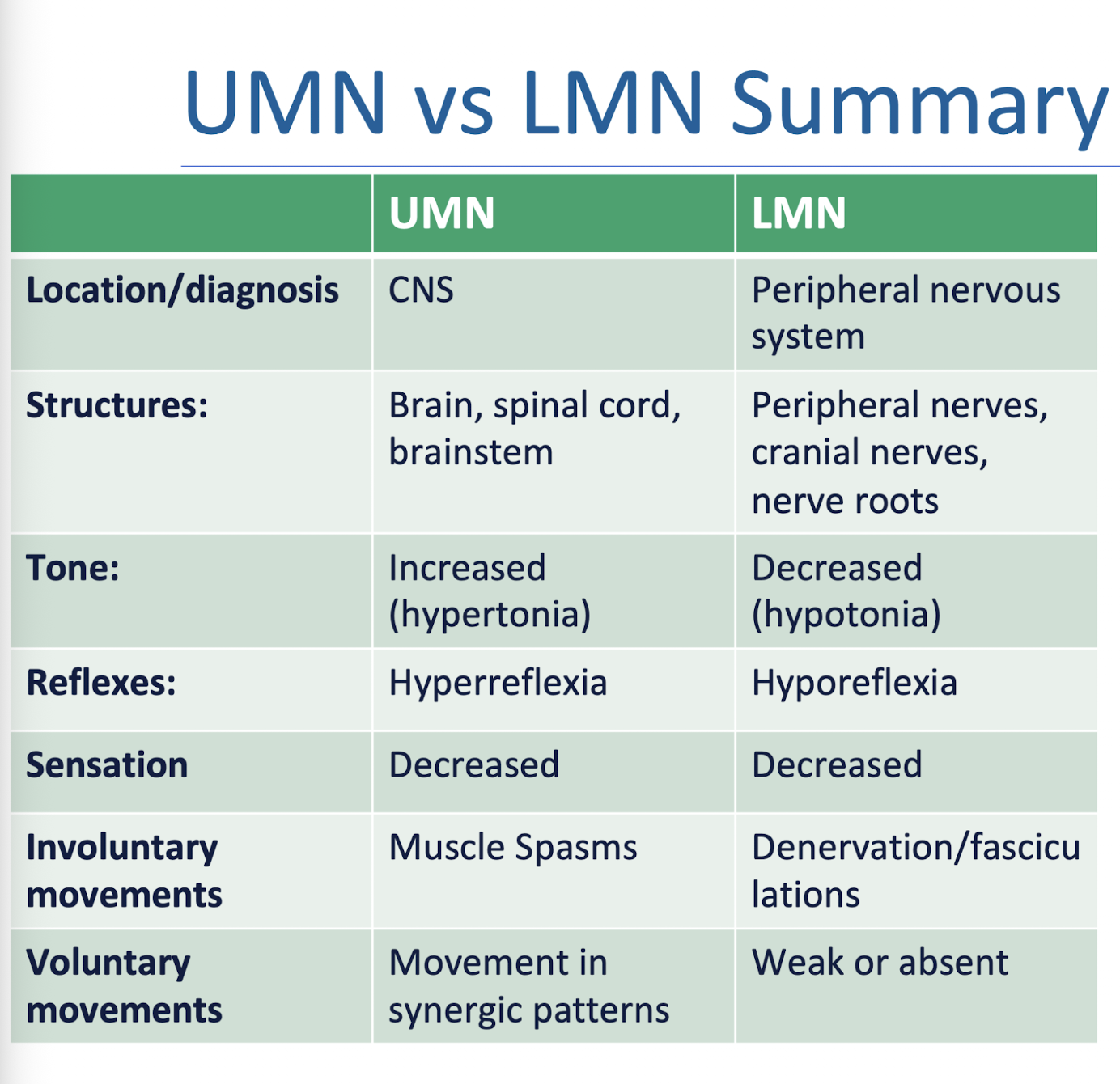
UMN v LMN
FLIP »
DTR Grading
Reflex
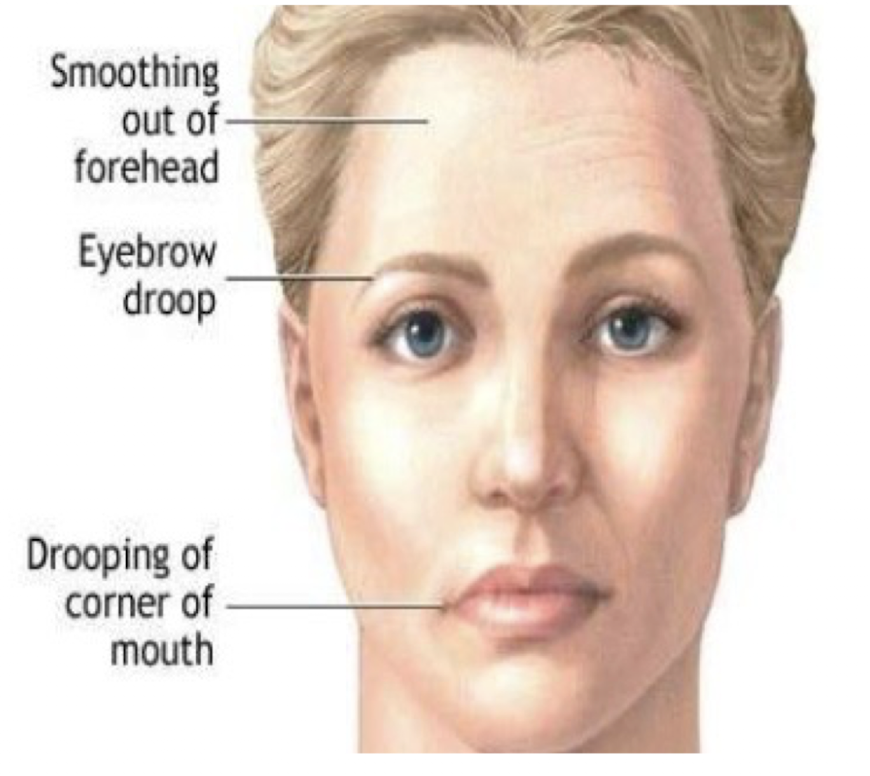
