Inclusive communication & collaboration
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
superdiversity
superdiversity
Interdynamic
some part of identity pops up more/you relate to more than the other (ex feeling more student in sep than in July)
Intersectional discrimination
a structured form of discrimination based on race and gender
Identity markers
characteristics that have meaning to us and the society in which we exist (age, religion,.)
Intersectionality
intersection of identity markers (being a girl + a student + a daughter …)
Intersectional thinking
being aware of how different parts of someone’s identity affect each other
Culture
Culture refers to habits of a social group
(culture onion metaphor)
Equality vs equity
Equality is giving everyone the same vs equity is giving everyone what they need to get on the same level (not same level because everyone’s starting level is different -> fence example)
etnocentrism
the notion that one’s own culture or company knows best how to do things
Unconscious or implicit bias
learned stereotypes and prejudices, positive or negative
like me bias
pull we feel to similar people, we tend to feel more comfortable ⇢ can be a problem when hiring
Negativity bias
negative experiences have a bigger impact than positive ⇢ generalization
(ex. One dog bit me, all dogs will bite me, we give more weight to criticism than compliment)
halo effect
one positive trait = generally positive impression (unintentionally on a pedestal)
horn effect
one negative trait/experience = overall negative impression
confirmation bias
one things confirms it ⇢ applies for all
(ex you think donuts are jelly-filled, you see a donut that is jelly-filled, it is confirmed: all donuts are jelly-filled)
beauty bias, name bias, authority bias…
biases
Why? Biases are shortcuts in our brain shaped by past experiences, to quickly make decisions.
D.I.V.E model
Describe (neutral, objective observation, stick to facts)
Interpret (various explanations, at least 3)
Verifiy (cultural informant, someone who might understand the situation better, reliable sources)
Evaluate (reflect possible biases, evaluate interpretations)
No verify? D.I.V.E model ⇢ D.I.E. model
Hofstede’s 6 cultural dimensions
Power distance
Individualism & collectivism
Masculinity & femininity
Uncertainty avoidance
Long term & short-term orientation
Indulge & restraint
PDI – Power Distance Index
the extent to which people expect and accept hierarchy/unequal distribution of power
High power distance = extremely hierarchical
Low power distance = most egalitarian (EU)
↳ impact on organizational structure
Vertical: formal, clarity, time to specialize, promotional opportunities, bureaucratic, meh communication, opinion leader > employee
Horizontal: few management layers, involvement, more communication, fast decision-making process, final decisions?, little/no clear ranking system
IND – Individualism vs Collectivism
Individualistic = everyone is supposed to take care of themselves and their immediate family
Collective = from birth you are part of a strong, tight group who will take care of you and protect you (in exchange for unconditional loyalty)
↳ impact on organizational structure
Individualistic: hiring on skills, individual achievements are rewarded, focus on personal growth,
task > personal relationships, (social) media is form of information, showing happiness is encouraged showing sadness isn’t
Collective: hiring through existing employees or network, team results are rewarded, focus on harmony and loyalty, stability is more important than individual opinions, information comes from your network, showing sadness is encouraged happiness isn’t, personal relationships > task
MAS – Masculinity vs Femininity
Masculine = performance-oriented, gender roles are clearly separated (men are tough and focused on success, women are modest and focused on quality of life
Feminine = quality of life-oriented, social gender roles overlap, both are expected to be modest and tender and focus on quality of life and development
↳ impact on organizational structure
Masculine: live to work, performance, money, status, competition, confrontation, sharp
Feminine: work to live, appreciation, care for oneself, rest, balance, harmony, discussion, compromise, intuitive, soft
UAI – Uncertainty Avoidance
the more anxious/nervous, the more likely they are to obey and want clear rules, which makes them stay with the same organization longer
High UA = low tolerance for uncertainty and risk-taking, minimize the unknown with strict rules etc (tend to be more emotional) ⇢ religion, lucky charms, laws,…
Low UA = accept and feel comfortable in unstructured situations or changeable environments, try to have as few rules as possible, more tolerant of change
↳ impact on the organizational structure
High UA: accurate, needs rules, stays with employer for a long time, avoid risks, thinks long before acting, theoretical
Low UA: flexible, creative, changes jobs more often, likes trying new ideas, practical, experimental, takes risks
LTO – Long vs short term orientation
degree to which culture delays gratification or the material, social and emotional needs of its members, how far ahead they think
Long term orientation = focus on the future by delaying short-term success in favor of long-term success, perseverance, persistence
Short term orientation = focus on the near future, short-term success, emphasis on present, quick results and respect for tradition (unrestrained spending ⇢ social or ecological pressure)
IND – Indulgence vs Restraint
extent and tendency for a society to fulfill its desires, societal impulse and desire control
High levels of indulgence = high level of bon de vivre, spend more on luxuries, leisure time activities
