Lecture 25: Endocrine System II
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:59 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
1
New cards
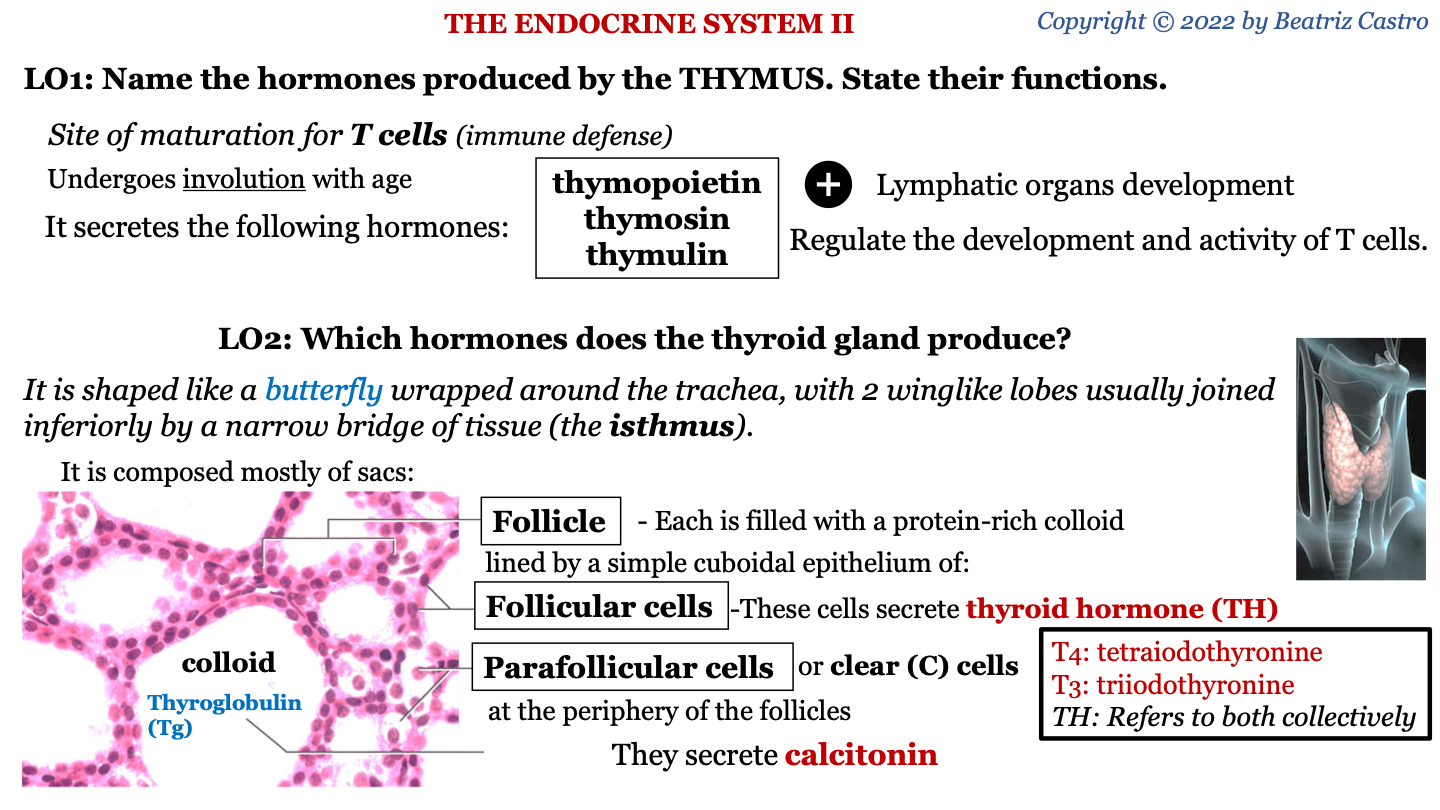
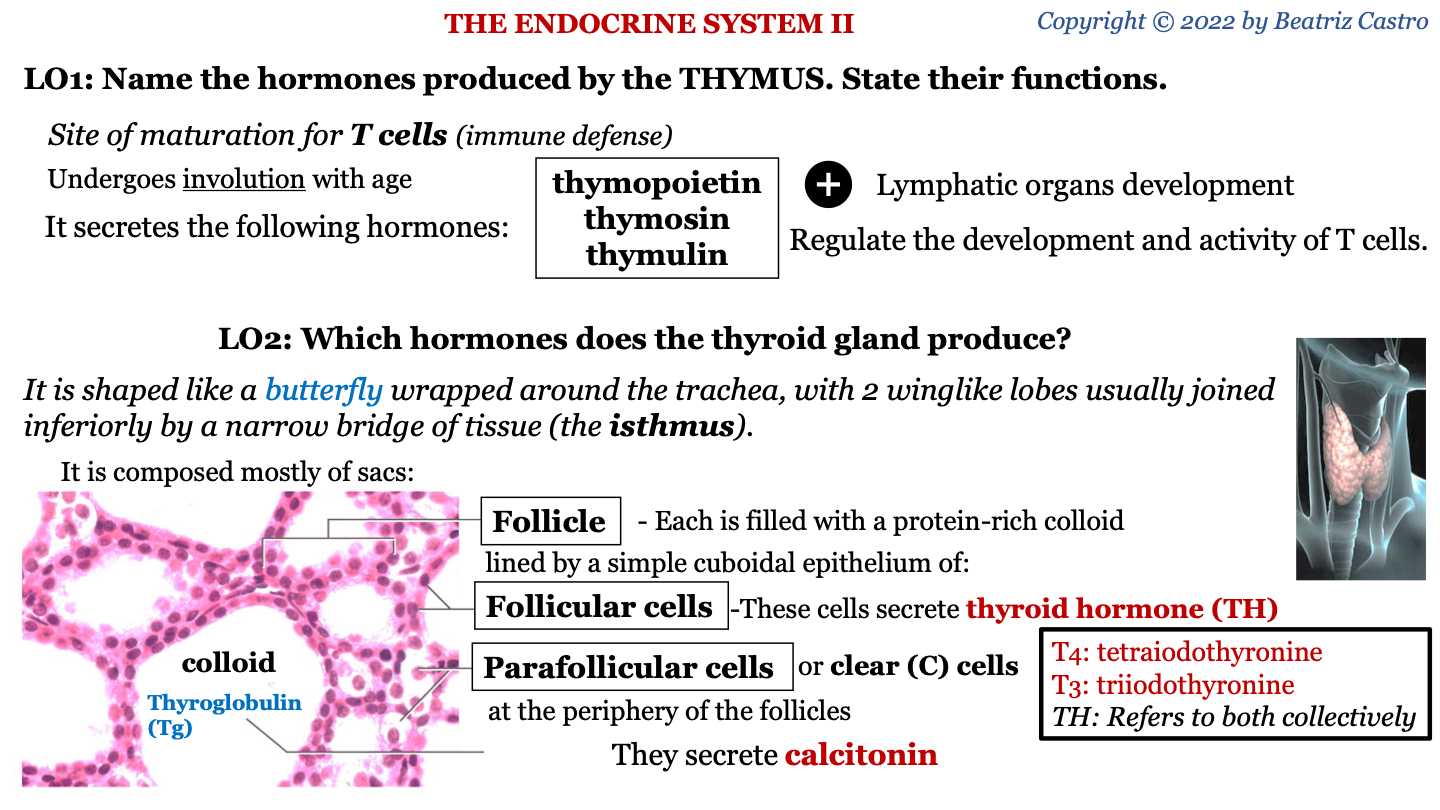
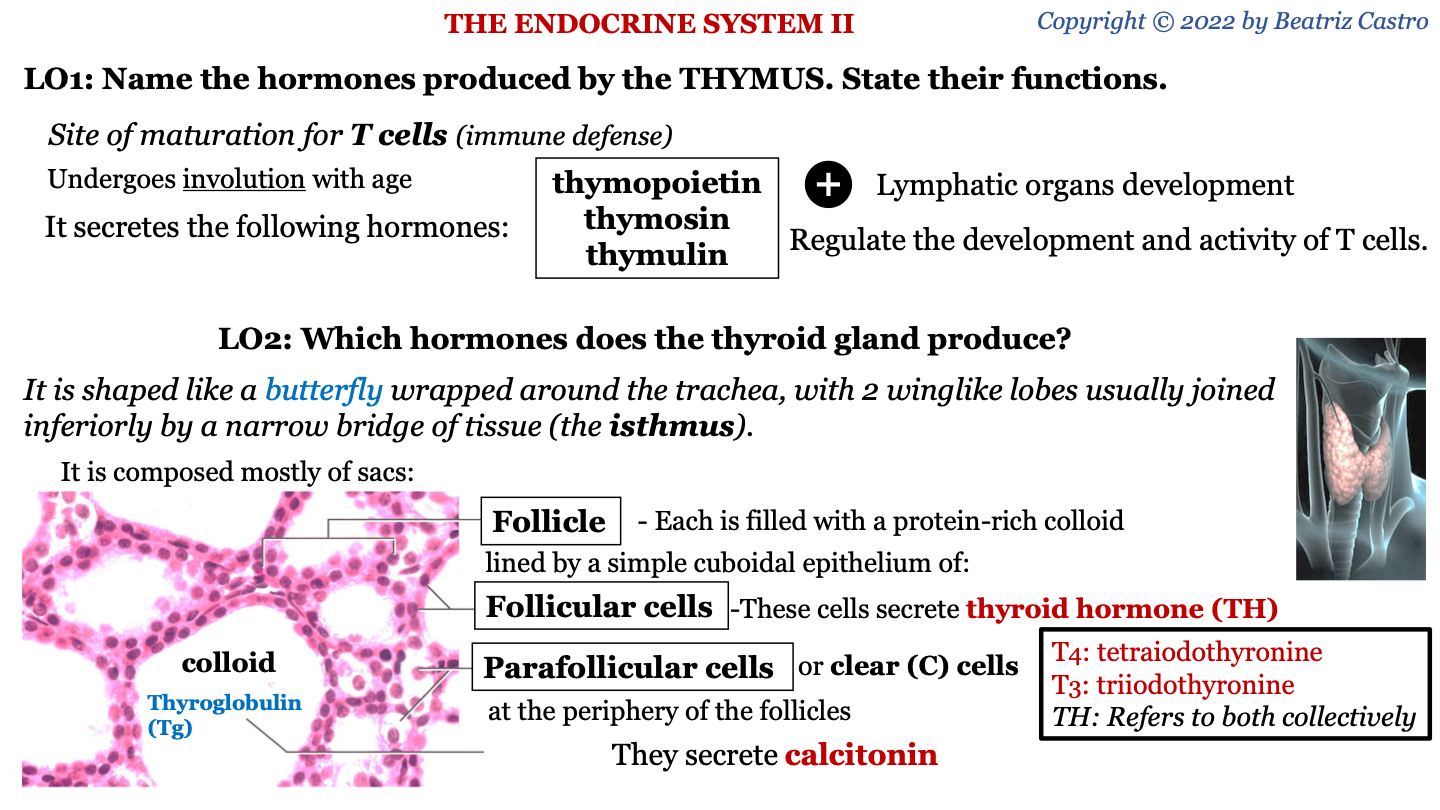
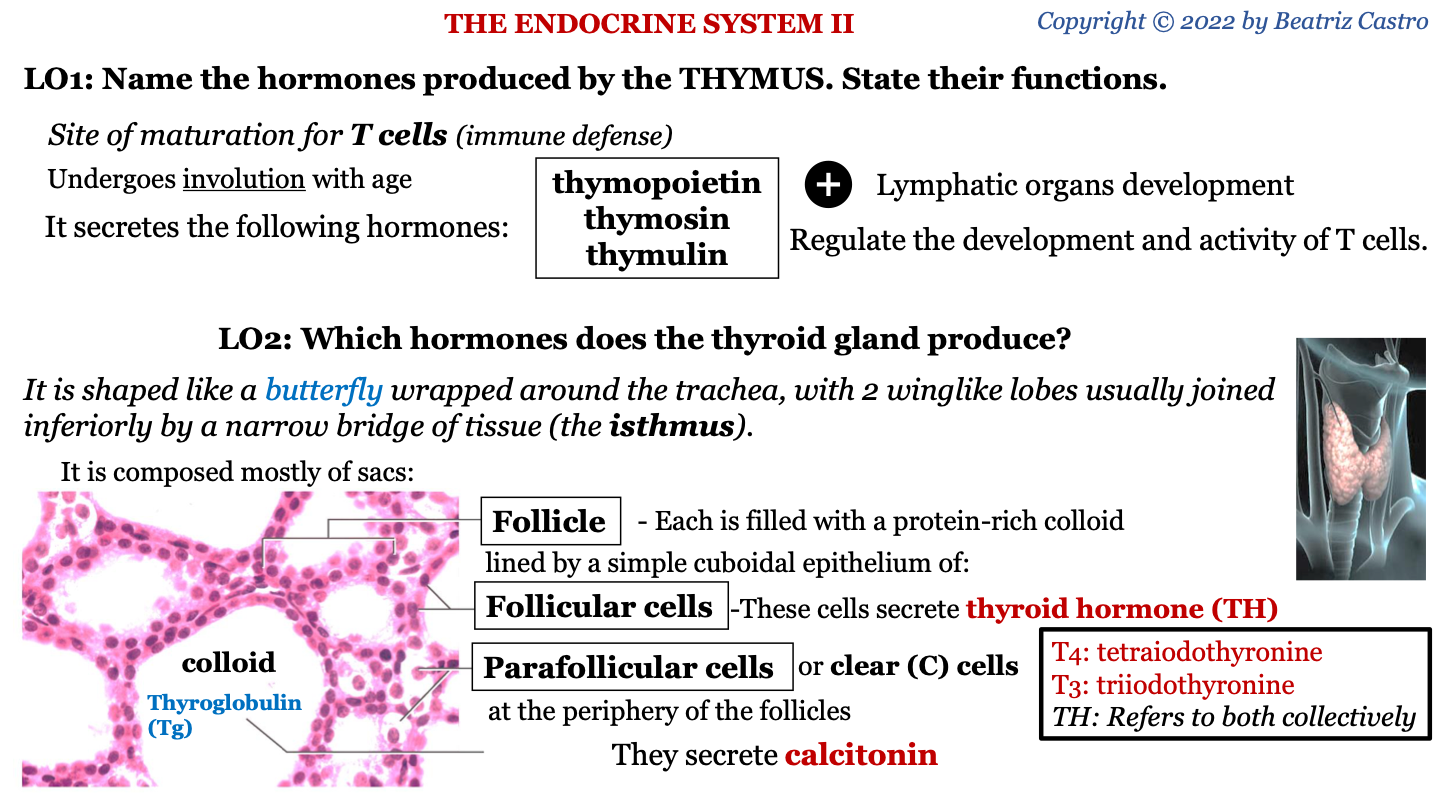
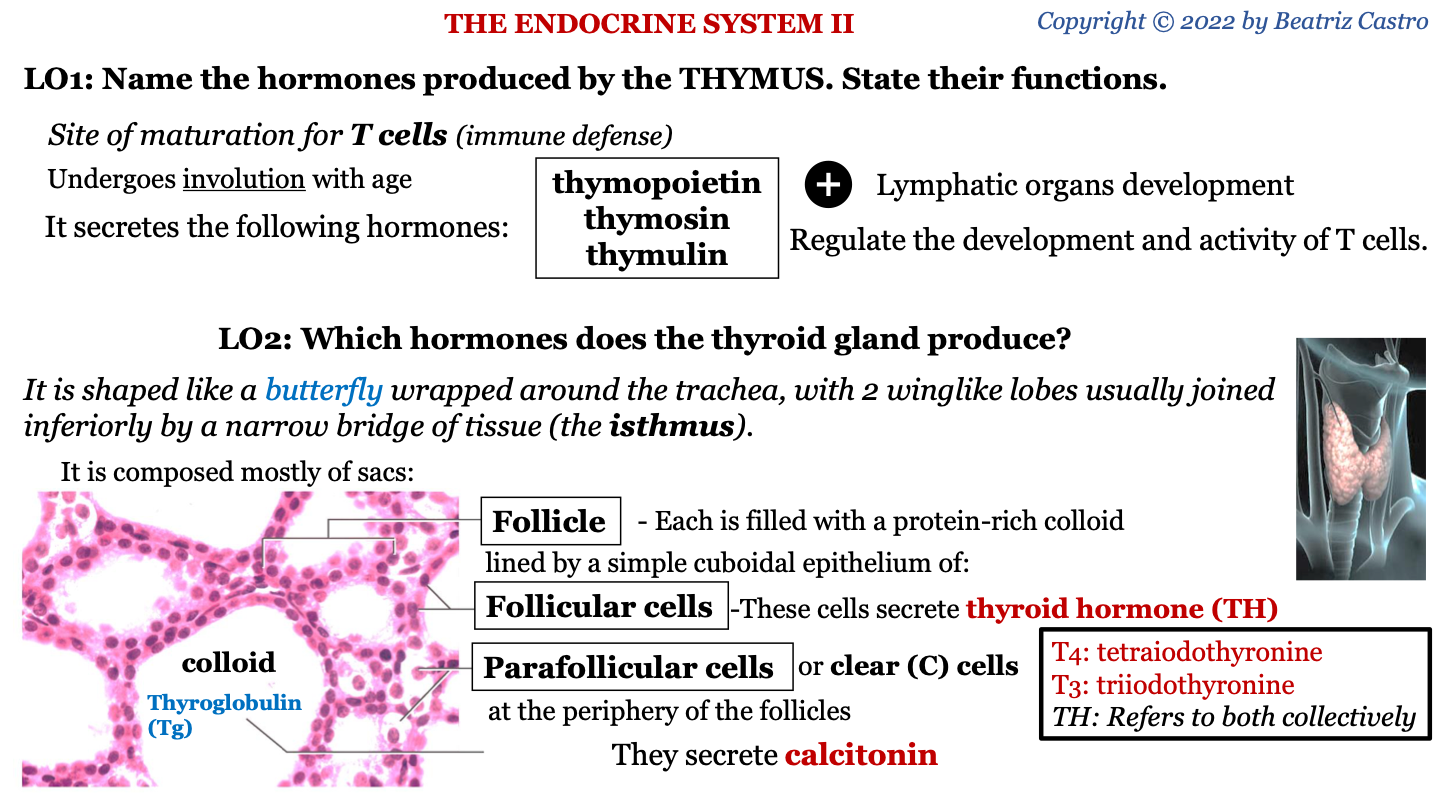
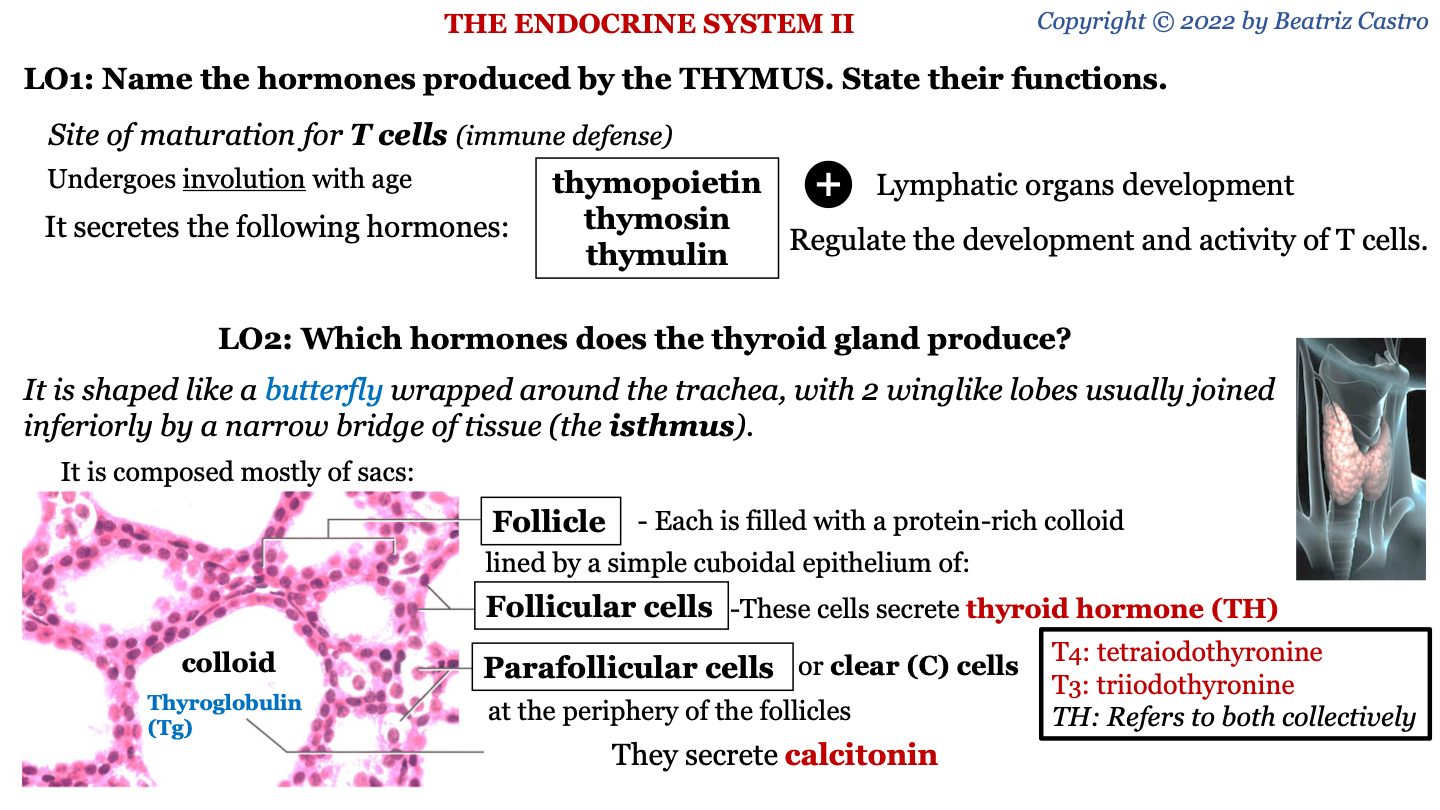
thymus
site of maturation for T cells (immune defense); undergoes involution with age
2
New cards
hormones secreted by thymus
-thymopoietin
-thymosin
-thymulin
-thymosin
-thymulin
3
New cards
functions of hormones secreted by thymus
lymphatic organs development; regulate the development and activity of T cells
4
New cards
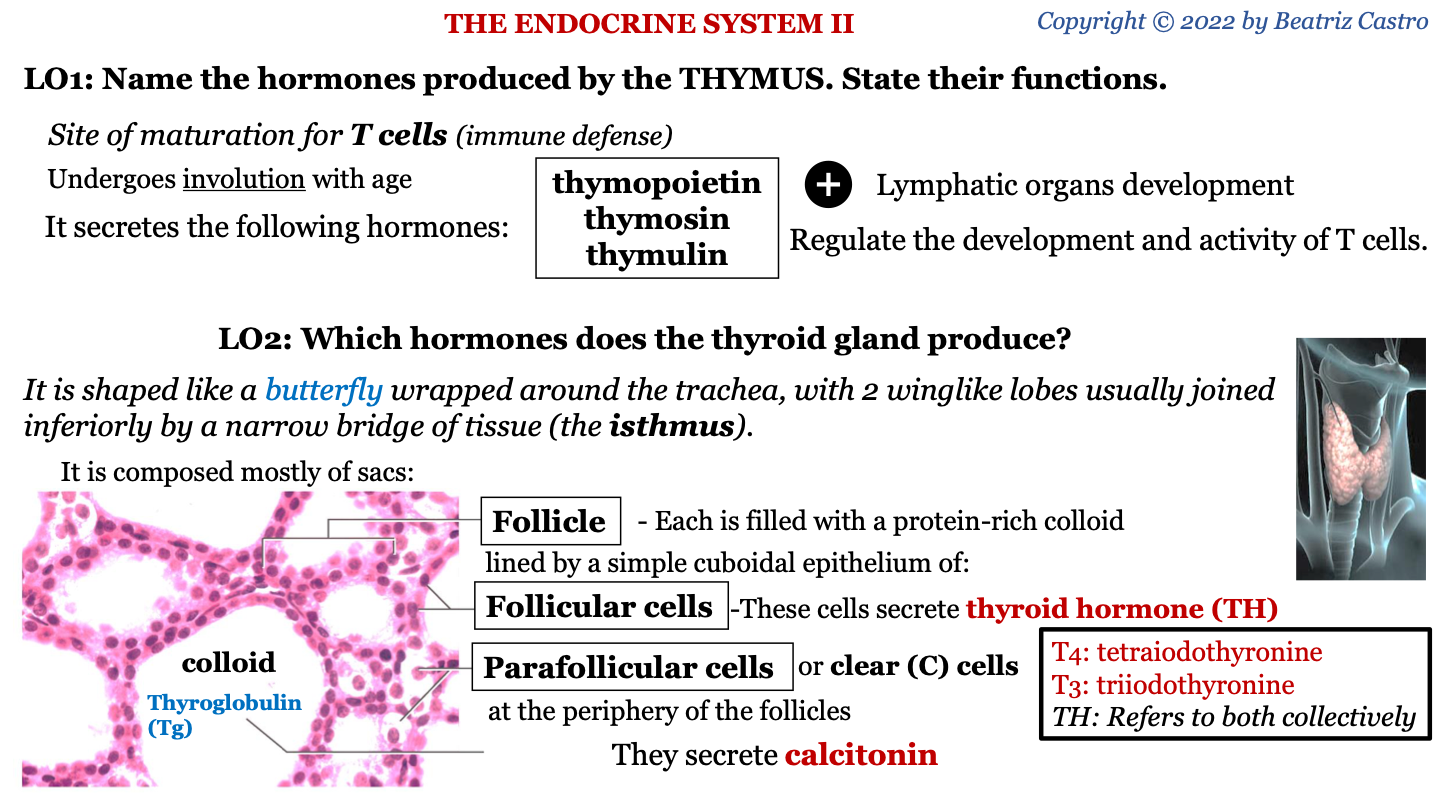
shape of thyroid gland
it is shaped like a butterfly wrapped around the trachea, with 2 winglike lobes usually joined inferiorly by a narrow bridge of tissue (the isthmus)
5
New cards
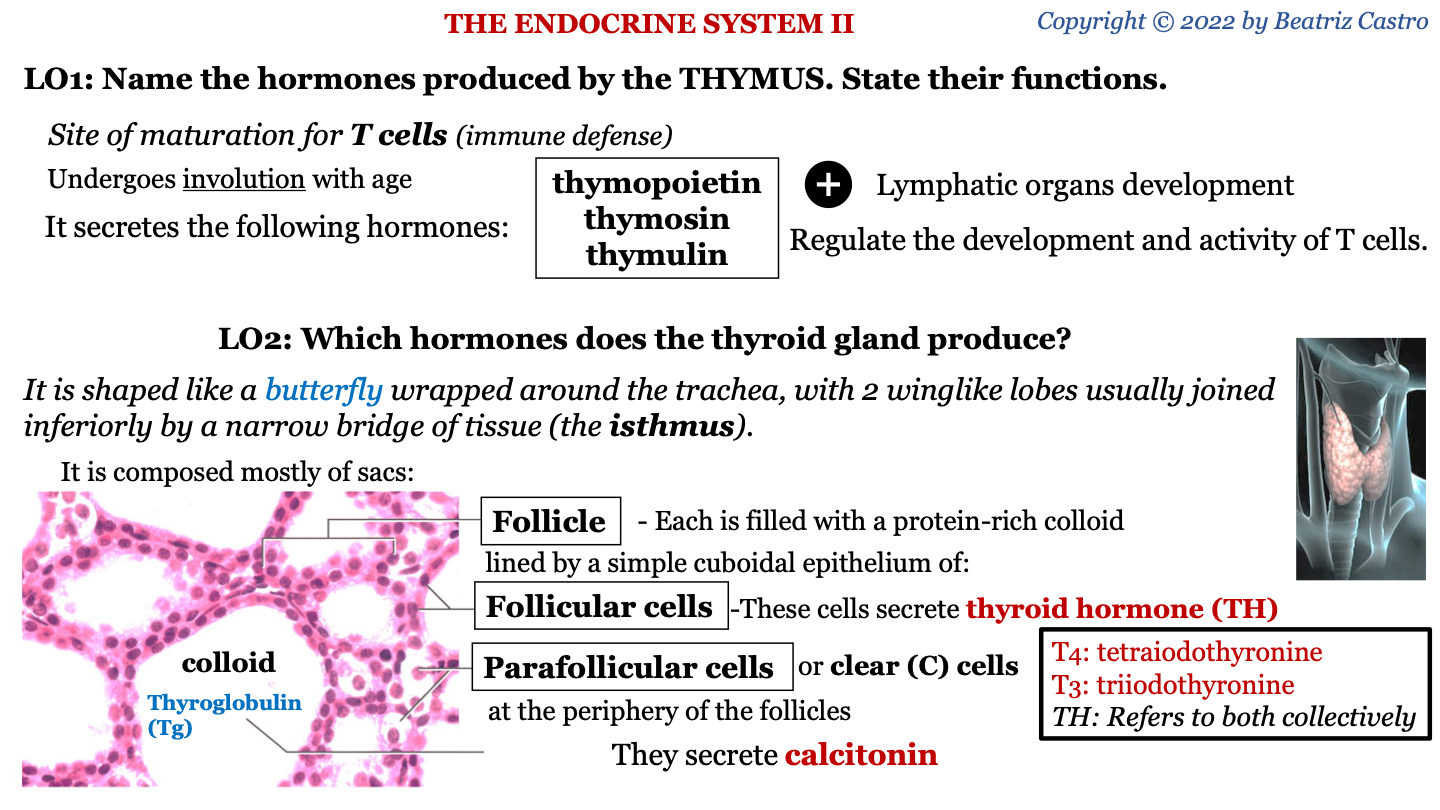
follicle
sac of the thyroid gland; each is filled with a protein-rich colloid lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium of follicular cells and parafollicular cells
6
New cards
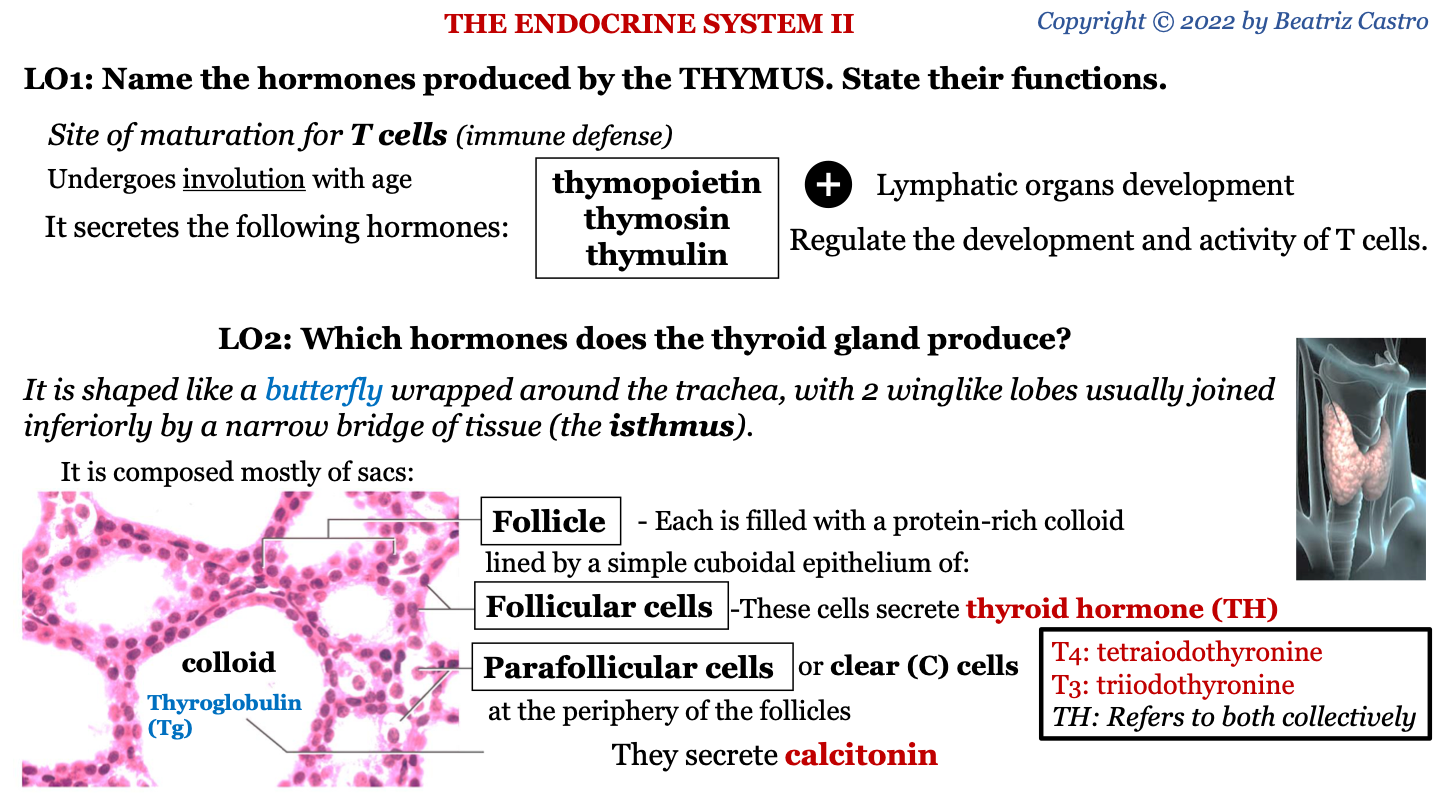
what protein makes up the colloid of the thyroid gland?
