Unit 8 - Capital Investment Appraisal Cartes | Quizlet
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
The nature of investment decisions
Often large amounts of resources, long timescales and expensive price
What are the investment appraisal methods?
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR), Payback Period (PP), Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
What is Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)?
Taking the average accounting profit that the investment will generate and expresses is as a percentage of the average investment over the life of the project, this is specifically for this investment
How to calculate Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
(Average annual operating profit / Average investment to earn that profit) x 100
How to calculate average annual profit
(The inflows of each year - Annual expenses - Depreciation) / 12
How to calculate average investment
(Cost of machine + Disposal value) / 2
How to find disposal value
The straight line method = depreciation = Depreciated percentage x Value of the previous year
How does Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) help make a decision?
It needs to be a minimum
What is a disadvantage of Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)?
It ignores the time factors and the cost of financing the project
What is Payback Period (PP)?
The time taken for an initial investment to be repaid out of the net cash inflows from a project
How to plot a table for Payback Period (PP)
Put the options, years, cash flows for each year in separate columns, beginning with Year 0 with the purchase price (in brackets as it is - & putting brackets around the cumulative cash flows that are before the payback. Then, write the cash flow (the amount earned on each year), taking any expenditures for specific years from the cash flow
What does Residual Value mean?
Extra cash flow added onto a period
What should you do if you aren't given the period of time for residual value or extra costs?
Add/subtract it to/from the last period of time (before multiplying it by the discount factor)
How to find out the cumulative cash flows
For Year 0, start with the purchase price (in brackets), then add (or take away if the cash flow is negative) the cash to the cumulative cash flow
How to find the Payback Period (PP)
When the table is finished, find the year where the cumulative cash flow becomes 0 (not positive or negative)
If the cumulative cash flow is 0 exactly on the Payback Period
The Payback Period (PP) is the number of years exactly)
If the cumulative cash flow isn't 0 on the Payback Period
Start from the year complete before that divide the cumulative cash flow of the complete year, then by the cash flow of the next incomplete year, then multiply by 12, then round the decimal to the nearest month
What is a disadvantage of Payback Period (PP)?
It takes more into account the timing, but this isn't a complete answer to the problem
What is Net Present Value (NPV)?
The difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows over a period of time
What are the 3 factors that influence the required return to business owners (the opportunity cost of finance)? Net Present Value (NPV) takes these into account
Interest lost, risk, inflation and overall the time value of money
How to calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
Create separate landscape tables with the years, net cash flows (don't forget to take any expenditures for specific years from the cash flow), discount factors & present values (the net cash flows x the discount factor)
What to do if you aren't given the discount factor
1 / (1 x (1 + discount factor as a decimal)^year number)
How to calculate the present values
Multiply the cash flow by the present value of each year
How to find the Net Present Value (NPV)
Add all your present values together (make sure you put Year 0 as a -)
Advantages of Net Present Value (NPV)
The timing of the cash flows, the cash flows are relevant and it reflects on the objectives of the business
When advising which project should be purchased
You have a choice between: Both, One or Neither. A project with a positive NPV is acceptable. A project with a negative NPV is not acceptable. The payback period is not important to the decision, unless the question states that it has to be paid back by a certain period
What does it mean when the projects are mutually exclusive?
Only one should be accepted, based on the better Net Present Value (NPV)
What does it mean when the projects are not mutually exclusive?
All projects with a positive NPV can be accepted
What is Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
The discount rate that, when applied to future cash flows, will produce an NPV of precisely 0, representing the yield from a particular investment opportunity
The relationship between the NPV & IRR on a graph
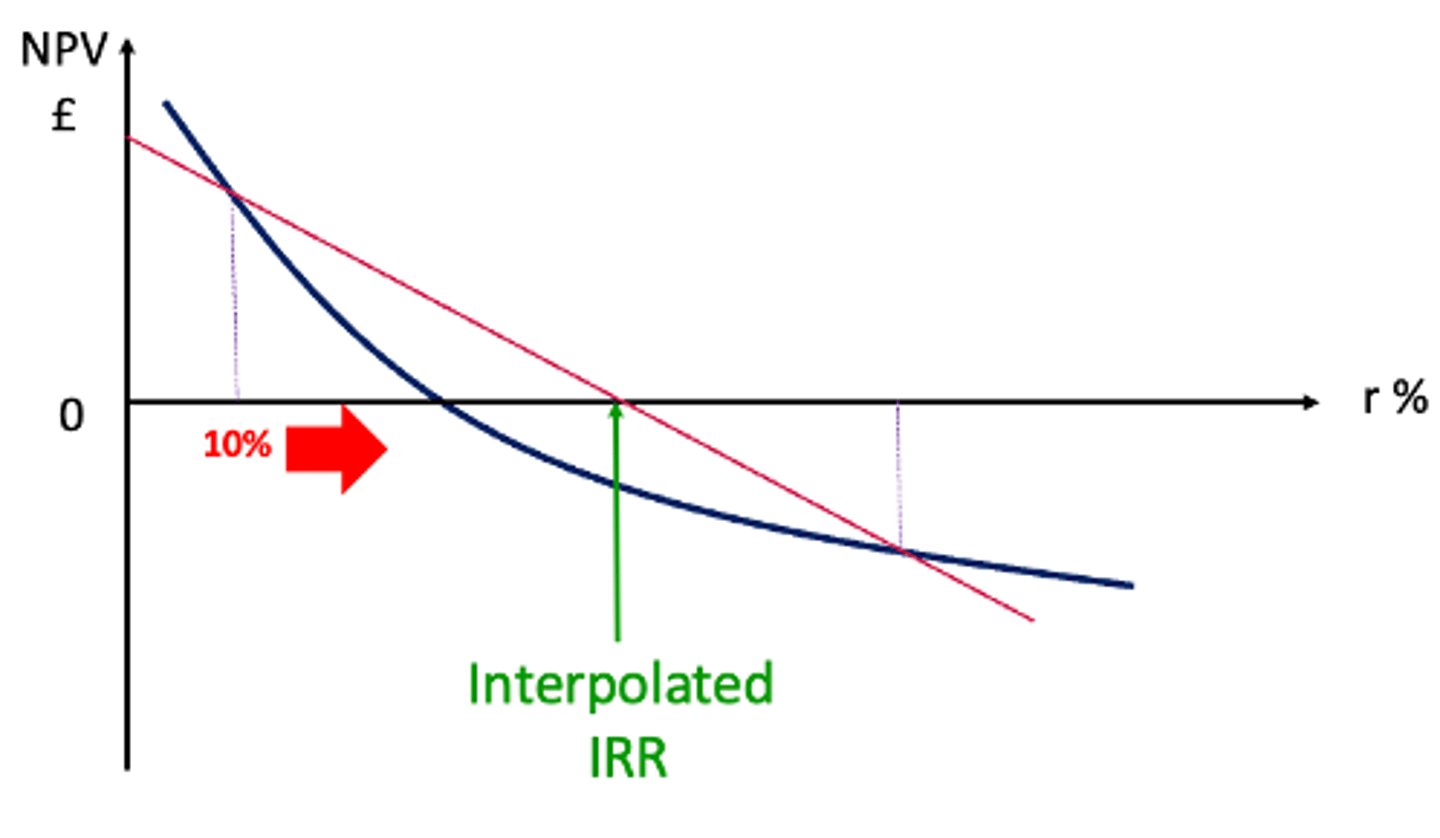
How is Internal Rate of Return (IRR) calculated?
Use trial or error with a discount factor percentage to calculate the NPV - for the year where it starts to become 0, if it isn't 0 on that year, then try a higher or lower percentage
How to save time for the trial and error process
FInd the difference between the NPV's, then divide it by the difference between the percentages to find the change in NPV for 1%, then divide a discount rate by the NPV for 1% & multiply it by 0.1% to get the amount of a 0 NPV, then take the the result from closest discount factor to a 0 NPV
What is a disadvantage of Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
It doesn't directly address the the question of wealth generation, potentially leading to the wrong decision being made