physiology final practice questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:06 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
1
New cards
what compounds are involved in firefly light production?
luciferase and luciferin and luciferyll-Amp
2
New cards
steps of flirefly light producing cascade in mitochondria
when oxygen is introduced to make ATP, that ATP activates luciferin to produce luciferyl-AMP, luciferase then shuts down the photon producing reaction
3
New cards
result of heterotypy of fetal rat growth factors
causes different structures to arise at different times and lets structures arise at the correct timing with development and not all at once
4
New cards
enzymes involved in glucose regulation in young/fetal mice
glycogen synthetase before birth, phosphophenol pyruvate and then glucokinase for childhood glucose regulation in blood plasma
5
New cards
what ability do some mollusks possess to protect themselves from predators?
they sense predators nearby and can vary their shell thickness to be thicker and more protective against potential threats
6
New cards
what structure in midgut is responsible for absorbing nutrients and glucose?
microvilli
figure 6.19
figure 6.19
7
New cards
T/F glucose and nutrients passively pass through endothelium membrane in the midgut
False, all these nutrients are transported through facilitated diffusion using the gradient from the sodium potassium pump
\
GLUT5, GLUT1, SGLT1
figure 6.19
\
GLUT5, GLUT1, SGLT1
figure 6.19
8
New cards
list the major steps in fatty acid absorption through the midgut
fatty acid crosses into endothelium, triglycerol formed then bonded with protein, chylomicrons formed and transported into the villus interior
\
figure 6.20
\
figure 6.20
9
New cards
name of the concept that some animals operate by where their demands change as if on a certain rhythm
circadian clock/ rhythm
10
New cards
Why is the body forced to go into anaerobic ATP produciton/use in the first few stages of activity, then continue explaining the phases of activity and oxygen use
the demand for oxygen within muscles is often greater than the supply of oxygen at the beginning of activity. This is known as the oxygen deficit stage of activity. At this point anaerobic glycolysis and phosphogen use is the only way to supply muscles with the necessary amounts of ATP until breathing increases to the point that it can support the activity which is known as the pay as you go phase. At this point the exact amount of oxygen taken in is being used to produce ATP through aerobic glycolysis and the electron transport train. This stage produces a much larger amount of ATP compared to anaerobic production. After the activity is more or less stopped, there will be a period of time where the same level of high oxygen intake is kept up to produce a store of ATP that will be used in the next beginning of activity.
\
figure 8.10
\
figure 8.10
11
New cards
why would an organism go into a metabolic depression and what is that?
metabolic depression is when there are periods of time that an animal takes in much smaller amounts of oxygen and survives on corresponding decreased amounts of ATP. This concept describes an ability of organisms to survive on depleated resources when necessary.
\
figure 8.14
\
figure 8.14
12
New cards
how is lactic acid changed and then transported back into the hemolymph stream in fish?
it is turned into Pyruvic acid and then ethanol
13
New cards
what is a difference in organism cells that help them survive in colder temperatures
cold acclimated organisms often have larger amounts of mitochondria which also link to higher oxygen uptake (f)
\
the higher the temp, the more fluid the membrane(f)
\
antifreeze in membranes increase as temperature decreases(r)
\
figure 10.14, 10.22, 10.25
\
the higher the temp, the more fluid the membrane(f)
\
antifreeze in membranes increase as temperature decreases(r)
\
figure 10.14, 10.22, 10.25
14
New cards
what are the methods reindeer use to survive in the extreme cold?
\
they have very large hooves which allow them to walk on snow and frozen lakes, they use heterothermy to conserve on metabolic energy, they are able to survive on nutrient stores when they have to predominantly use lichen for nutrition in the winter, fatty acids that act as antifreeze are in higher concentrations in reindeer legs where their body temp is coldest (helps from blood freezing), further growing reindeer use brown fat thermogenesis when they are young in order to thermoregulate until their body weights are high enough to thermoregulate using conventional metabolic processes,
\
figures 11.4, 11.6, 11.8
they have very large hooves which allow them to walk on snow and frozen lakes, they use heterothermy to conserve on metabolic energy, they are able to survive on nutrient stores when they have to predominantly use lichen for nutrition in the winter, fatty acids that act as antifreeze are in higher concentrations in reindeer legs where their body temp is coldest (helps from blood freezing), further growing reindeer use brown fat thermogenesis when they are young in order to thermoregulate until their body weights are high enough to thermoregulate using conventional metabolic processes,
\
figures 11.4, 11.6, 11.8
15
New cards
why do hibernating animals go through periodic arousals during their hibernation?
