Biopsychosocial Model and Socioecological Approaches in Health
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the Biopsychosocial (BPS) model?
A model that incorporates biological, psychological, and social factors in understanding health and disease.
What are the key risk factors associated with catching the common cold?
Biological, behavioral, psychological, and social risk factors.
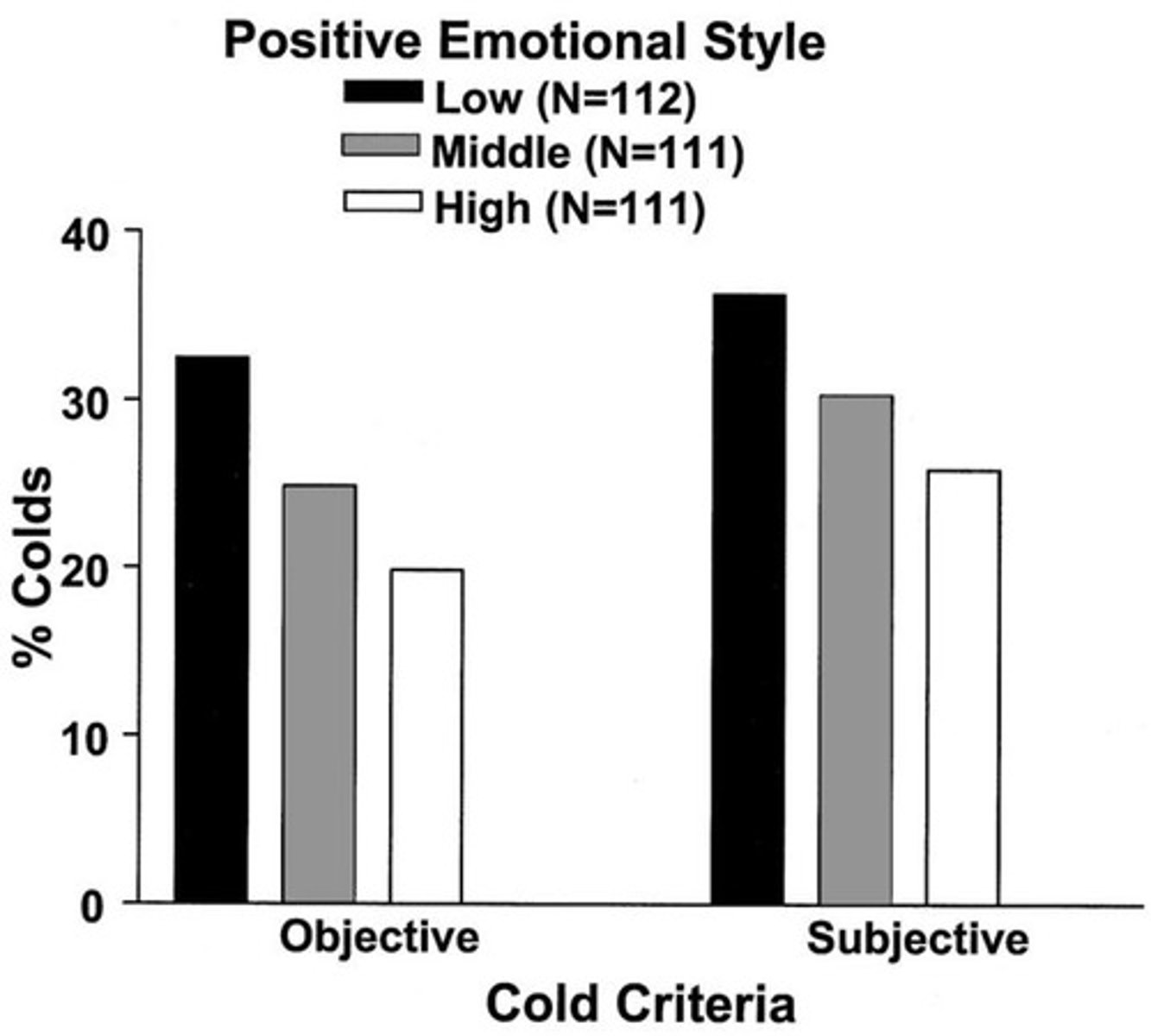
How does positive emotion relate to resilience against the common cold?
A tendency to experience positive emotions predicts resilience, as shown in studies with healthy volunteers.