thyroglobulin (Tg)
7
New cards
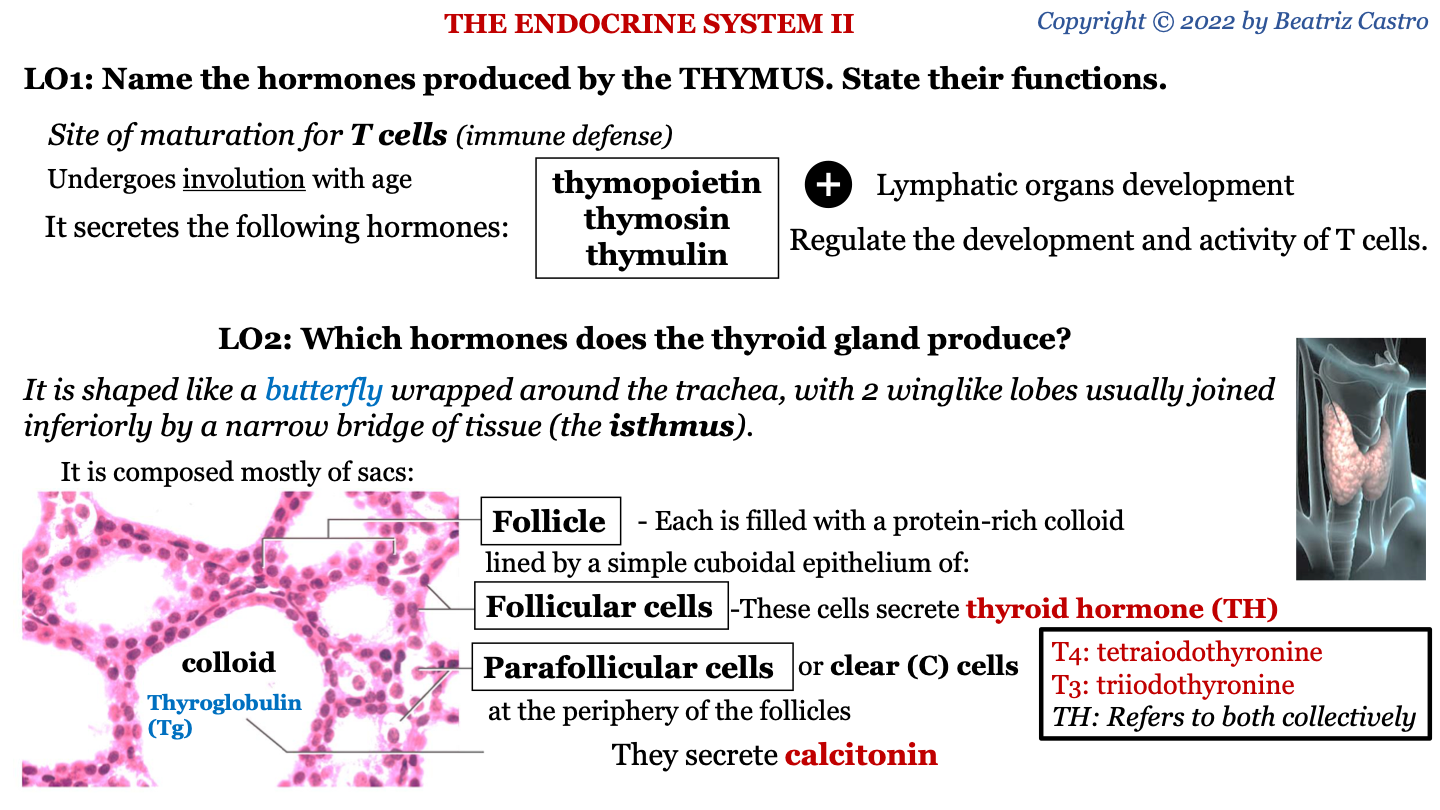
what do follicular cells of thyroid gland secrete?
thyroid hormone (TH)
8
New cards
parafollicular cells of thyroid gland
AKA clear (C) cells; located between the follicles; they secrete calcitonin
9
New cards
what are the two forms of thyroid hormone?
-T4: tetraiodothyronine
-T3: triiodothyronine
-T3: triiodothyronine
10
New cards
what does the number in T4 and T3 refer to?
the number of iodines in the molecule
11
New cards
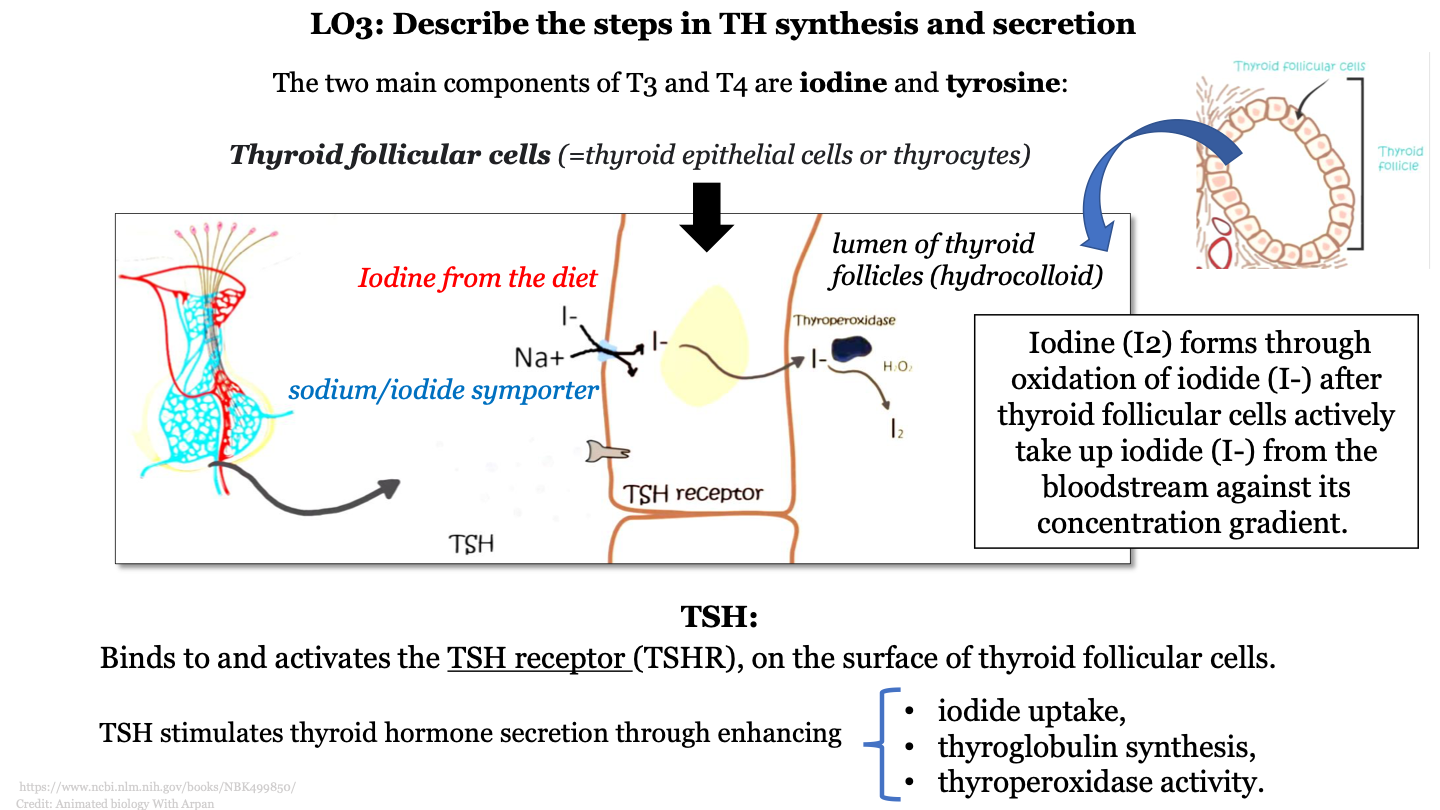
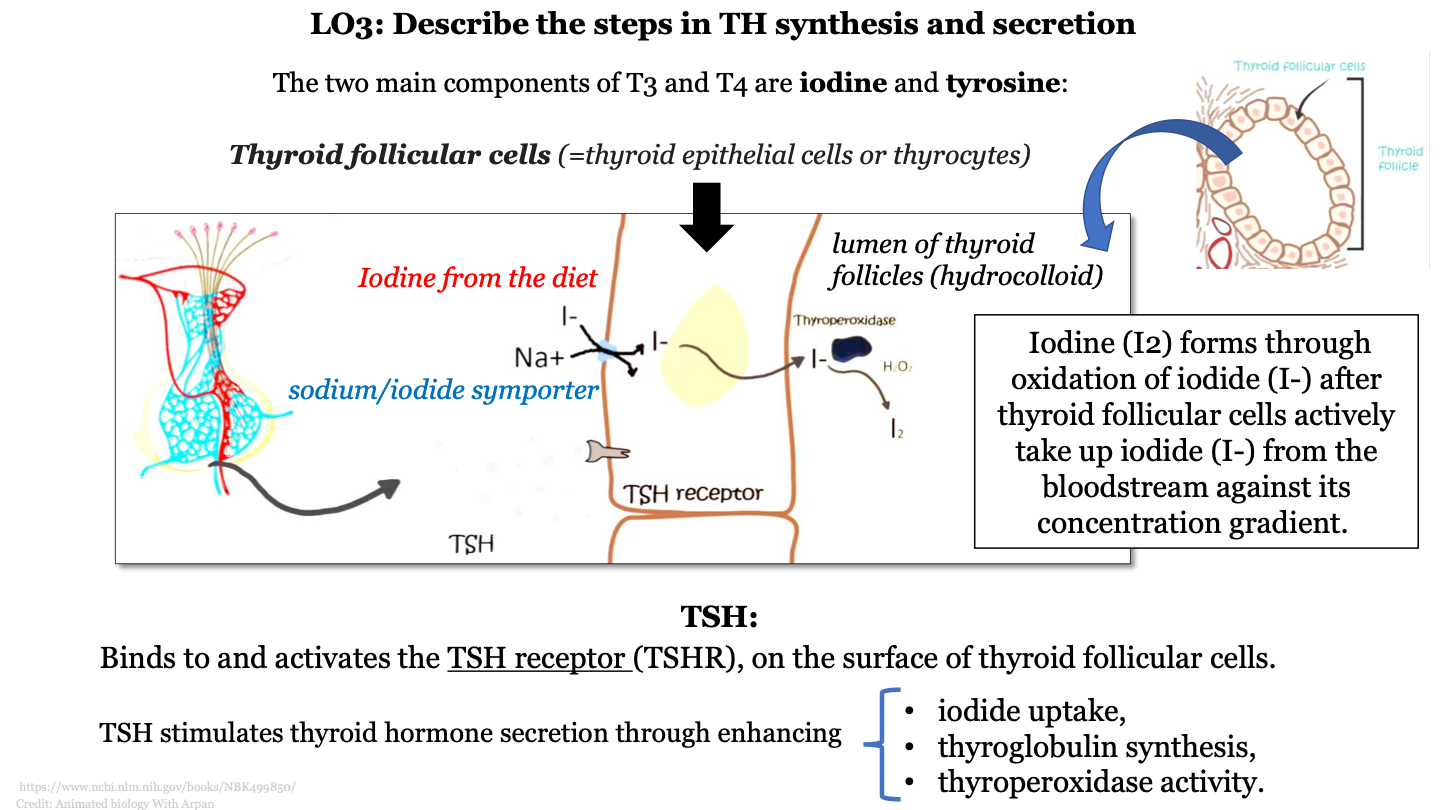
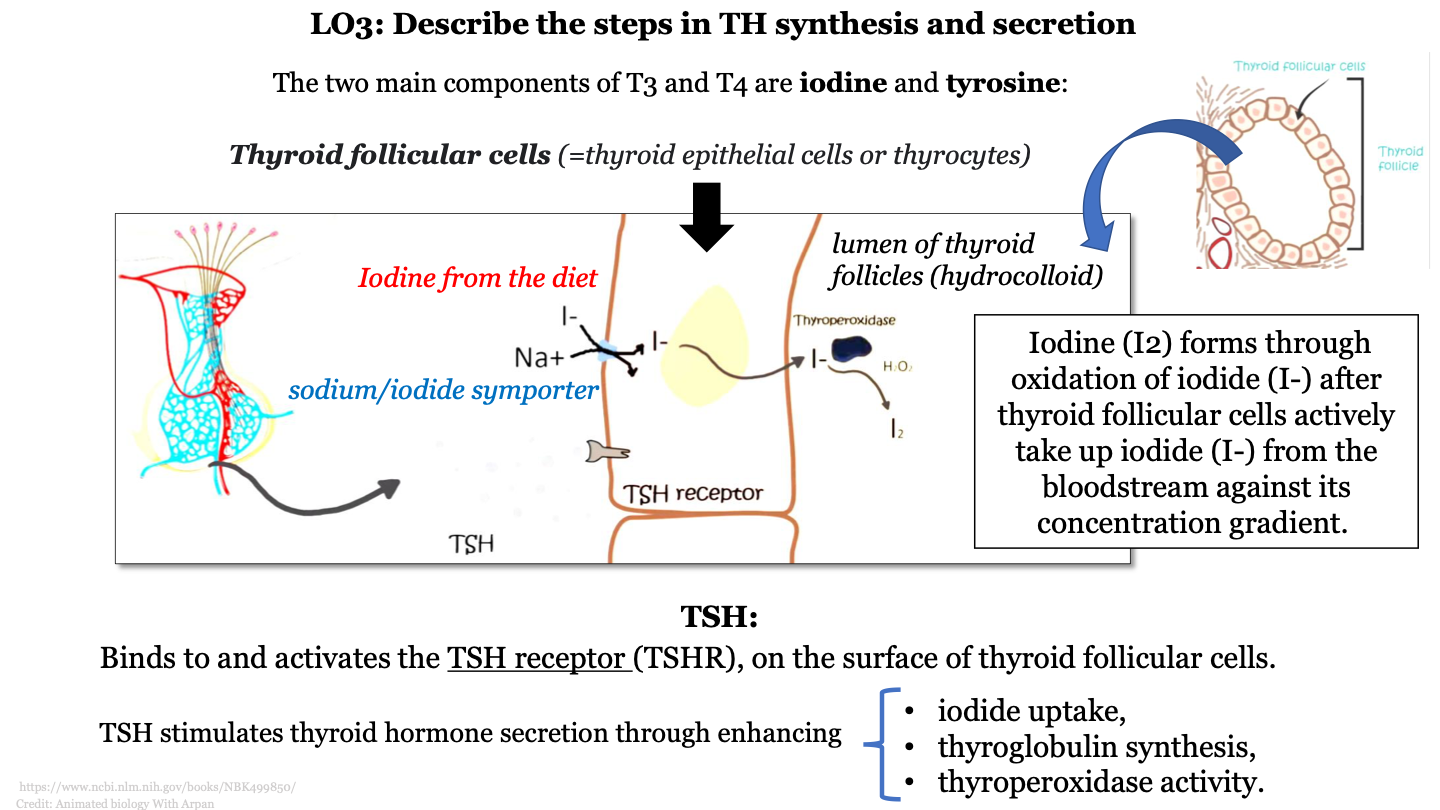
what are the two main components of T3 and T4
iodine and tyrosine
12
New cards
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 1
iodine from the diet is transported from the bloodstream into the colloid by sodium/iodide symporters (movement of iodine against concentration gradient)
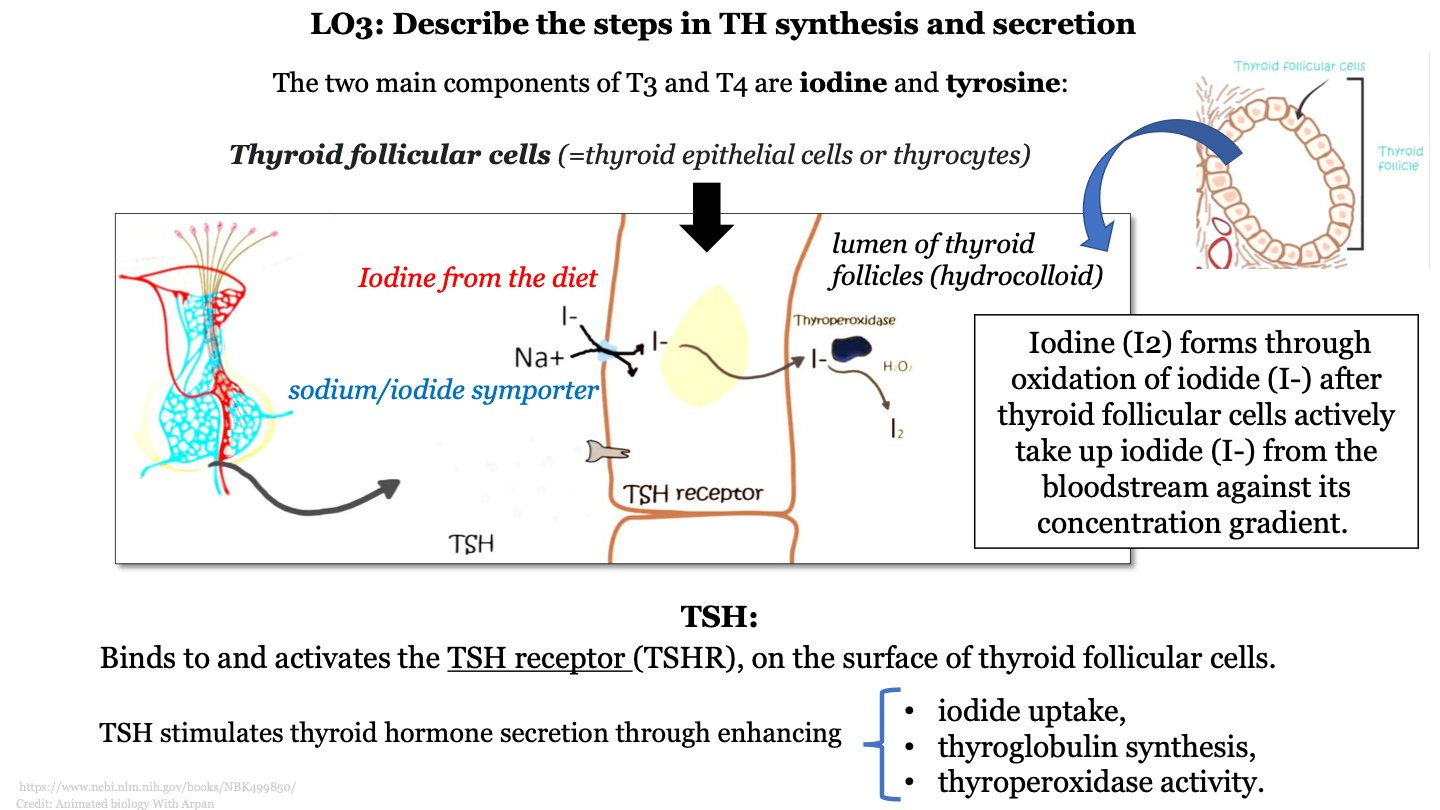
13
New cards
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 2
iodine (I2) forms through oxidation of iodide (I-) by thyroperoxidase
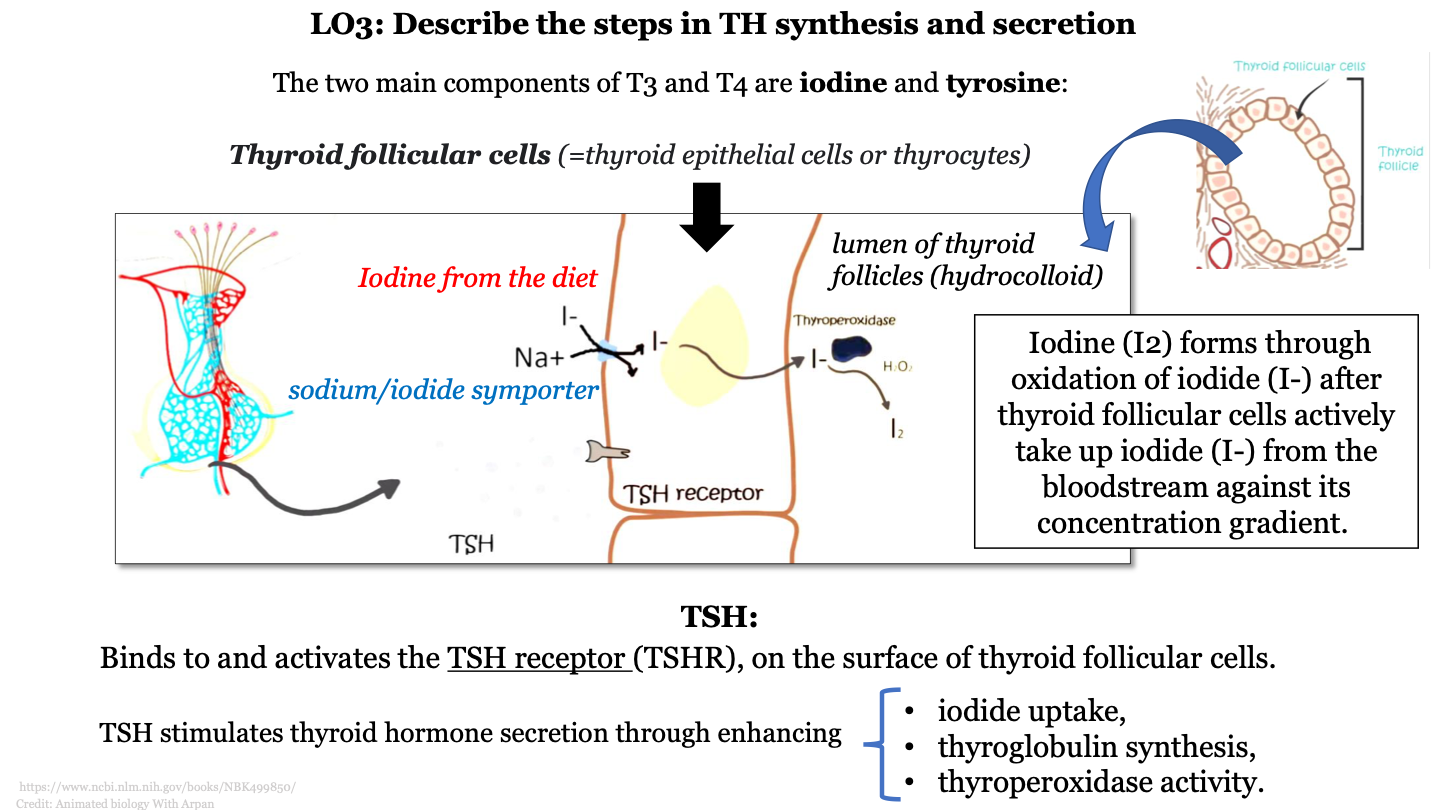
14
New cards
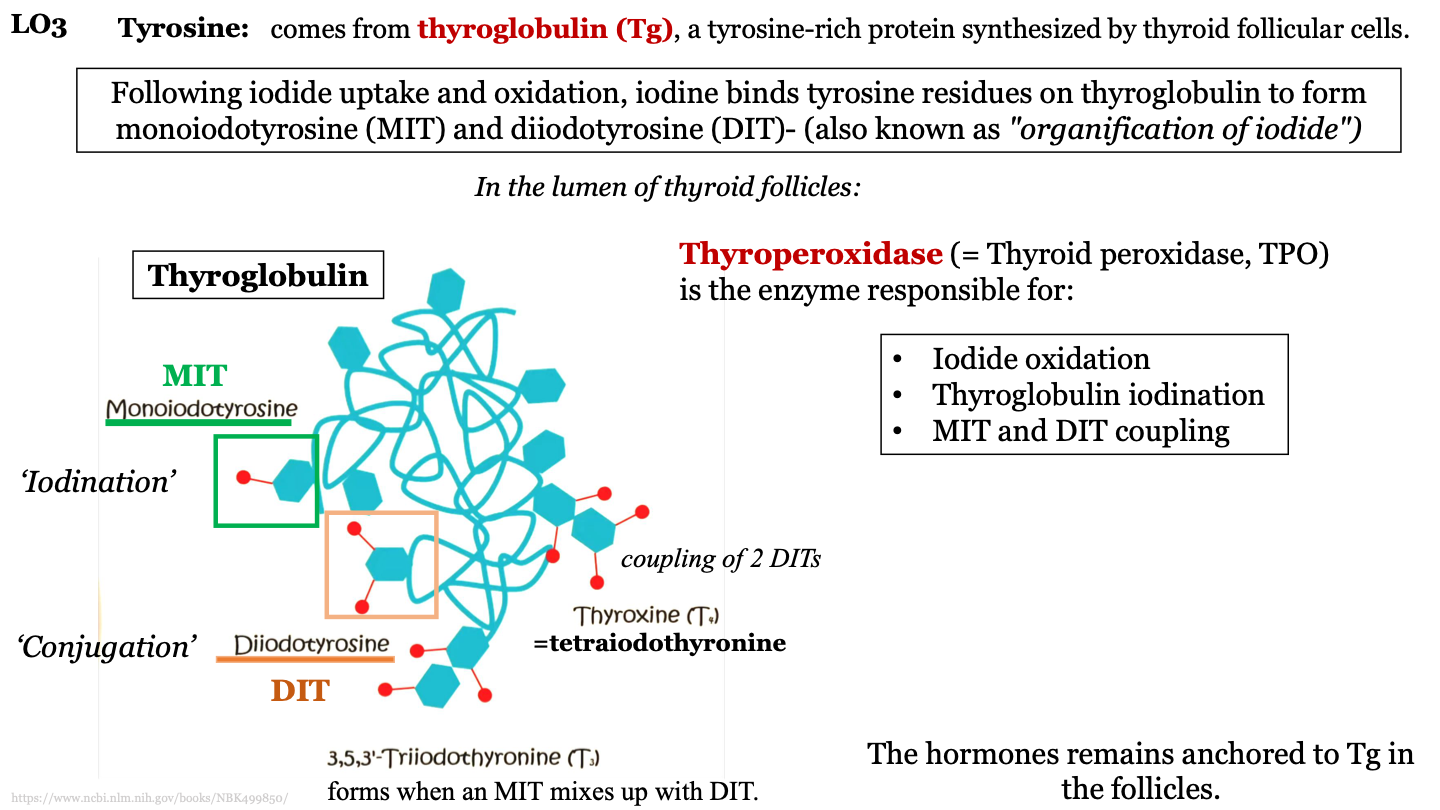
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 3