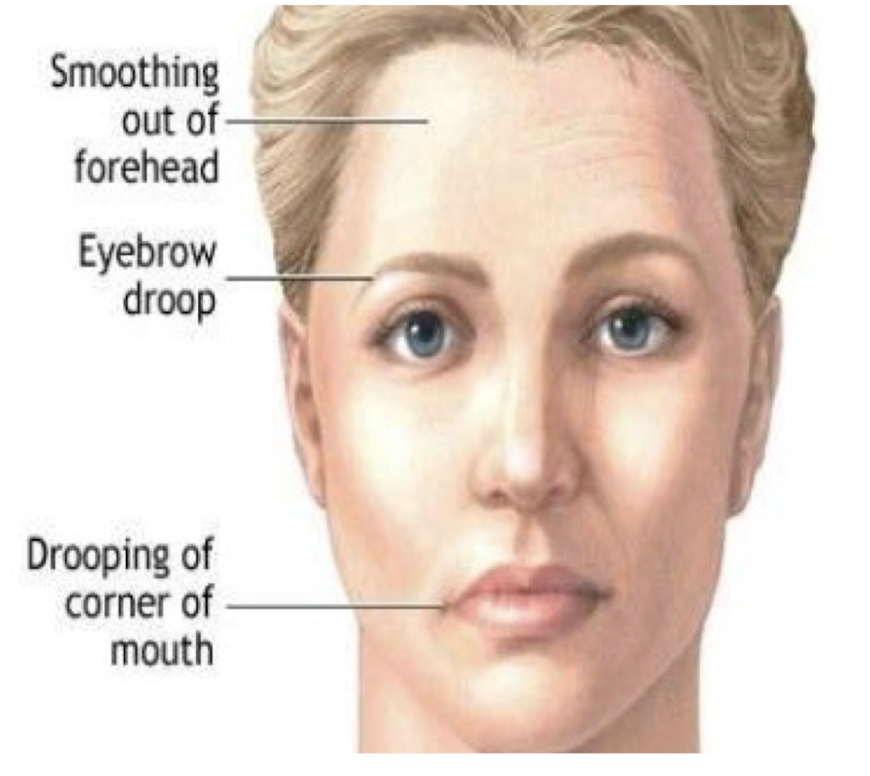
Myesthenia Gravis:
Describe: (3)
Cause:
UMN or LMN?