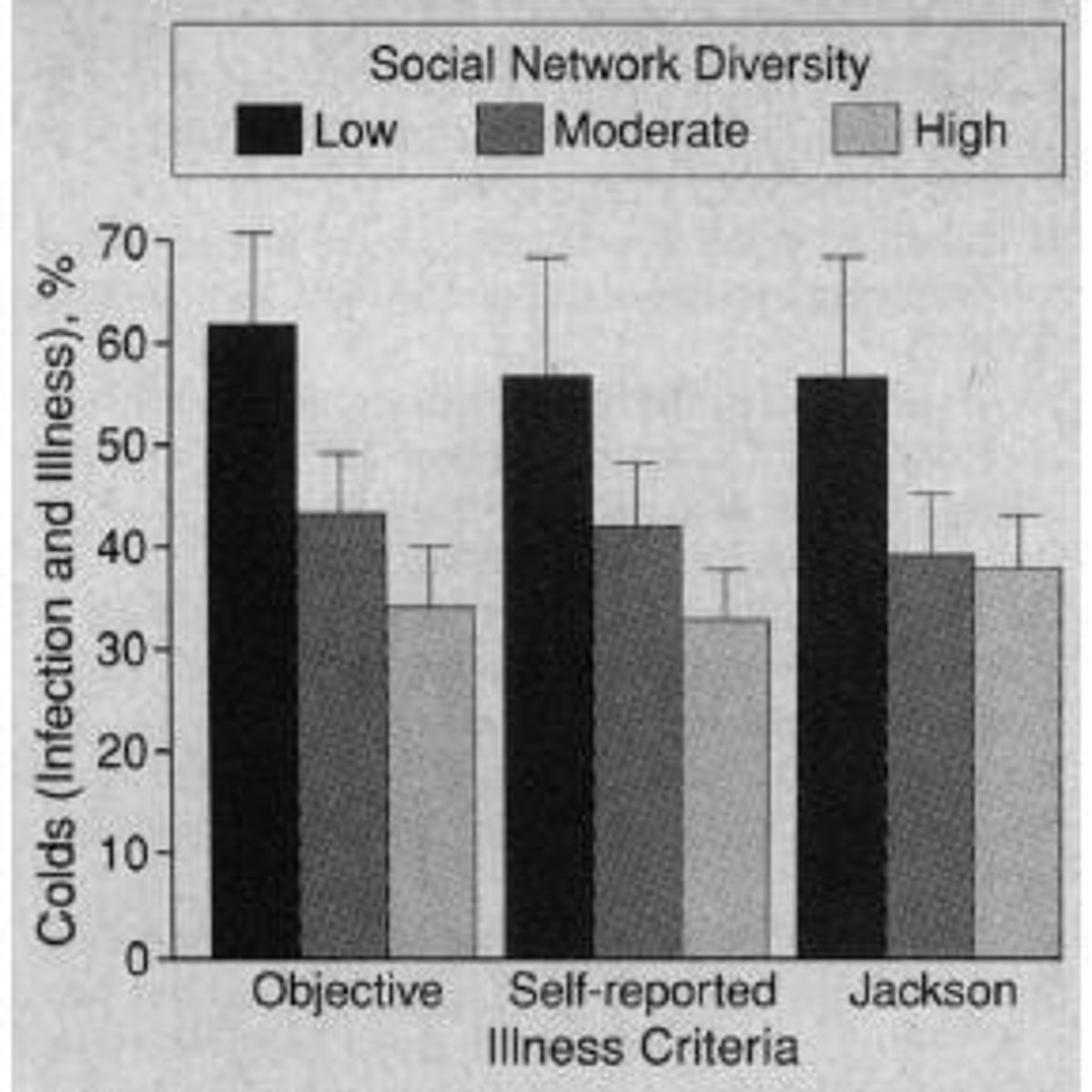
What role do social ties play in resilience against illness?
Diversity in social ties is associated with increased resilience, as evidenced by studies involving healthy volunteers.
What biological risk factor is mentioned in relation to the common cold?
Chronic pulmonary vulnerability, such as asthma or COPD.
What psychological factor can affect the risk of catching a cold?
Stress.
How do living conditions influence health risks?
Living conditions and population density can increase vulnerability to illnesses.
What cultural/societal factors may impact health risk?
Expectations to work while sick, limited/no sick leave, social norms, and resistance to infection control measures.
What environmental factor is noted as a risk for health?
Air quality.
What was the dominant health model from the early 1900s to today?
The Biomedical Model.
What are the implications of the Biomedical Model?
