W2L2: Noradrenaline, Arousal, Anxiety and Decision-Making
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
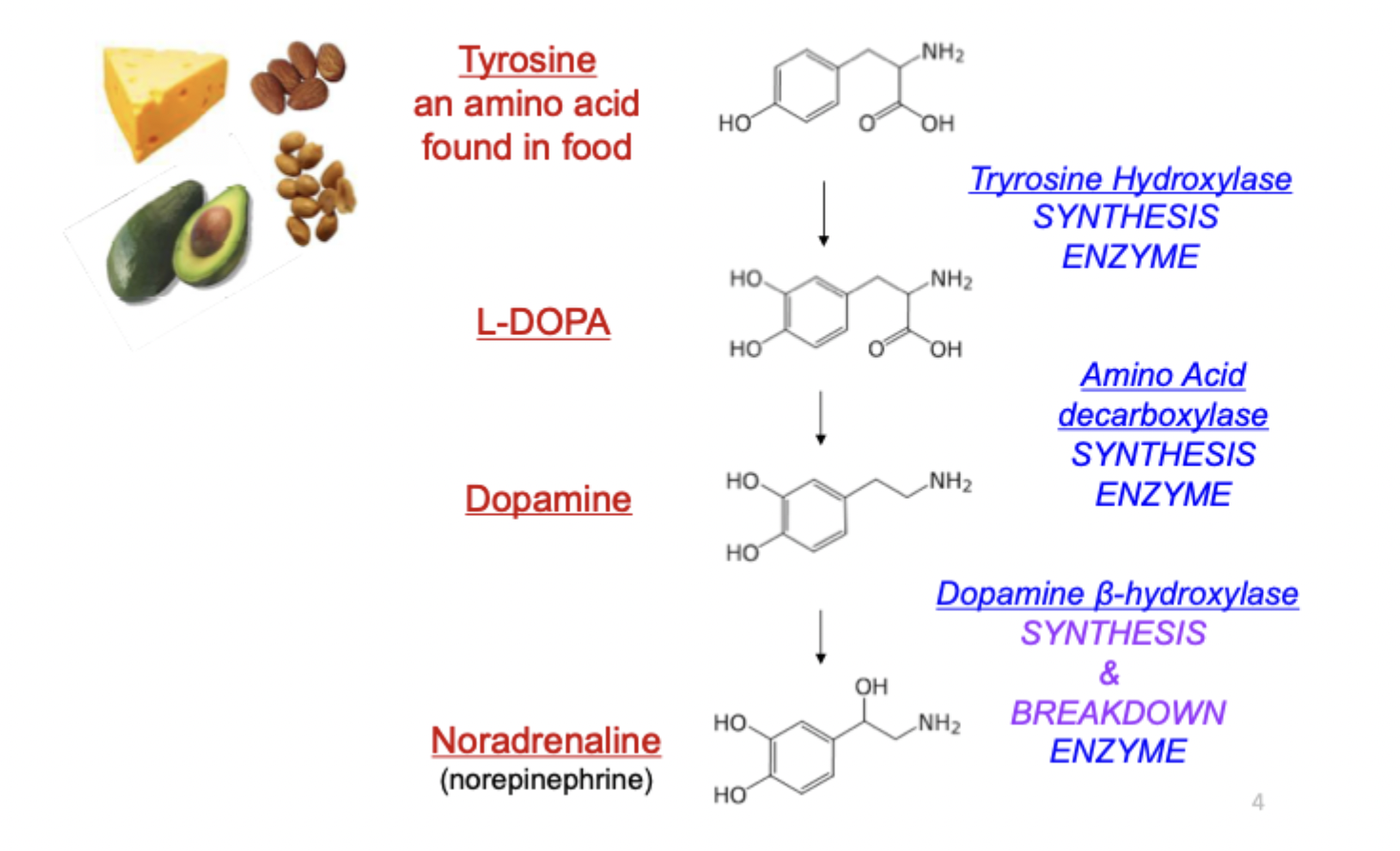
noradrenaline: synthesis
get dopamine from tyrosine, amino acid converted into L-DOPA and then converted to dopamine then synthesised into noradrenaline (noradrenaline needs dopamine to be synthesised)
noradrenaline: function
regulates arousal, cognitive function, stress, flight-fight response, reward/addiction, memory consolidation, exploitation vs exploration
noradrenaline: breakdown
one additional synthesis step in adrenal gland results in hormone adrenaline (drives effects in body)
noradrenaline: adrenaline
from brainstem where noradrenaline is produced in locus coereleus innovates medulla of adrenal organs above kidneys which leads to release of adrenaline
monoamine oxidase
breakdown for monoamine enzymes (dopamine, serotonin, noradrenaline)`
noradrenaline: location
locus coeruleus (LC), hypothalamus, amygdala, neocortex
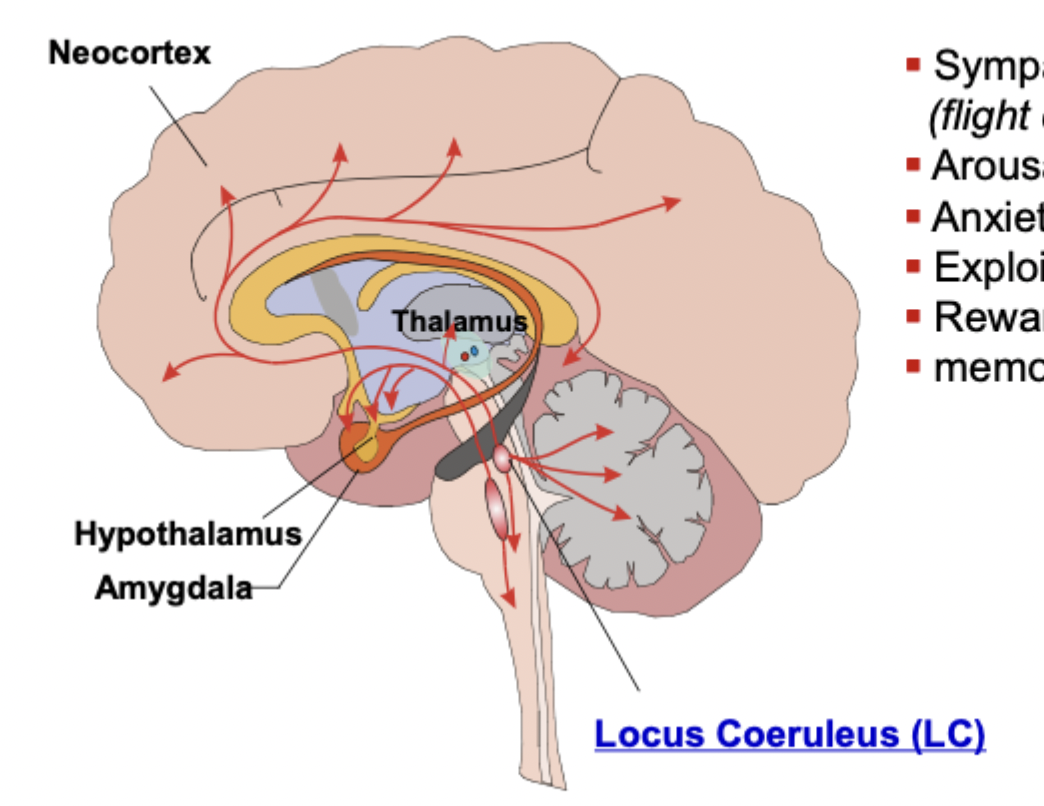
noradrenaline: locus coeruleus
during highest rates of neurotransmitter release neutrons fire after extremely positive or negative stimulus event (more salient the even the greater the arousal)
LC: high activity: 4 F’s
state of hyperarousal adapted for evolutionary important situations where individual or sexual fitness is involved
LC: high activity: stress
experienced when LC/NA activity is sustained due to environmental factors
LC: high activity: anxiety
brief intense episodes believed to reflect spikes of LC/NA activity due to triggers
noradrenaline: flow state
when own skill level and difficulty of task is well matched
noradrenaline: low levels of arousal/noradrenaline