Restraint = tendency to suppress gratification and regulate them through social norms, sve money and focus on practical need
Successful collaboration =
awareness + respect + flexibility
Edward T. Hall
the hidden dimensions
Communication style (high vs low-context)
Time orientation (monochronic vs polychronic)
Proxemics (personal space)
High-context cultures
non-verbal cues and implicit (indirect) messages, face-saving, harmony, between the lines, meaning dependent on context, content: how, emphasis on verbal communication, repetition is appreciated if it helps clarify the communication
Slow messages (high-context)
Poetry
Books
Ambassador
Documentary
High-context perceive low-context as
- Too explicit
- I can think for myself
- Rude
- Don’t stick to verbal agreements
- Focus too much on details
- So many rules
- Not interested in me
Low-context cultures
explicit, direct, verbal expression, “honest”, meaning independent of context, content: what, emphasis on written communication, messages are both spoken and read between the lines, often implied but not plainly expressed
Fast messages (low-context)
Prose
Headlines
Press release
Tv commercial
Direct reply
Low-context perceive high-context as
- Confusing
- They are unclear
- Rude
- Don’t stick to written agreements
- Withhold information
- There are no rules
- They are nosy
Monochronic
linear time, punctuality, tasks are handled one at a time, step by step, systematically
Polychronic
time is flexible, multitasking, relationships > schedules, patience, relativity of punctuality, interruptions
Proxemics
the study of how people use space and distance to communicate
Personal space preferences vary by culture, with some cultures comfortable with close proximity and others needing more distance
Richard D. Lewis
when cultures collide
linear active
multi-active
reactive
Linear active
talks half of the time, plans ahead step by step one thing at a time, polite but direct, partly conceals feelings, dislike losing face, rarely interrupts, job-oriented, sticks to facts, truth before diplomacy, sometimes impatient, limited body language, separates social/professional
Multi-active
talks most of the time, multitasking, plans grand outline only, emotional, displays feelings, confronts emotionally, often interrupts, people-oriented, feelings > facts, impatient, unlimited body language, seeks out key person, mixes social/professional
Reactive
listens most of the time, reacts, polite, indirect, conceals feelings, never confronts, must not lose face, doesn’t interrupt, very people-oriented, statements are promises, diplomacy > truth, patient, subtle body language, uses connections, connects social/professional
Attribution bias
judge the cause of someone’s behavior in a one-sided or unfair way, instead of considering all possible reasons. We blame the person and ignore the situation.
Your classmate fails a test → you think: “They’re lazy.”
But if you fail a test → you think: “The test was unfair.”
That difference is attribution bias: judging others by their character, but yourself by the situation.
Pillars of inclusive campaigns
Inclusive and positive representation
People decide for themselves
“Nothing about us without us!” → ask them → engage in dialogue
Be mindful of tokenism (wrong motivation)
Ensure coherence with your internal policy
Tokenism
when a person from a minority group is included only to give the appearance of diversity, without giving them real power, respect, or equal treatment
Visual impairments
Difficulty or inability to read text: blindness and low vision
Auditory impairments
Difficulty or inability to understand spoken words: deafness and hearing loss
Mobility/motor impairments
Use of wheelchairs, walking sticks, or difficulty standing for long periods
Neurodiversity
he diversity in human neurocognitive functioning (different ways of thinking, learning, perceiving, and interpreting).
Difficulty concentrating in highly stimulating environments
Challenges with processing complex information
Feeling different or misunderstood (a sense of belonging)
→ ASS, AD(H)D, Tourette Syndrome, Giftedness, Dyslexia, Dyscalculia,…
Gender
he biological and physical characteristics with which a person is born such as male, female or intersex
Gender identity
how a person identifies internally, such as male, female, non-binary or gender fluid
Gender expression
the way a person expresses their gender outwardly, such as through clothing, behavior and appearance
Agender
someone who does not experience gender identity or identifies as genderless.
Gender fluid
someone whose gender identity varies over time or context.
Cisgender
a term that is used to describe people whose gender identity matches the sex they were assigned at birth
Male
someone who identifies as male, regardless of biological sex.
Female
someone who identifies as female, regardless of biological sex.
Non-binary
someone who does not exclusively identify as male or female.
Androgynous
a gender expression that combines both masculine and feminine characteristics or remains ambiguous.
Gender-conforming
is an expression that conforms to the cultural expectations of one's gender.
Gender-nonconforming
an expression that deviates from the cultural expectations of one's gender.
Gender-neutral
an expression without distinct male or female characteristics, often intentionally neutral.
Masculine expression
a person behaves, dresses and presents according to traditional masculine characteristics.
Female expression
a person behaves, dresses and presents according to traditional female characteristics.
Asexuality
little to no sexual attraction to others
Bisexuality
attraction to both men and women
Demisexuality
sexual attraction that occurs only after a strong emotional attachment.
Heterosexuality
ttraction to people of the opposite sex.
Homosexuality
attraction to people of the same sex.
Pansexuality
attraction to people regardless of gender or gender identity
Sapiosexuality
attraction based on a person's intelligence or intellectual connection
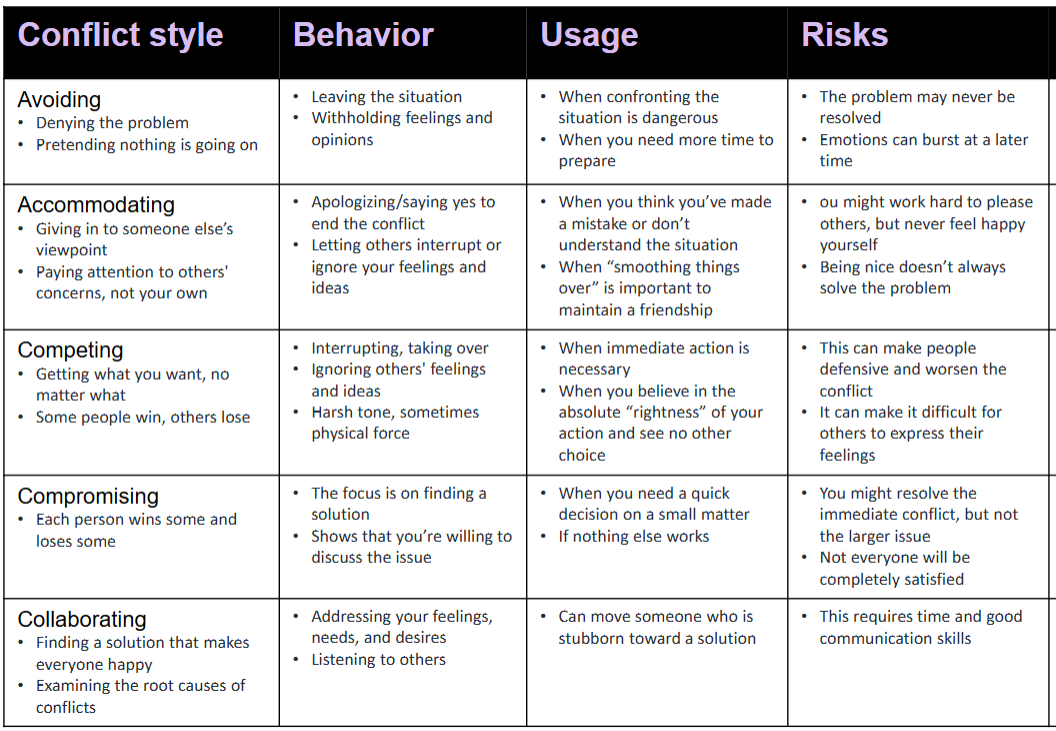
Five Conflict Styles
Avoiding: Sidestepping the conflict altogether.
Accommodating: Prioritizing the other party’s needs over one’s own.
Competing: Asserting one’s position at the expense of others.
Compromising: Finding a middle ground to satisfy both parties.
Collaborating: Working together to find a solution that fully satisfies both parties.
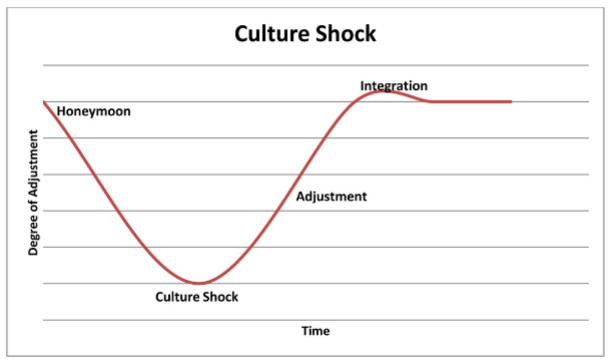
U-curve of culture shock
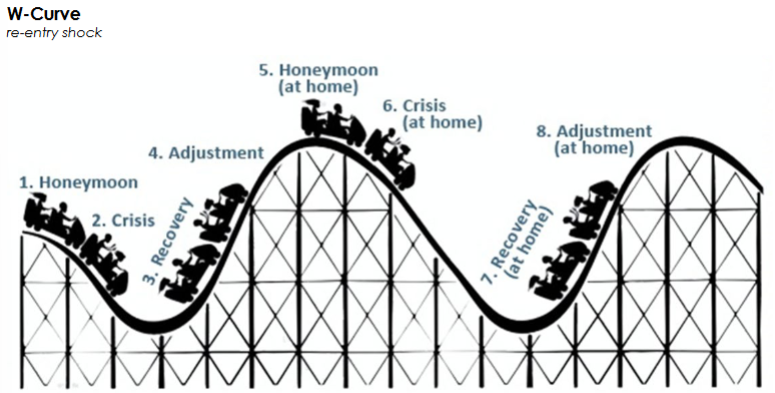
W-curve of re-entry shock
In work context:
Initial Excitement:
When an employee starts a new job, they often feel a sense of excitement and enthusiasm. They are eager to learn, meet new colleagues, and contribute to the organization. This stage is characterized by high energy and optimism about the new environment.
