YEAR NINE EOY BIO
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
what does bile do?
emulsifies fat
where is bile made?
in the liver
bile _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the _ _ _ _ released from the _ _ _ _ _ _ _
bile NEUTRALISES the ACID released from the STOMACH
Name the three parts of the human digestive system that produce amylase. (pss)
salivary gland, pancreas, small intestine
what do arteries do?
these carry blood AWAY from the heart
what do capillaries do?
connect arteries and veins
what do veins do?
these carry blood TOWARDS the heart
Explain how amylase breaks down starch. Answer in terms of the ‘lock and key theory’.
Amylase breaks down starch by fitting into its specific structure, like a key in a lock. This fitting allows amylase to catalyze the reaction that splits starch into simpler sugars such as maltose.
what are enzymes?
enzymes are large protein molecules, made up of amino acids. they are biological catalysts that speed up reactions.
- a protein that speeds up chemical reactions
what is a polymer?
a long chain molecule made up of many individual molecules
what is the active site?
The active site is the place on the enzyme where the substrate binds.
what is a substrate?
A substance on which enzymes act.
what is it called when the active site shape is damaged?
denatured
what does the GLANDULAR TISSUE in the stomach do?
produces digestive juices that break down food
what does the EPITHELIAL TISSUE in the stomach do?
helps to protect the stomach lining from the harsh acidic environment
what does the MUSCULAR TISSUE in the stomach do?
Moves the stomach wall to churn the food
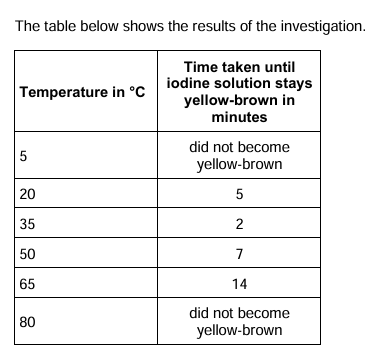
explain the results at 5 C and 80C (amylase practical)
at 5 °C amylase / starch / molecules have low (kinetic) energy (therefore) there are fewer (enzyme-substrate) collisions.
At 80 °C, amylase becomes denatured. this causes the shape of the active site to change so the starch can no longer fit.
what is the pancreas (gland) purpose?
- makes hormones to control blood sugar
- makes enzymes to digest
what is the livers purpose?
bile is produced here
what is the small intestines purpose?
digests and absorbs food
what is the stomachs purpose?
the digestion of proteins occur here
what is the large intestines purpose?
absorbs water from undigested food, producing feces.
what is the ph level of the mouth?
ph 7
what is the ph level of the stomach?
ph 2/3
what is the ph level of the small intestine?
ph 8
how do you test for starch?
- add a few drops of iodine
- a POSITIVE result would be it turning blue/black.
how do you test for reducing sugars?
- add benedict's solution
- heat to 80 degrees celcius in a water bath
- a POSITIVE result would be:
green = small amount
yellow = more sugar present
brick red = lot of sugar present
how do you test for proteins?
- add biuret reagent
- a POSITIVE result would be it turning purple/lilac
how do you test for lipids/fats?
- add a few drops of ethanol and distilled water
- then you gently shake the mixture
- a POSITIVE result would be a white emulsion forming.
what diffuses in/out of a red blood cell?
oxygen INTO the cell
adaptations of a red blood cell? (to maximise diffusion)
biconcave shape which equals a large surface and small volume for maximum diffusion
what diffuses in/out a root hair cell?
- water INTO the cell (osmosis)
- mineral ions INTO the cell (active transport)
adaptations of a root hair cell? (to maximise diffusion)
- contains mitochondria which release energy for active transport
- increased surface area
what diffuses in/out of the lungs? (alveoli)
- oxygen INTO the lungs
- carbon dioxide OUT of the lungs
adaptations of the lungs (alveoli)? (to maximise diffusion) (many _______ ____)
- MANY alveolar sacs = large SA:Volume
- alveoli walls are one cell thick so there is a short distance for the diffusion of gases
what diffuses in/out the small intestine?
- nutrients INTO the intestine
adaptations of the small intestine? (to maximise diffusion)
- inner surface is covered in finger like projections called villi, and each villus is covered in even smaller projections called microvilli. These villi provide a large surface area.
- walls of the villi are extremely thin, which minimises the distance that nutrients need to travel to enter the bloodstream
what is the formula to find surface area to volume ratio?
surface area / volume
what is the surface area equation? (cube)
area of each face x 6
what is the definition of diffusion?
diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until an even concentration is achieved.
in what states can particles diffuse?
liquid and gas
how does SA:VOLUME affect diffusion? (“A higher surface area-to-volume ratio _____ __ because theres more…”)
A higher surface area-to-volume ratio speeds up diffusion because there's more outer space for particles to pass through compared to the "inside" size. Smaller objects have higher ratios, making diffusion faster.
definition of osmosis?
diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane.
hypertonic means?
more concentrated
hypotonic means?
less concentrated
isotonic means?
same level of concentration
explain how to perform the osmosis practical? (potato practical)
1. peel the potato
2. use a cork borer to make three cylinders of potato
3. trim the cylinders to the same length
4. measure the length and width of each cylinder
5. place each cylinder into a test tube
6. put 0.2M sucrose solution, 1M sucrose solution, and distilled water into the test tubes. (one each 10cm cubed of each)
7. leave them in for 20 minutes
8. take them out and put then on paper towels to remove excess liquid
9. measure the length and mass again
10. measure the percentage change
what is the equation for percentage change?