Iodine binds tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin to form monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT); this process is AKA "organification of iodide"
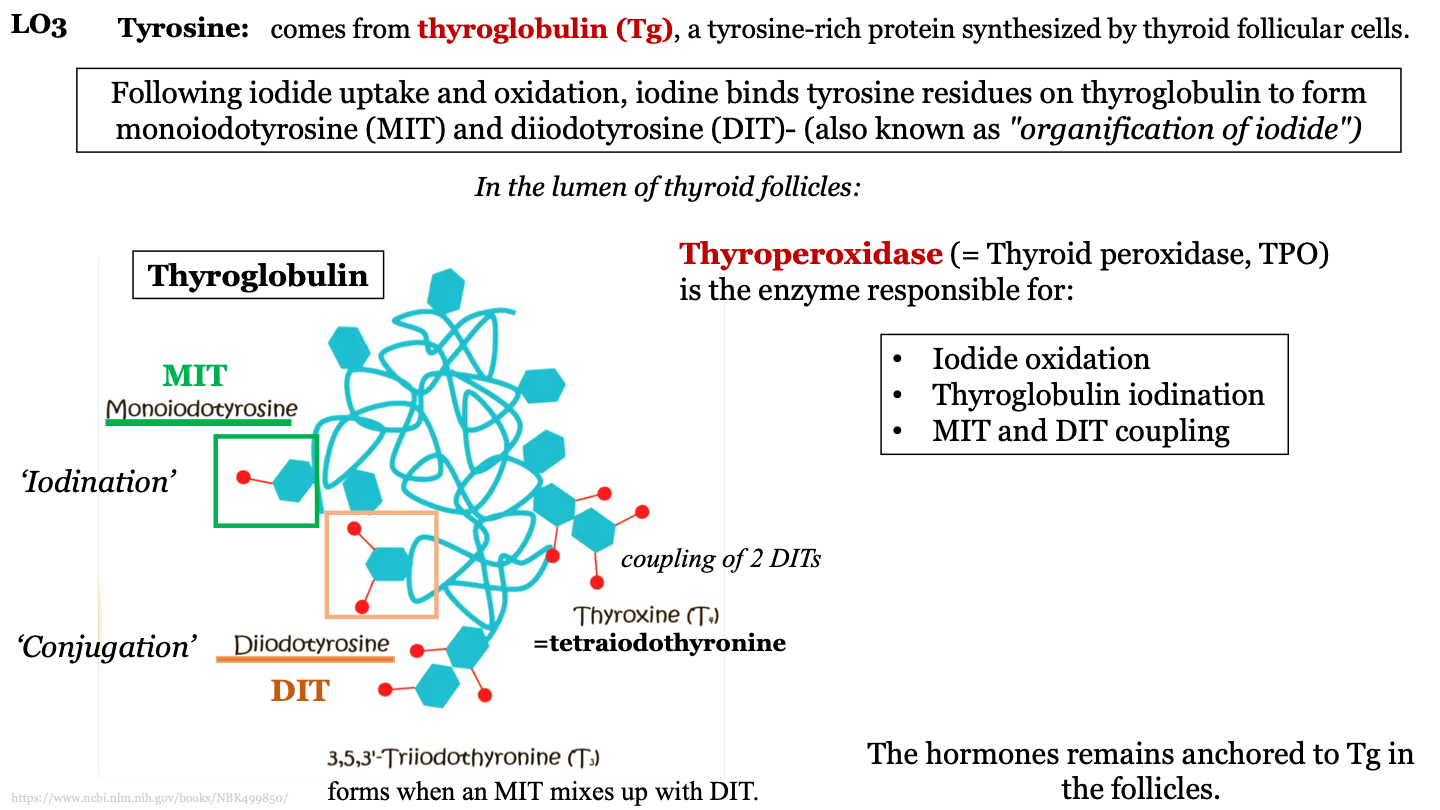
15
New cards
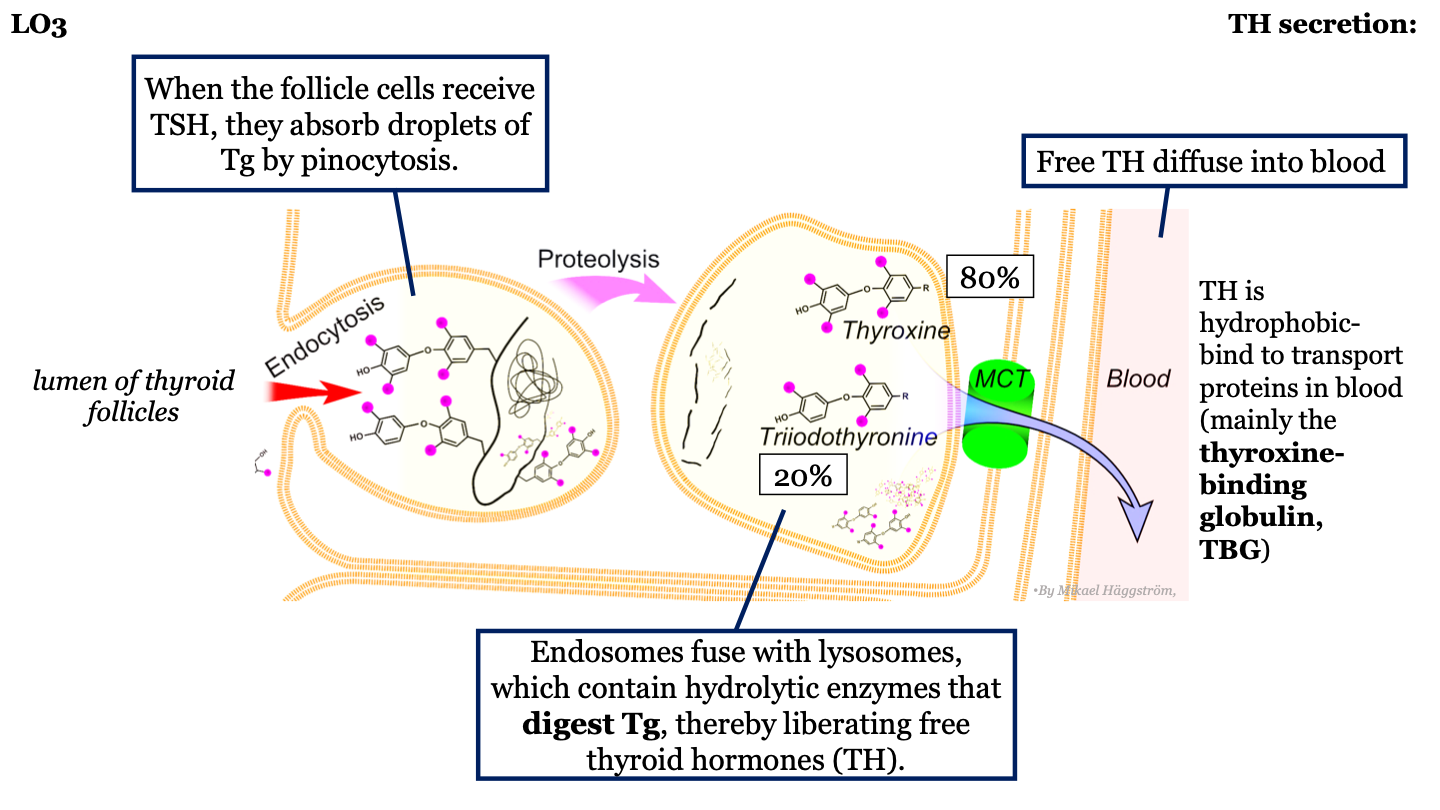
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 4
When the follicle cells receive TSH, they absorb droplets of thyroglobulin by pinocytosis
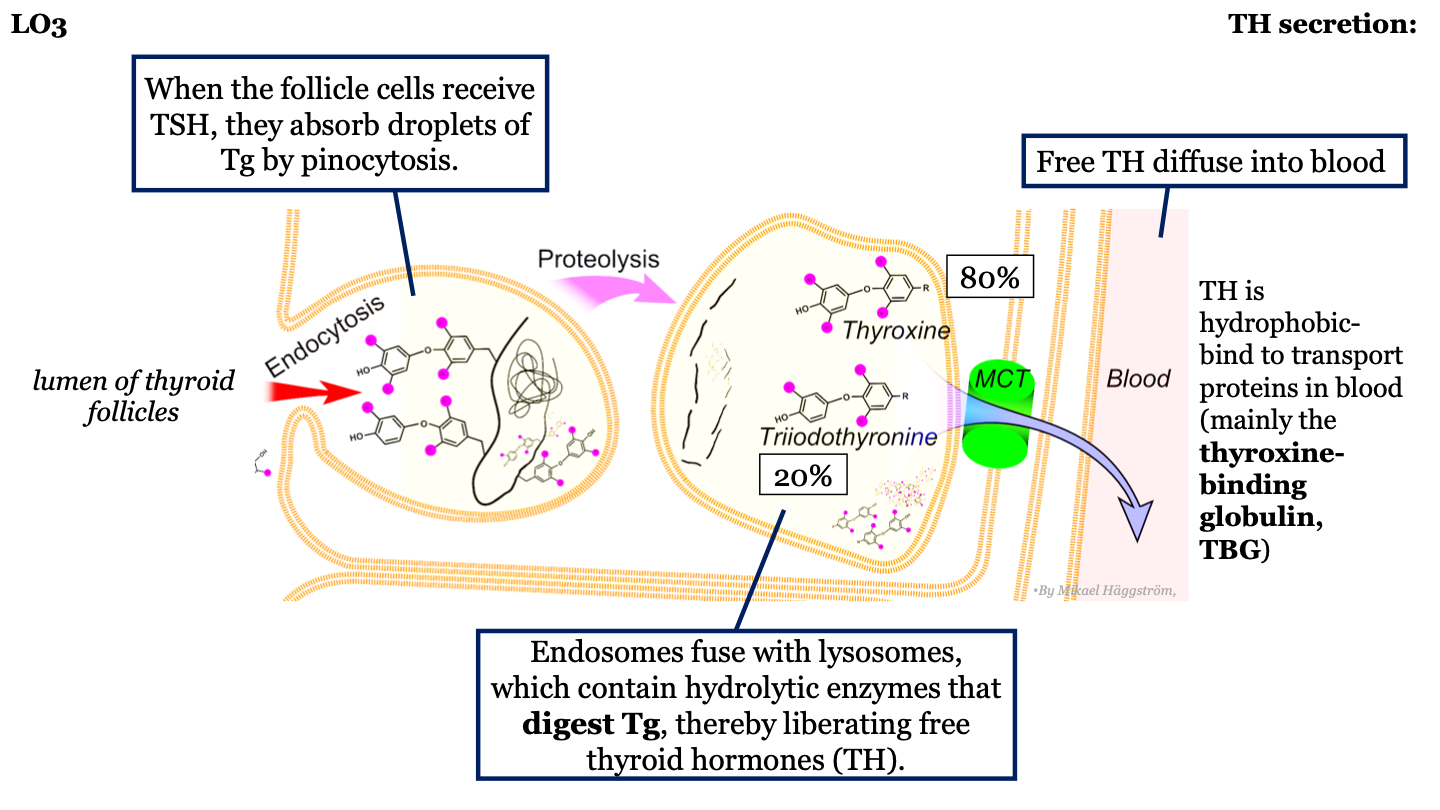
16
New cards
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 5
Endosome fuse with lysosomes which contain hydrolytic enzymes that digest thyroglobulin, thus releasing free thyroid hormones
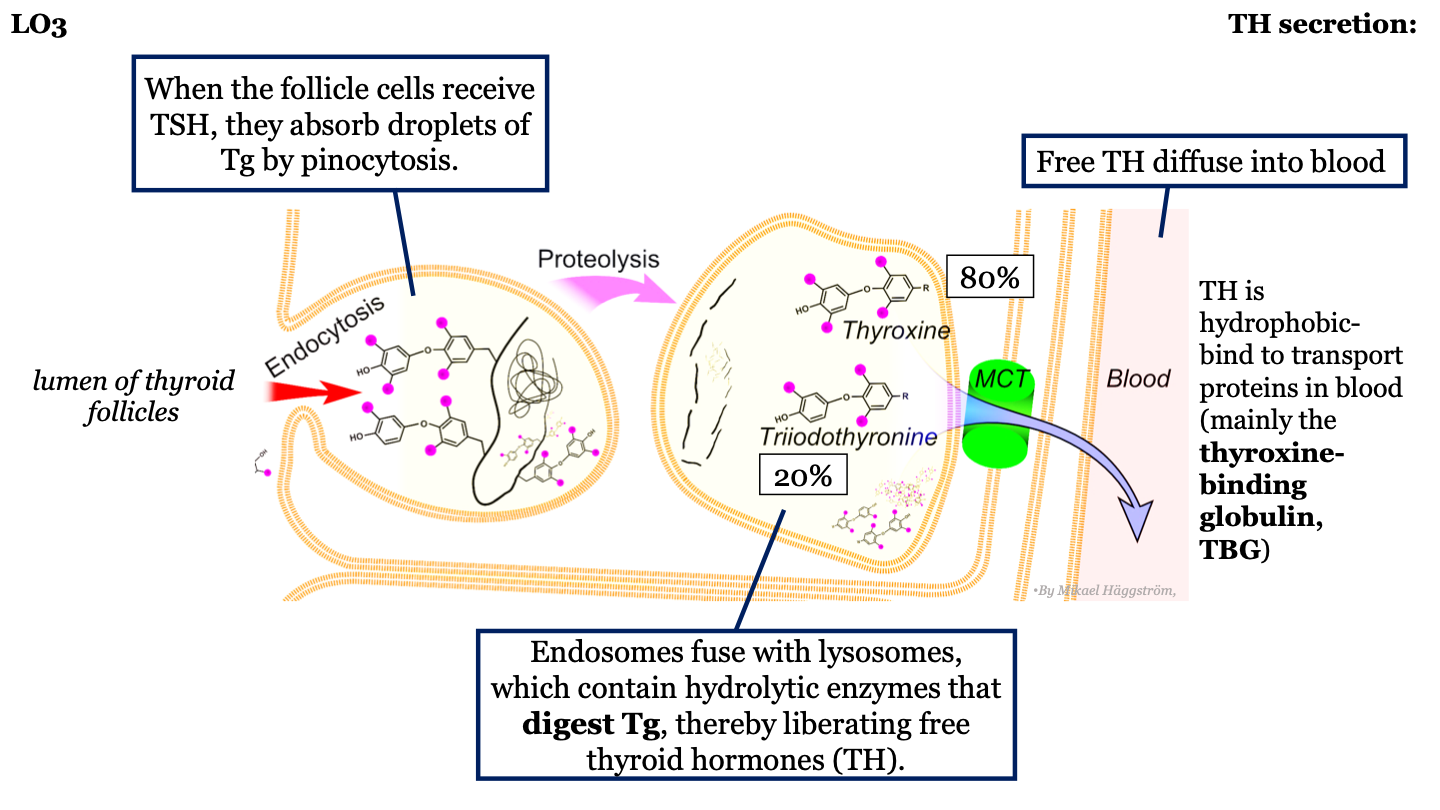
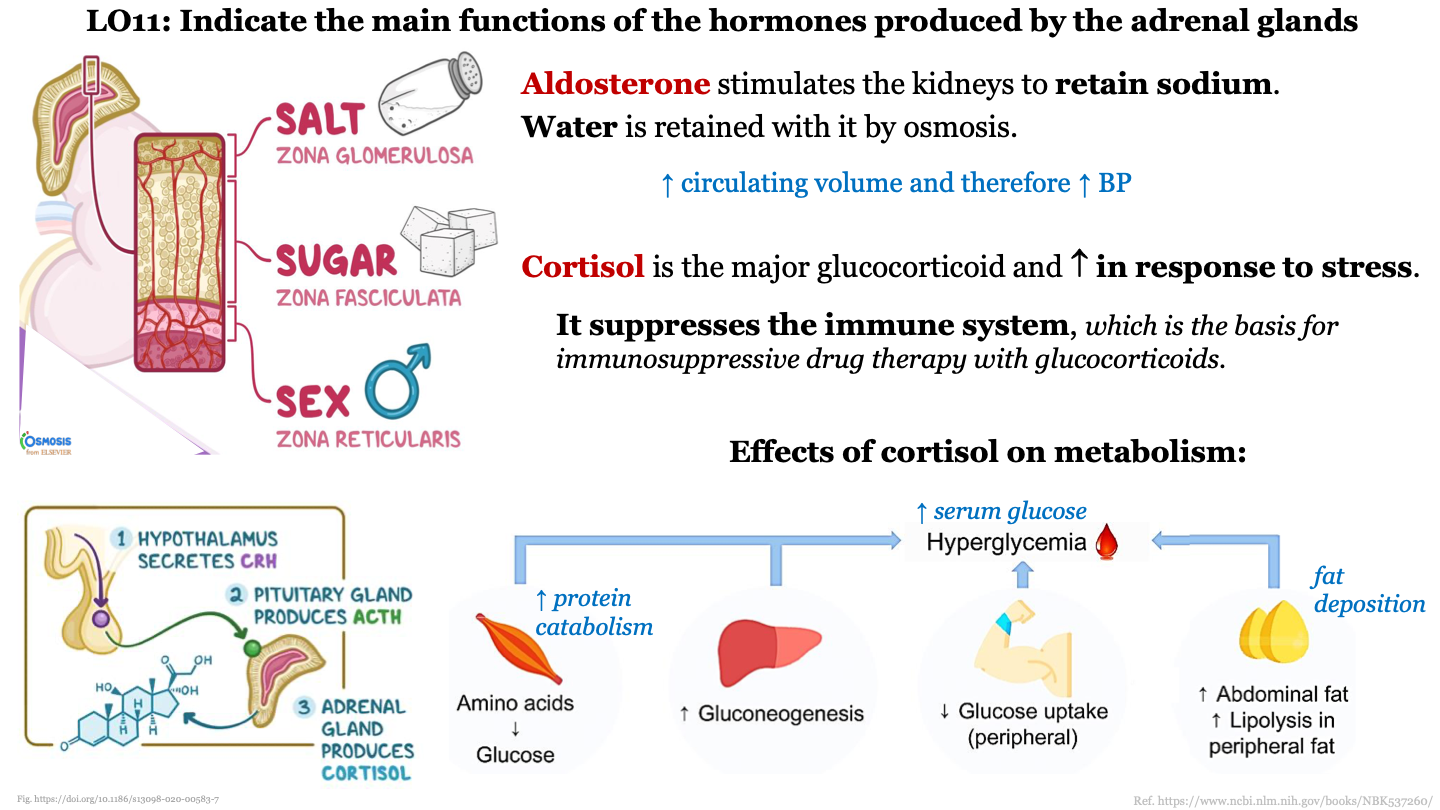
17
New cards
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 6
Free thyroid hormone diffuses into the blood
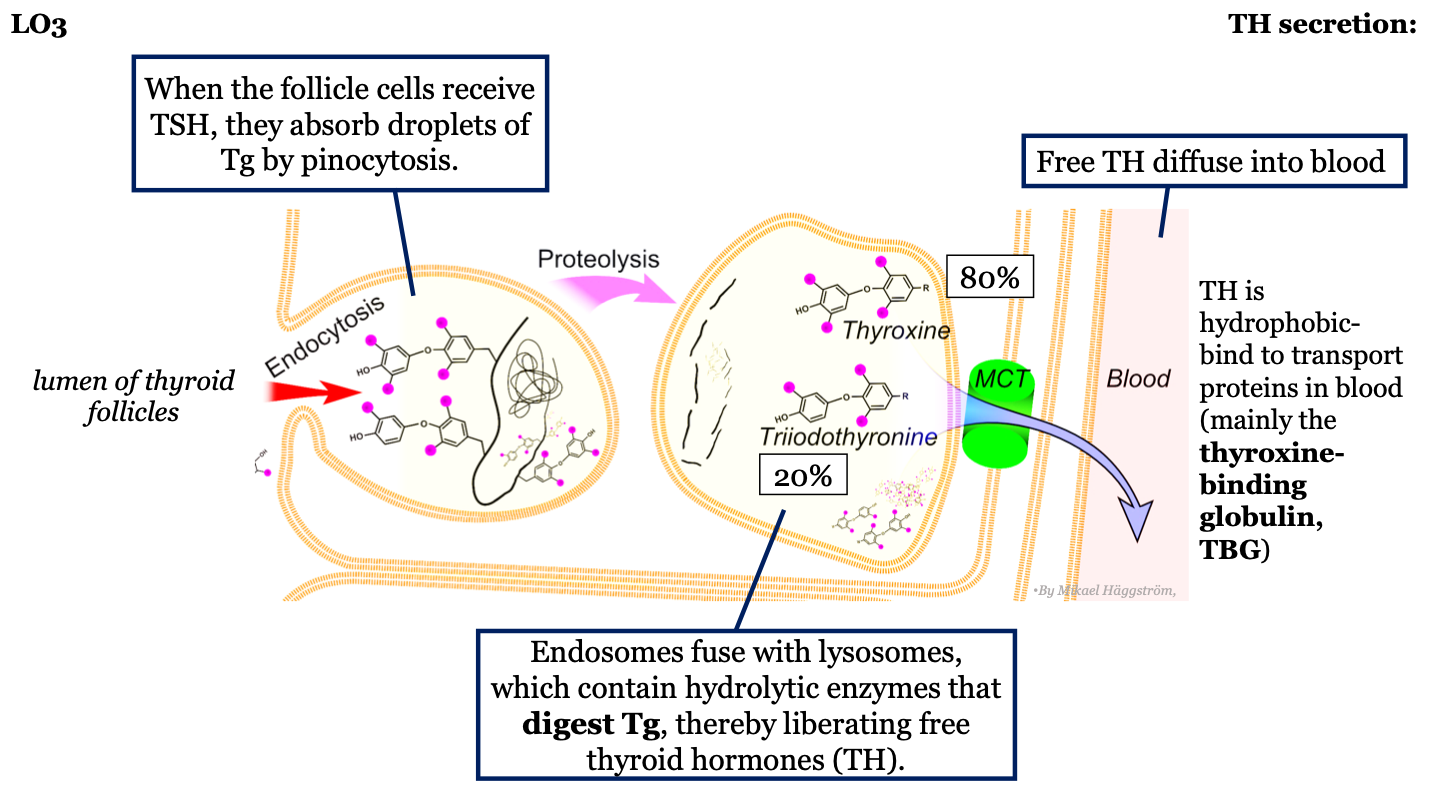
18
New cards
steps in TH synthesis and secretion - 7
TH is hydrophobic, so when it is released into the blood it binds to transport proteins (mainly thyroxine-binding globulin: TBG)
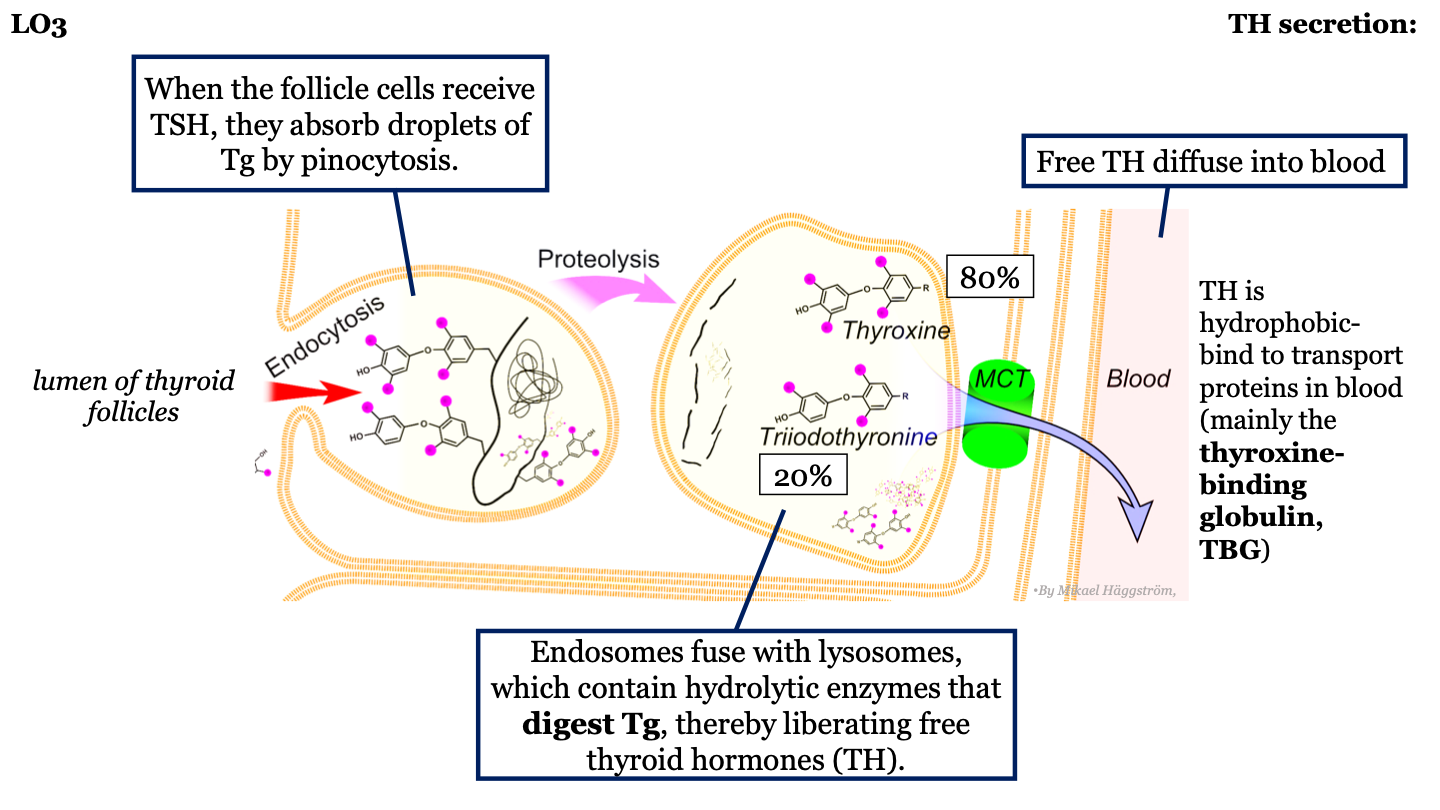
19
New cards
____% of TH that diffuses into the blood is thyroxine (T4)
80%
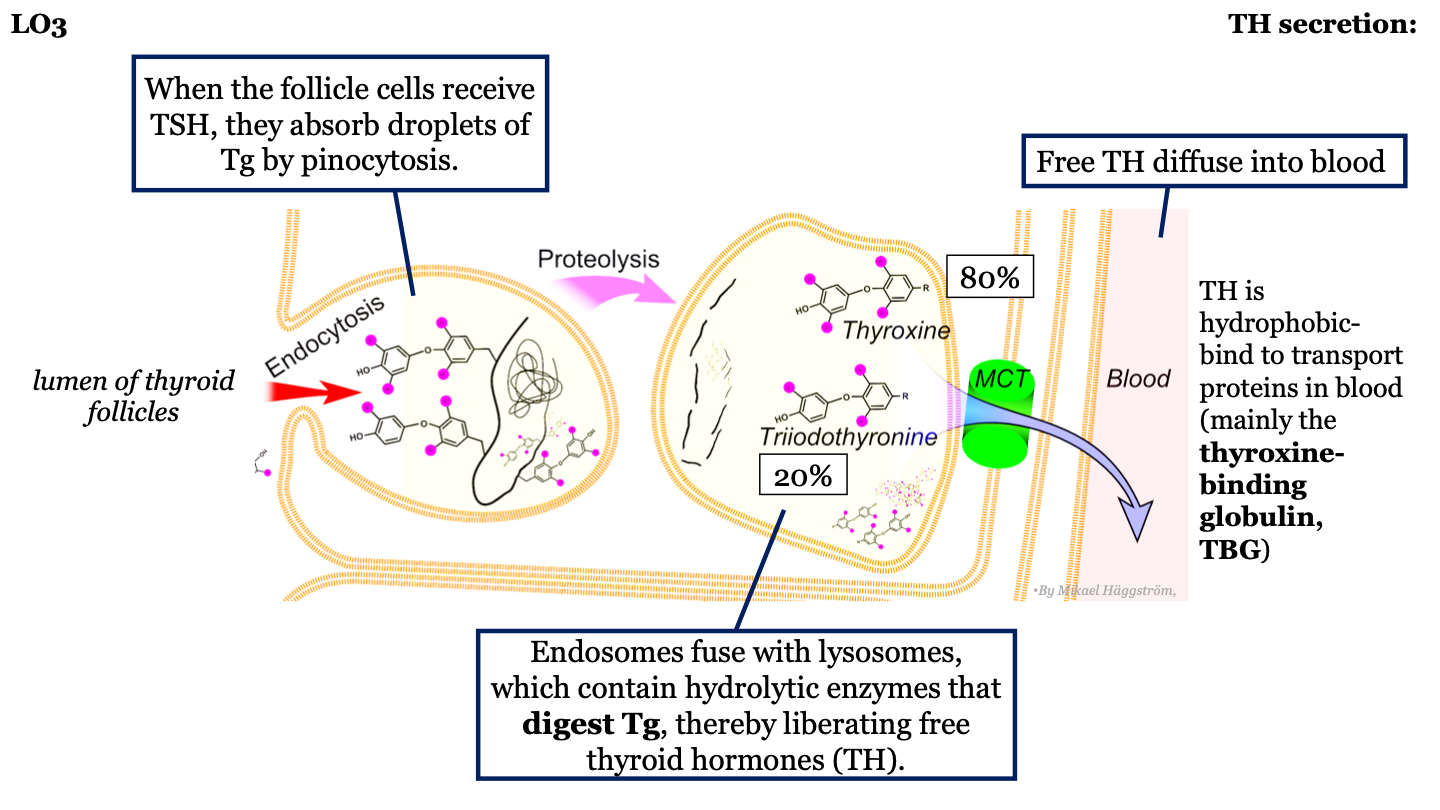
20
New cards
____% of TH that diffuses into the blood is triiodothyronine (T3)
20
21
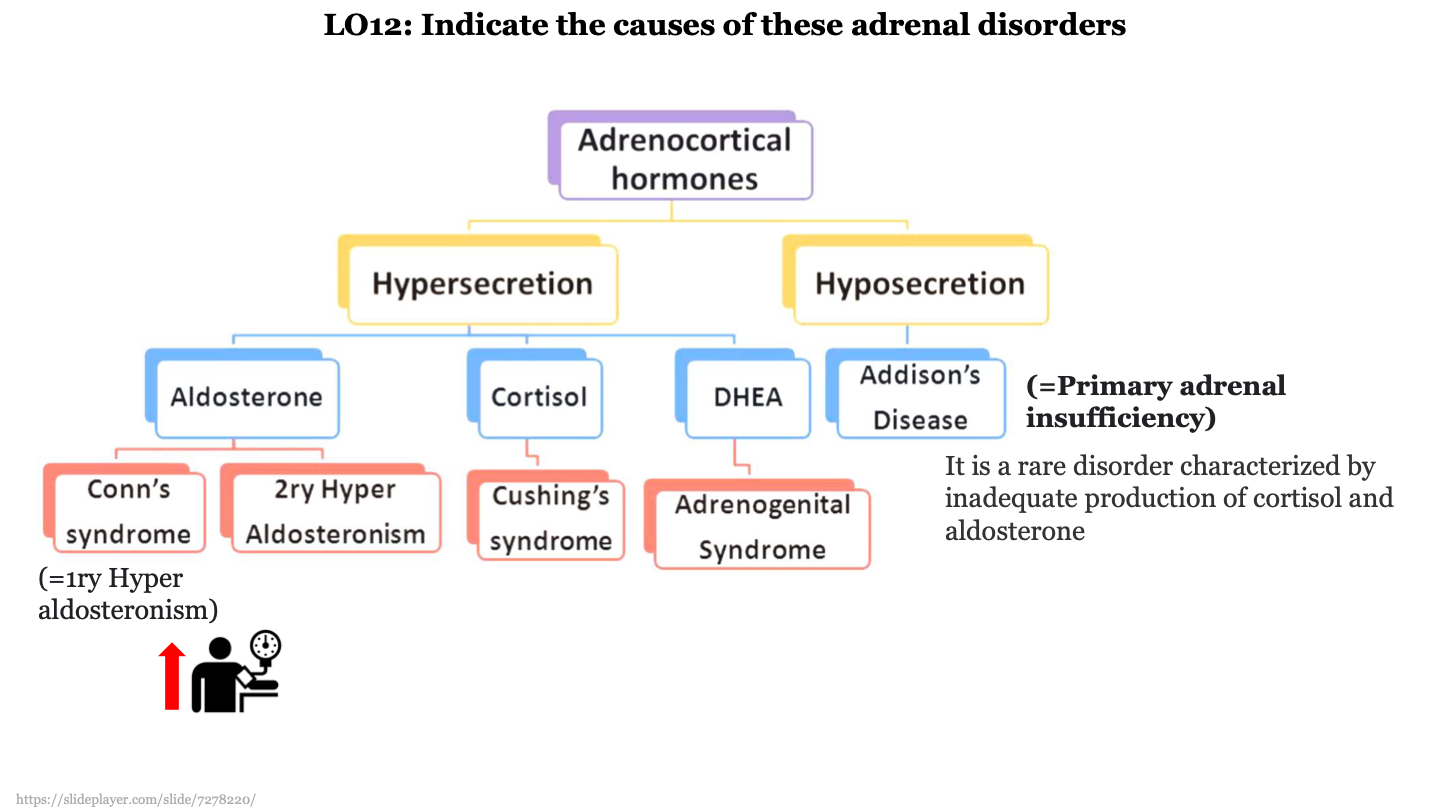
New cards
what does TSH do?
