Li1 phonetics
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
How can you describe a vowel?
Height, backness, rounding
Describe /t/
Voiceless alveolar plosive
Describe /d/
Voiced alveolar plosive
Describe /k/
Voiceless velar plosive
Describe /g/
Voiced velar plosive
Describe /ŋ/
Voiced velar nasal
Describe /n/
Voiced alveolar nasal
Describe /m/
Voiced bilabial nasal
Describe /f/
Voiceless labiodental fricative
Describe /v/
Voiced labiodental fricative
Describe /ð/
Voiced dental fricative
Describe /θ/
Voiceless dental fricative
Describe /s/
Voiceless alveolar fricative
Describe /z/
Voiced alveolar fricative
Describe /ʃ/
Voiceless post-alveolar fricative
Describe /ʒ/
Voiced post-alveolar fricative
Describe /h/
Voiceless glottal fricative
Describe /ʤ/
Voiced post-alveolar affricate
Describe /ʧ/
Voiceless post-alveolar affricate
Describe /l/
Voiced alveolar lateral approximant
Describe /r/
Voiced alveolar approximant
What does F1 represent?
Vowel height. The lower the vowel, the higher the frequency
What does F2 represent?
Vowel backness. The fronter the vowel, the higher the frequency
What does this diacritic represent: x̥?
Voiceless
What does this diacritic represent: x̬?
Voiced
What does this diacritic represent: xh ?
Aspirated
What does this diacritic represent: xw?
Labaliased
What does this diacritic represent: x̰?
Creaky voiced
What does this diacritic represent: x̤?
Breathy voiced
What does this diacritic represent: xj?
Palatalised
What does this diacritic represent: x̃?
Nasalised
What does this diacritic represent: t̪?
Dental
What does this diacritic represent: tˠ?
Velarised
What does this diacritic represent: d̚?
No audible release
What does this diacritic represent: ɫ?
Velarised/pharyngealised (dark l)
What does this diacritic represent: e̝?
Raised
What does this diacritic represent: tˤ?
Pharyngealised
What does this diacritic represent: dⁿ?
Nasal release
What does this diacritic represent: dˡ?
Lateral release
What does this diacritic represent: e̞?
Lowered
What does this diacritic represent: u̟?
Advanced
What does this diacritic represent: e̠?
Retracted
What does this diacritic represent: ɔ̹"?
More rounded
What does this diacritic represent: ɔ̜?
Less rounded
What does this diacritic represent: ë?
Centralised
What does this diacritic represent: n̩?
Syllabic
What does this diacritic represent: e̯?
Non-syllabic
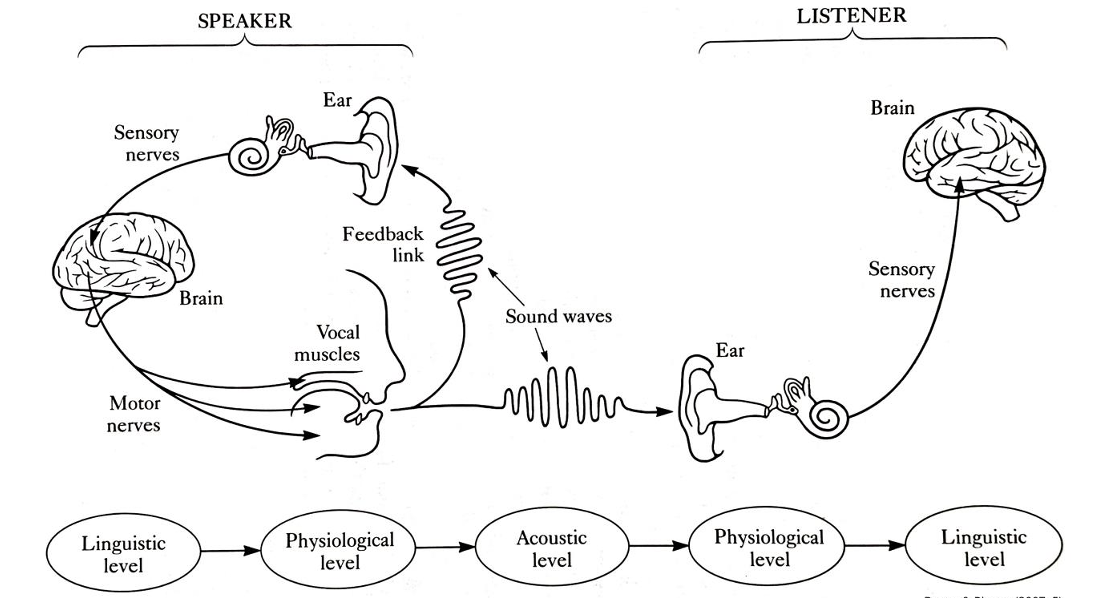
Speech signal
1) Speaker wants to transfer information to listener, so decides what to say, puts it in linguistic form.