the periodic arousals “wake up” the muscles and prevent large scale atrophy during their hibernation period
\
figure 11.12
\
figure 11.12
16
New cards
how do salmon get to the same breeding ground each year?
they use a technique called homing which allows them to return to the same spot every year, then after the breeding or after birth they migrate away and restart the cycle
\
figure 18.1
\
figure 18.1
17
New cards
how do bees communicate where food can be found to each other?
bees will do a “dance” that goes in a triangle like pattern where the bees change the angle of the triangle compared to the horizon depending on the location of the food
\
figure 18.2
\
figure 18.2
18
New cards
what are the navigation types
trail following, piloting, path integration, compass navigation, map and compass navigation
\
figure 18.1
\
figure 18.1
19
New cards
how do ants change their navigation patterns after they reach their destination
ants will take a circuitous route when they are out looking for prey/food. when they find the destination, they will then take the shortest route back to their starting location. this shows that they map locations out when they travel to varying places by monitoring their steps
\
figure 18.3
\
figure 18.3
20
New cards
experiment used to determine ant navigation technique
experimenters created mutants with different length legs and found that ants with shorter legs walked a shorter distance but the same number of steps
\
figure 18.4
\
figure 18.4
21
New cards
how do homing pigeons naivgate?
they use circadian clocks that correspond to the sun, when the pigeons where manipulated to have varying set times, they used the sun to navigate and went in varying directions due to differences in clock points
\
figure 18.5
\
figure 18.5
22
New cards
explain the experiment used to investigate how nocturnal birds navigate
when the star patterns were flipped, the birds traveled in the opposite direction which shows they navigate using stars
\
figure 18.7
\
figure 18.7
23
New cards
what is the form of global navigation that very little about the internal mechanisms is known
magnetic navigation using the earth’s magnetic field, internal compass
\
figure 18.8, 18.9
\
figure 18.8, 18.9
24
New cards
what enzymes are used in the light organ of fireflies to produce their photon effect?
luciferin, luciferyl-AMP, and luciferase
25
New cards
what are the three different ways to produce ATP for muscular contractile activity
creatine-phosphate/ phosphogens, glycolysis (anaerobic, aerobic), oxidative phosphorylation
\
figure 20.13
\
figure 20.13
26
New cards
what is myoglobin used for
it is used to store oxygen in muscles, it is usually found in slow oxidative muscle fibers because they are primarily aerobic
27
New cards
what form of exercise and which fiber type would be activated by immediate exercise?
anaerobic exercise would happen during the first stages of activity and this would mainly involve fast glycolytic muscles
\
figure 20.1
\
figure 20.1
28
New cards
what happens during the stages of liver enzyme regulation in a developing rat?
1. glycogen synthetase is used to synthesize and store glycogen stores a few days before birth
2. phosphophenolypyruvate- creatine is used to produce glucose at/after birth
3. glucokinase is upregulated as rat begins to be independent, it is used to regulate blood sugar
\
figure 4.5, 4.6
29
New cards
what is phenotypic plasticity
when organisms can show different manifestations of the same gene without any genetic changes, same genotype leads to different phenotypes- usually a result of environmental changes
30
New cards
list the stages of fatty acid absorption
fatty acid enters (GLUT5 and SGLT1) microvilli endothelium, changes to triglycerols, then proteins are added to make chylomicron (triglycerols + protein+ glycerol), they are then transported (GLUT 2) into the internal villa
\
figure 6.19, 6.20
\
figure 6.19, 6.20
31
New cards
list the major steps in smooth muscle regulation
hormone activates g-protein cascade which uses ATP to activate myosin to activate smooth muscle contraction
\
figure 20.18
\
figure 20.18
32
New cards
effect of aerobic training on mitochondria and lipid droplets
training increases mitochondria and lipid droplets, associated with higher aerobic abilities
\
figure 21.3
\
figure 21.3
33
New cards
what does PGC-1alpha do in relation to transcription
it acts as a coactivator of muscle gene expression with TFs to activate certain sets of genes
\
figure 21.4
\
figure 21.4
34
New cards
difference between PGC-1alpha1 an dPGC1alpha4
\#1 is upregulated in muscle gene expression during endurance exercise which increases the amount of slow oxidative fibers present
\
\#4 is upregulated in muscle gene expression during resistance exercise which increases the amount of fast glycolytic fibers present (bigger muscle size)
\
figure 21.6
\
\#4 is upregulated in muscle gene expression during resistance exercise which increases the amount of fast glycolytic fibers present (bigger muscle size)
\
figure 21.6
35
New cards
differences between SO and FG fibers
SO is aerobically operating and is used in endurance training situations, don’t fatigue easily
\
FG is anaerobically operating and quickly fatiguing, used in resistance training situations
\
FG is anaerobically operating and quickly fatiguing, used in resistance training situations
36
New cards
what is an oxygen deficit?
the stage when activity first begins and there isn’t enough anaerobically generated ATP to support contraction, at this stage the oxygen stores cannot support activity without the help of phosphogens or anaerobic glycolysis
37
New cards
how does a burmese python’s physiology change during its lifetime and why?
a python will change the size of its heart ventricles to support digestion after eating, it will decrease to its original size after 28 days post meal
38
New cards
what is the role of myostatin
regulates hypertrophy in muscles, myostatin knockout causes abnormally enlarged muscle mass
\
figure 21.12, that picture of the two whippets
\
figure 21.12, that picture of the two whippets
39
New cards
thermoregulation vs. thermoconformity
regulation occurs when the organism maintains a constant temperature vs. a conformer’s body temp mirrors closely with the environmental temperature, this is the lower energy cost option
40
New cards
what enzymes are important to rat liver development?
glucokinase, phosphophenolpyruvate- creatine, glycogen synthetase
41
New cards
what is an endotherm?
organism that can produce its own body heat with necessary conditions
42
New cards
define homeotherm
a thermoregulator, usually at a temperature above the environmental temp.
43
New cards
ectotherm
an animal that depends on external sources of heat, a form or conformer
44
New cards
explain how the phospholipid bilayer works
the membrane is made up of a double layer of phospholipids arranged opposite to each other this effect allows only some molecules can diffuse through, covalent or small polar molecules can sometimes pass through depending on their size
45
New cards
why does salt make bubbles in a carbonated beverage?
each grain of salt increases the salinity and drives the dissolved CO2 out of the solution
\
figure 22.2
\
figure 22.2
46
New cards
how does a water beetle breath under water?
they do not have gills, but they use a refilling air bubble to keep a flow of oxygen available, the partial pressure of nitrogen is key here: the partial pressures of nitrogen and oxygen within the bubble keep it from collapsing, then the gradient caused by oxygen use within the bubble allows oxygen to keep diffusing into the bubble
\
figure 22.3
\
figure 22.3
47
New cards
why is it important for sea turtles to lay their eggs in a dry place?
before sea turtles hatch, they depend on oxygen solely from diffusion of oxygen through the sand, if it rains/gets wet then the partial pressure falls to around zero and oxygen cannot diffuse
\
figure 22.5
\*look up why for partial pressure!!!
\
figure 22.5
\*look up why for partial pressure!!!
48
New cards
types of antifreezes in blood
changes to membranes, lipid, enzyme, and protein, composition- all must have a much lower freezing point and keep the membrane/fluid fluid in freezing temps
49
New cards
what is the difference between antifreeze and tolerance of freezing
antifreeze implies there are physiological changes that change the organism to freeze at lower temperatures than 0 celcius
\
tolerance implies that the organism can freeze over and survive that event
\
tolerance implies that the organism can freeze over and survive that event
50
New cards
how does oxygen diffuse from the lungs into the blood stream
countercurrent diffusion is used to ensure the most effective diffusion gradient is created when the two are within diffusion distance of each other
\
figure 22.7, 23.1
\
figure 22.7, 23.1
51
New cards
when does diffusion occur along an oxygen molecule’s journey to bodily tissue?
in the lungs to make it to the blood stream and when the blood moves to the capillaries
\
figure 23.1
\
figure 23.1
52
New cards
what is brown fat thermogenesis and why is it useful?
organisms use it mostly in infant stages as a way to supplement heat production, it is a way of directly burning fat with the purpose of creating heat, this often occurs before animals have enough fur/body mass to thermoregulate, but reindeer do this in adulthood to survive the norwegian winters.
\
activated by nervous system, mitochondria have UCP-1 present
\
figure 11.8
\
activated by nervous system, mitochondria have UCP-1 present
\
figure 11.8
53
New cards
what is HIF-1 used for?
hypoxia response TF
\
figure 23.6
\
RESEARCH FURTHER!!!
\
figure 23.6
\
RESEARCH FURTHER!!!
54
New cards
how does the bullfrog cycle through breathing methods during its life cycles?
as a tadpole: uses skin to get \~60% of oxygen, this decreases as frog reaches adulthood and develops lungs, skin is always used to get rid of CO2
\
figure 23.17
\
figure 23.17
55
New cards
explain the different respiratory capacities of a mammalian lung
inspiratory reserve volume
resting tidal volume
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
\
figure 23.21
resting tidal volume
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
\
figure 23.21
56
New cards
natal philopatry
the return to the area the animal was born in, or to animals remaining in their natal territory
57
New cards
describe the structure of hemoglobin
4 subunits of heme with 4 subunits of globin, iron is in between all these subunits
\
figure 24.1
\
figure 24.1
58
New cards
go through the changes in human development and types of globin used at each stage
after conception epsilon, alpha, zeta hemoglobin present
mid fetal devo alpha and gama hemoglobin present
after birth alpha and beta hemoglobin present
\
figure 24.2
mid fetal devo alpha and gama hemoglobin present
after birth alpha and beta hemoglobin present
\
figure 24.2
59
New cards
How does Bohr’s Effect pertain to hemoglobin and blood?
increase in acidity like increase in H+ or CO2 will decrease the ability of hemoglobin to bind with oxygen and carry it to various tissues
\
notes slide for figure 24.11
\
notes slide for figure 24.11
60
New cards
what are the three different ways the myocardium is supplied with blood
compact, spongey, combination
\
figure 25.3
\
figure 25.3
61
New cards
describe the pathway of blood in the circulatory system and through the heart along with its oxygenation status
blood goes to tissue and returned/ filtered through the lymphatic system
figure 25.4
figure 25.4
62
New cards
difference between troponin and tropoyosin
Troponin and tropomyosin are two proteins that are present on the thin filaments of the muscle cells and help in the contraction of muscles. However, they have opposite functions. While troponin promotes muscle contraction, tropomyosin blocks muscle contraction.
63
New cards
how do fluid column effects translate to elevating a foot injury?
figure 25.7
64
New cards
How does pressure change throughout the circulatory pathway?
it is highest in the aorta and lowest in the veins
\
figure 25.12, 25.13
\
figure 25.12, 25.13
65
New cards
what mechanism allows blood to diffuse in and out of tissues
diffusion down the osmotic gradient
\
figure 27.2
\
figure 27.2
66
New cards
give an example of an osmotic regulator
salmon when they move from salt to fresh water, muscle
\
figure 27.3
\
figure 27.3
67
New cards
solubility of gas question
int
68
New cards
interpret U/P values
figure 27.7, urine/plasma
69
New cards
calculate the obligatory water loss etc.
figure 27.4
70
New cards
explain the differences between water/salt relations in a freshwater lineage vs. salt water lineage animal
figure 28.1, 28.2, 28.2, 28.3, 28.5, 28.7, 28.8, 28.12
71
New cards
explain myogenic vs. neurogenic
72
New cards
how are some birds able to survive off of salt water?
salt gland
\
figure 28.9
\
figure 28.9
73
New cards
hyper isosmotic regulators, hyper-hyperosmotic regulators
figure 28.x with the two graphs and teh crab-
74
New cards
figure 28.17
75
New cards
what is a nephron and how is its structure important
nephron is the bowman’s capsule, glomerulus, descending/ascending limbs, medulla, cortex
\
it is this primary filtering structure within the kidneys
\
it is this primary filtering structure within the kidneys
76
New cards
3 different fluids in mammals
interstitial, intercellular, plasma
77
New cards
2 types of urine stages
primary, definite
78
New cards
question on singular effect
figure 29.2, 29.12
79
New cards
diuresis vs. antidiuresis
diuresis is expelling too much water, antidiuresis is the opposite
figure 29.5
figure 29.5
80
New cards
ammonatelic vs. ureotelic,
excrete ammonia vs. urea
81
New cards
differences in water budgets of oryxes and wildebeasts
figure 30.6
82
New cards
what are MRCs?
mitochondria rich cells
83
New cards
what is the difference between a hyper-iso regulator and a hypo-iso regulator?
84
New cards
how is countercurrent multiplication used in urine formation?
it is part of the mechanism behind the single effect, the descending and ascending limbs have counter currents which are manipulated with the permeability of the nephron tubes that manipulate the osmotic pressure in the interstitial space and allow for this high difference in osmotic pressure to concentrate excreted ions in waste.
\
figure 29.1, 29.12,
\
figure 29.1, 29.12,
85
New cards
what are the different types of excretory waste?
ammonia, urea, uric acid
86
New cards
how is water regained through the urine formation system?
water is regained in the ascending limb of the nephron which is not permeable to ions, but is permeable to water, this water then makes it way back to the blood stream
\
figure 29.5
\
figure 29.5
87
New cards
what is the function of ADH in urine formation
ADH is short for “antidiuretic hormone” which functions as an endocrine signal that when active it induces the excretory system to produce less urine and for the kidneys to hold onto water
88
New cards
what is the difference between ureotelic and uricotellic
they describe organisms that excrete different substances. Ureotelic individuals produce urea in their excretion and uricotellic produce uric acid in their urine
89
New cards
how does the beneficial nature of plants change throughout certain season or times in the day
there is the most available water to a plant at dawn, also the overall makeup of the plant changes in the dry season to have less nutrients, and in the winter plants generally have more protein
\
figure 30.8
\
figure 30.8
90
New cards
list some interesting characteristics about wildebeasts
they have some of the most efficiently contracting muscles that produce virtually no heat and helps in body temp maintaining, can survive with minimal water stores in the desert due to their conservation techniques (concentrated urine, dawn foraging, ability to travel far for water,
\
figure 30.10
\
figure 30.10
91
New cards
which of the following would be the most reasonable method of calculating how much energy a bird would require for migration
\
A. tracking bird for the duration of the migratory path + estimating its energy usage
\
B. using a wind tunnel to measure metabolic rates at different speeds and use that information to calculate energy usage
\
C. measuring resting metabolic rate and then calculating its exercise rate to estimate total energy usage
\
D. Measuring ocygen concumption with some sort of implanted device that the bird carries for the duration of the migration
\
A. tracking bird for the duration of the migratory path + estimating its energy usage
\
B. using a wind tunnel to measure metabolic rates at different speeds and use that information to calculate energy usage
\
C. measuring resting metabolic rate and then calculating its exercise rate to estimate total energy usage
\
D. Measuring ocygen concumption with some sort of implanted device that the bird carries for the duration of the migration
\
B
B
92
New cards
How is the light reaction in fireflies inhibited
\
A. Mitochondria prevent oxygen from reacting with luciferyl-AMP
\
B. Nitric oxide combines with oxygen to prevent reaction with luciferyl-AMP
\
C. ATP is prevented from combining with luciferin
\
D. Luciferase is prevented from catalyzing the reaction
\
A. Mitochondria prevent oxygen from reacting with luciferyl-AMP
\
B. Nitric oxide combines with oxygen to prevent reaction with luciferyl-AMP
\
C. ATP is prevented from combining with luciferin
\
D. Luciferase is prevented from catalyzing the reaction
B, you answered C on the test
93
New cards
which of the following is a similarity between an octopus and a fish
\
A. evolutionary adaptation of excellent vision
\
B. the mechanism of vision
\
C. the processing of visual signals before reaching the optic nerve
\
D. the neuroanatomy of the eye
\
A. evolutionary adaptation of excellent vision
\
B. the mechanism of vision
\
C. the processing of visual signals before reaching the optic nerve
\
D. the neuroanatomy of the eye
A
94
New cards
which mechanism is *not* used for epigenetic marking
\
A. DNA methylation
B. mRNA methylation
C. Histone methylation
D. Histone phosphorylation
\
A. DNA methylation
B. mRNA methylation
C. Histone methylation
D. Histone phosphorylation
B
95
New cards
describe how a graph of an animal that their body temperature stayed constant as the environmental temp increased
horizontal line
96
New cards
the physiological regulation of body temperature is called _________.