Describe:
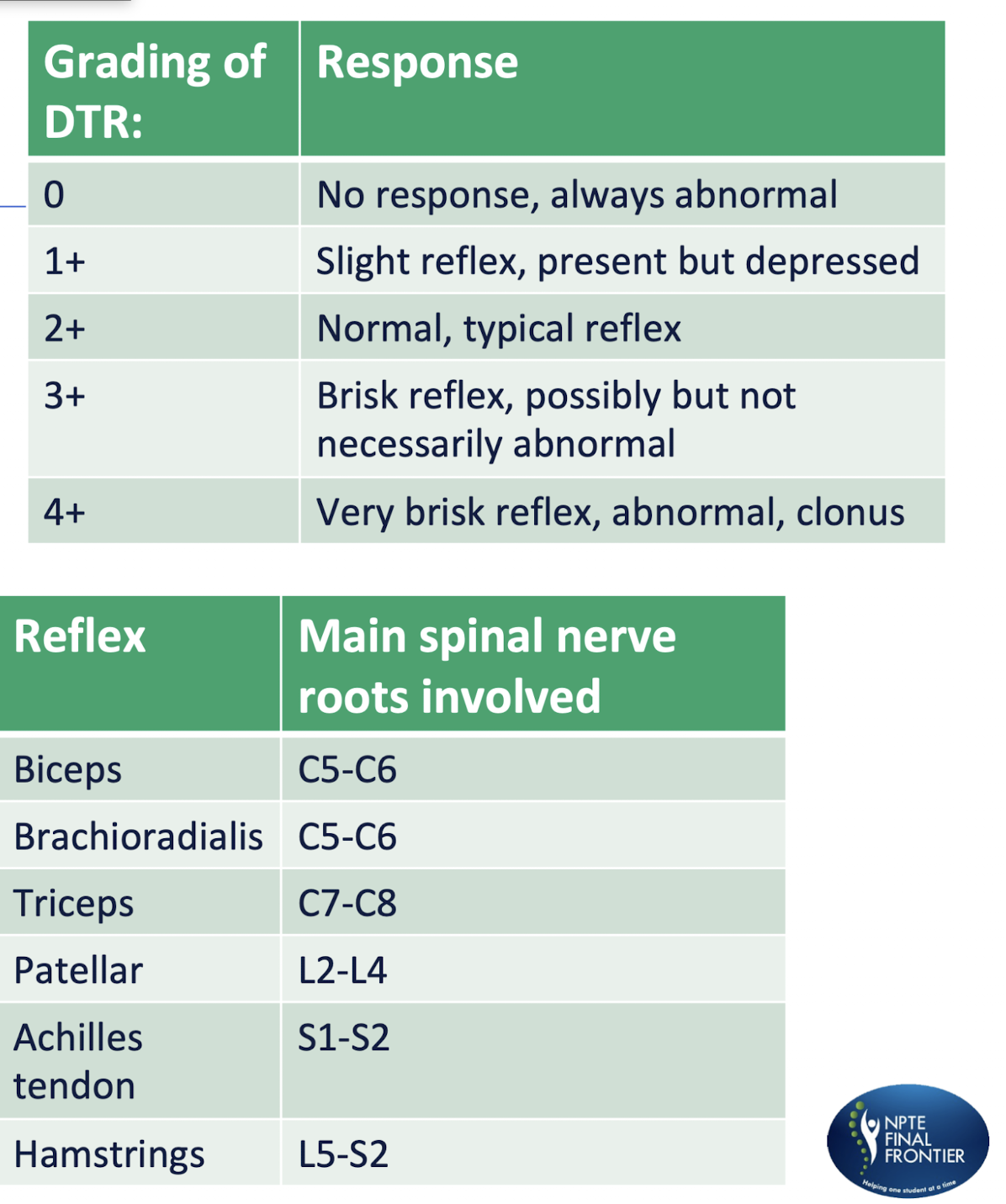
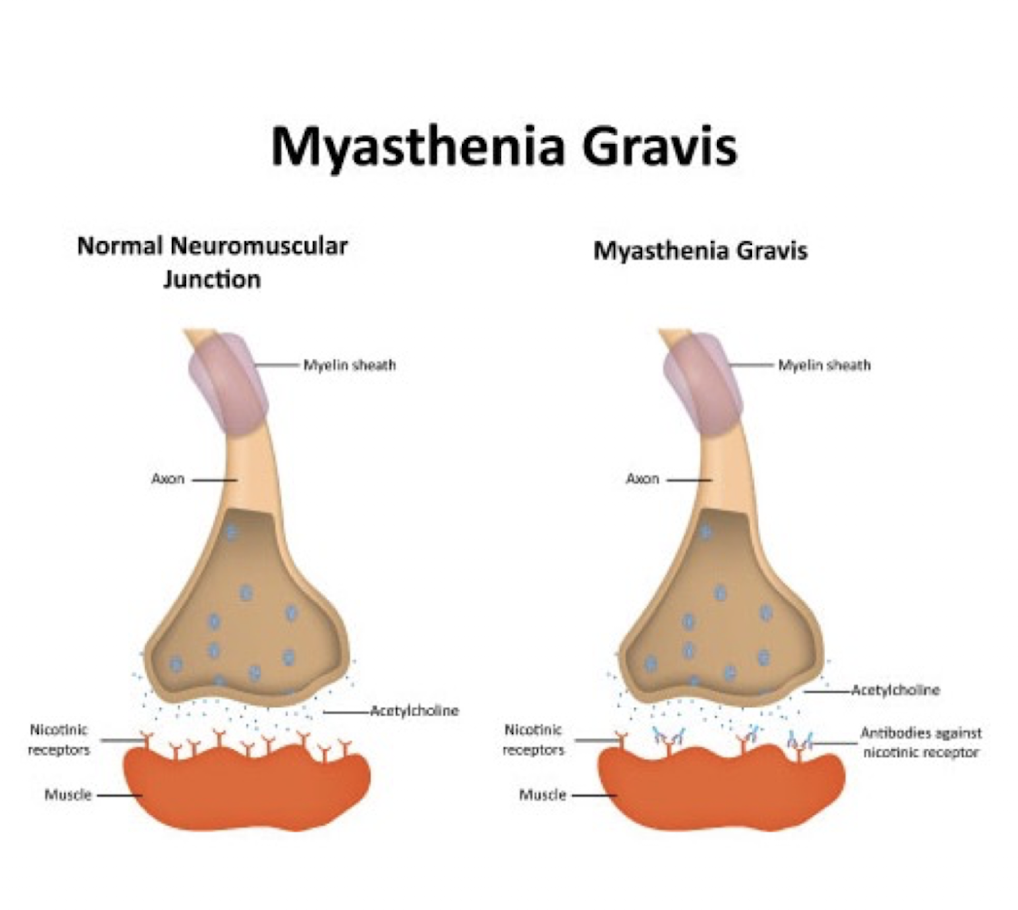
Autoimmune
NMJ Disorder
Postsynaptic NMJ Disorder
Disruption of nerve impulses to muscles d/t antibodies blocking ACH receptors
Cause:
Enlarged Thymus AND associated c other immune disorders (DM, RA, SLE (Lupus))
UMN or LMN:
Neither » NMJ
Myesthenia Gravis:
