Genetic diversity as a result of meiosis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is meiosis and what does it produce
A type of cell division that produces daughter cells with:
-half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
-different combinations of alleles from each daughter cell and the parent cell
What are the starting and ending chromosome states in meiosis?
Meiosis starts with diploid cell and ends with haploid cells.
Why is meiosis important?
It produces haploid gametes for sexual reproduction and creates genetic variation, which increases diversity allowing natural selection.
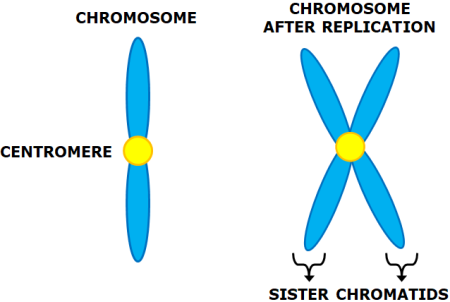
What is a centromere?
The part of a chromosome where two chromatids are held together in which in the becomes sister chromatids, found at the centre of the chromosome
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, that contain the same genes and are of the same size.
What is the difference between chromatids and sister chromatids
A chromatid is one of two identical strands of a chromosome and sister chromatids are formed when a chromatid is replicated
What does the acronym IPMATPMAT stand for in meiosis?
Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Cytokinesis, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, Cytokinesis.
What happens during interphase?
DNA is replicated, resulting in chromosomes that contain two chromatids so has become a sister chromatid
What occurs during Prophase I of meiosis?
Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes pair up, and spindle fibres start forming.
What happens during Metaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell and attach to spindle fibers by their centromeres.
What happens during Anaphase I?
Homologous chromosome pairs are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
What occurs during Telophase I and cytokinesis?
Chromosomes reach opposite poles, the cell pinches in the middle, and the cytoplasm divides to form two cells.
What occurs during Prophase II?
There are now two daughter cells
The chromosomes condense and centrioles migrate to opposite poles of the cell where each centriole starts forming spindle fibres
What happens during Metaphase II?
The chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell
Each chromosome attaches to the spindle by their centromere
What happens during Anaphase II
At the centromeres the chromosomes divide and separate each pair of chromatids
What happens during Telophase II and Cytokinesis?
The chromatids reach the opposite poles of the cell and the cell pinches in the middle
The cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) and 4 cells are produced.
What is crossing over in meiosis?
The process during Prophase I where homologous chromosomes exchange alleles, increasing genetic variation.
State the number of chromosomes and chromatids at each stage of meiosis in one cell
-Start of with parent cell
46 sister chromatids so 23 chromosomes
-Interphase
96 sister chromatids so 46 chromosomes
-Anaphase 1
46 sister chromatids so 23 chromosomes
-Telophase II
23 Chromatids so 23 chromosomes (haploid cell)
What are the three ways in which the process of meiosis increase genetic diversity?
Crossing over of Chromatids/recombination
Independent assortment/ random assortment
Random fertilisation but is technically not due to meiosis
What is crossing over/recombination?
Occurs during prophase I of meiosis
The homologous chromosomes condense and pair up
The chromatids of each chromosome then twist around one another, forming a chiasmata
What is the effect of a crossing over?
This swaps alleles between the homologous chromosomes to produce different combinations on each chromosome
Each cell has a different chromatid (and different set of alleles), increasing the genetic variation of the offspring
What is independent assortment?
The random arrangement of homologous chromosomes during Metaphase I and II, leading to genetic diversity.
What is the effect of independent assortment?
it is completely random as a result which chromosomes end up in each daughter cell is also random
How do you calculate the possible number of different combinations of chromosomes follwing meiosis, without crossing over?
2 to the power of n
n is the number of homologous chromosome pairs
so in humans it would be 2 to the power of 23
How does random fertilization contribute to genetic variation?
It is random which male gamete fertilizes which female gamete, leading to diverse offspring.
What can chromosome mutations lead to?
Chromosome mutations lead to inherited conditions
What is non-disjunction?
A mutation during meiosis where chromosomes fail to separate properly, leading to gametes with abnormal chromosome numbers because one daughter cell may have two copies of a chromosome whereas another may be missing a chromosome
What disorder can result from non-disjunction during meiosis in humans and how does it occur?
Down syndrome
Down syndrome is caused by a person having an extra copy of chromosome 21 or an extra copy of part of chromosome 21
Non disjunction means that chromosome 21 fails to separate properly during meiosis, so one cell gets an extra copy of 21 and another gets none
What is the effect of non-disjunction during fertilsiation?
when the gamete with the extra copy fuses to another gamete at fertilisation, the resulting zygote will have three copies of chromosome 21
What are the final products of meiosis?
Four haploid cells, each with 23 chromosomes that are genetically different from each other and the parent cell
What is the role of spindle fibers during meiosis?
They help in the movement and separation of chromosomes during anaphase I and II
What is the difference between diploid and haploid cells?
Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes (2n), while haploid cells have one set (n).
What is a chiasmata?
The point where chromatids twist around each other during crossing over in Prophase I.