Communicable Dis.
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
by TRA Jesse Daclis; PHN White Book
Last updated 5:51 AM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
**Communicable Dis.**
→ can be transmitted from one person to another
→ (+) Causative Agent
* *pano mo malalaman if communicable dis. siya?* ***CA***
→ **Stages of Infection: (**`IPACR`**)**
* ***“IPA-CR mo”***
→ (+) Causative Agent
* *pano mo malalaman if communicable dis. siya?* ***CA***
→ **Stages of Infection: (**`IPACR`**)**
* ***“IPA-CR mo”***
2
New cards
**COVID-19**
→ CA: Beta Corona Virus
3
New cards
**Incubation Period**
→ first stage of infection
→ duration: entry until first s/sx appeared
→ Asymptomatic
→ duration: entry until first s/sx appeared
→ Asymptomatic
4
New cards
**Prodromal Period**
→ (+) non-specific s/sx
* example: flu-like s/sx
* example: flu-like s/sx
5
New cards
**Acute Period**
→ (+) specific signs & symptoms
→ __**Pathognomonic Signs**__
* **Rabies**: Hydrophobia
* **Dengue**: petechiae & Herman’s sign (flushing of the skin)
* **Leprosy**: Leonile Appearance (a lion-like appearance)
→ __**Pathognomonic Signs**__
* **Rabies**: Hydrophobia
* **Dengue**: petechiae & Herman’s sign (flushing of the skin)
* **Leprosy**: Leonile Appearance (a lion-like appearance)
6
New cards
**Convalescence Period**
→ s/sx start to disappear
7
New cards
**Resolution Period**
→ last stage
8
New cards
**IMMUNITY**
* **Antigen**
* foreign bodies
* **“AntigENEMY”**
* from Sir Kenneth
\
* **Antibody**
* “papatayin ang mga antigen”
* CHON (protein)
* destroy familiar antigen
\
**Immunoglobulin (GAMED)**
\
**Ig**__**M**__: first Ab → “__Mauna__ ako”
* first to respond
**Ig**__**G**__: 2nd Ab → “__Gagi__ sunod ako”
* foreign bodies
* **“AntigENEMY”**
* from Sir Kenneth
\
* **Antibody**
* “papatayin ang mga antigen”
* CHON (protein)
* destroy familiar antigen
\
**Immunoglobulin (GAMED)**
\
**Ig**__**M**__: first Ab → “__Mauna__ ako”
* first to respond
**Ig**__**G**__: 2nd Ab → “__Gagi__ sunod ako”
9
New cards
**Immunity General Types**
* **Natural Immunity**
* inherent in the body
* from the word natural
\
* **Acquired Immunity**
* **acquired when exposed to the environment**
\
\
**Active Acquired Immunity**
* Antibodies are __*produced by the individual itself*__
* !! LONG-TERM PROTECTION
* “Active Acquired = AKO”
\
**Passive Acquired Immunity**
* Antibodies are __*given*__ to the individual
* !! SHORT-TERM PROTECTION
* inherent in the body
* from the word natural
\
* **Acquired Immunity**
* **acquired when exposed to the environment**
\
\
**Active Acquired Immunity**
* Antibodies are __*produced by the individual itself*__
* !! LONG-TERM PROTECTION
* “Active Acquired = AKO”
\
**Passive Acquired Immunity**
* Antibodies are __*given*__ to the individual
* !! SHORT-TERM PROTECTION
10
New cards
**Active Acquired Immunity (ANTIGEN)**
* **Natural Active Immunity**
* stimulus: exposed to antigen
* `NARS - natural active nagrecover ka sa sakit`
\
* **Artificial Active Immunity (**`LIT`**)**
* vaccine → laman ay Antigen
* **L**ive Attenuated → buhay na pinahina na mikrobyo; bawal for immunocompromised
* **I**nactivated → killed; pwede sa immunocompromised
* **T**oxoid (modified toxins)
* stimulus: exposed to antigen
* `NARS - natural active nagrecover ka sa sakit`
\
* **Artificial Active Immunity (**`LIT`**)**
* vaccine → laman ay Antigen
* **L**ive Attenuated → buhay na pinahina na mikrobyo; bawal for immunocompromised
* **I**nactivated → killed; pwede sa immunocompromised
* **T**oxoid (modified toxins)
11
New cards
**Passive Acquired (IMMUNOGLOBULIN)**
* **Natural Passive Immunity**
* transplacental → IgG
* breastfeeding → IgA
\
* **Artificial Passive Immunity**
* post-exposure
* immunoglobulin na iniinject
* transplacental → IgG
* breastfeeding → IgA
\
* **Artificial Passive Immunity**
* post-exposure
* immunoglobulin na iniinject
12
New cards
**Mode of Transmission** (`CAVEVE`)
1. **Contact**
1. **Direct** → physical touch
2. **Indirect** → contaminated object
3. **Droplet**
1. respiratory secretions → __large particles__ → within 3 ft.