Diagnostic Test:
First S/S:
Diagnostic Test: Ice Pack Test
Take baseline ptosis » ice pack for 2-5 min » take ptosis measurement
Less ptosis/improvement ≥ 2mm = Positive Ice Pack Test
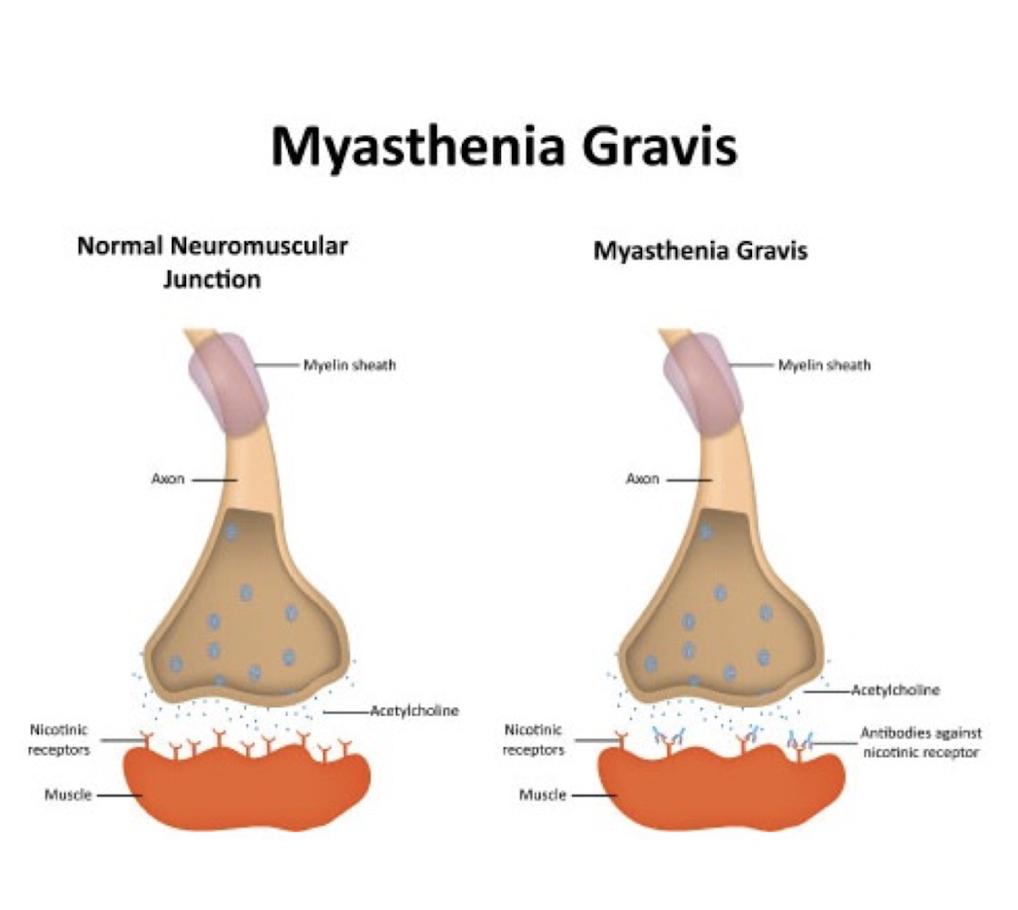
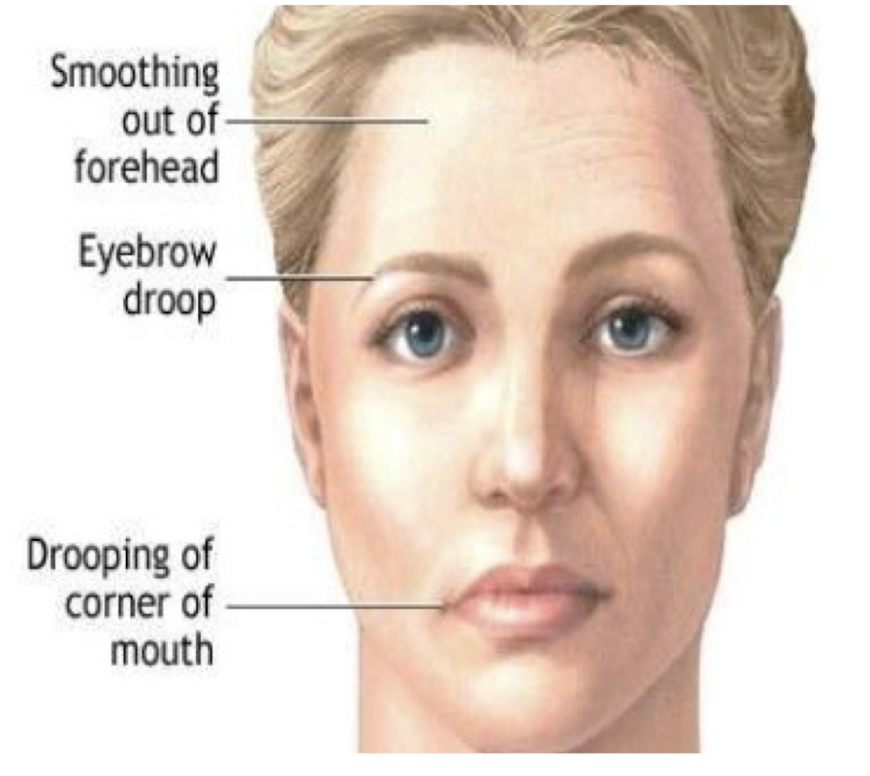
First S/S:
Ocular (and bulbar) muscles affected first
Diplopia