Disillusionment:
As the employee becomes more familiar with their new role and the workplace dynamics, they may encounter challenges, such as unclear expectations, difficulty adapting to company culture, or interpersonal conflicts. This can lead to feelings of frustration, confusion, and disappointment. The employee may feel overwhelmed or underappreciated, leading to a drop in morale.
Adjustment:
Over time, the employee starts to understand the organizational culture better and develops coping strategies to navigate the challenges. They might seek feedback from colleagues, engage in training, or develop supportive relationships with peers. This gradual adjustment is marked by increased confidence and comfort in their role.
Acceptance:
Eventually, the employee reaches a point where they feel integrated into the workplace. They are comfortable with their tasks, have established good relationships with coworkers, and understand the organizational expectations. They now have a realistic view of their role and the organization, leading to a sense of satisfaction and belonging.
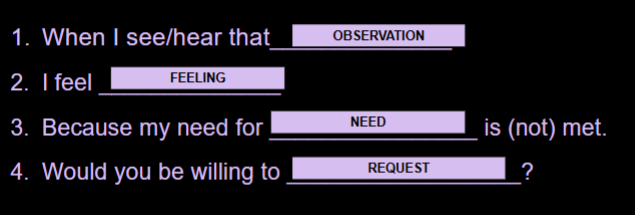
Non-Violent Communication
OBSERVATION: Identify behavior in an unbiased and factual way.
FEELING: Express the feelings triggered by the behavior. Acknowledge your feelings. “I feel… / I am…”
NEED: Identify a (un)met need.
REQUEST: Formulate a request after clarifying your feelings and needs.
E. Hoffman
Prisma Method
A – Acknowledged Similarity
B – Acknowledged Difference
C – Thinking and Acting Inclusively
Miller & Katz Inclusion Model: The D&I Continuum
The model describes 3 levels of collaboration:
Exclusion: certain individuals or groups are left out. E.g.: only dominant voices determine policy.
Assimilation: everyone must adapt to the dominant norm; diversity is ignored rather than valued.
Inclusion: differences are valued and used; everyone feels seen, heard, appreciated.
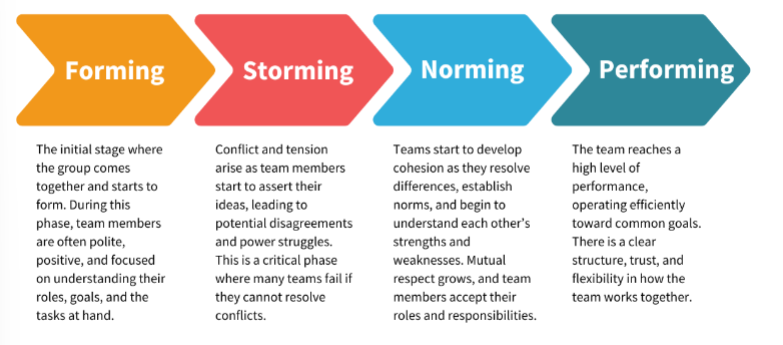
Tuckman’s Team Development Model
5. Adjourning (added 1977)
Temporary team dissolves after completingits task
Reflection & closure
Challenge: dealing with ending/letting go
Traits: evaluation, farewells, celebrating success
Belbin’s Team Roles
Thinkers
Plant: Creative, idea generator
Monitor Evaluator: Objective, analytical
Specialist: Deep expertise
Doers
Shaper: Driven, pushes team forward
Implementer: Practical, turns plans into action
Completer Finisher: Careful, detail-oriented
People-roles
Coordinator: Organiser, focuses on team goals
Teamworker: Diplomatic, promotes harmony
Resource Investigator: Extravert, brings contacts/opportunities
The TOPOI Model
“Cultures Don’t Meet, People Do”
analyzing and addressing potential miscommunication
Tongue: How does verbal and non-verbal communication influence the interaction? (accents, body language)
Order: How do cultural filters, assumptions or logic shape how we interpret the situation? (norms about hierarchy, time, communication style)
Persons: How do identity and relationships influence what people say or don’t say? (stereotypes, prejudices, power)
Organization: What contextual, organizational or societal factors influence the communication? (rules, procedures, time zones)
Intentions: What motivates each person? What needs, values or emotions drive their behaviour? (goals, emotions, fears, expectations, values)