2. use surgical mask
\
2. **Airborne (**`MTV`**)**
1. respiratory secretions → __fine particles__ → greater than 3 ft.
2. use N95
3. **“MTV”**
1. measles
2. tuberculosis
3. varicella
\
3. **Vehicle T.**
1. taga-bitbit lamang ng mikrobyo (carrier)
2. non-living → water, food
\
4. **Vector T.**
1. living
1. mosquito
2. fly
13
New cards
**RABIES (Lyssa)**
CA: **Rhabdo Virus** → bullet shape virus
\
* KAPAG NASA EXTREMETIES
* (-) s/sx
* (-) contagious
* (-) death
\
* KAPAG NASA __**BRAIN**__
* (+) contagious
* (+) s/sx
* (+) death
\
**Mode of Transmission:**
* animal bite
* scratch
* tissue transplant
\
\***RA 7170: Organ Donation Act**
\
* KAPAG NASA EXTREMETIES
* (-) s/sx
* (-) contagious
* (-) death
\
* KAPAG NASA __**BRAIN**__
* (+) contagious
* (+) s/sx
* (+) death
\
**Mode of Transmission:**
* animal bite
* scratch
* tissue transplant
\
\***RA 7170: Organ Donation Act**
14
New cards
**Rabies: Signs & Symptoms**
1. **Invasive Stage**
1. Prodromal s/sx → nonspecific
2. fever, photophobia, headache, numbness
\
2. **Excitement Stage**
1. Acute
1. Hydrophobia (laryngospasm)
2. Aerophobia (fear of flying)
3. Maniacal behavior (like a wild animal)
\
3. **Paralytic Stage**
1. Generalized Paralysis
1. Respiratory Paralysis → cause of death
15
New cards
**Rabies: Diagnostics**
1. Brain Biopsy
2. **Fluorescent Rabies Antibody Test (FRAT)**
1. confirmatory test
16
New cards
**Rabies: Immunization (preventing the virus from reaching the brain)**
**First Aid**: Wash with soap & water + betadine
\
**Tetanus Toxoid: Prophylaxis**
\
**Artificial Active (Vaccine)**
* **Verorab / Imurab**
* inactivated virus
* stimulate immune system to produce antibodies
* 5 doses
* IM
* ID (cost-effective)
* Day 0, 3, 7, 14, 28
\
**Artificial Passive (Immunoglobulin)**
* **Rabies Ig (Rabuman)**
* laman ay antibodies
* immediate effect
* half is injected on the wound site; half is injected IM
* depends on the weight of the pt
\
**Tetanus Toxoid: Prophylaxis**
\
**Artificial Active (Vaccine)**
* **Verorab / Imurab**
* inactivated virus
* stimulate immune system to produce antibodies
* 5 doses
* IM
* ID (cost-effective)
* Day 0, 3, 7, 14, 28
\
**Artificial Passive (Immunoglobulin)**
* **Rabies Ig (Rabuman)**
* laman ay antibodies
* immediate effect
* half is injected on the wound site; half is injected IM
* depends on the weight of the pt
17
New cards
**Rabies: Palliative Care**
For patients na nasa brain na ang rabies:
\
1. Strict Isolation → Use all PPE
2. Nonstimulating Environment
3. Use of Restraints
4. No any sense of fluids
5. Cover IVF
\
1. Strict Isolation → Use all PPE
2. Nonstimulating Environment
3. Use of Restraints
4. No any sense of fluids
5. Cover IVF
18
New cards
**Rabies: Responsible Pet Ownership**
→ prevention
→ Dog Immunization: 3 months; Booster yearly
\
\***RA No. 9482: Anti-Rabies Act of 2007**
* “Ninenay Four Dog Eight 2”
* “Nanay poor dog ito”
→ Dog Immunization: 3 months; Booster yearly
\
\***RA No. 9482: Anti-Rabies Act of 2007**
* “Ninenay Four Dog Eight 2”
* “Nanay poor dog ito”
19
New cards
**Dengue vs. Malaria vs. Filariasis**
* **Dengue - H-fever**
* CA: Dengue Virus 1, 2, 3, 4 or Chikungunya virus
* Vector: Aedes Aegypti or the common household mosquito
* Peak Age of Susceptibility: 5-9 yrs
* Peak Months: September & October
\
* **Malaria - Marsh Fever**
* CA: protozoal parasite → plasmodium
* Vector: Anopheles
* Plasmodium
* P. vivax
* P. orale
* P. malaria
* P. Falciparum - fatal; common in the Phil.
\
* **Filariasis - Elephantiasis**
* Vector: Aedes Poecillus
* Roundworms
* Wuchereria bancrofti
* Brugia Malayi
* Brugia timori
\
**Mode of Transmission**
* Mosquito Bite
* CA: Dengue Virus 1, 2, 3, 4 or Chikungunya virus
* Vector: Aedes Aegypti or the common household mosquito
* Peak Age of Susceptibility: 5-9 yrs
* Peak Months: September & October
\
* **Malaria - Marsh Fever**
* CA: protozoal parasite → plasmodium
* Vector: Anopheles
* Plasmodium
* P. vivax
* P. orale
* P. malaria
* P. Falciparum - fatal; common in the Phil.
\
* **Filariasis - Elephantiasis**
* Vector: Aedes Poecillus
* Roundworms
* Wuchereria bancrofti
* Brugia Malayi
* Brugia timori
\
**Mode of Transmission**
* Mosquito Bite
20
New cards
**Dengue: Grade 1**
→ Fever (High) → 2-4 days
→ Pattern: Biphasic/ Saddleback
* will remain elevated for 2-4 days, then okay for 1-2 days, then will elevate again
* \*BEQ: low fever of dengue = low platelet → bleeding
\
* Bradykinin
* Prostaglandin
* Histamine
* → after producing → releasing fever
\
**S/sx**
* Herman’s sign (flushing of the skin)
* Petechiae
→ Pattern: Biphasic/ Saddleback
* will remain elevated for 2-4 days, then okay for 1-2 days, then will elevate again
* \*BEQ: low fever of dengue = low platelet → bleeding
\
* Bradykinin
* Prostaglandin
* Histamine
* → after producing → releasing fever
\
**S/sx**
* Herman’s sign (flushing of the skin)
* Petechiae
21
New cards
**Dengue: Grade II**
**S/sx** of Grade 1 + Spontaneous Bleeding
* Platelets less than 50, 000
* Epistaxis
* Hematemesis
* Melena
\
**MGT**
* bawal ang dark-colored food & drinks
* Platelets less than 50, 000
* Epistaxis
* Hematemesis
* Melena
\
**MGT**
* bawal ang dark-colored food & drinks
22
New cards
**Dengue: Grade III Shock**
(+) Plasma Leakage
→ Hypotension
→ tachycardia
→ tachypnea
→ Narrow Pulse Pressure
→ Hypotension
→ tachycardia
→ tachypnea
→ Narrow Pulse Pressure
23
New cards
**Dengue: Grade IV Profound Shock**
→ undetectable BP/pulse
→ DSS: Dengue Shock Syndrome
\
**Warning Signs**
* abdominal pain → damaged liver
* persistent vomiting
* clinical fluid accumulation → pleural effusion; ascites
* inc HCT → plasma leakage
→ DSS: Dengue Shock Syndrome
\
**Warning Signs**
* abdominal pain → damaged liver
* persistent vomiting
* clinical fluid accumulation → pleural effusion; ascites
* inc HCT → plasma leakage
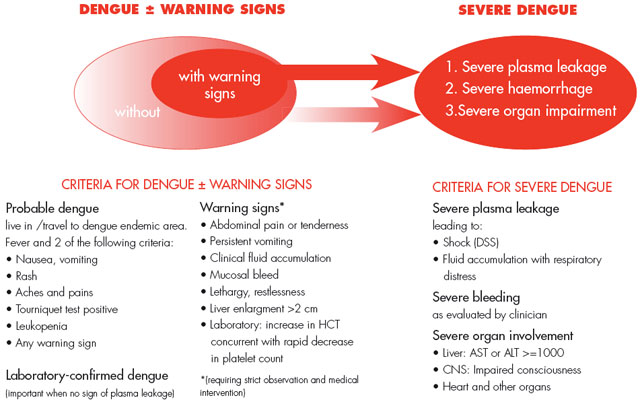
24
New cards
**Dengue: Diagnostics**
1. **Tourniquet Test / Rumpel Lead Test**
1. screening test → assesses the vascular resistance
2. not for dehydration or bleeding
1. link: (https://youtu.be/LSpo9fJOz0c?si=4DrN45_heMNEb9Dm)
__STEPS:__
1. Check BP