Bilateral Ptosis
Myesthenia Gravis:
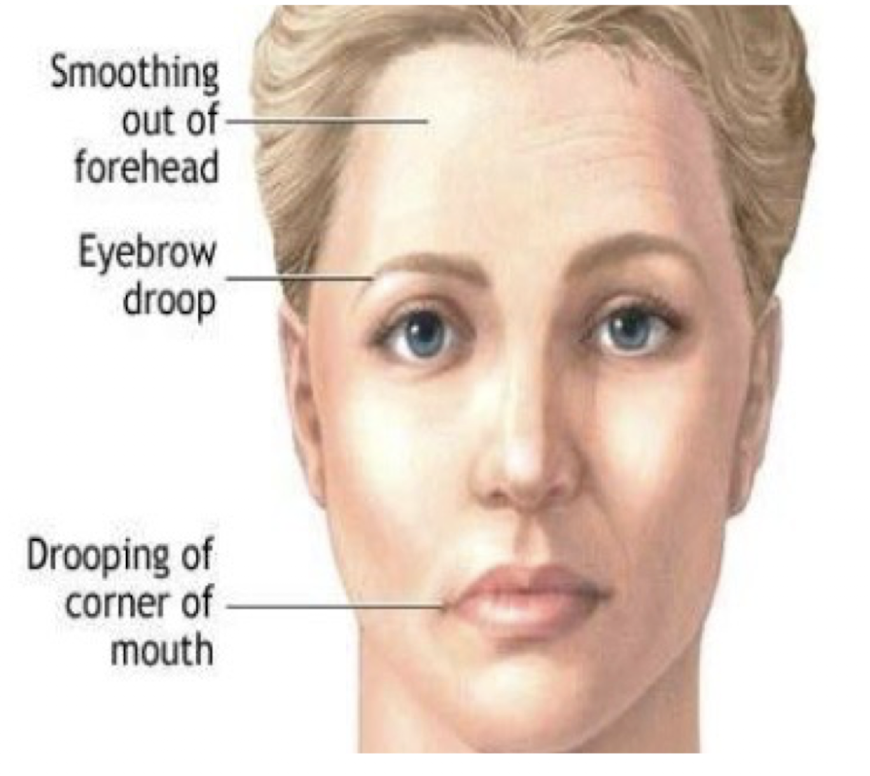
Other S/S: (4)
Progressive muscle weakness » fatiguability on exertion or repeated contractions
Worsens c activity and improves c rest
Activity Pacing
AM Exercise
Proximal limb-girdle muscle most affected
Prox > Dist
Resp Issues
Practice Q 8:
A patient reports progressive arm and leg weakness over 4 months with fine motor difficulty and frequent tripping. They have muscle cramps, fasciculations, muscle weakness, hyperreflexia (lower extremity deep tendon reflex 3+), mild dysarthria, and intact sensation with no ptosis or diplopia. Which of the following is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis?
