electrochemistry
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Reduction
Gain of electrons (e on reactants side)
Substance that is reduced is the oxidizing agent (high Ep°)
Cathode
Oxidation
Loss of electrons (e on products side)
Substance that is oxidized is the reducing agent (low Ep°)
Anode
How to balance
find the atom that are reduced and oxidized
write skeleton equation for each
balance with major OH-
multiply to equalize electrons
combine to make net equation
Energy cell potential formula
Ecathode - Eanode
Energy minimum formula
Eanode - Ecathode
Cell stoic, charge formula
Q = Lt
cell stoic combined formula
ne = lt/F
(F = 9.65 × 10 ^ 4)
cell stoic mole formula
n = ne/number of electrons per 1 molecule
mass loss/gain
solid to aqueous = loses mass
aquaous to solid = gain mass
voltaic cell
cathode will be the one with higher reduction potential
electroytic cell
if cation is higher than R. of water (-0.83) it is cathode
if anion is lower than Ox. of water (1.23) it is anode
determine if something can reduce other
lower Ep° reduces higher Ep°
determine if something can oxidize other
higher Ep° oxidizes the lower Ep°
titration
write net equation from the half reactions from table
the higher substance is the reaction that is reduction (written forwards)
3. combine both reduction and oxidation half reactions
4. find the coeficets and plug into formula
titration formula
(n is the coeficent on the substance from the balanced equation)
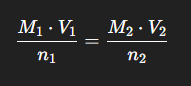
corrosion
use water half reaction at +0.40