2. Solve Mid Systolic Diastolic Pressure
1. Add the systole and diastole divided by 2
3. Reinflate the BP Cuff until the answer for no. 2 for at least 5 mins
4. Observe Petechiae: 1 inch or 2.5 cm square
1. normal: 1-2 petechiae
2. positive: 20 or more petechiae
\
\
5. **CBC**
1. Platelet: low
2. HCT: high (concentrated)
\
3. **Serological test** → (+) Antibody
1. **Elisa / EIA: Enzyme Immunosorbent Assay**
1. Confirmatory Test
\
4. **Dengue Duo**
1. rapid test
1. (+) NS1 Antigen Test (Viral Particle)
2. (+) Ab → IgM; IgG
25
New cards
**Dengue: Palliative Management**
* Paracetamol
* NO aspirin (platelet inhibitor)
\
**NSG Management:**
* Rest
* Fluid Replacement
* Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) → Most Important for Dengue
* 2-3 L for adults
* IVF → LR NSS
* Ice Pack → for bleeding
* Diet: No colored foods & drinks
* NO aspirin (platelet inhibitor)
\
**NSG Management:**
* Rest
* Fluid Replacement
* Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) → Most Important for Dengue
* 2-3 L for adults
* IVF → LR NSS
* Ice Pack → for bleeding
* Diet: No colored foods & drinks
26
New cards
**MALARIA**
→ protozoal parasite
→ Sporozoites
* immature protozoa → will live in liver → hepatomegaly
→ Merozoites
* matured merozoites → will exit liver into the RBC → Anemia
* (+) Severe anemia: Malarial Cachexia
\
S/sx every 2-3 days
1. Cold Stage (10-15 mins)
1. chills
2. clatter teeth
2. Hot Stage Stage 4-6 hrs
1. high fever
2. headache
3. malaise
3. Diaphoretic Stage
1. wet stage
2. mag-papawis
→ Sporozoites
* immature protozoa → will live in liver → hepatomegaly
→ Merozoites
* matured merozoites → will exit liver into the RBC → Anemia
* (+) Severe anemia: Malarial Cachexia
\
S/sx every 2-3 days
1. Cold Stage (10-15 mins)
1. chills
2. clatter teeth
2. Hot Stage Stage 4-6 hrs
1. high fever
2. headache
3. malaise
3. Diaphoretic Stage
1. wet stage
2. mag-papawis
27
New cards
Diagnostics Test
1. Blood Smear → “Peak”
\
MGT
**Artemether Lumefrantine** → first-line
Primaquine - ff-up drug; 3-14 days
Chloroquine → prophyliactic drug; P. Virax
Quinine IM/IV
* supine for 1 hr
* wof dizziness
28
New cards
Filariasis
Stages
\
1. Asymptomatics S. → 8-16 months
2. Acute Stqge
1. Lymphdenitis
2. Lymphangitis
3. Funiculitis → spermatic cord
4. Orchitis → testes
5. Epididymitis
3. Chronic S. (10-15 years)
1. Hydrocele
2. Elephantiasis
3. Lyphmedema
\
1. Asymptomatics S. → 8-16 months
2. Acute Stqge
1. Lymphdenitis
2. Lymphangitis
3. Funiculitis → spermatic cord
4. Orchitis → testes
5. Epididymitis
3. Chronic S. (10-15 years)
1. Hydrocele
2. Elephantiasis
3. Lyphmedema
29
New cards
Diagnostics
1. Nocturnal Blood Exam