A. Guillain-Barré Syndrome
B. Multiple Sclerosis
C. Myasthenia Gravis
D. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
D. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
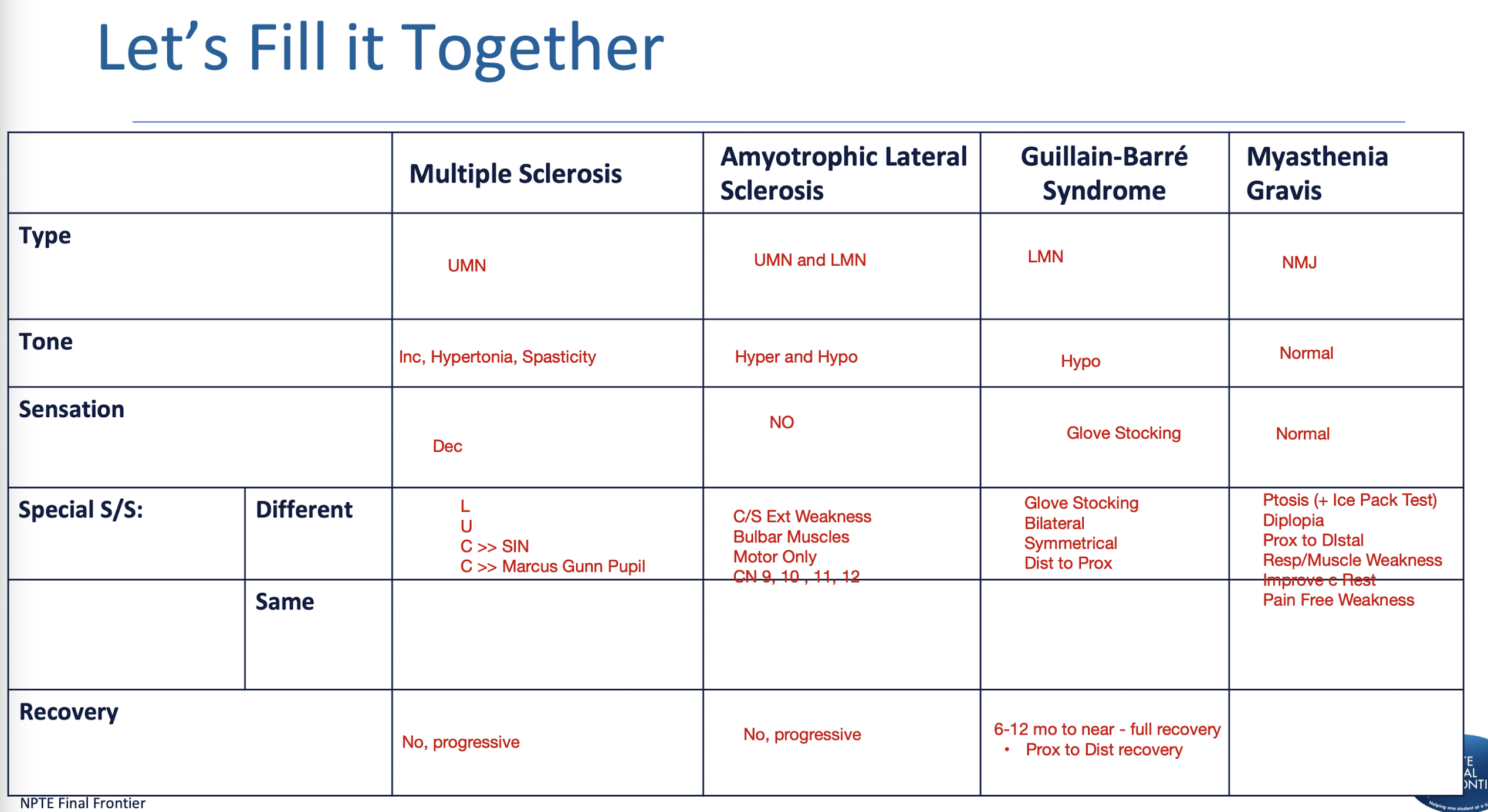
DDx: