Human Sociobiology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Human Sociobiology
Scientific study that drives the evolution of social behavior that borrows disciplines of psychology, evolutionary biology, anthropology, and genetics
Humans adapted to living in a social environment
Example of an adaptive, evolved physical traits
of sociobiology
Bipedalism in the primate lineage
Thick fur in animals living in cold regions
Examples of adaptive, evolved social behaviors of Sociobiology
Mothers protective of their offspring
Altruism: Food sharing among chimpanzees
Infanticide: killing of infants by newly dominant male
Aggression: Mate & resource competition
MIT Press Reader
Dmitry Belyaev’s (1954)
attempts to domesticate
foxes and influence
behavioral traits

Dmitry Belyaev
Started fox breeding program and selectively bred foxes that showed low fear and high friendliness toward humans
Findings: Behavior can be evolved the same way physical traits can, dogs have evolved due to human interference to be more docile
Social Biology of Facial Expressions: Darwin - Today
First to consider human behavioral characteristics through evolutionary lens
Noticed humans around the world display similar emotions through their facial expressions
Paul Ekman (FACS)
Study of how biology correlates with emotions and how humans convey them through facial expressions
Developed Facial Action Coding System to categorize emotions expressed in the face
AU - Units of FACS is a combination of AU’s to produce basic emotion expression
Cross Cultural Conservation
Facial expressions are universal with basic emotions
Do exhibit unconscious biases in attending to info based on familiarity with groups of people
Helps others from the community to stay away from food or objects, danger/safety

Own Race Advantage
People can ID emotion in own racial/ethnic group vs of other groups
History of Sociobiology: E.O Watson
His book combined humans and animals into Sociobiology
Controversial
Last chapter most controversial it addressed the evolutionary basis of social behavior
Argued we should analyze social behaviors through evolutionary lenses instead of psychological or sociological lens
Evolutionary Psychology
Identifies how psychological processes emotions and behaviors evolved from early humans and examines how natural selection shaped human psych traits
Some evolved behaviors may be maladaptive since environments change i.e motivation for high sugar/high-fat foods to find high quality food now causes health issues when food is abundant.
Nature vs Nuture
Social, cultural factors (nurture) change human behavior, genetic factors (nature) can also play a significant role
Humans have the capacity to change their behaviors to better fit in with society. This capacity is likely evolved. For example, Phineas Gage
Interestingly enough, your environment can actually change how your genes are expressed
Basic tenets of human sociobiology research
The human mind and human behavior are/were shaped by natural selection
The human mind uses heuristics (strategies) to increase the likelihood of solving problems our ancestors routinely faces
There is a shared, and more or less universal, core human nature
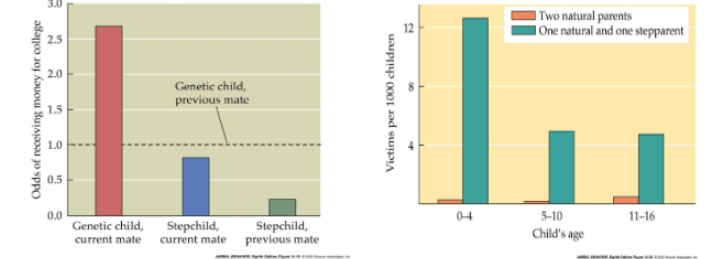
1. The Cinderella Effect
HUMAN MIND + BEHAVIOR SHAPED BY NATURAL SELECTION
Evolution favors ensuring survival and reproduction of genetically related offspring (Inclusive Fitness).
The phenomenon of favoritism for genetically related children and higher incidence of mistreatment by stepparents than by biological parents.
2. Oxytocin and Social Trusting
HUMAN MIND + BEHAVIOR SHAPED BY NATURAL SELECTION
Oxytocin is colloquially described as the love hormone because of its prosocial effect
Participants were given oxytocin or placebo and played a trust game or a lottery game
Participants who took oxytocin bet more than placebo in a game of trust rather than a game of lottery
Oxytocin makes people more trusting of other people but doesn’t make them more risky
Findings: Oxytocin prevented distrust of another person but did not affect risking behavior
Wason Task & Cheater Detection
HUMAN MIND USES HEURISTICS (STRATS) TO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF SOLVING PROBLEMS OUR ANCESTORS ROUTINELY FACES
Tasks were logically identical, but one seemed easier to complete than the other.
Superior performance on the second version of the task may be due to the human possession of a specialized cheater detection module.
Such a module would presumably benefit individuals in
environments where repeated, reciprocal interactions occurred
Why detect cheaters
So you can punish people who cheat!
And, if you really want to support cooperation, you can even use such a module to punish others who neglect to punish cheaters (strong reciprocity)
If you do not punish cheaters, cooperation doesn’t happen in large groups
Visiting Green Spaces Increases Mindfulness
SHARED CORE HUMAN NATURE RESULTING IN COMMON EXPERIENCE
Researchers found that people who went on walks throughout the parks and forests were less stressed, more mindful, and happier compared to those who went to the city happens appreciate green space since it is connected to feelings of wellbeing
Facial symmetry is attractive
SHARED CORE HUMAN NATURE RESULTING IN COMMON EXPERIENCE
Suggest health and fertility → enhance reproductive success
A biological pattern symmetry = attractiveness
The Naturalistic Fallacy
Is the idea that what is found in nature is inherently good
Biological Determinism
Assumption: -the idea that most human characteristics, physical and mental, are determined at conception by hereditary factors passed from parent to offspring
‘Just so’ Stories + Ancient Humans
Some scientists have been/are guilty of “adaptive storytelling”
• an ad hoc evolutionary narrative to explain a behavior that is unverifiable and unfalsifiable