A. endothermy
B. homeothermy
C. ectothermy
D. poikilothermy
A. endothermy
B. homeothermy
C. ectothermy
D. poikilothermy
B, you answered A on the test
97
New cards
the phenomenon in which genetically identical individuals can assume two or more distinct body forms induced by differences in the environment is called
\
A. polyphenic development
B. epigenetics
C. phenotypic plasticity
D. seasonal polyphenism
\
A. polyphenic development
B. epigenetics
C. phenotypic plasticity
D. seasonal polyphenism
Kumar’s answer was A, you got points back for answering C
98
New cards
“According to the graph, spiders that fed most on protein rich flies during the 24-hour period before testing
\
A.were more active compared to those fed lipid-rich flies
\
B.preferred lipid rich flies over the next 72 h
\
C. had a body composition higher in protein compared to fat
\
D. had the highest metabolic rate
\
A.were more active compared to those fed lipid-rich flies
\
B.preferred lipid rich flies over the next 72 h
\
C. had a body composition higher in protein compared to fat
\
D. had the highest metabolic rate
B
99
New cards
which molecule is *not* generated when phosphogens are used
\
A. creatine
B. arginine
C. ATP
D. ADP
\
A. creatine
B. arginine
C. ATP
D. ADP
you answered C on the test, this was marked wrong
\
I would guess the answer would be B
\
I would guess the answer would be B
100
New cards
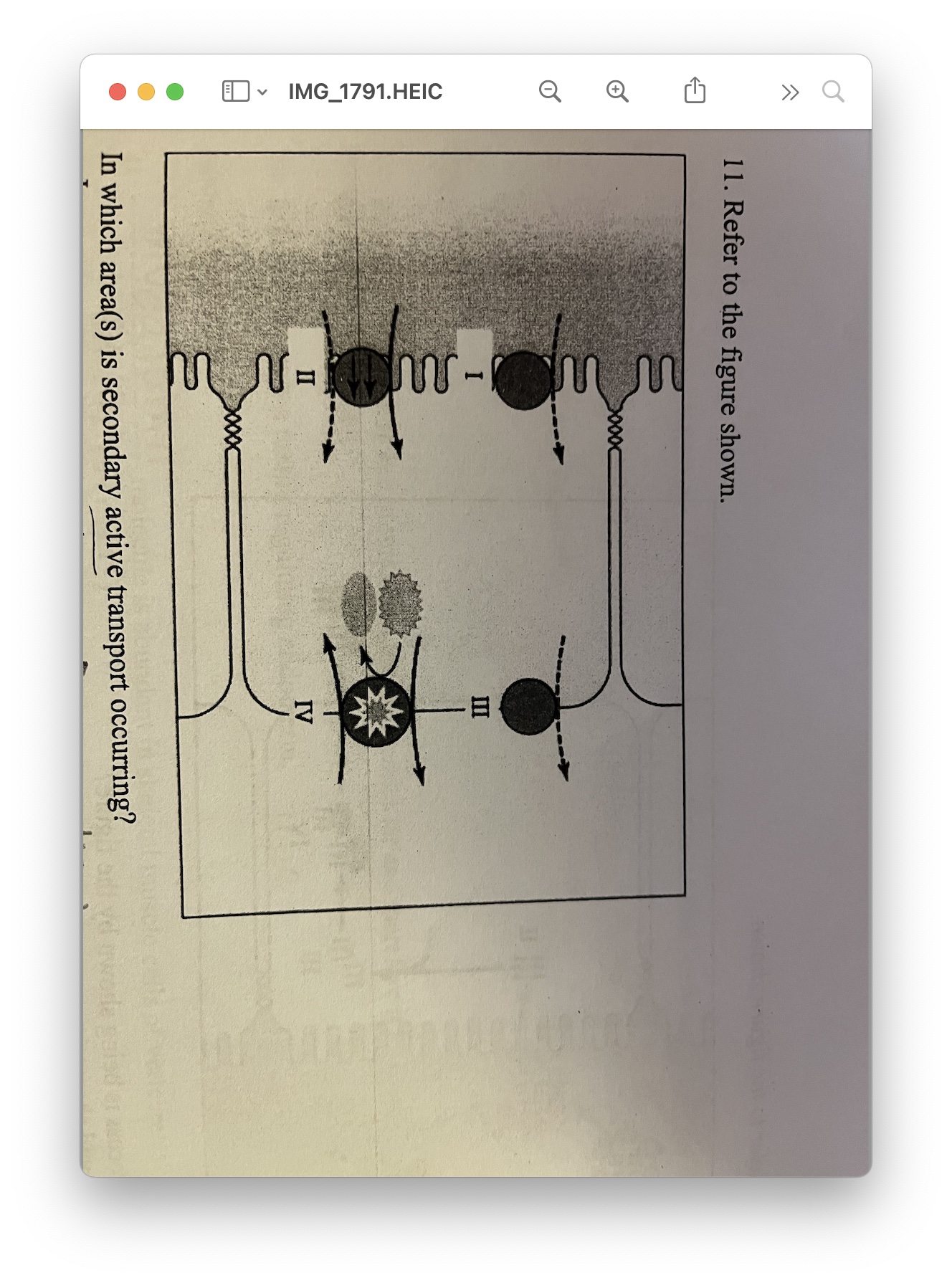
in which area(s) is secondary active transport occuring?
\
A. I
B. II
C. I and III
D. IV
\
A. I
B. II
C. I and III
D. IV
C, you answered D on the test