binds to and activates the TSH receptor (TSHR), on the surface of thyroid follicular cells
22
New cards
how does TSH stimulate thyroid hormone secretion?
enhances iodide uptake, thyroglobulin synthesis, and thyroperoxidase activity
23
New cards
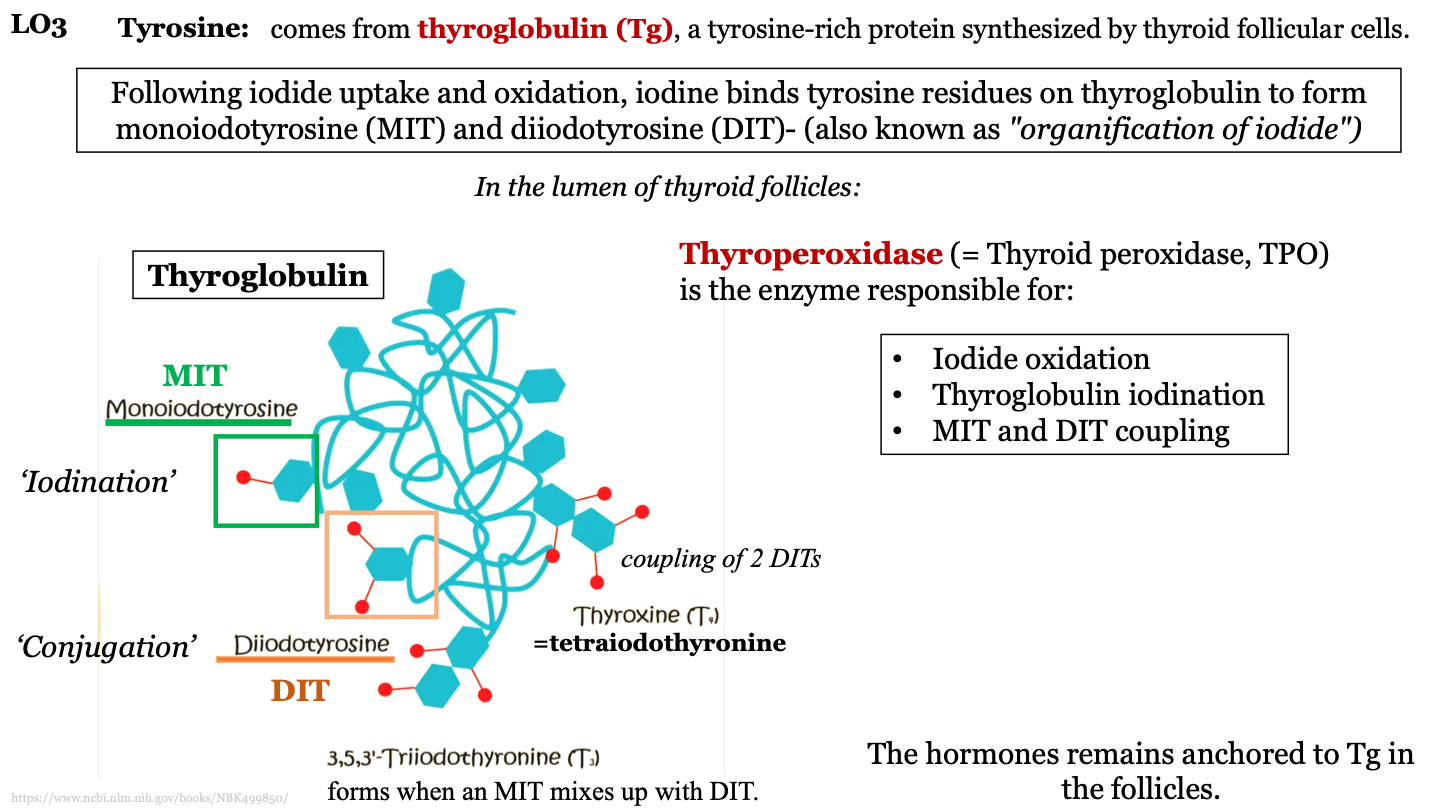
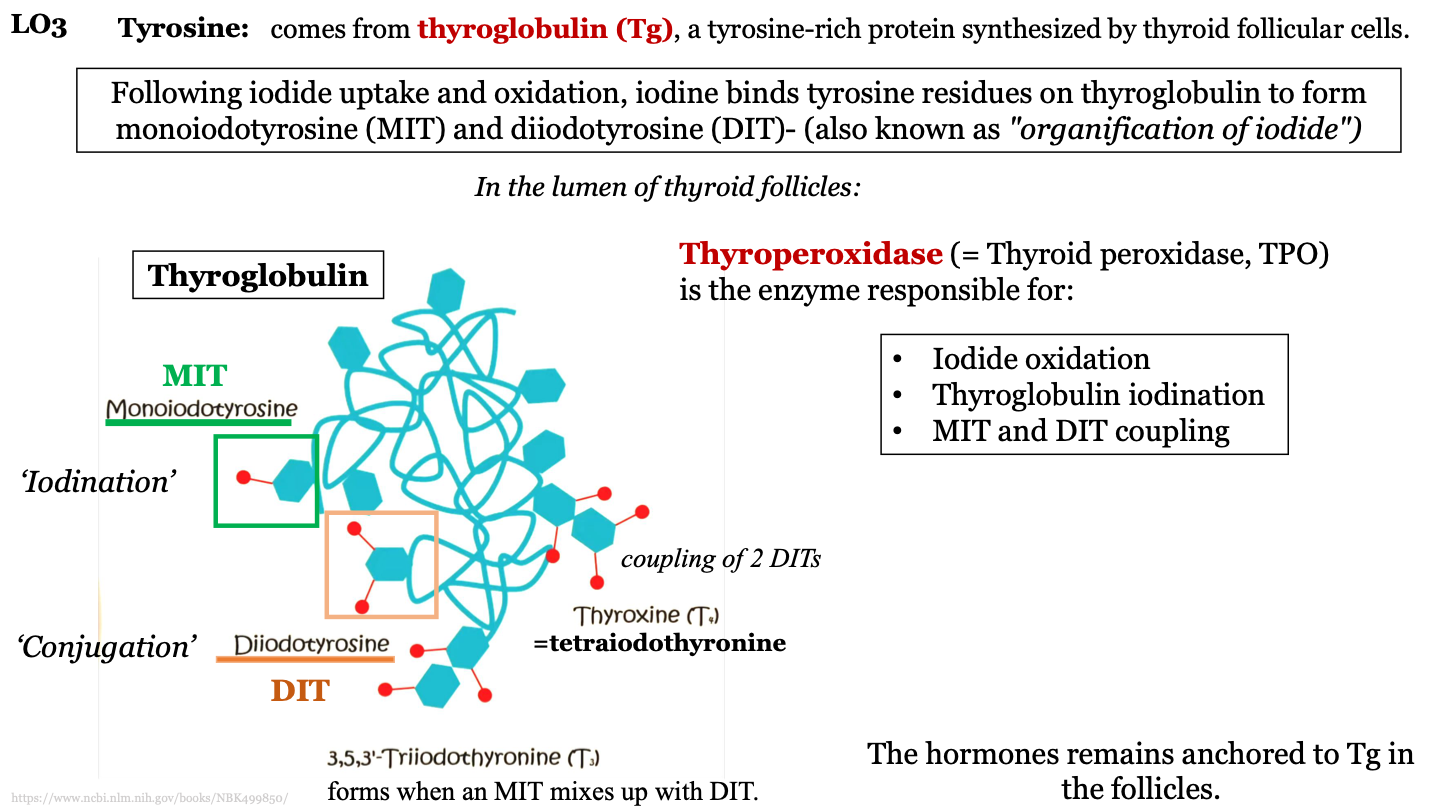
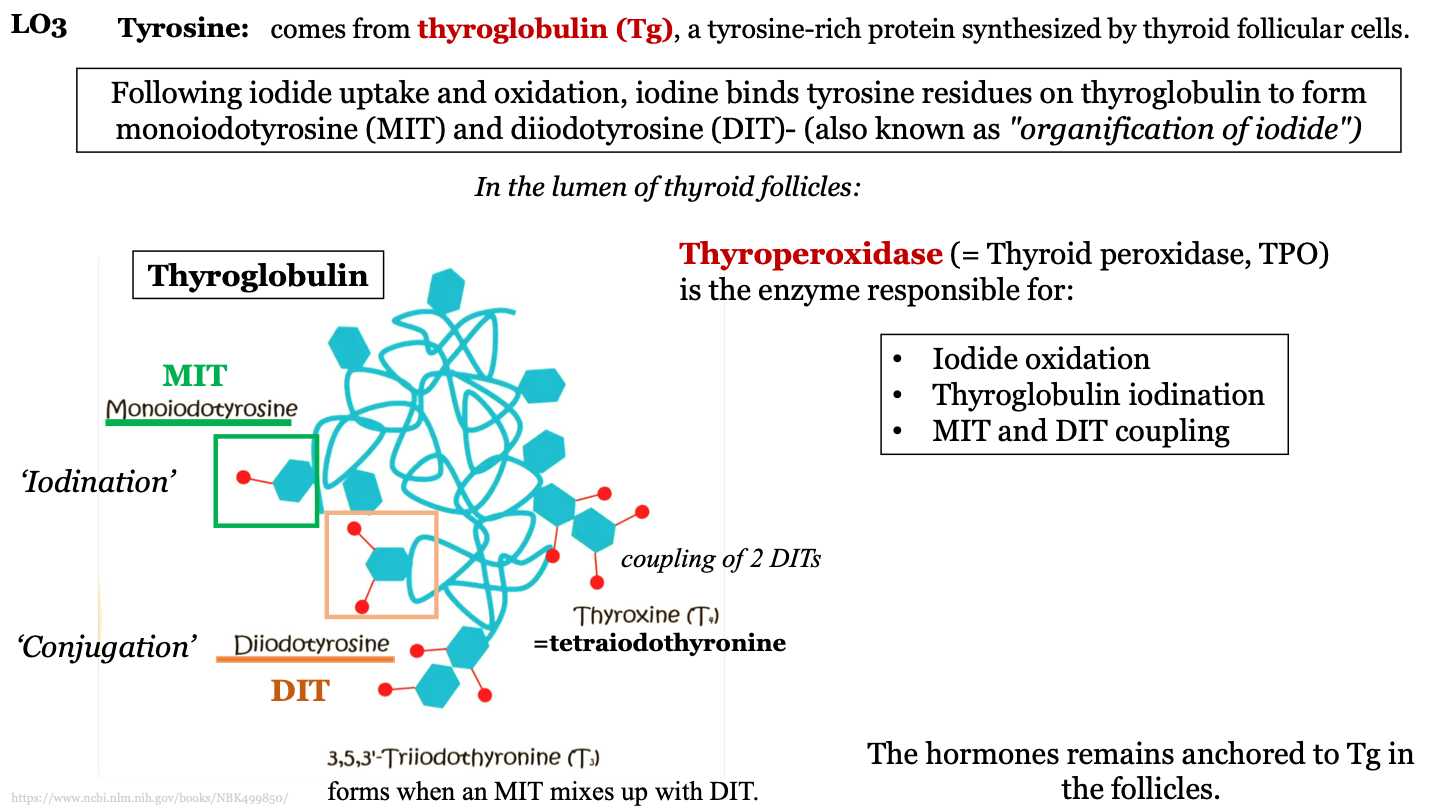
where does tyrosine come from?
thyroglobulin (Tg); a tyrosine-rich protein synthesized by thyroid follicular cells
24
New cards
MIT
monoiodotyrosine; one iodine molecule attached to a tyrosine in thyroglobulin
25
New cards
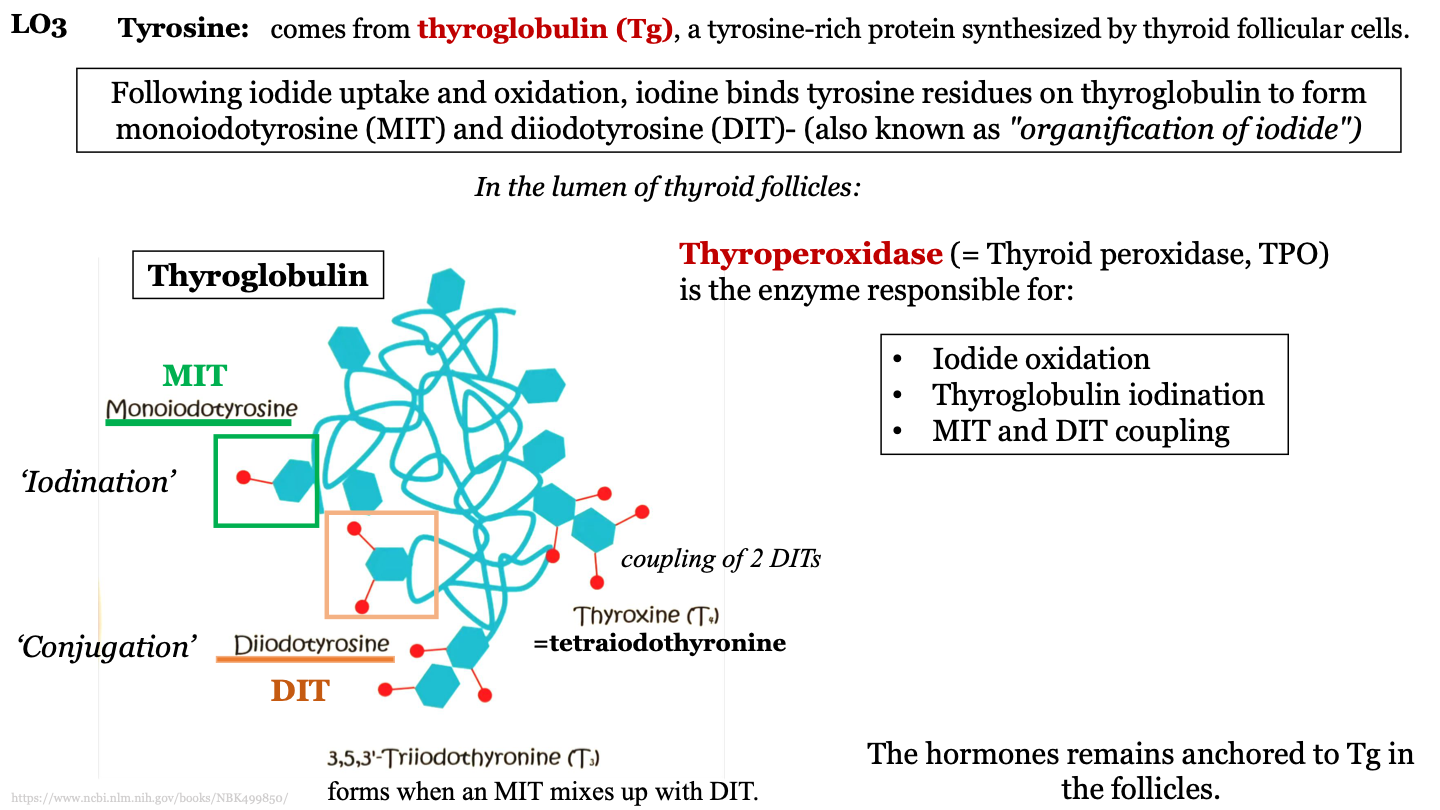
DIT
diiodotyrosine; 2 iodine molecules attached to a tyrosine in thyroglobulin
26
New cards
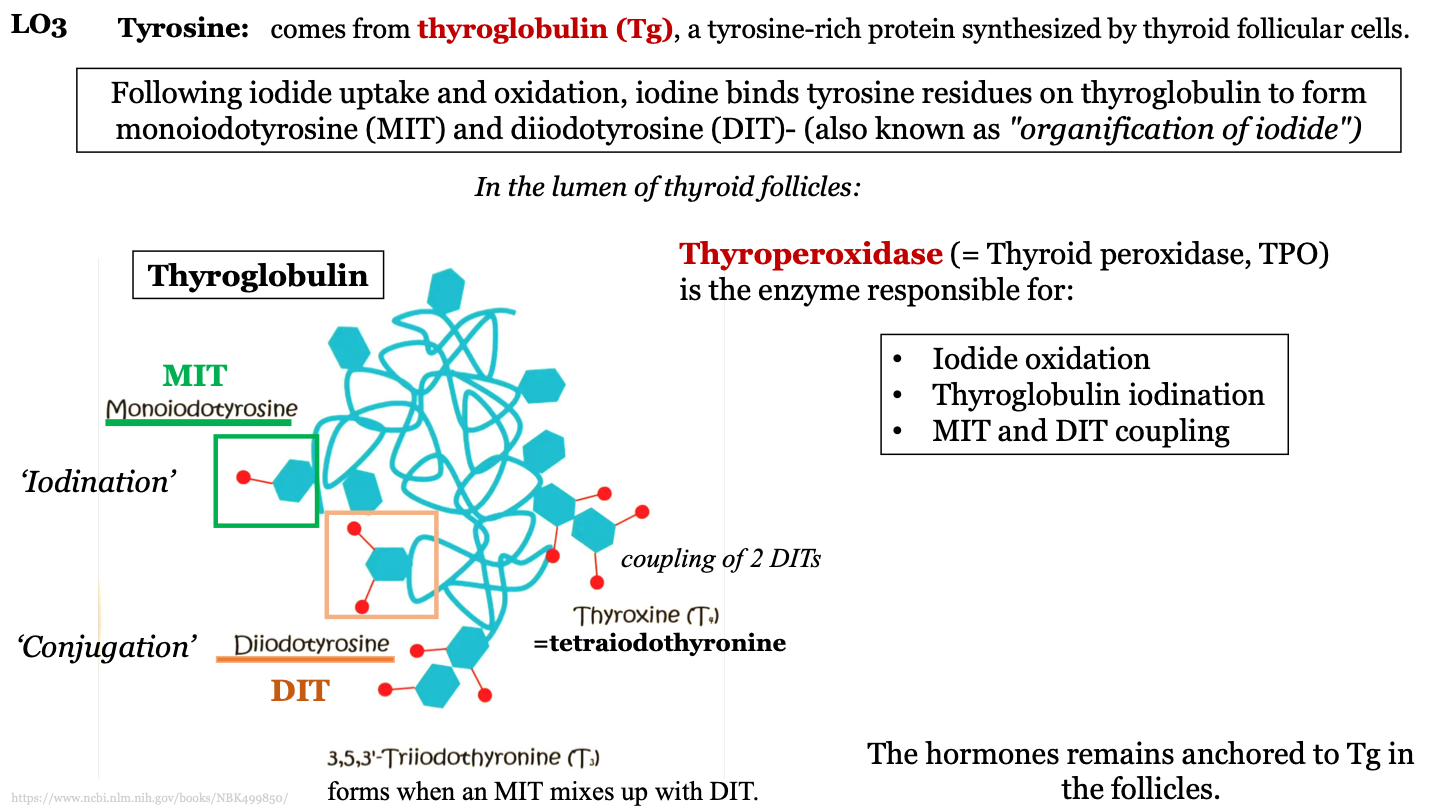
what is iodination?
when thyroperoxidase add iodine molecules to the tyrosine molecules of the thyroglobulin protein
27
New cards
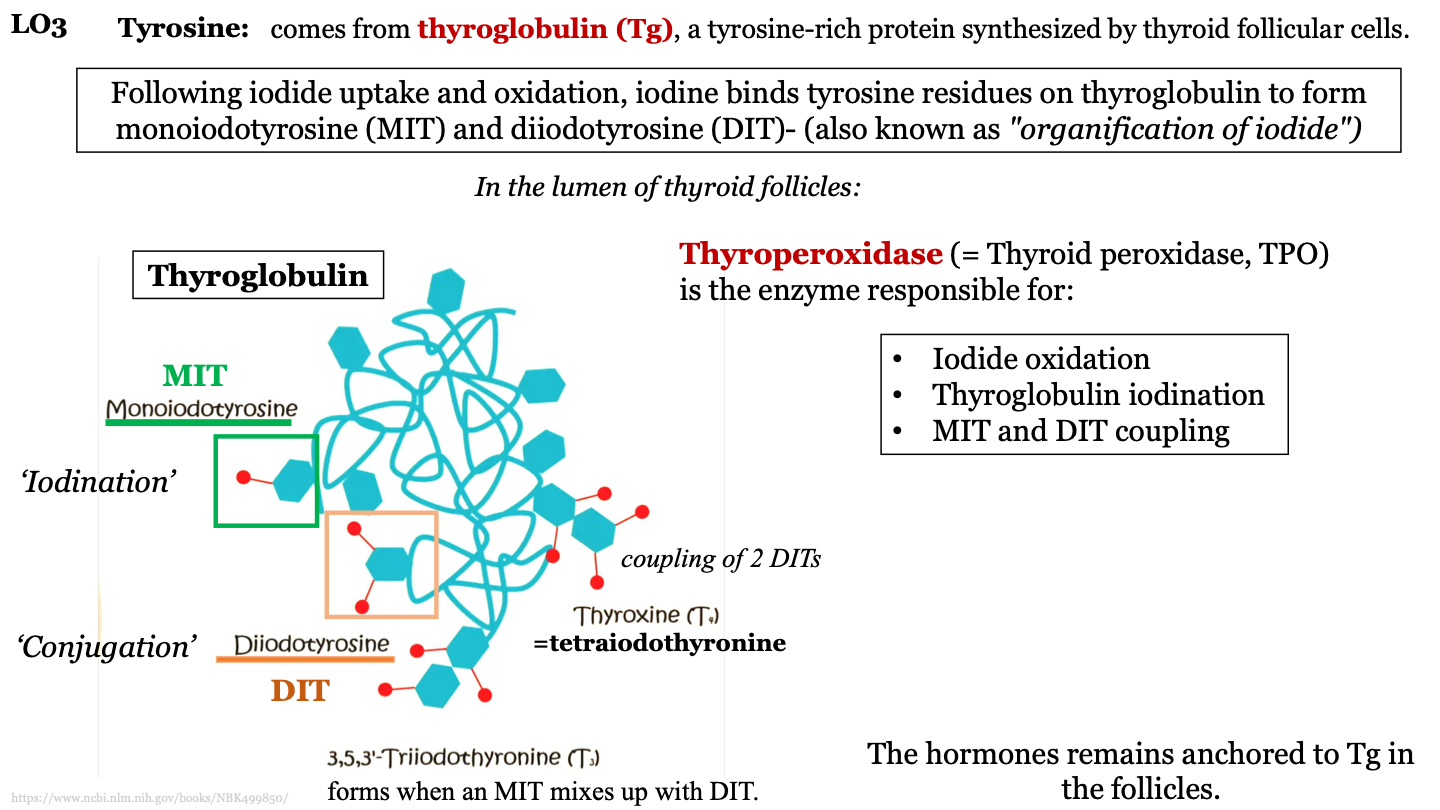
what is conjugation?
process where MITs and DITs mix; can form T3 or T4
28
New cards
how does trioodothyronine (T3) form?