It suggests that all diseases can be cured by medicine and that psychological and social processes are irrelevant.
What shift in causes of death has occurred from 1900 to 2004?
A shift from infectious diseases to chronic illnesses.
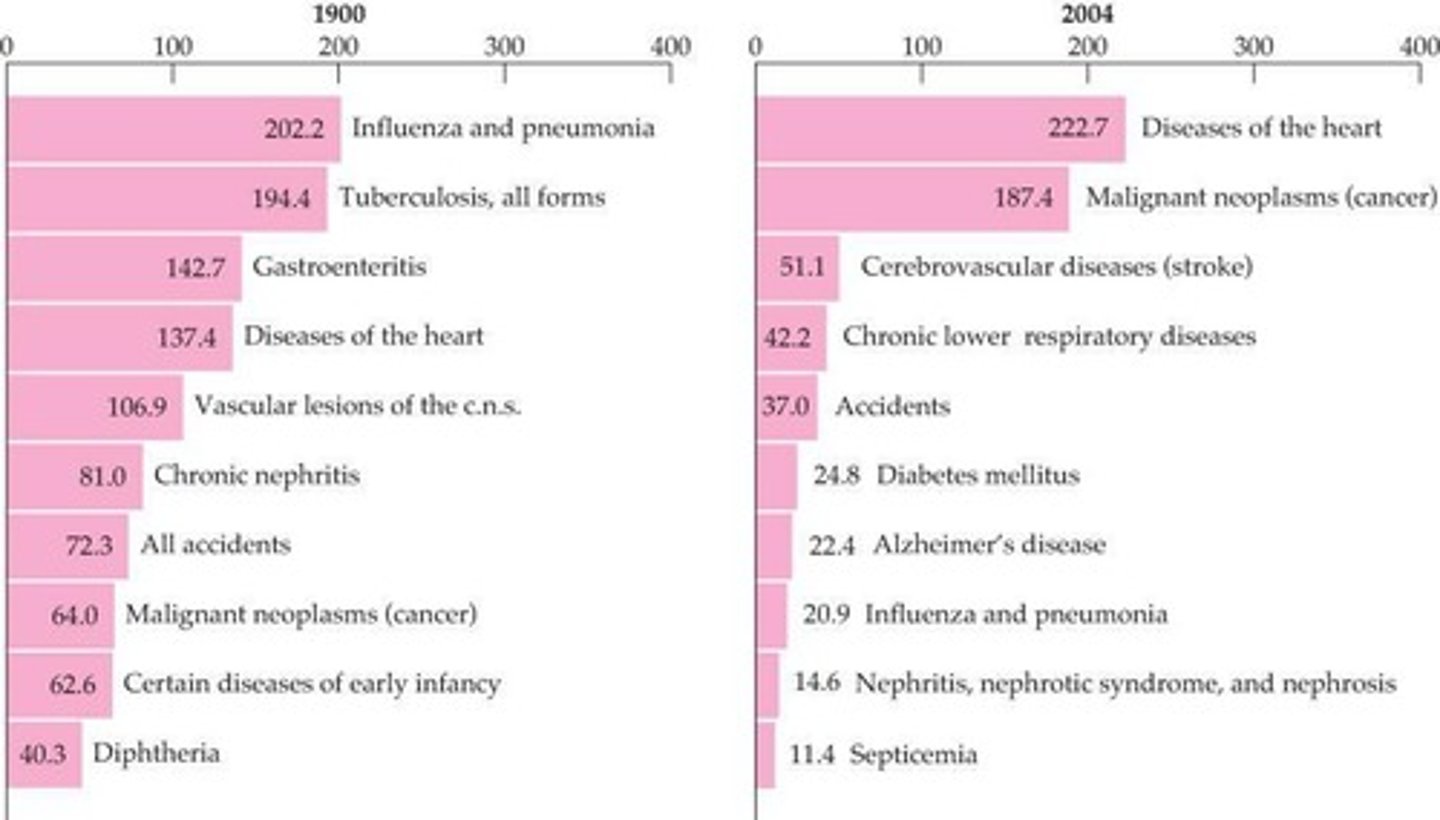
What are some chronic illnesses that have become significant causes of death?
Cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer's.