\
MGT
DEC _> diethyl carbamezapine (hetrazan)
30
New cards
4 S
Search & destroy
Self-protection
Say No to indiscriminate fogging
Seek Early Consultation
Self-protection
Say No to indiscriminate fogging
Seek Early Consultation
31
New cards
Tuberculosis
CA: mycobacterium tubercle
MOT: airborne droplet → cough
\
LatenT
\
Acrive
Afternoon low-grade fever
blood in sputum (hemoptysis)
Cough (less than 2 wks)
ddec in weight
eevening sweat (night sweats)
\
extrapulmonary tb
\
\
MOT: airborne droplet → cough
\
LatenT
\
Acrive
Afternoon low-grade fever
blood in sputum (hemoptysis)
Cough (less than 2 wks)
ddec in weight
eevening sweat (night sweats)
\
extrapulmonary tb
\
\
32
New cards
RIPES OF TB
* Rifampicin
* S/E: red-orange body fluids
* A/E: hepatotoxic
* bawal alak &
\
Inad Vit. B6 (Pyridoxine) → peripheral neuritis
No to tyramine foods → HPN crisis
Hepatotoxic
\
* Pyrazinamine
* A
* I
* N
* → inhibit the excretion of uric acid → Inc. fluid intake, NSAIDs, Allopurinol
\
* Ethambutol
* Eyes → Optic Neuritis → Blindness
* Not for children 6 yo and below
\
* Streptomycin
* aminoglycoside
* Nephrotoxicity
* Ototoxicity
* S/E: red-orange body fluids
* A/E: hepatotoxic
* bawal alak &
\
Inad Vit. B6 (Pyridoxine) → peripheral neuritis
No to tyramine foods → HPN crisis
Hepatotoxic
\
* Pyrazinamine
* A
* I
* N
* → inhibit the excretion of uric acid → Inc. fluid intake, NSAIDs, Allopurinol
\
* Ethambutol
* Eyes → Optic Neuritis → Blindness
* Not for children 6 yo and below
\
* Streptomycin
* aminoglycoside
* Nephrotoxicity
* Ototoxicity
33
New cards
Leprosy: Hansen’s Disease
C.A. Mycobacterium Leprae
MOT: Airborne-Droplet
\
Skin
Mucuos-Membrane
Peripheral nerve
Testes
\
early
* Loss of skin sensation
* extremities paralysis
* painful/thick nerves
* redness eyes
* obstruction nose
* skin color changes → reddish / white
* your ulcer do not heal
\
late
* large breast in male
* achronic ulcer contracture
* toes & fingers clawing
* eyebrows loss (madarosis)
* eyelids can’t close completely
MOT: Airborne-Droplet
\
Skin
Mucuos-Membrane
Peripheral nerve
Testes
\
early
* Loss of skin sensation
* extremities paralysis
* painful/thick nerves
* redness eyes
* obstruction nose
* skin color changes → reddish / white
* your ulcer do not heal
\
late
* large breast in male
* achronic ulcer contracture
* toes & fingers clawing
* eyebrows loss (madarosis)
* eyelids can’t close completely
34
New cards
**Leprosy: Types**
* Paucibacillary (Tuberculoid & Intermediate)
* Tx: Rifampicin & Isoniazid
\
* Multibacillary (Lepromatous & Borderline)
* \
* Tx: Rifampicin & Isoniazid
\
* Multibacillary (Lepromatous & Borderline)
* \
35
New cards