forms when an MIT mixes with a DIT
29
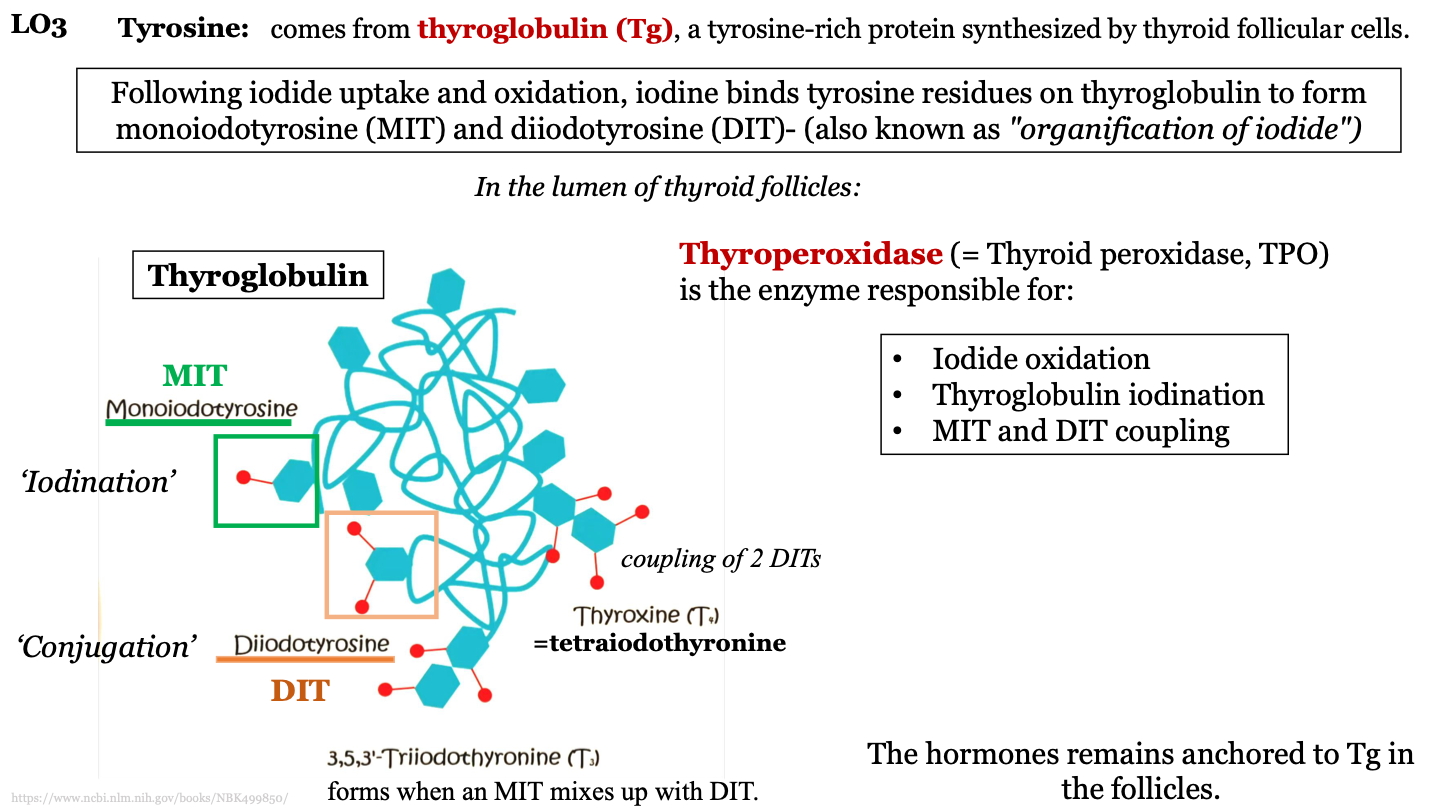
New cards
how does tetraiodothyonine (T4) form?
when two DITs join together
30
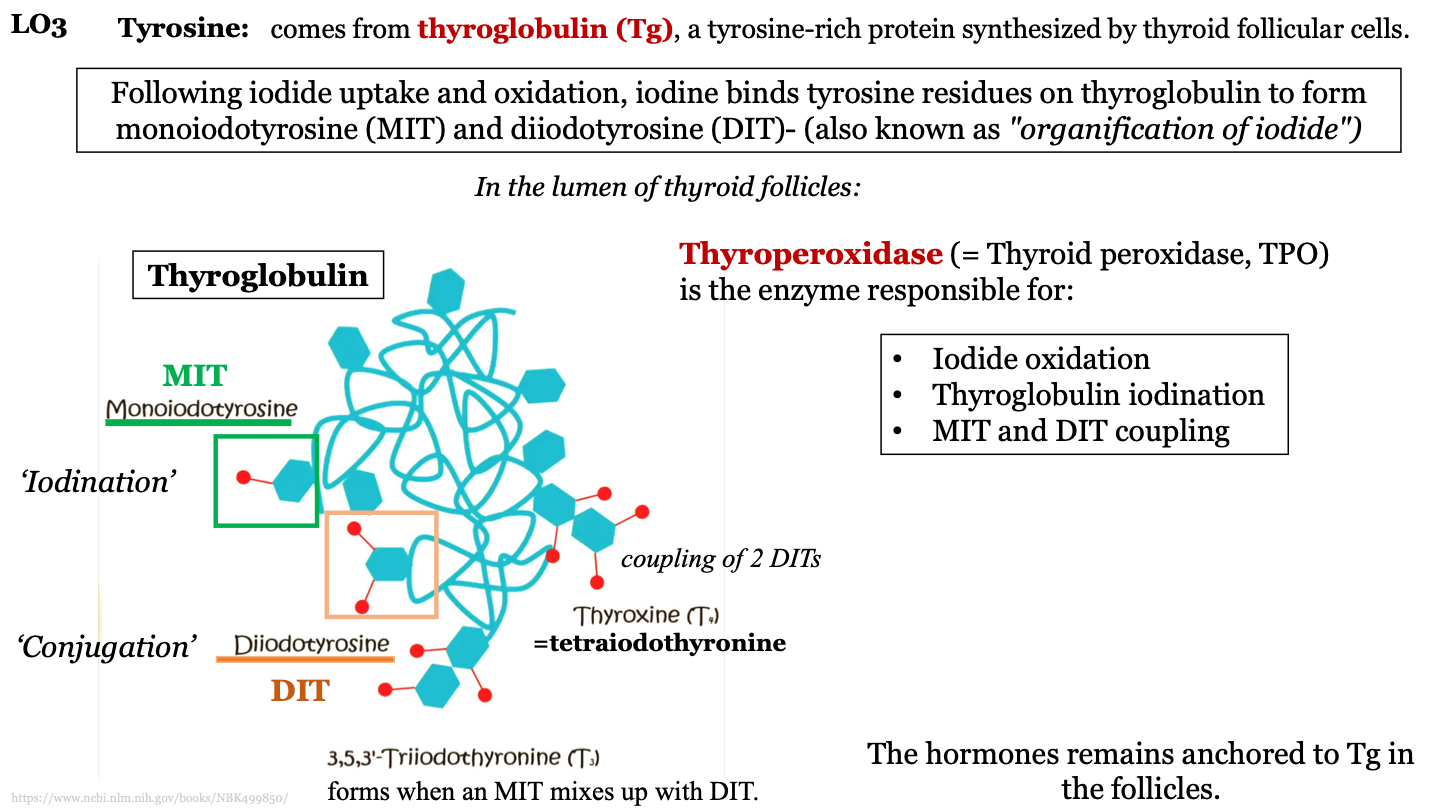
New cards
other names for thyroperoxidase
thyroid peroxidase; TPO
31
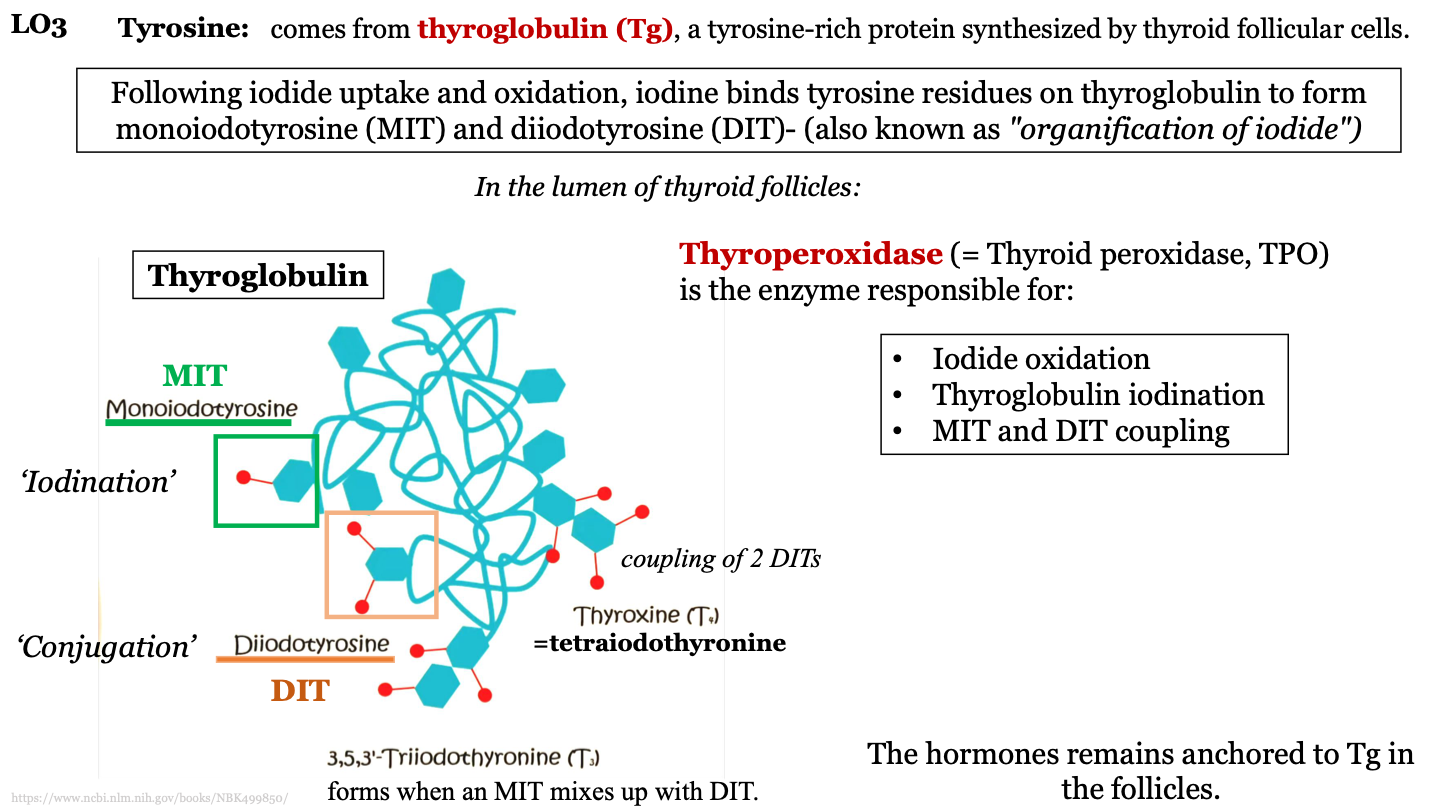
New cards
T or F: hormones remain anchored to thyroglobulin in the follicles and wait for stimulation by TSH
T
32
New cards
functions of thyroperoxidase
-iodide oxidation
-thyroglobulin iodination
-MIT and DIT coupling
-thyroglobulin iodination
-MIT and DIT coupling
33
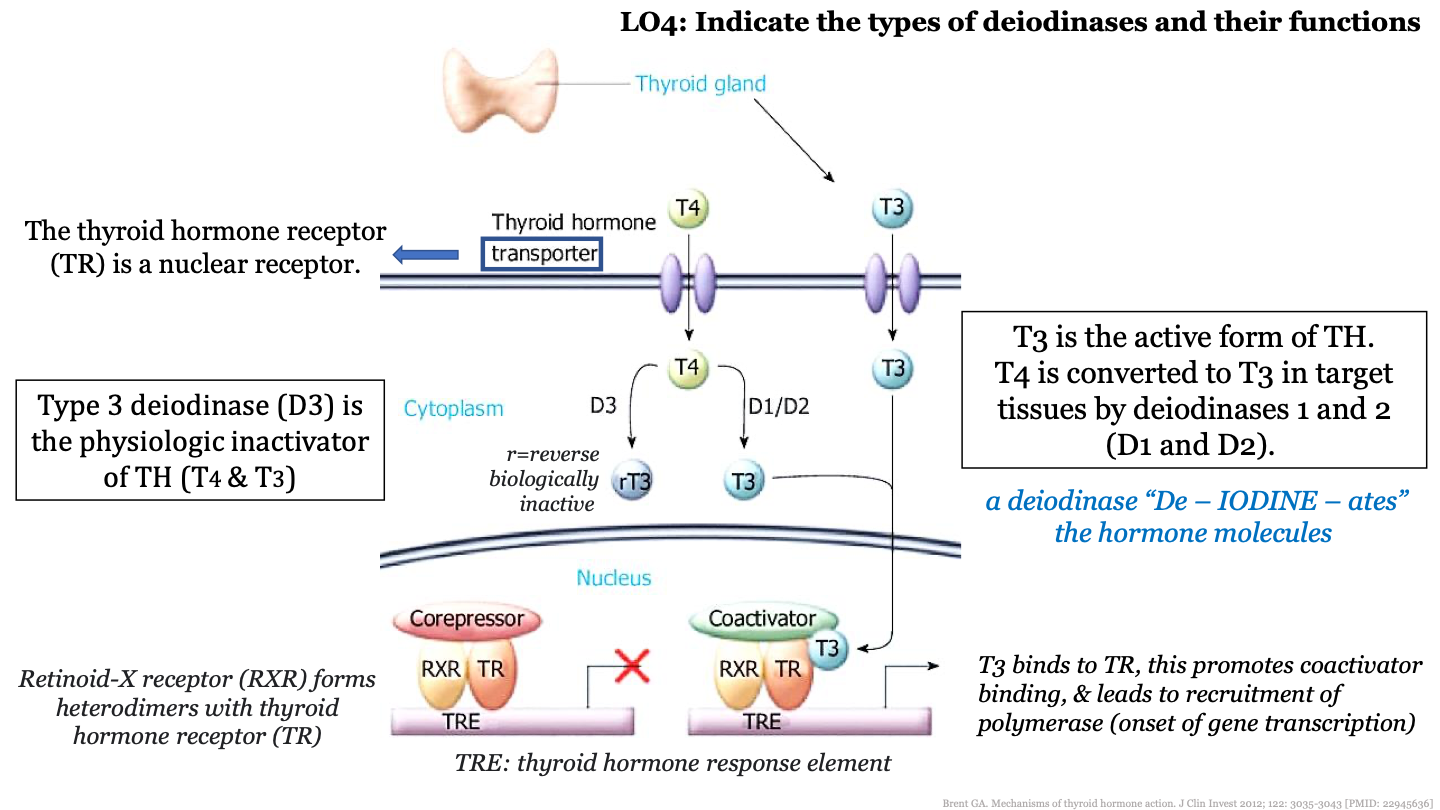
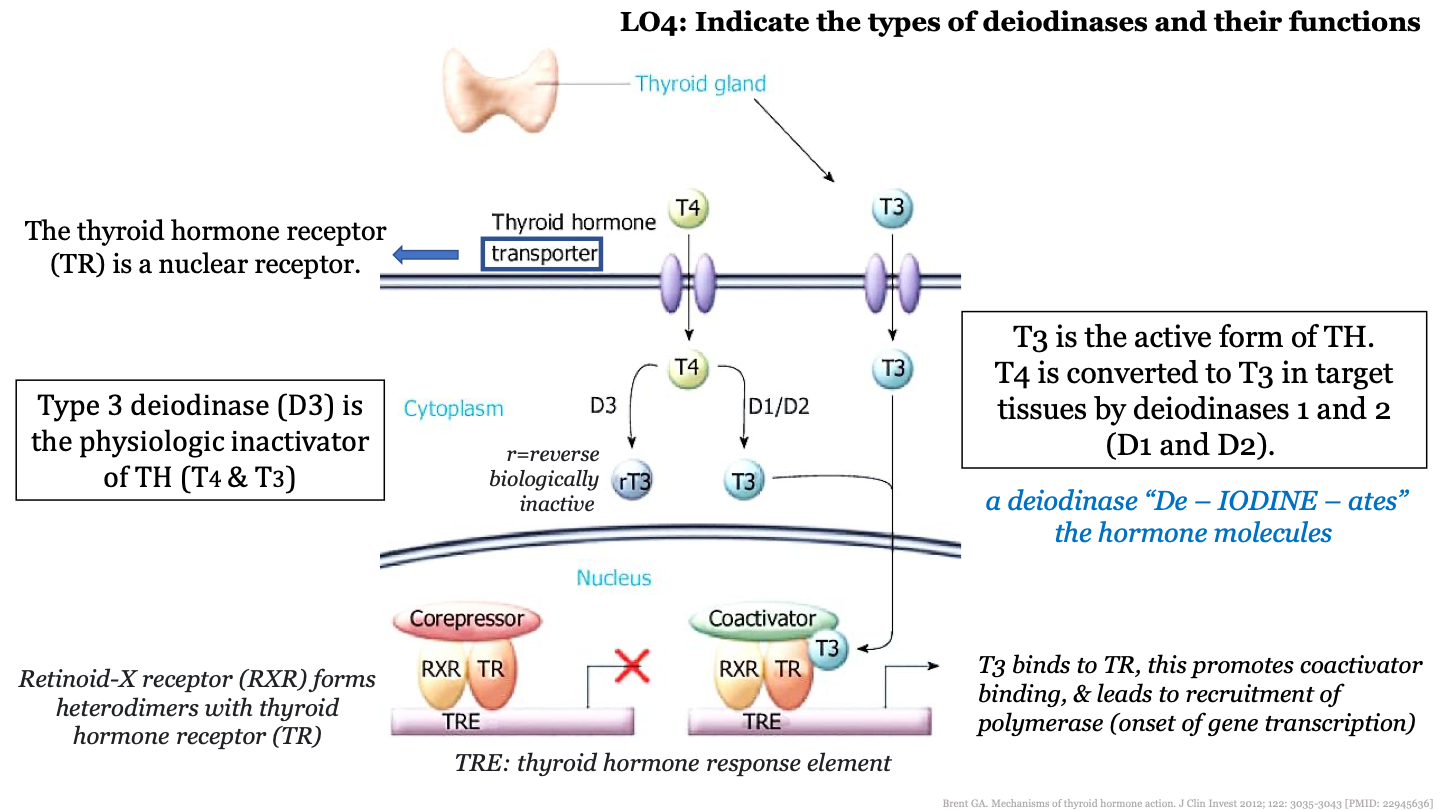
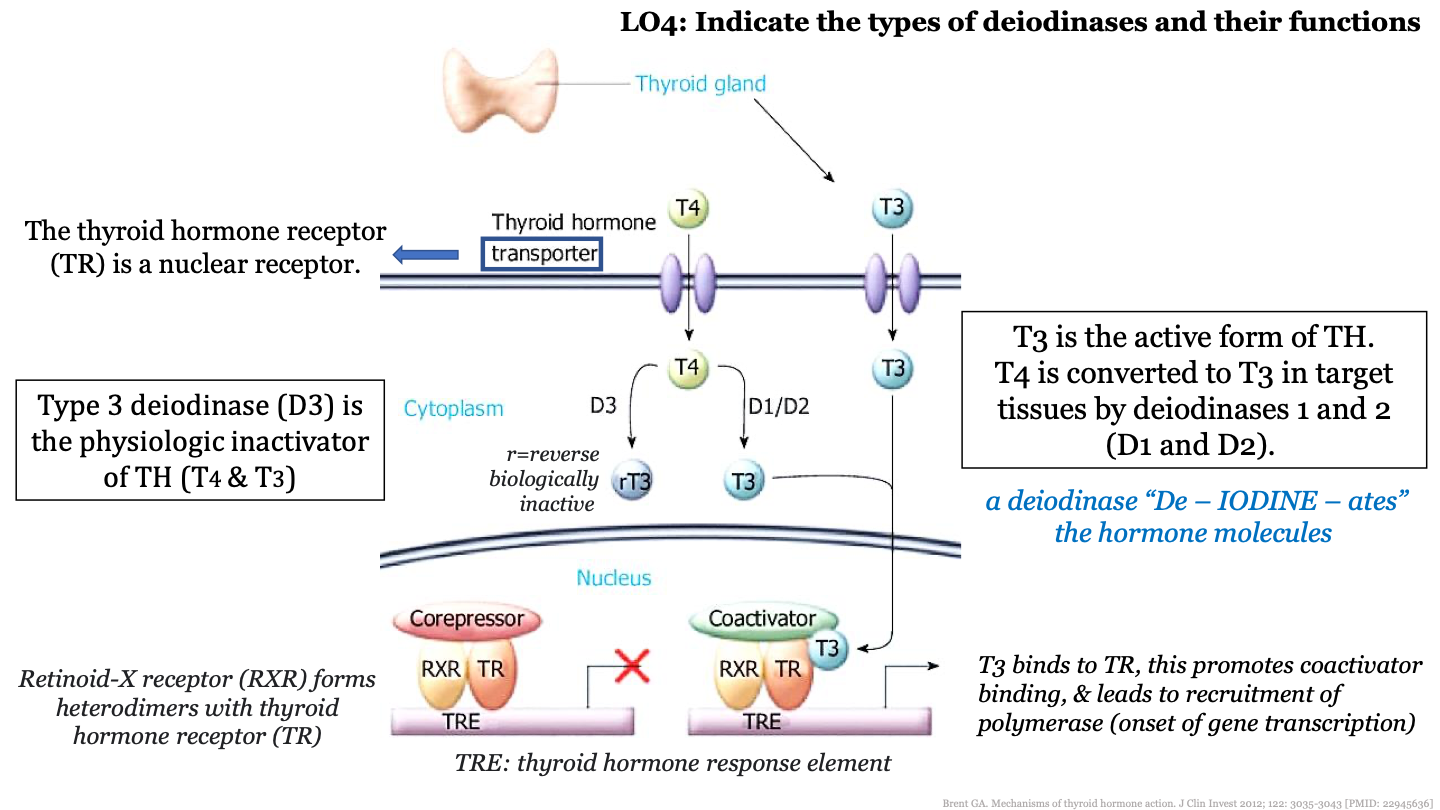
New cards
what kind of receptor is the thyroid hormone receptor (TR)?
nuclear receptor; it is in the nucleus
34
New cards
T3 is the active/inactive form of TH
active
35
New cards
T4 is the active/inactive form of TH
inactive
36
New cards
what enzymes convert T4 into T3?
deiodinases 1 and 2 (D1 and D2)
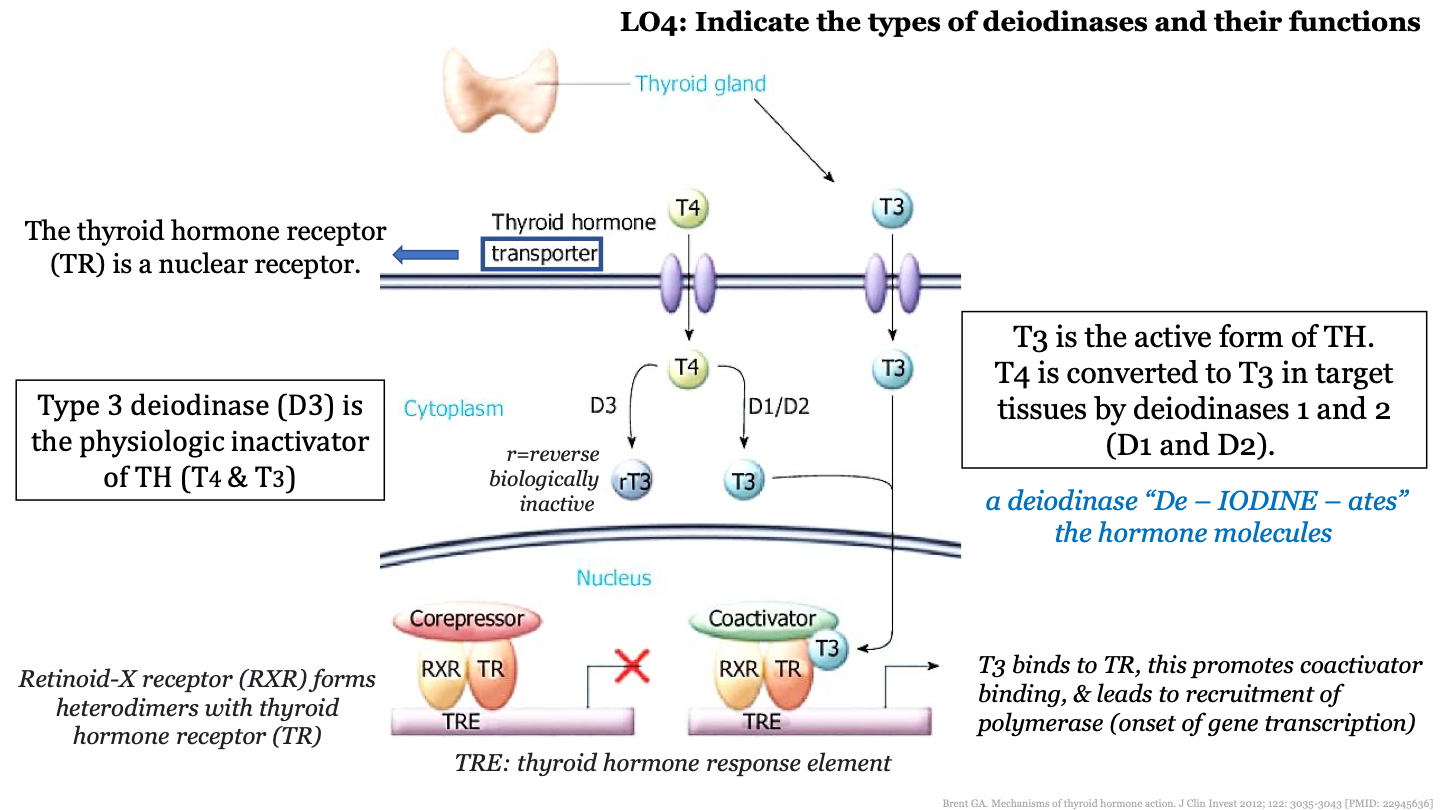
37
New cards
what does deiodinase 3 (D3) do?
inactivates TH (T3 and T4)
38
New cards
what does the thyroid hormone transporter do?
transports T4 and T3 from the blood into the nucleus of cells
39
New cards
what is the amino acid precursor for the synthesis of thyroid hormones?
tyrosine

40
New cards
what is the main transport (carrier) protein of Th in blood?
thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
41
New cards
what is one example of a reaction that the enzyme thyroperoxidase catalyzes?
thyroglobulin iodination
42
New cards
in peripheral tissues, T4 is converted to T3 by _____ or _____
D1 or D2
43
New cards
what is the element and protein needed for the synthesis of TH?
iodine thyroglobulin
44
New cards
which transporter is responsible for the transport of iodine into the thyroid cells against the concentration gradient?
Na+ I- symport
45
New cards
physiological effect of TH on metabolism
increases basal metabolic rate (the amount of energy that is expended at rest)
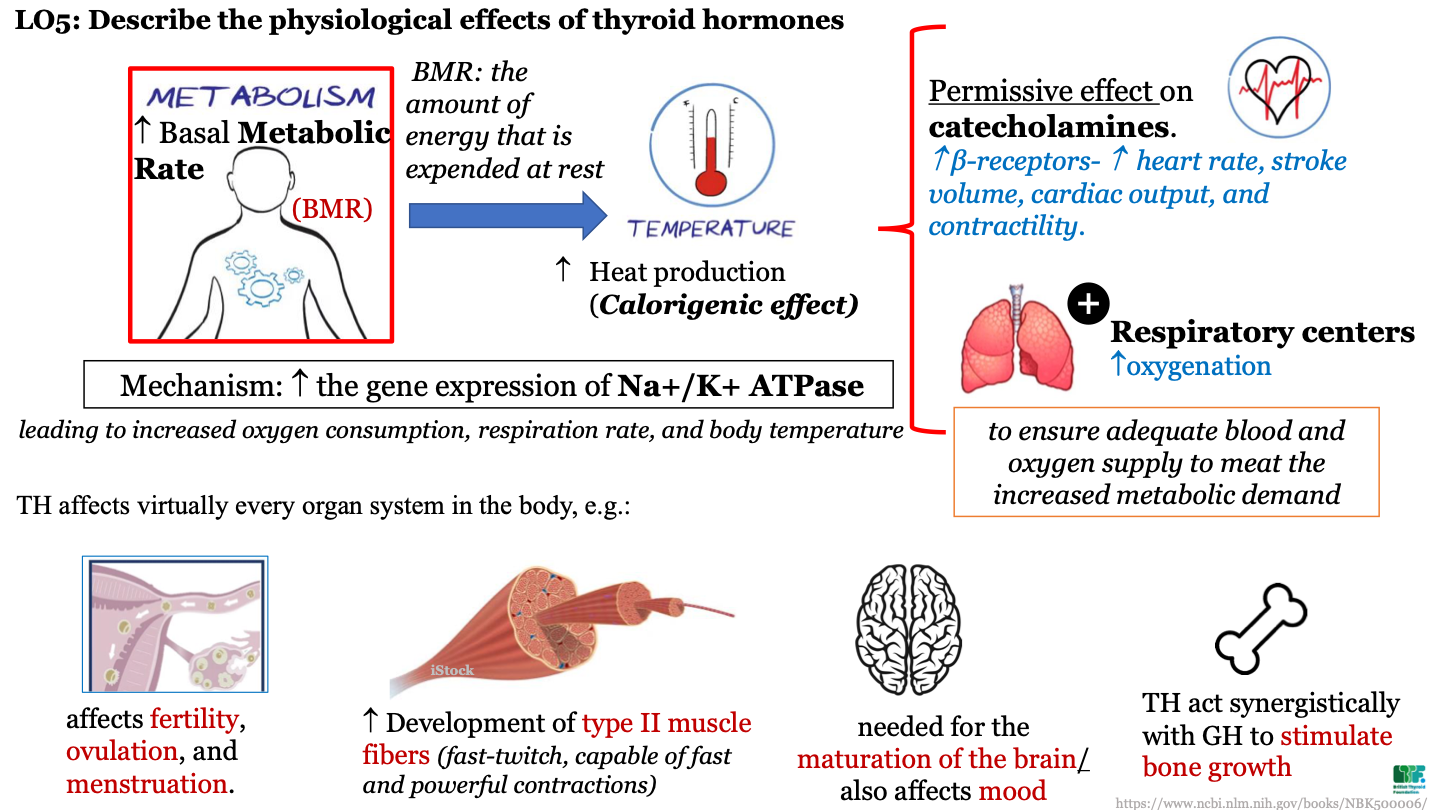
46
New cards
physiological effect of TH on temperature
increased heat production (calorigenic effect)
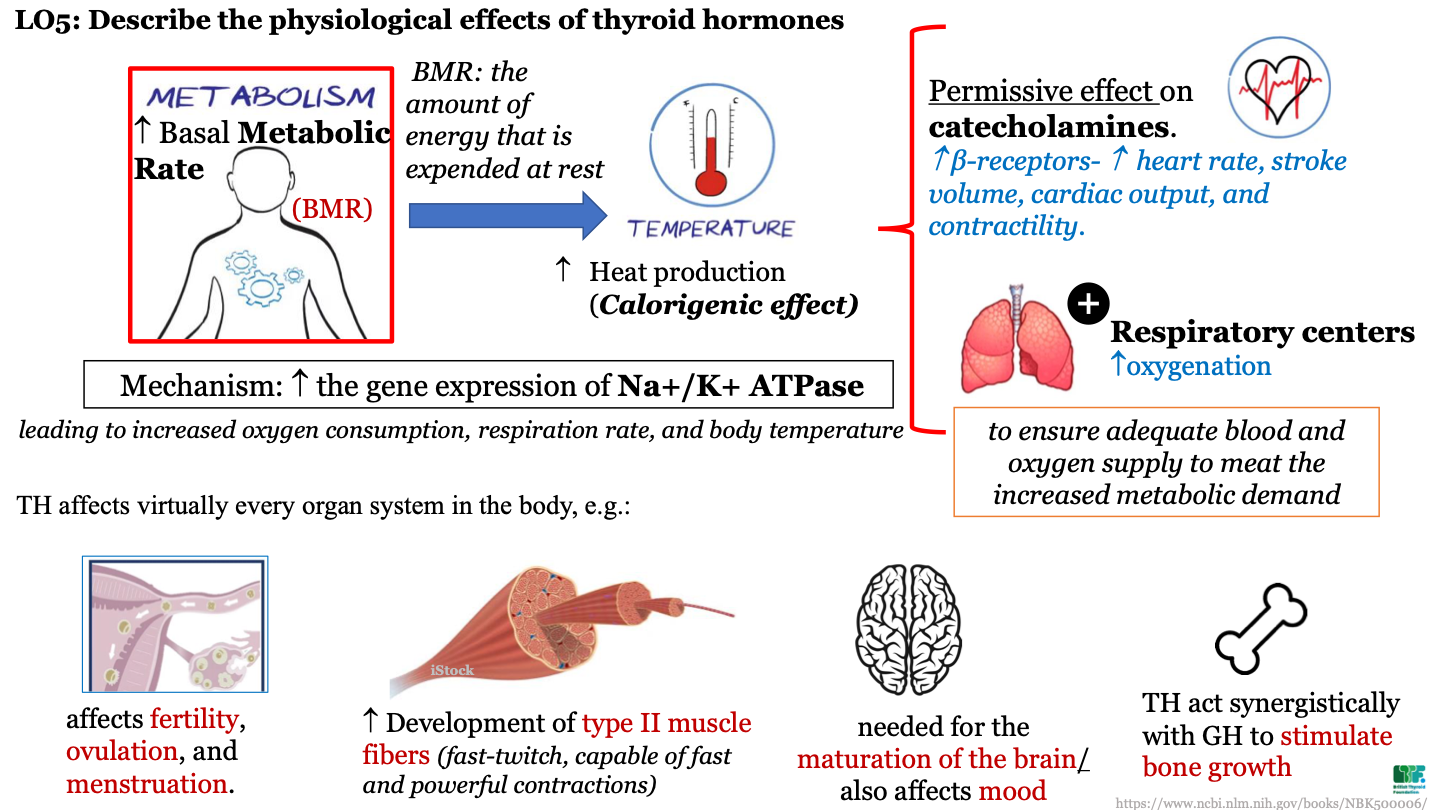
47
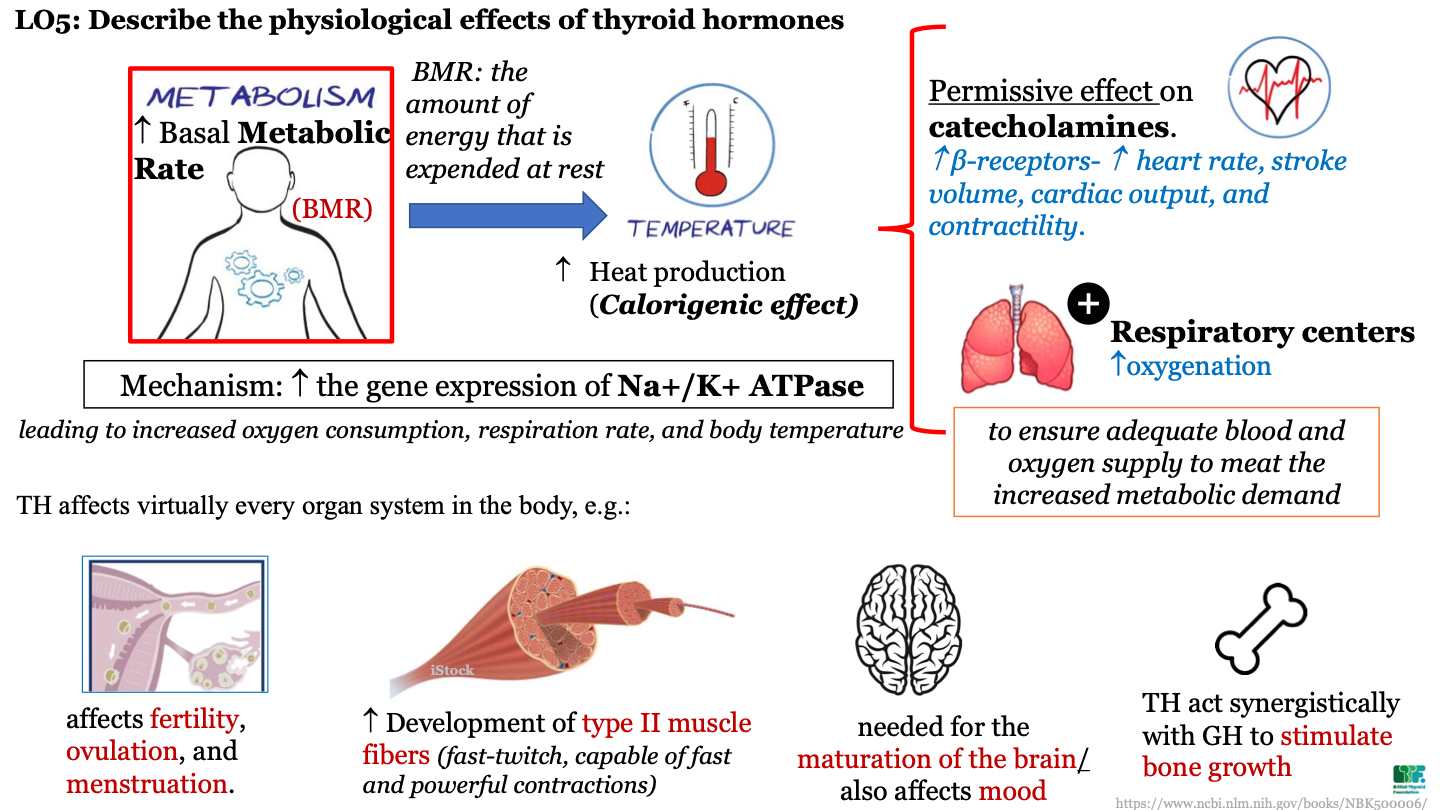
New cards
how does TH influence other hormones?
TH has a permissive effect on catecholamines; there is an increase in beta receptors which causes an increase in HR, stroke volume, cardiac output, and contractility
48
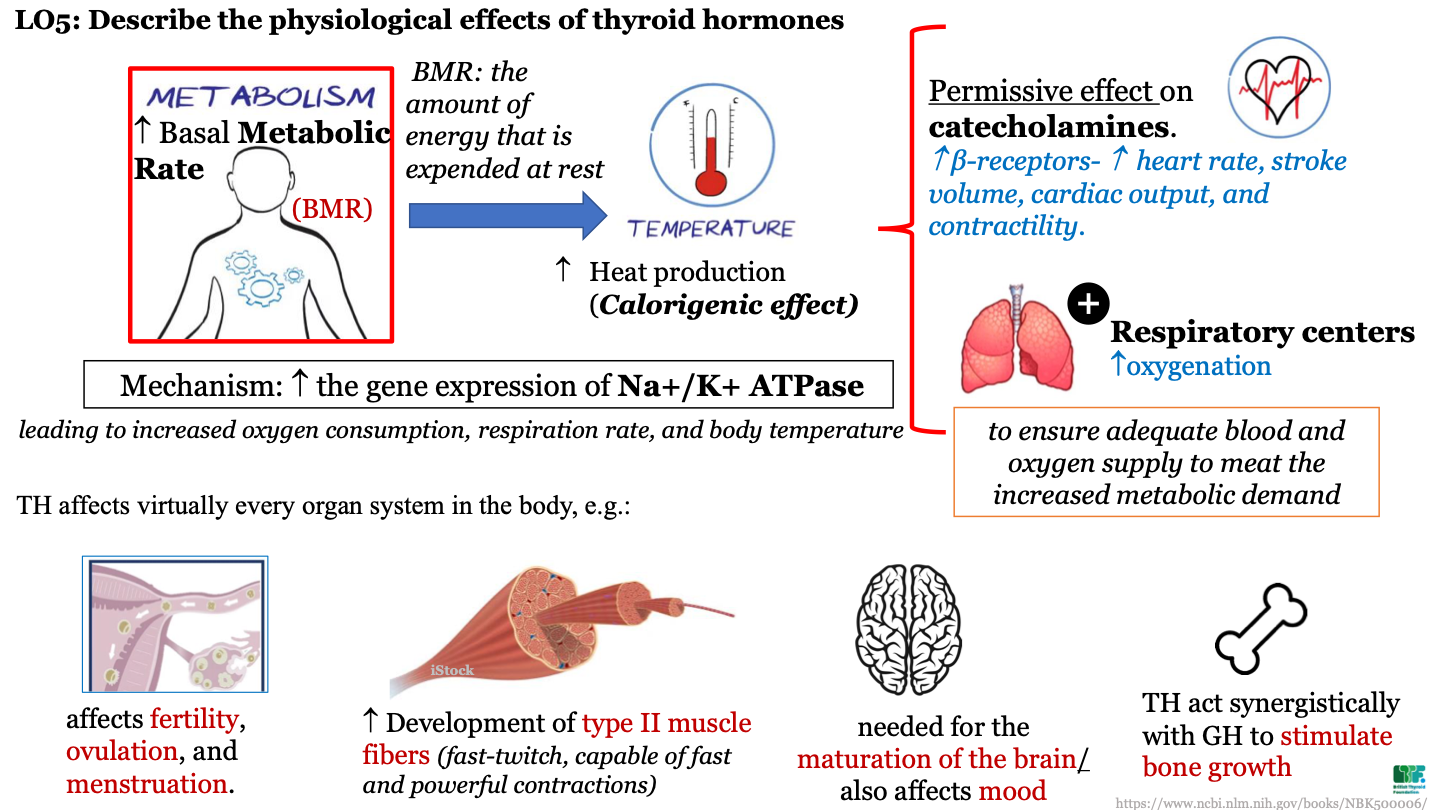
New cards
TH effect on respiratory centers
increase oxygenation; this ensures adequate blood and oxygen supply to meet the increased metabolic demand
49
New cards
what is a consequence of increased temperature after TH secretion?
increased gene expression of Na+ and K+ ATPase; this leads to increased oxygen consumption, respiration rate, and body temp
50
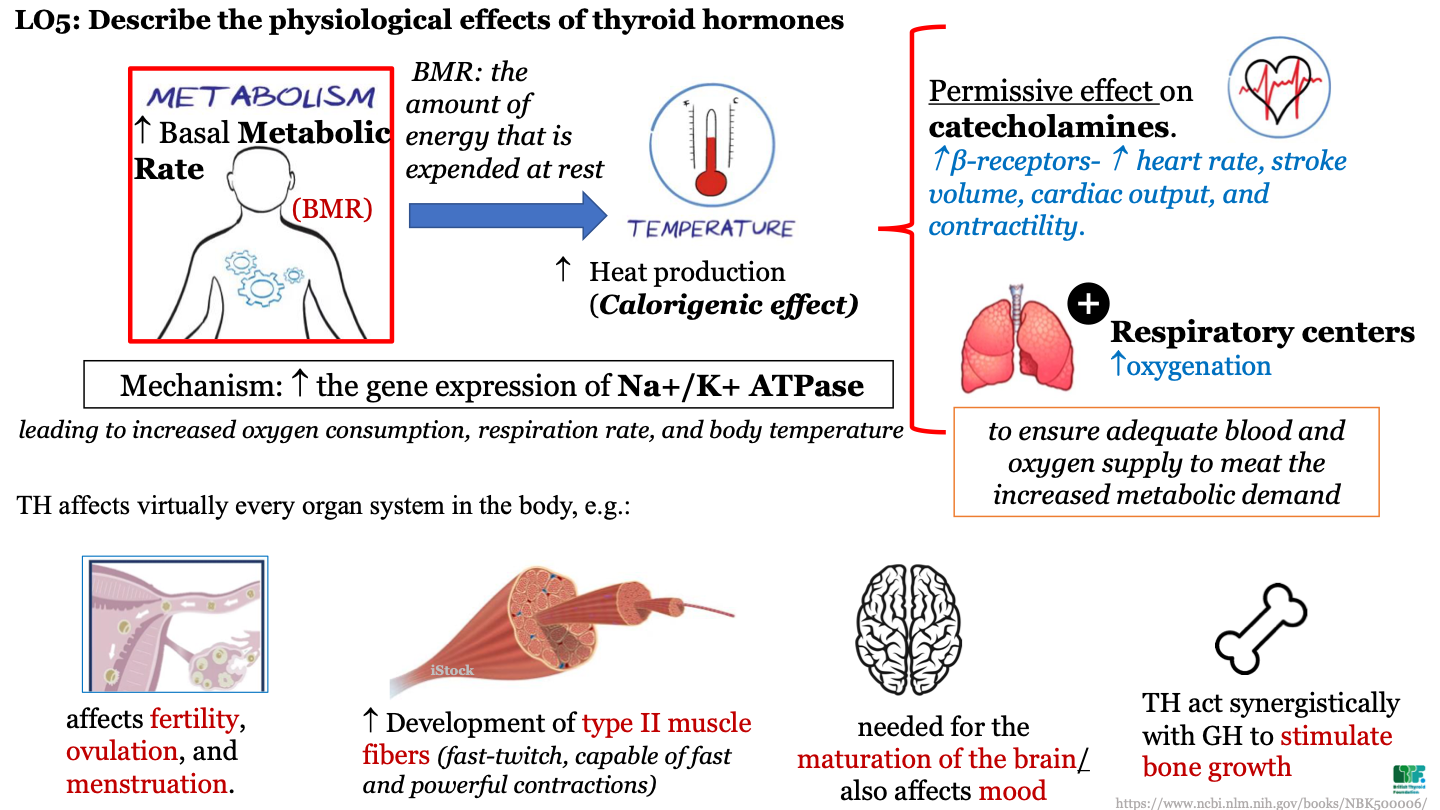
New cards
TH affects on body organ systems
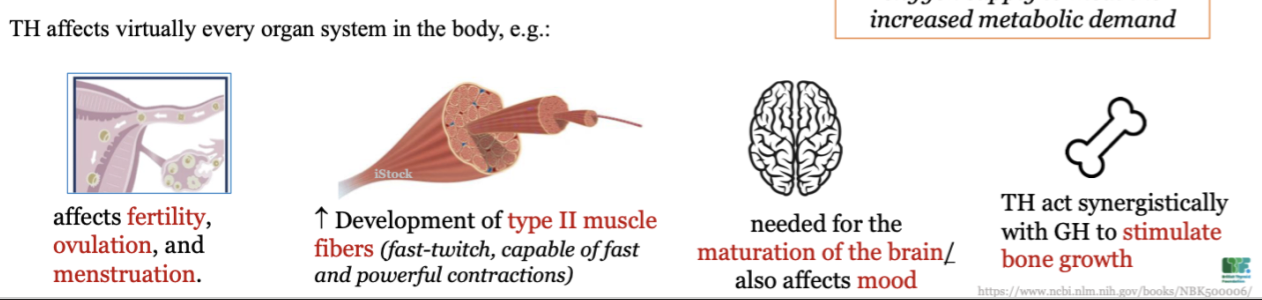
51
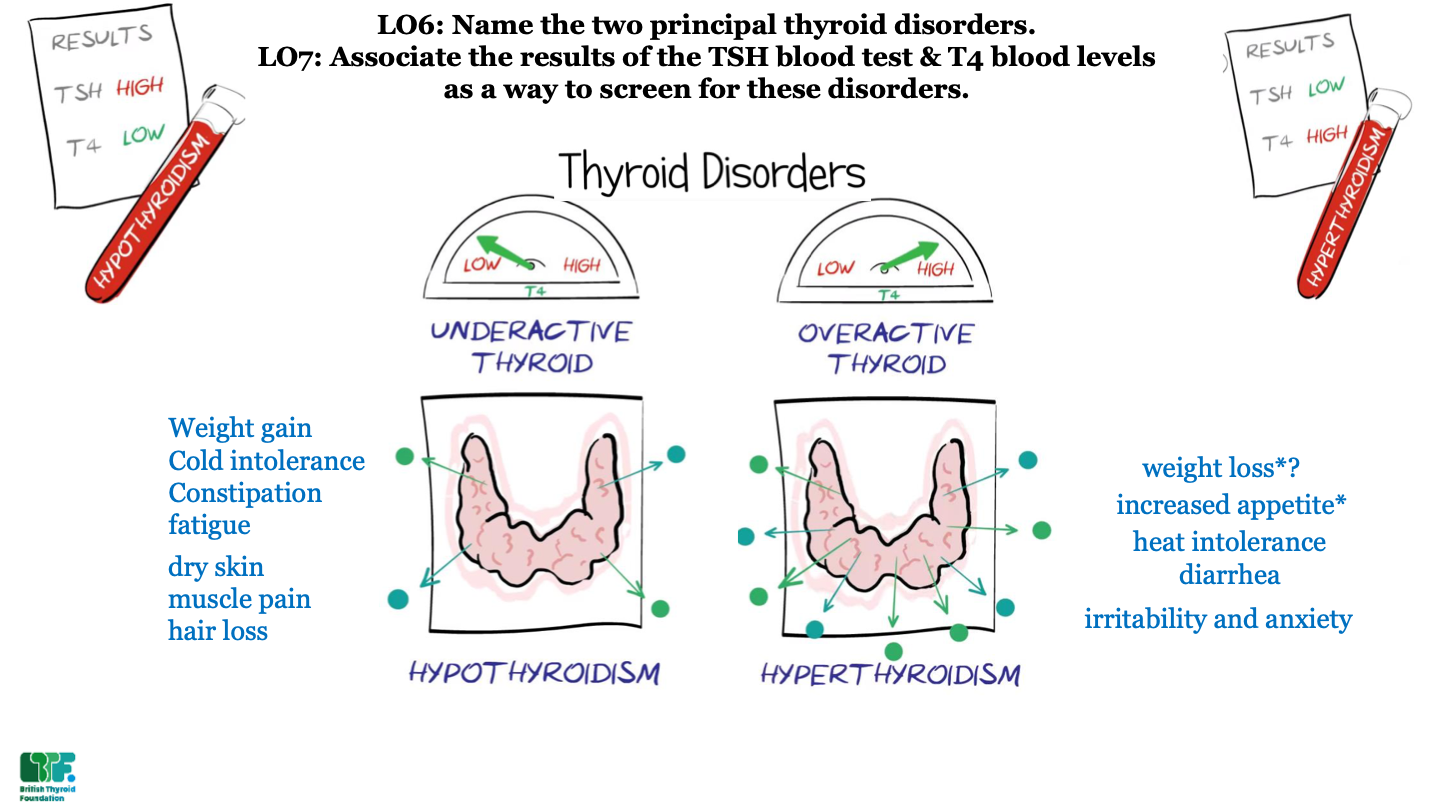
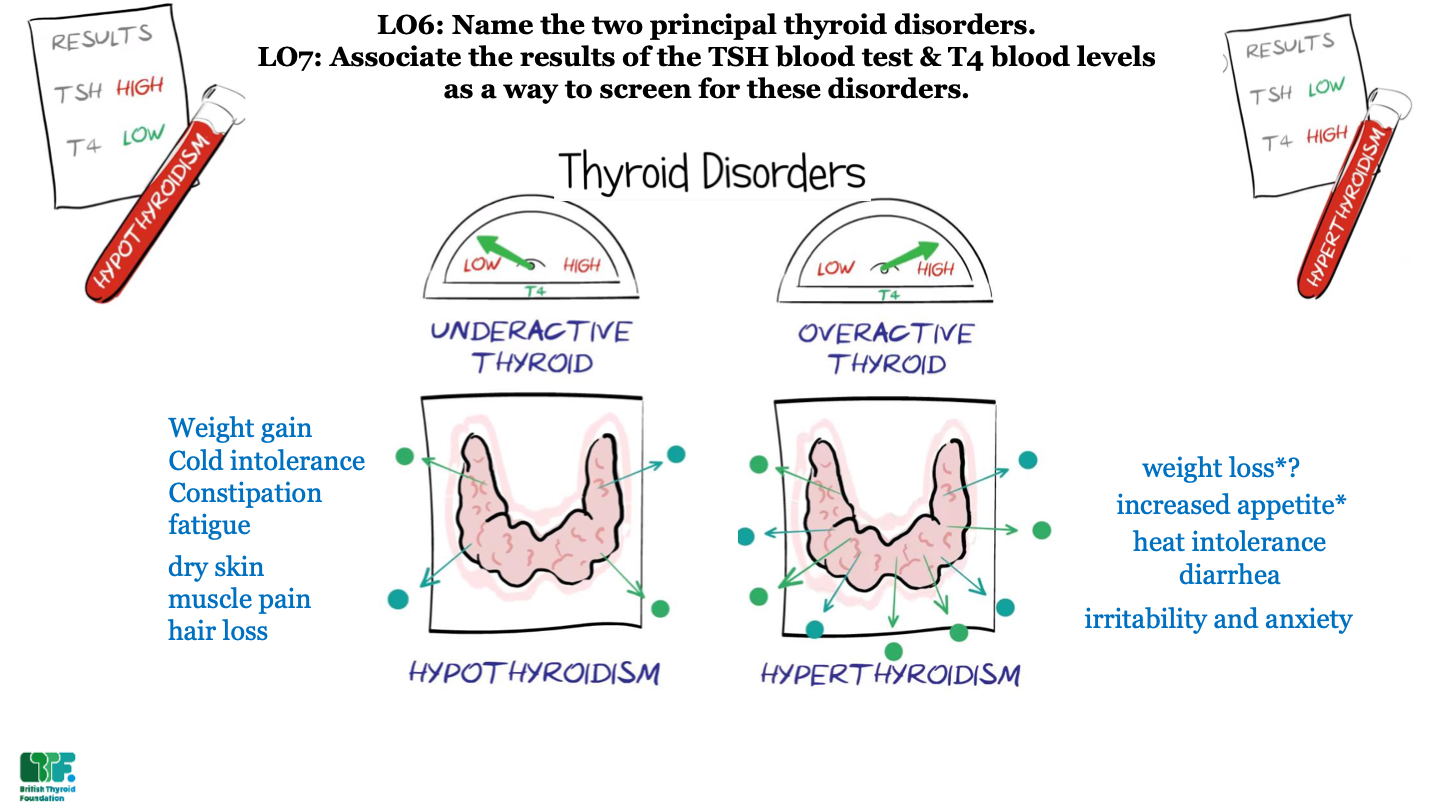
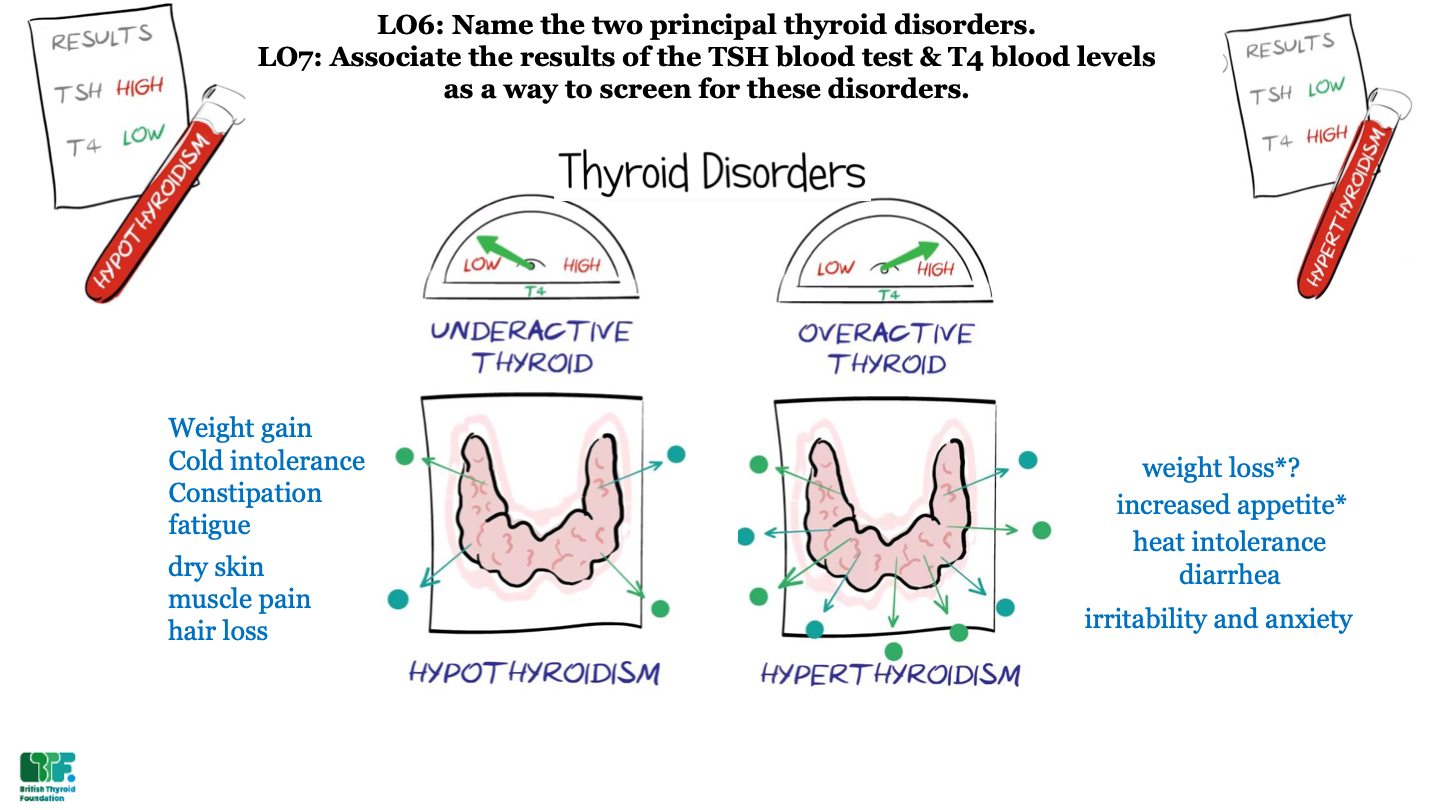
New cards
what are the 2 most common thyroid disorders?
hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
52
New cards
what is hypothyroidism?
underactive thyroid; not enough thyroid hormone
53
New cards
what is hyperthyroidism?
overactive thyroid; too much thyroid hormone
54
New cards
what results would you expect from a patient with hypothyroidism?
high TSH and low T4
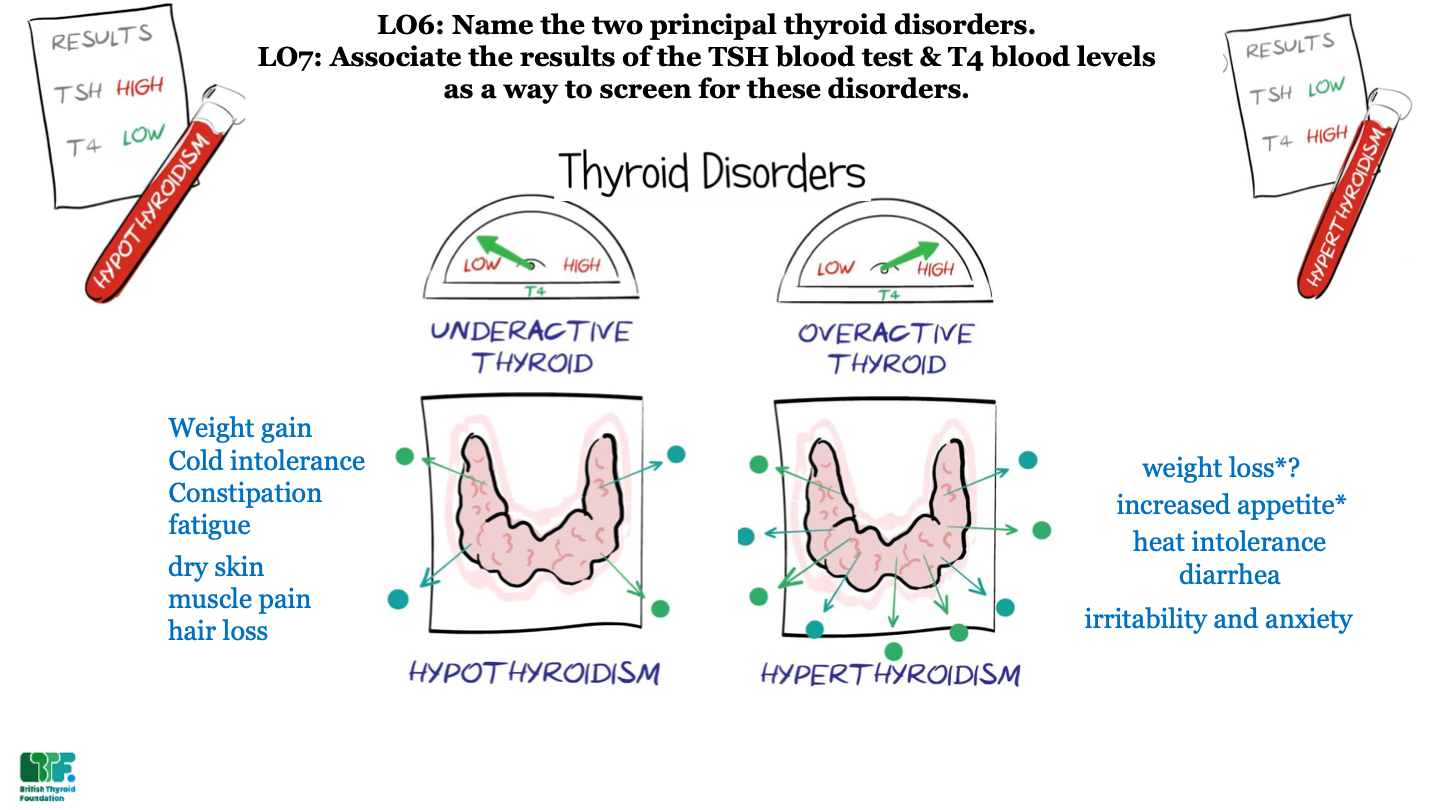
55
New cards
what results would you expect from a patient with hyperthyroidism?
low TSH and high T4
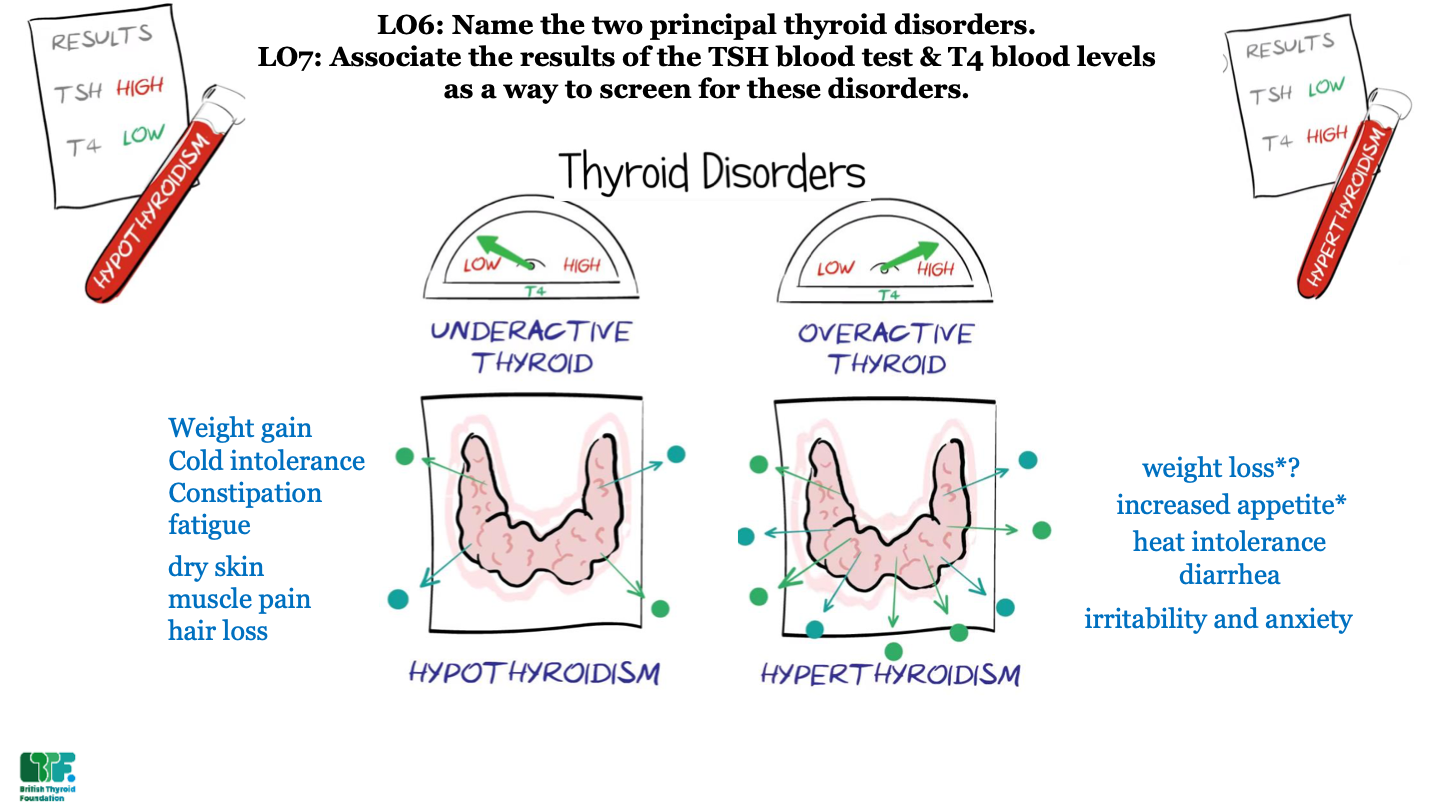
56
New cards
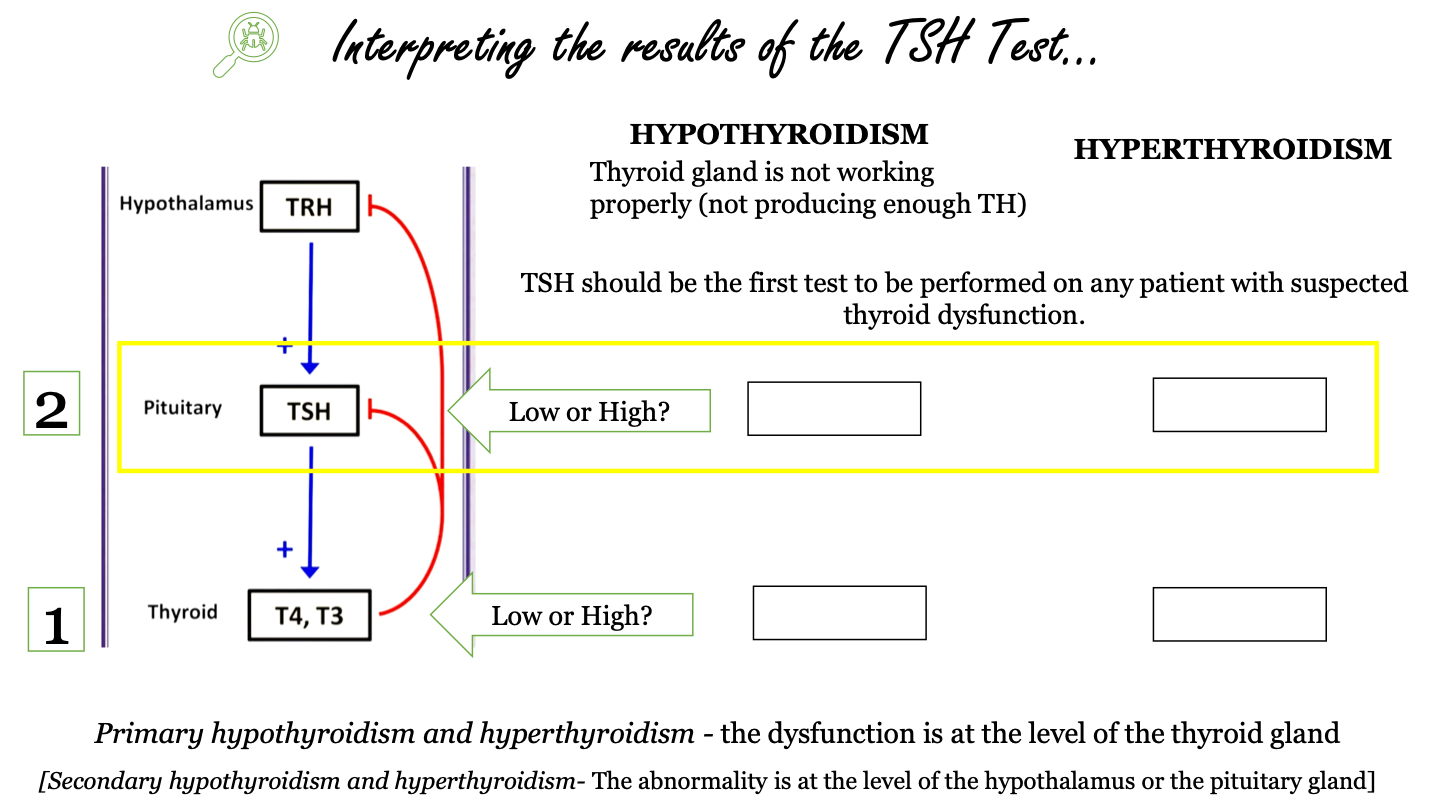
_______ should be the first test to be performed on any patient with suspected thyroid disfunction
TSH
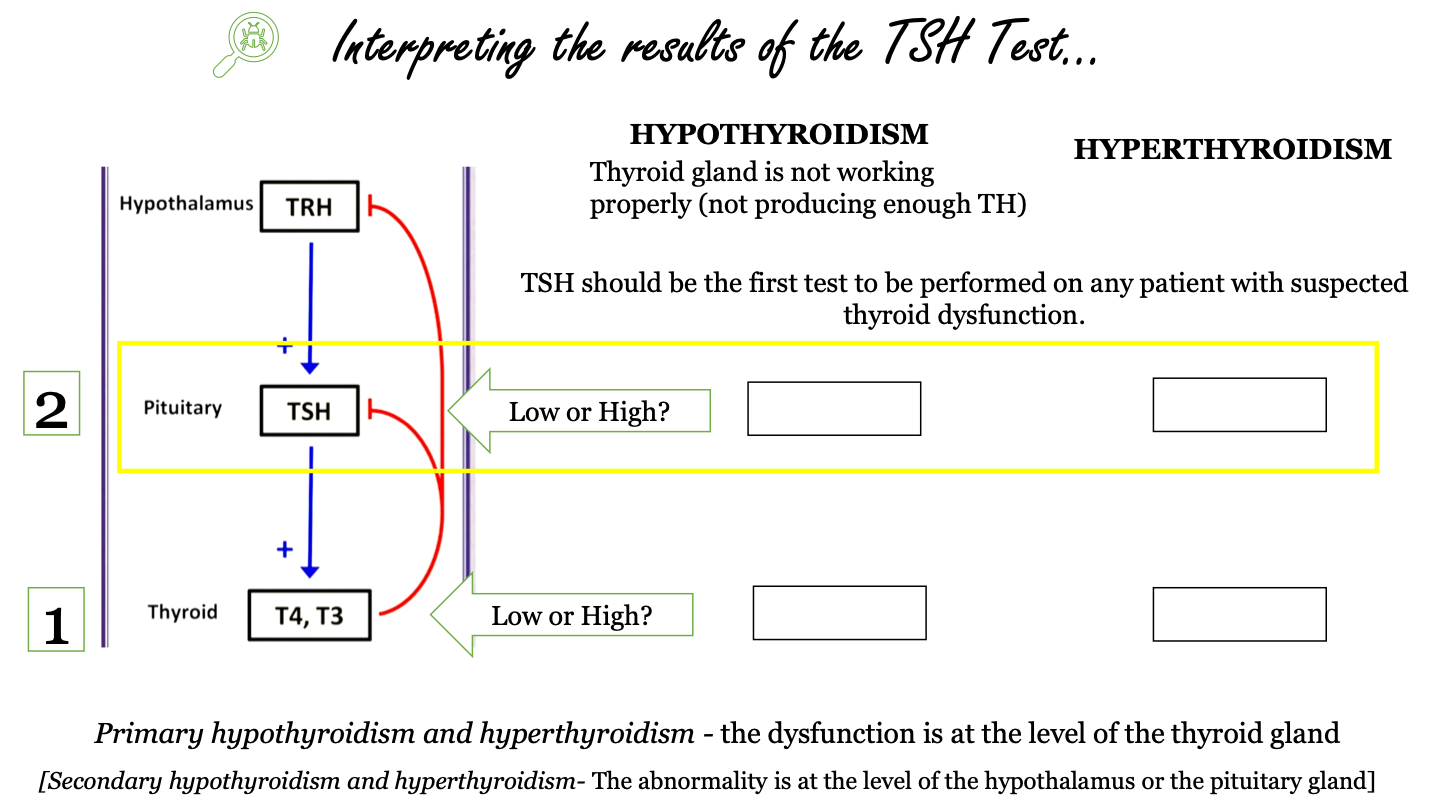
57
New cards
what does primary hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism indicate?
the dysfunction is at the level of the thyroid gland
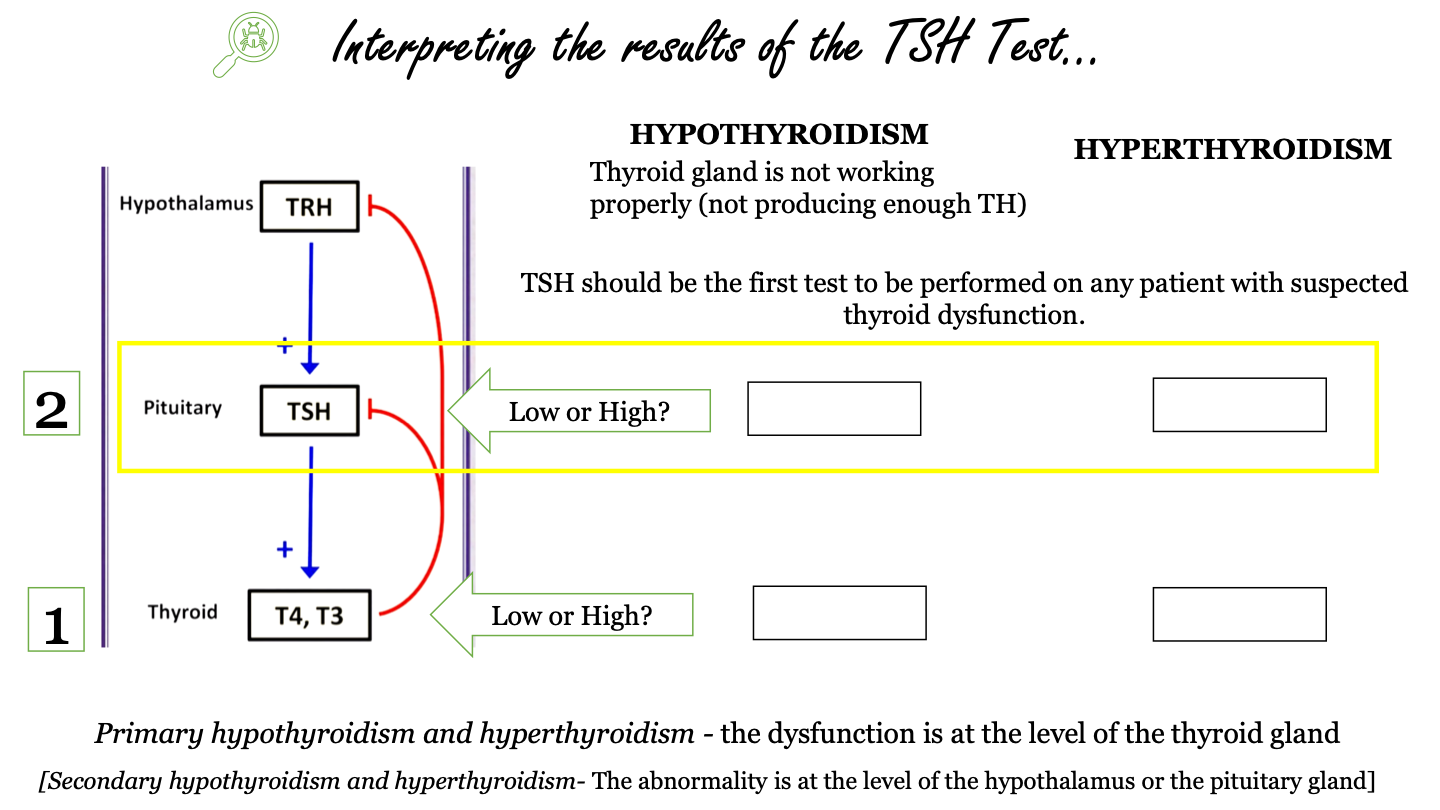
58
New cards
what does secondary hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism indicate?
the dysfunction is at the level of the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland
59
New cards
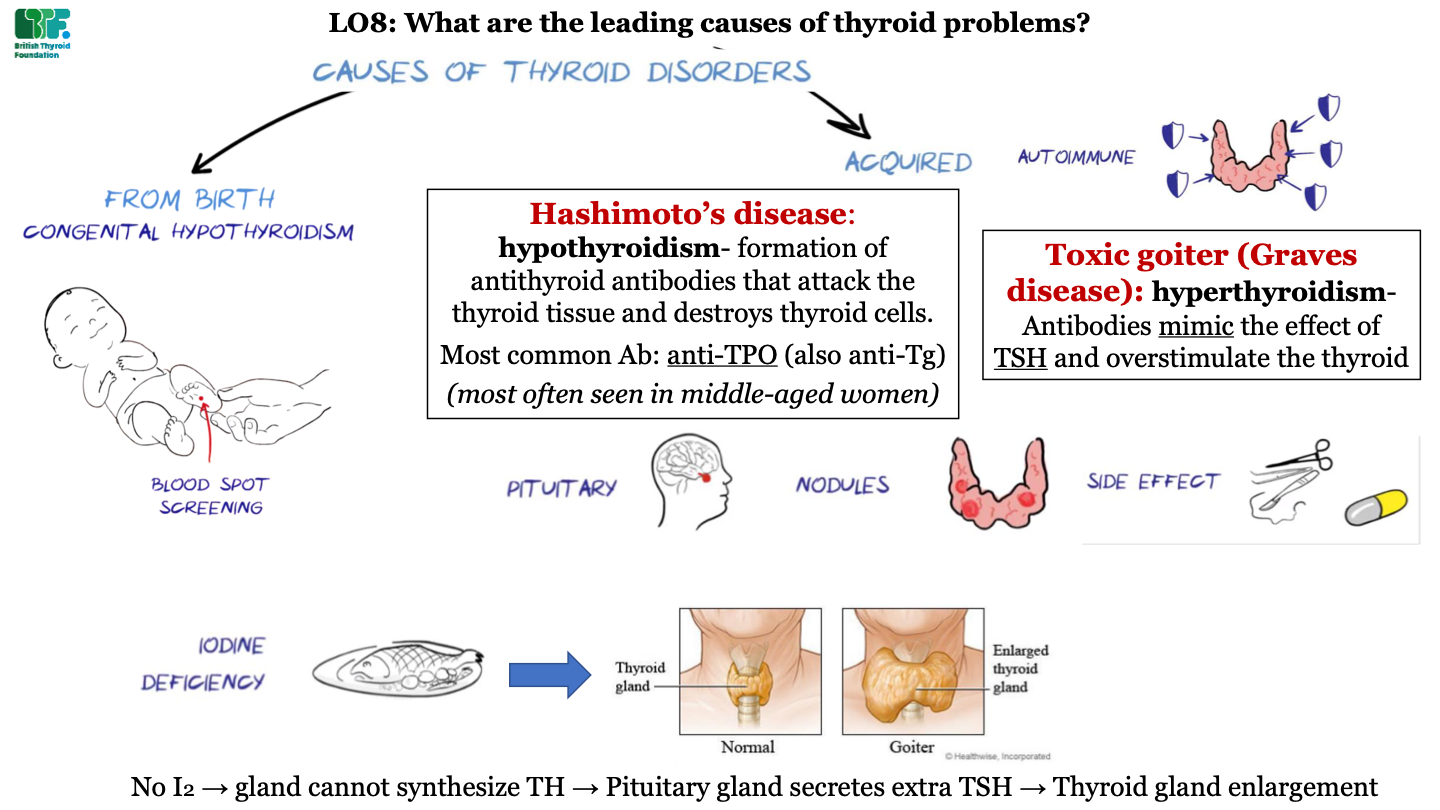
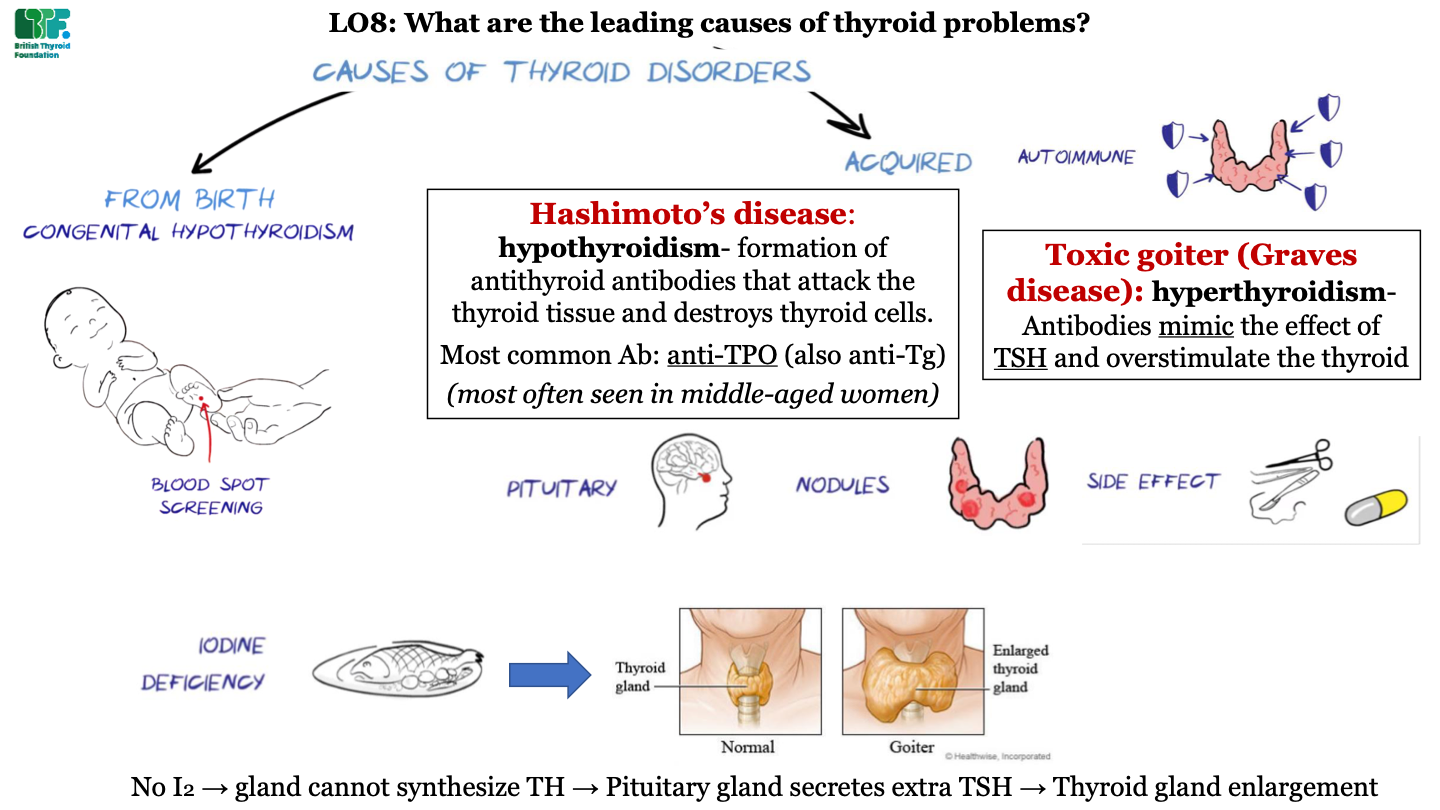
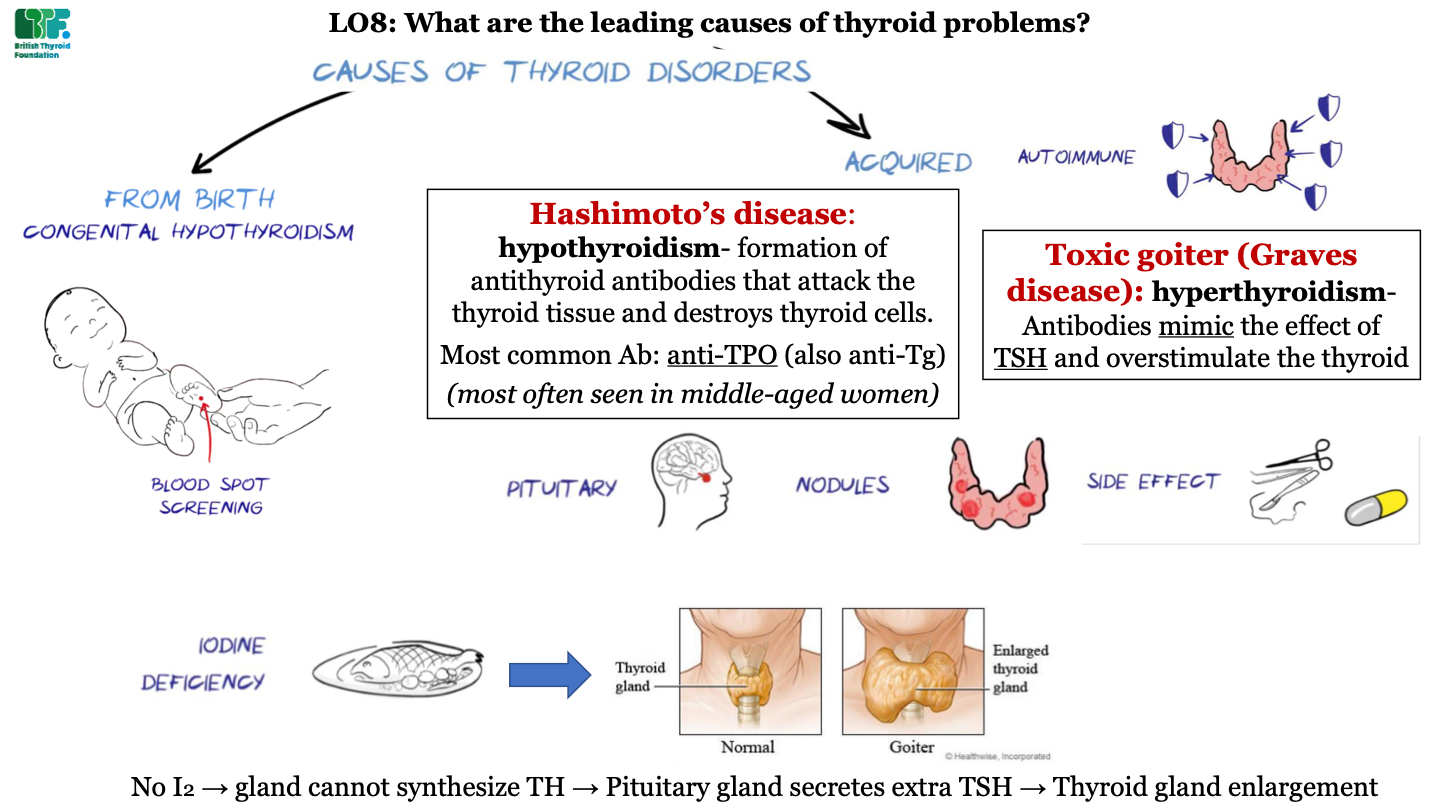
what are the two main causes of thyroid disorders
-from birth (e.g. congenital hypothyroidism)
-acquired
-acquired
60
New cards
how are infants tested for thyroid disorder?
blood spot screening
61
New cards
types of acquired thyroid diseases -autoimmune
-Hashimoto's disease
-toxic goiter (Graves disease)
-toxic goiter (Graves disease)
62
New cards
what is Hashimoto's disease?