2) Brain activity —> instructions, nerve impulses to muscles activating vocal organs.
3) Movement of vocal organs —> pressure changes to form sound wave, sound wave travel through air to listener.
4) Pressure changes at listener’s ear activates hearing mechanism —> produce nerve impulses along acoustic nerve to listener’s brain, brain activity leads to recognition of speaker’s message
Communicative Intent
Cognitive, affective, self presentational, social, regulatory
Linguisitc Mechanism
Lexicon and morphology, syntax, phonology and prosody, tone of voice
Indexical Factors
Social Background, age, sex, psychological state, health, physique
How do size and proportions of speech organs determine indexical info?
Vocal tract - length, particularly proportions of mouth and pharynx, determines range of resonant frequencies
Vocal folds - length and mass determines a speaker’s pitch range
Pulmonic airstream mechanism
Movement of air from the lungs, producing nearly all speech sounds
Glottalic airstream mechanism
Movement of body of air in pharynx by the action of the glottis. 2 closures, 1 at glottis, 1 higher up. If air squeezed out, ejectives. If air drawn in, implosives
Velaric airstream mechanism
Movement of body of air in the mouth in front of a velaric closure, ingressive direction. Used for producing clicks
Voiced sounds
Vocal forms held close together and made to vibrate due to pressure of airflow from the lungs
Voiceless sounds
Vocal folds pulled apart, with little to no airflow
Cardinal Vowels
Reflect maximal values of high and frontness-backness found in languages (primary CVs = back+rounded tendency, secondary CVs = reverse lip position)
Secondary articulations for vowels
Nasalisation, rhoticisation, Advanced/retracted tongue root
What does the syllable split up into?
Onset, Rhyme (nucleus and coda)
Intonation
Prosodic patterns with a domain larger than the syllable or word, interplay with pitch, loudness, length and voice quality
Chunking
Part of intonation, in which an utterance is divided into intonational phrases
Accenting
Part of intonation, in which some words are highlighted as important
Tone
Part of intonation, in which there is a specific selected pattern of pitch targets, aligned with a accented syllable or boundary
Intonational Phrase (IP)
A chunk with a complete intonation pattern, with at least one accent
Nucleur accent
The last accent in an IP
Word accent
The degree of relative prominence of a syllable in relation to surrounding syllables
Stress-accent languages
Languages which use all prosodic parameters simultaneously (English, Dutch, Russian etc.)
Pitch-accent languages
Languages which use a limited set of pitch patterns to convey lexical distinctions (Japanese, Norwegian, Swedish etc.). Words are distinguished by fixed pitch patterns
Distinction between stress and accent
Stress is the phonological, abstract potential of a syllable to carry accent, whilst accent is the actual realisation
Fixed stress languages
Languages where there is a predictable location of stress
Free stress languages
Languages where patterns are not predictable, and often contrastive
Accent/stress shift
Accent clash resolution, reflecting the preference of languages to avoid adjacent accents
Minimal pair
A pair of words that differ y one sound and mean different things
What determines allophones?
Structural position (in the syllable/word boundary), environment, sociolinguistic effects
How can you describe a consonant?
Place of articulation, manner of articulation, voicing
Intrusion
When a sound is inserted between two words, often to make pronunciation easier: can be /r/ (‘law and’), /w/ (‘go on’), /j/ (‘I am)
Elission
When a phoneme is not articulated in a word, often due to speed of speech (‘frienship’)
Assimilation
When a neighbouring sound influences the way that a phoneme is pronounced. Can be:
1) Progressive - previous sound influences the next
2) Regressive - following sound influences the previous one
3) Reciprocal - sounds mutually influence each other
Glottalisation
/t/ sound is replaced with a glottal stop, [ʔ]
Replacement with weak form
When a sound is replaced with an unstressed schwa (to, the, for, a)
Syncope
The loss of an unstressed vowel from the middle of a word (‘different’)