bored, sleep, not challenging
noradrenaline: high levels of arousal/noradrenaline
anxiety, too hard
LC: moderate levels of activity
noradrenaline acts to consolidate decisions
exploration and exploitation
adaptive behaviour represents tradeoff between exploiting known sources of reward and exploring environment for alternative sources of reward
noradrenaline: behavioural selection
competition between two behaviours, burst of noradrenaline release tips balance in favour of a winner (increases strength of activating and inhibiting signals)
LC neurons: behavioural selection
neurons in LC fire when behavioural response is selected and executed, after they fire neutrons are inhibited allowing selected behaviour to be exploited
noradrenaline: behavioural selection: high arousal
larger burst of noradrenaline release tips balance in favour of winner with more strength
noradrenaline: LC neurons: during high arousal
larger response of neutrons in LC more noradrenaline released and longer following period of inhibition
LC neurons: low arousal
in absence of recent decisions or arousing events baseline levels of firing increase and more noradrenaline is released throughout brain forcing individual to seek other options and take exploration (find things to do), switching to a new decision
low levels of LC and NA release
tired, vague, poor performance
high levels of LC and NA release
restless, stressed, poor performance
noradrenaline: visual perception
helps consolidate perceptual representations + sensations (when visual stimuli is ambiguous helps choose one percept over another, revises as percept become clearer)
noradrenaline: pupil
pupil dilates when making decisions