% change = change in value / original value x 100
explain how to conduct the microbiology practical? (innoculating loop one)
7
1. Flame the inoculating loop
2. Open the bottle containing the bacteria culture and flame the mouth of the bottle.
3. Dip the cool inoculating loop into the bacterial culture.
4. Replace the lid of the bottle
5. Streak the plate
6. Flame the inoculating loop again
7. Streak the plate again
what is an example of an aseptic technique? (the microbiology practical)
using equipment that has been sterilised to avoid contamination
why must we use aseptic technique when using microorganisms? (the microbiology practical)
so we only grow the microorganisms that we want
what preparation must we do before we start the microbiology practical and why?
wipe down the bench with disinfectant to sterilise the work surface
what do we use to inoculate our agar plates? (the microbiology practical)
a sterile metal loop
how can we check that the loop is not still hot? (the microbiology practical)
gently push it into the agar
why do we use the streak plate pattern to spread the bacteria on the agar plate? (the microbiology practical)
to dilute the number of colonies we need to see individual colonies
why do we re-flame the loop and put it back in the ethanol? (the microbiology practical)
to remove our microbe from the loop
why do we not tape up the whole circumference of the agar plate? (the microbiology practical)
these microbes need oxygen
why do we put the plates in the incubators at 25 degrees celsius and not higher? (the microbiology practical)
25 degrees celsius is the max because above this may encourage pathogenic bacteria.
where are embryonic stem cells located?
inside of young embryos
properties of embryonic stem cells?
- grow and divide rapidly
- can transform into ANY cell
potential uses of embryonic stem cells?
treat a WIDE RANGE of diseases
disadvantages of embryonic stem cells?
- embryo is destroyed (has ethical/religious concerns)
- involves therapeutic cloning
describe therapeutic cloning:
- get human egg from donor
- you get the nucleus from the patient, then you get the empty unfertilised egg cell from an donor, and put the nucleus in the cell.
- the cell slowly starts to turn into an embryo
- after 4-5 days, the stem cells are removed
- after they are removed, they are cultured to grow into the required organ/tissue
where are adult stem cells located?
bone marrow
properties of adult stem cells?
can transform into a SMALL number of cells
potential uses of adult stem cells?
could be used to treat a LIMITED RANGE of diseases
disadvantages of adult stem cells?
- it can only treat a SMALL number of diseases
- could transfer viral infections
where are plant stem cells located?
in the meristem (active regions on stem and roots)
what are the properties of plant stem cells?
- can transform into ANY plant cell THROUGHOUT ITS LIFE
what are the potential uses of plant cells?
to make clones of plants to prevent extinction
disadvantages of plant cells?
n/a
definition of stem cells?
an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce the same type of cell and can transform to form other types of cells.
where can stem cells be found?
adult stem cells -> bone marrow
embryonic stem cells -> embryo
plant stem cells -> roots/buds
what can stem cells be used for?
- help repair and replace tissues/organs
- treat conditions like bone disease, Parkinson's, heart disease
interphase?
- spends most of its life in this phase
- the DNA in chromosomes copies itself ready for mitosis
prophase?
- the DNA in chromosomes and their copies condenses to become more visible.
- The membrane around the nucleus disappears.
metaphase?
- chromosomes and their copies line up in the middle of the cell
anaphase?
- chromosomes and their copies are pulled to different ends of the cell
telophase?
- new membranes form around the chromosomes at each end of the cell
cytokinesis?
- the cell membrane pinches in and eventually divides into two daughter cells.
what happens when mitosis goes wrong?
(- usually, cell only ______ at certain times
- sometimes this control stops working and cells ______ uncontrollably
- THIS IS ______ )
Ca nicer
function of sperm cell?
moves through the female reproductive organs to reach an egg. breaks the egg to fertilise it.
adaptations of the sperm cell?
- long tail to help the sperm move quickly
- contains many mitochondria to provide energy for the tail to move
function of xylem cell?
transports water and mineral ions from the roots to the rest of the plant
adaptations of xylem cell?
- lignin cell walls to make them very stron
- forms long hollow tubes to allow water to flow
function of muscle cell?
contracts and relax in pairs to move the bones of the skeleton.
adaptations of muscle cell?
- contains special proteins that slide over each other to make the fibres contract
- contains many mitochondria to transfer the energy needed for contracting and relaxing.
function of phloem cell?
transports sugars made in photosynthesis
adaptations of phloem cell?
- have sieve plates which allows sugar and amino acids to flow easily through
-companion cells attached to each sieve tube provides energy for the transport of substances in the phloem.
function of root hair cell?
helps absorb water and mineral ions
adaptations of root hair cell?
- large surface area to maximise uptake
- many mitochondria to provide energy for the active transport of mineral ions
function of nerve cell?
carrys electrical impulses around the body of an animal. Provides rapid communication between parts of the body.
adaptations of nerve cell?
- lots of dendrites to make connections to nerve cells
- an axon to carry the impulse
- lots of mitochondria to provide energy
magnification = ???
how many times bigger the image looks than the actual object
resolution = ???
the ability to see two diffrent points as seperate. the higher the revolving power of a microscope, the more detail you can see in the image.
equation for magnification = ???
magnification = image size / actual size
how to convert from nanometres to micrometres?
multiply by 1,000
cytoplasm = ???
most of the chemical reactions happen here. contains dissolved nutrients and salts called organelles/
mitochondria = ???
where most energy is released in respiration
ribosome = ???
where protein synthesis occurs