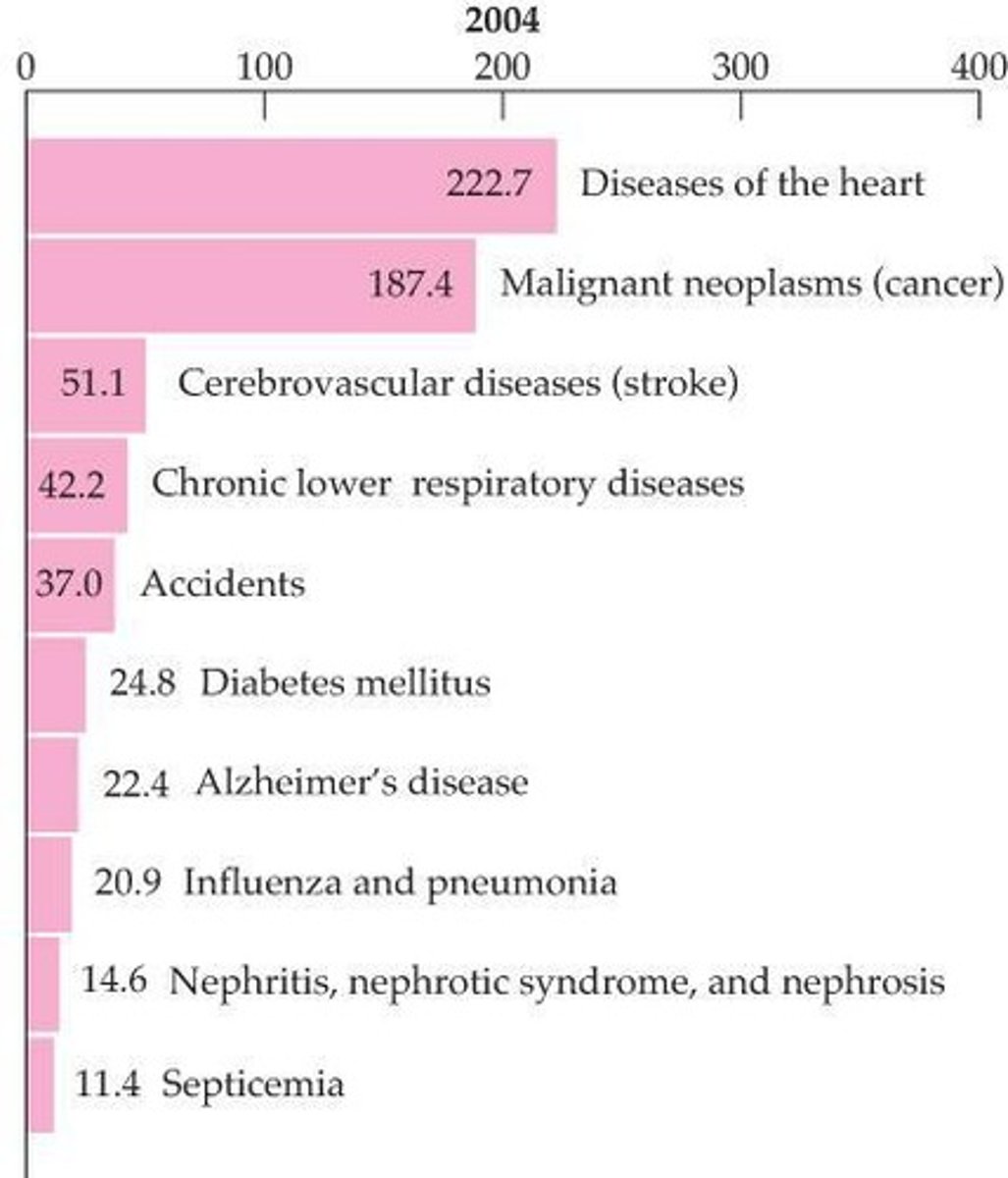
What is a major shortcoming of the Biomedical Model?
It does not adequately address chronic illnesses.
What is the current focus of health education campaigns?
Behavior modification and individualistic ideology, emphasizing personal choices for better health.
What is the Socioecological Model (SEM) of Health?
A model that illustrates the relationships and interactions between multiple levels of social and environmental systems.
What health issues were observed in children exposed to lead in Flint, Michigan?
Lowered IQ, brain damage, learning difficulties, and slowed growth.
What health issues were observed in adults exposed to lead?
Reproductive problems, high blood pressure, nerve disorders, and memory issues.
What public health intervention was implemented in Baltimore to reduce lead exposure?
Lead testing for children, mandatory risk reduction in rental properties, and funding for lead abatement.
What percentage decrease in childhood lead poisoning was achieved in Maryland since 1993?
98% decrease.
What are food deserts?
Urban neighborhoods and rural towns without ready access to fresh, healthy, and affordable food.
What potential health effects are associated with living in food deserts?
Increased risks of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
What disparities exist in mortality statistics between low-income countries and higher-income countries?
In low-income countries, treatable infectious diseases remain prime causes of death.
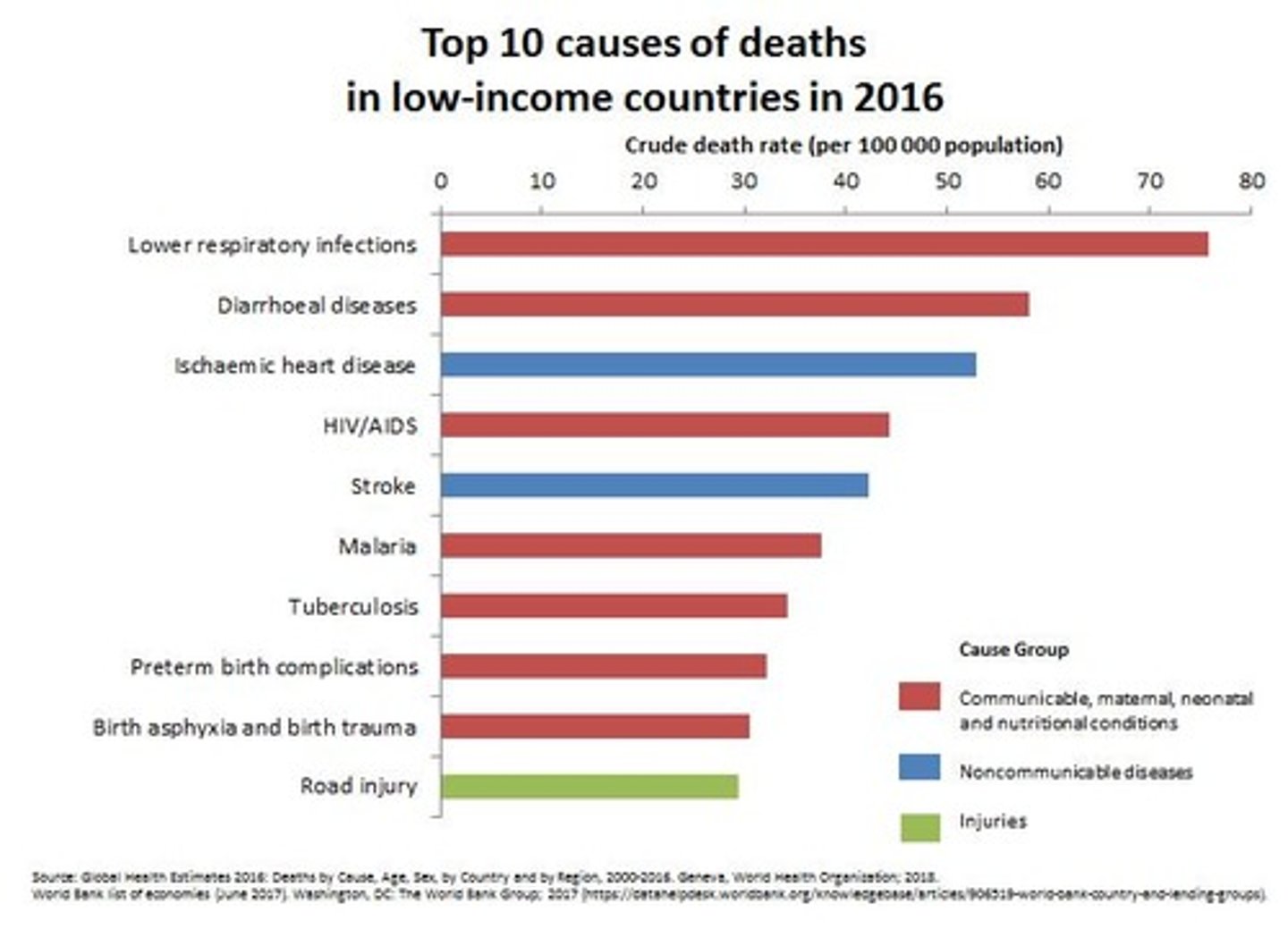
What questions are raised regarding current health approaches?
Whether current approaches adequately address the causes of health disparities and promote overall well-being.