hypothyroidism; formation of antithyroid antibodies that attack the thyroid tissue and destroy thyorid cells; most common antibody is anti-TPO (and also anti-Tg); this condition is most often seen in middle-aged women
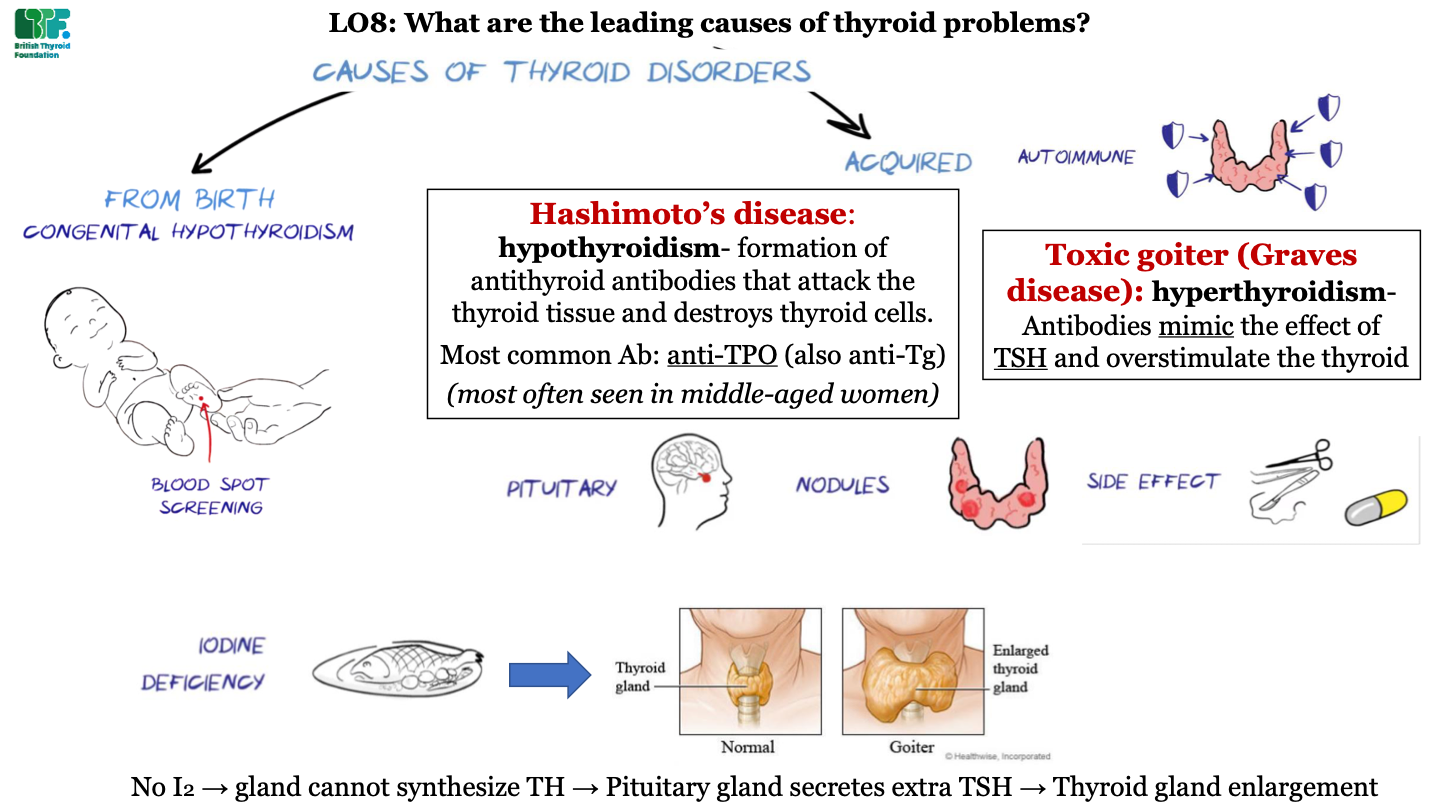
63
New cards
what is toxic goiter (Graves disease)?
hyperthyroidism; antibodies act like TSH and overstimulate the thyroid
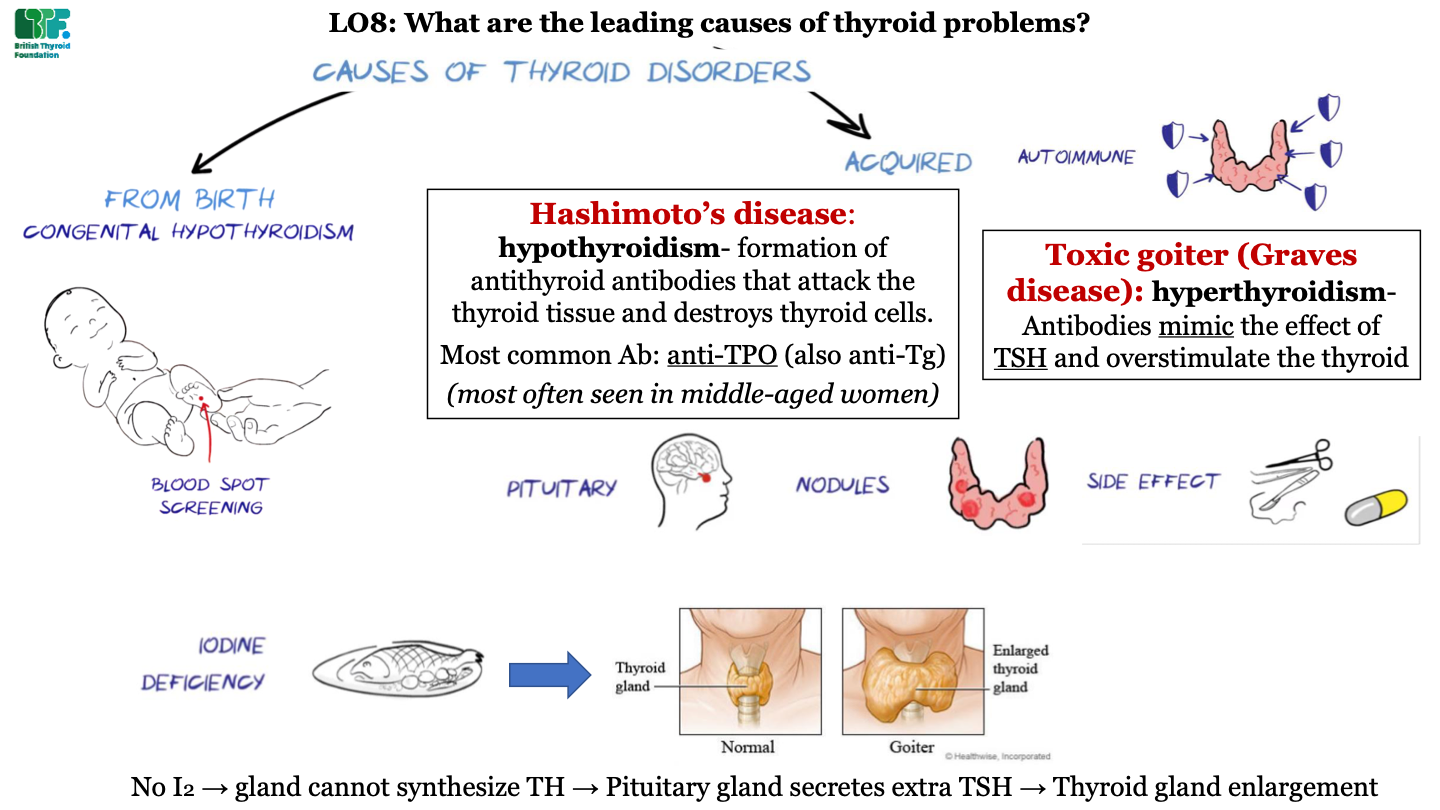
64
New cards
types of acquired thyroid diseases -pituitary
problems in the pituitary gland (like tumors) can cause thyroid disorders
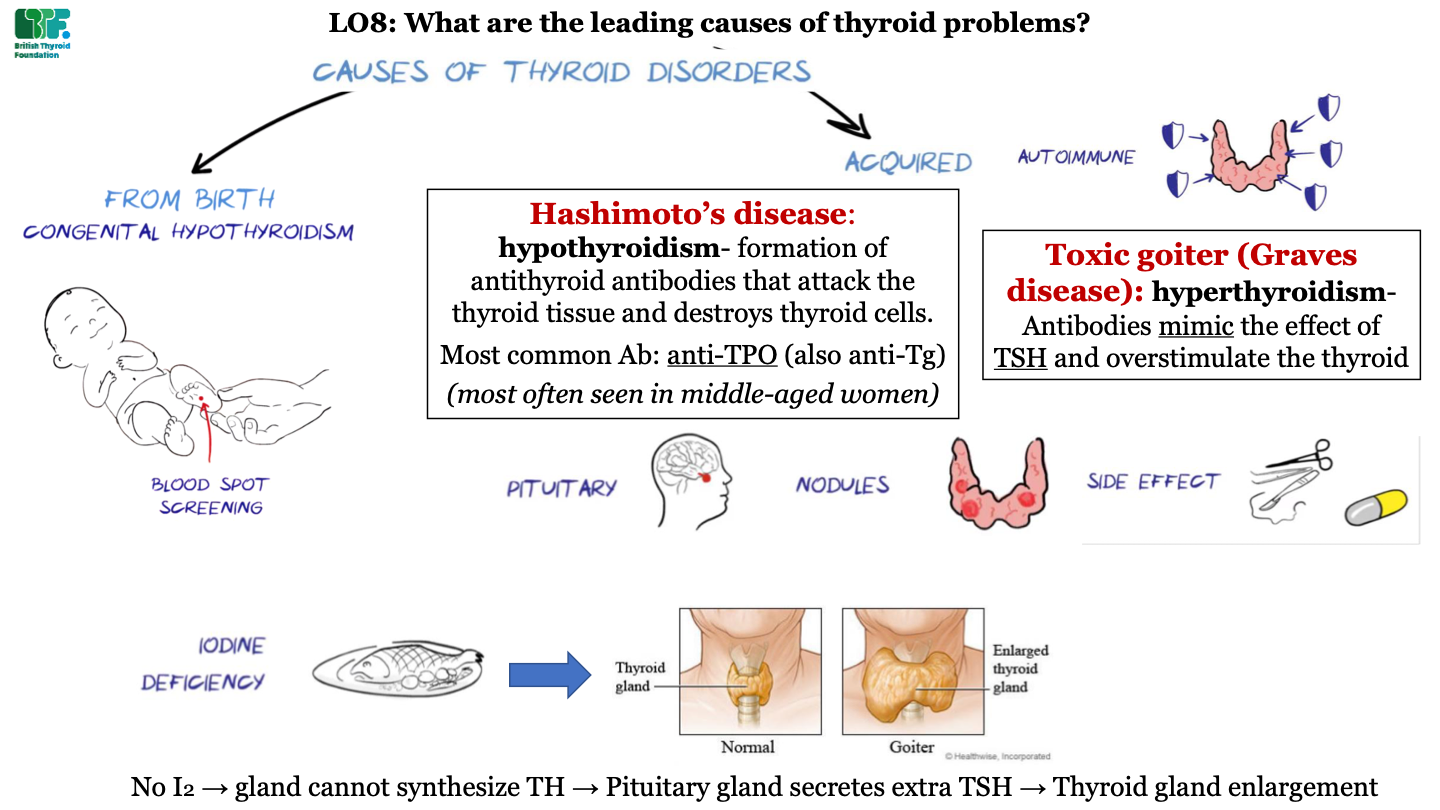
65
New cards
types of acquired thyroid diseases - nodules
growth of abnormal tissue
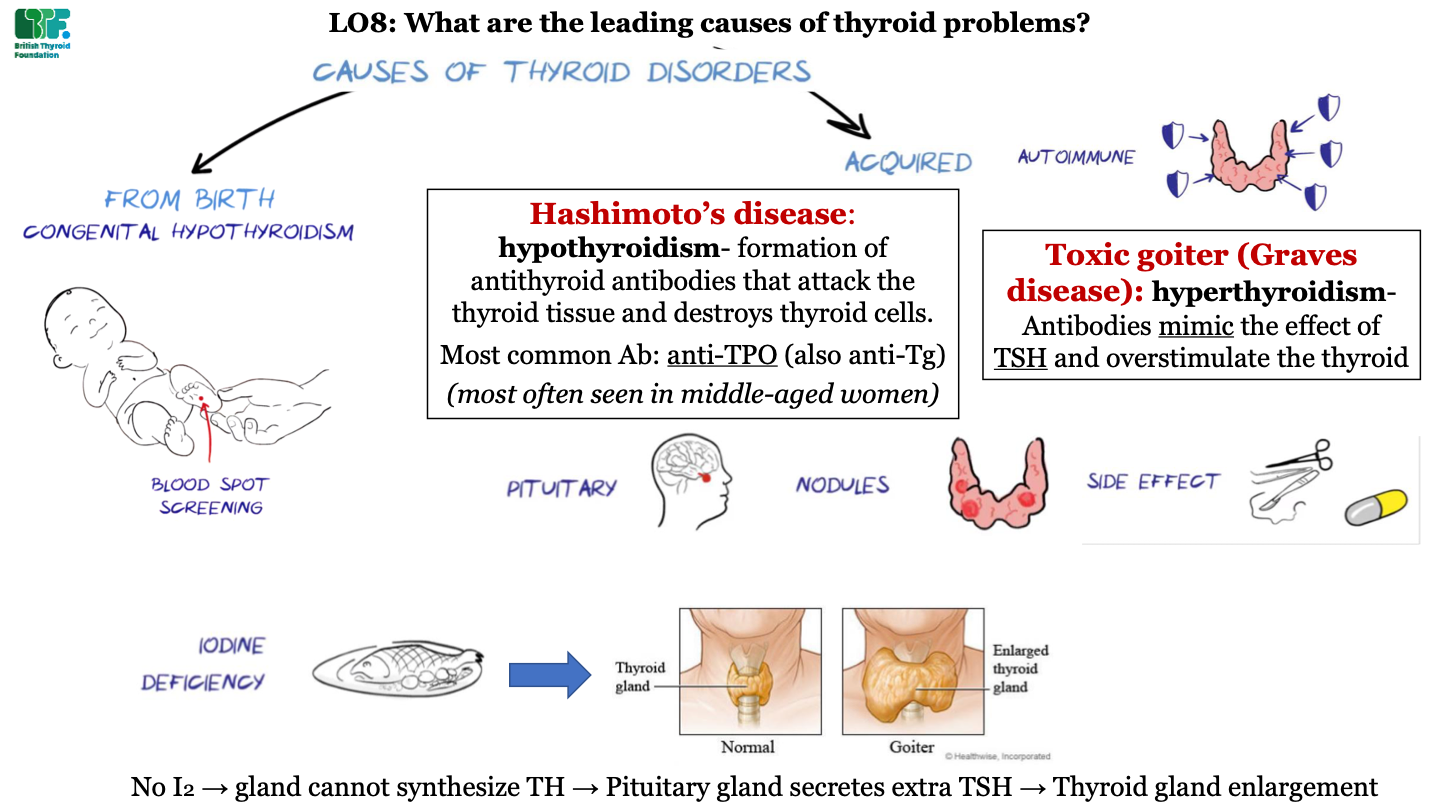
66
New cards
types of acquired thyroid diseases - side effects
side effects of surgery and drugs can cause thyroid disorders
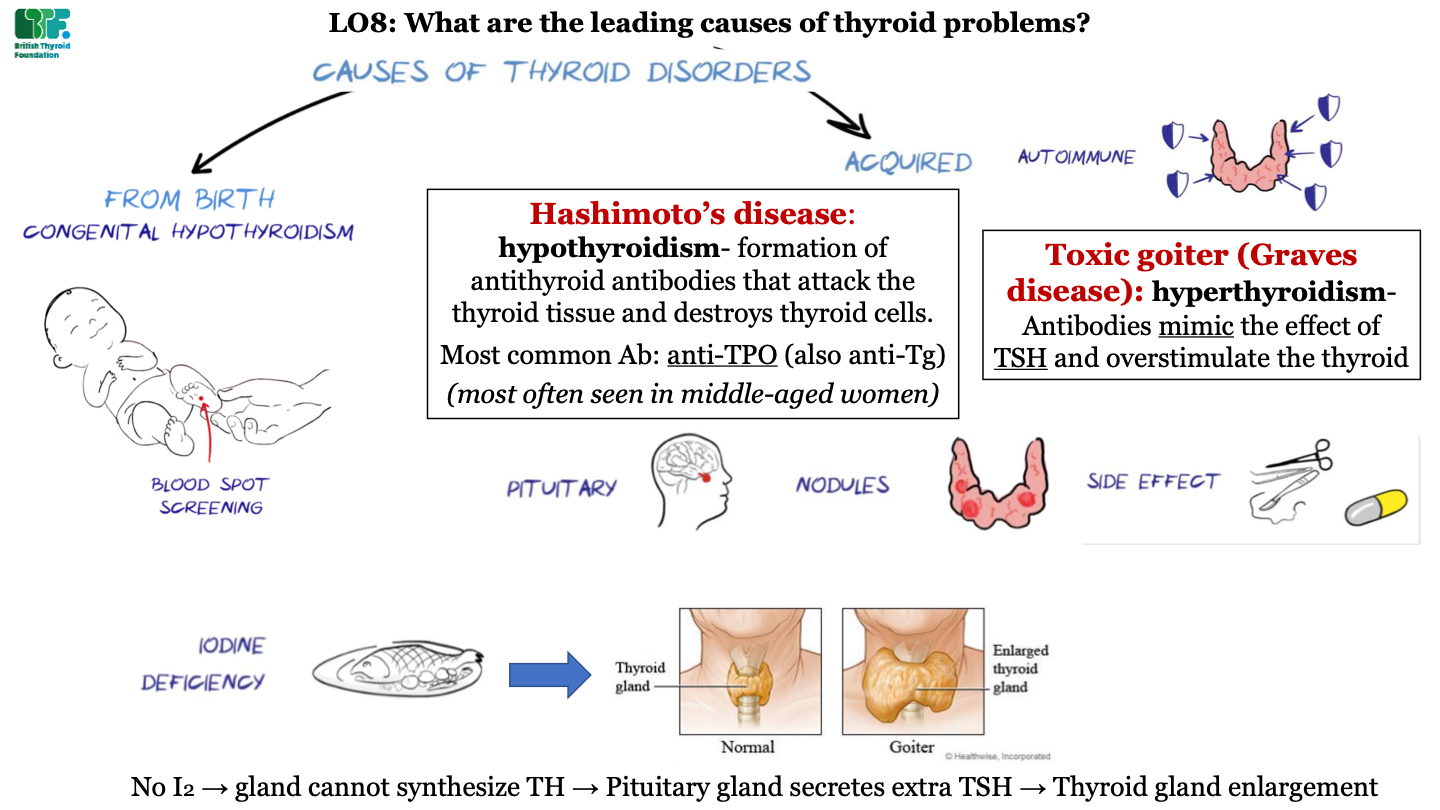
67
New cards
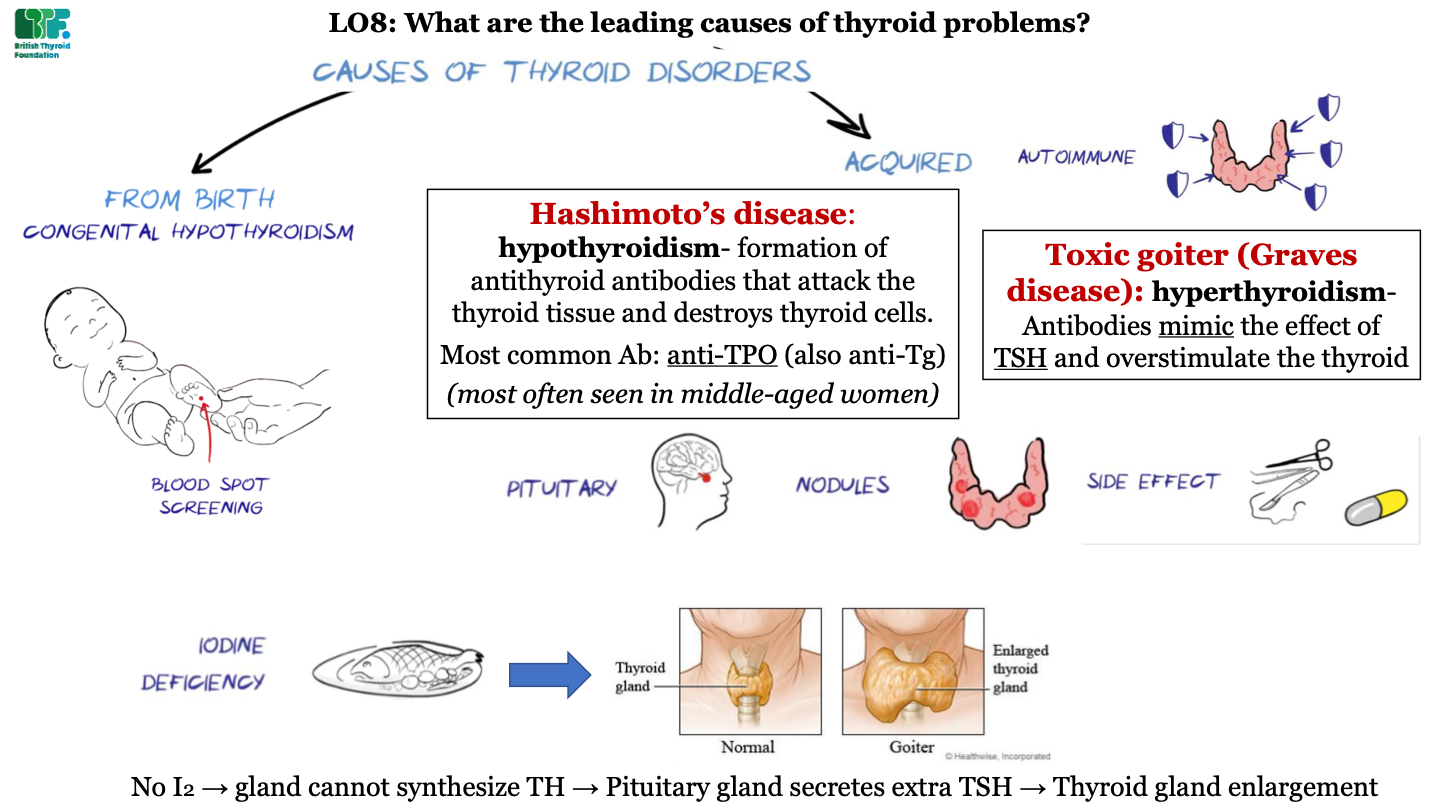
types of acquired thyroid diseases - iodine deficiency
dietary iodine deficiency can cause Goiter; this is an enlarged thyroid gland caused by a lack of thyroid hormone (due to low supply of iodine). This causes excess TSH secretion by the pituitary which enlarges the gland.
68
New cards
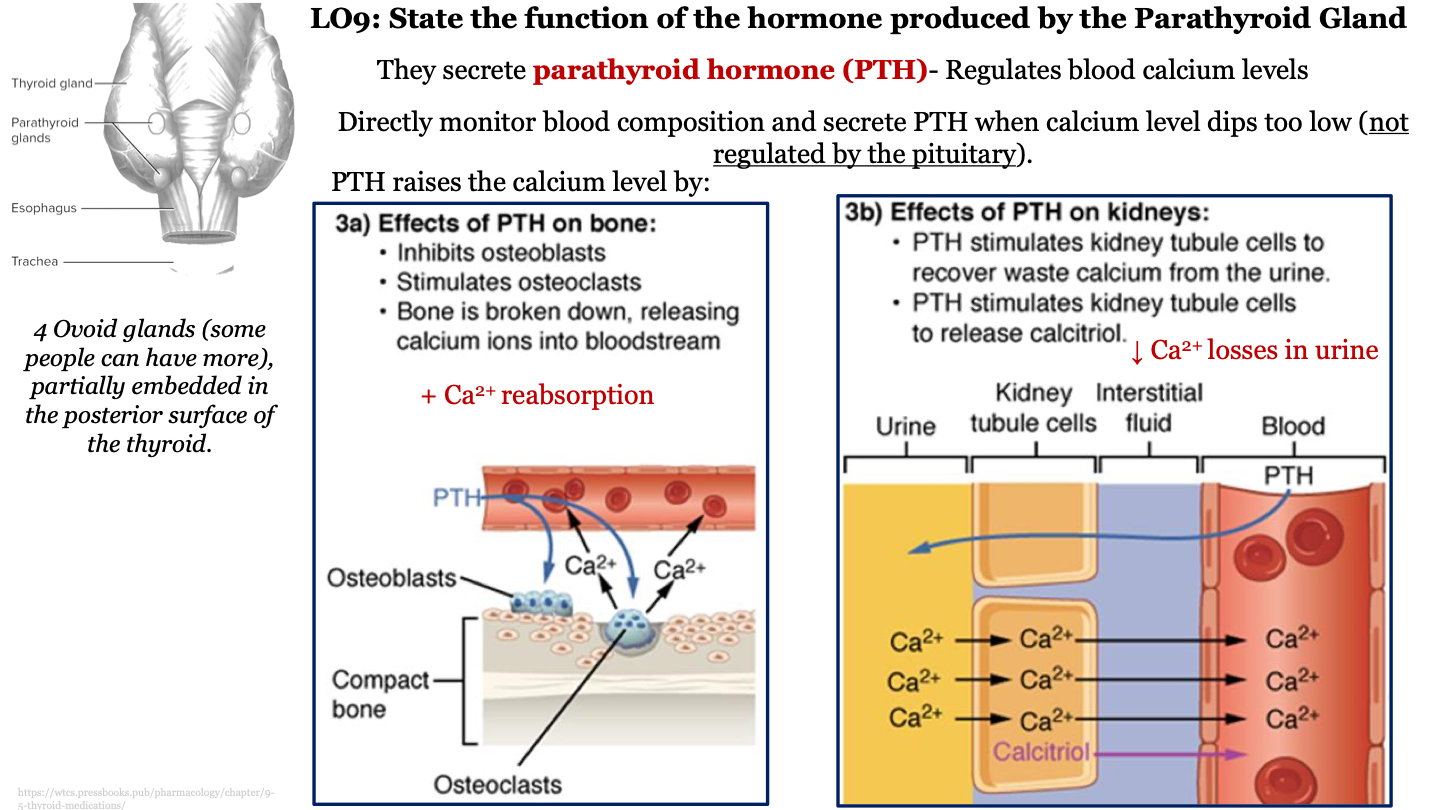
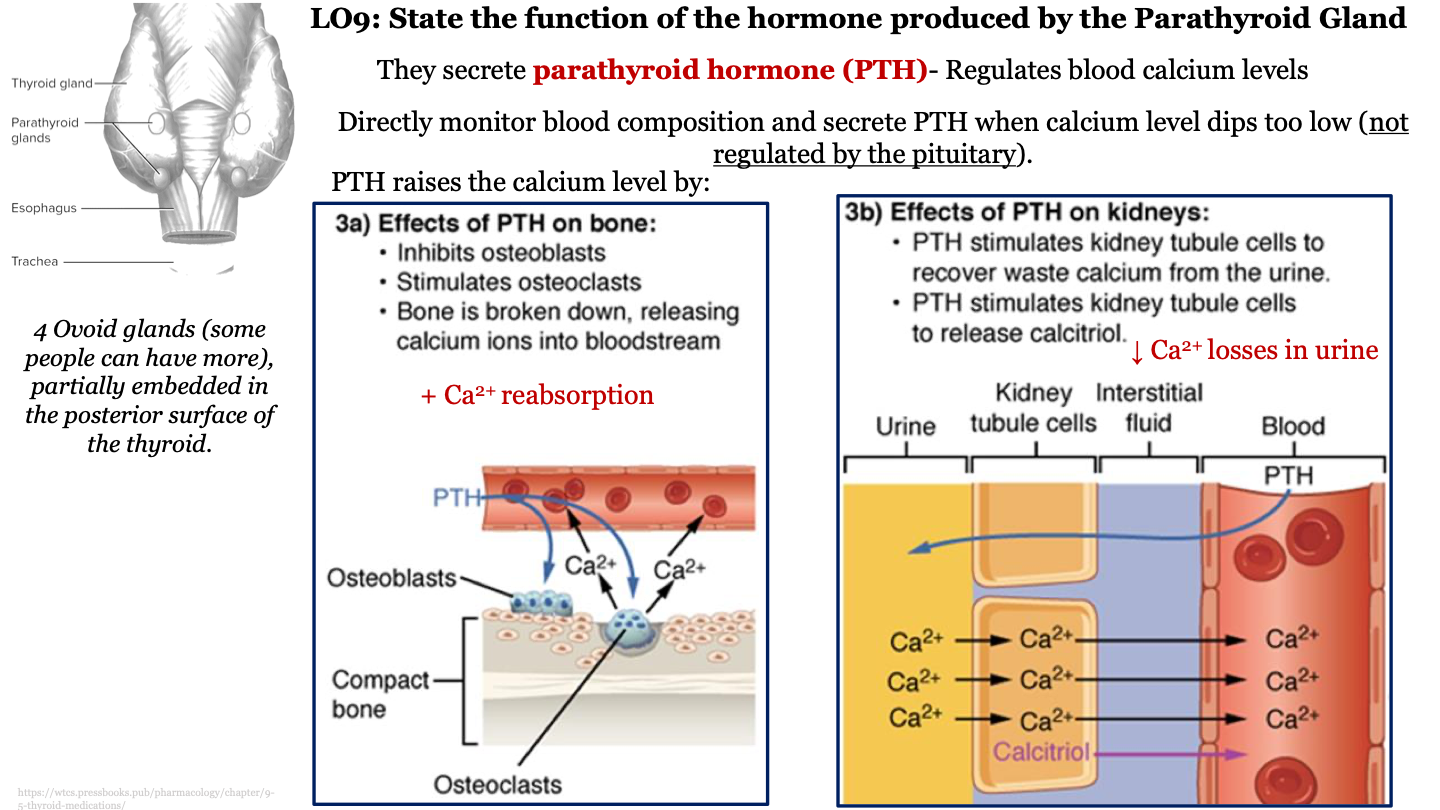
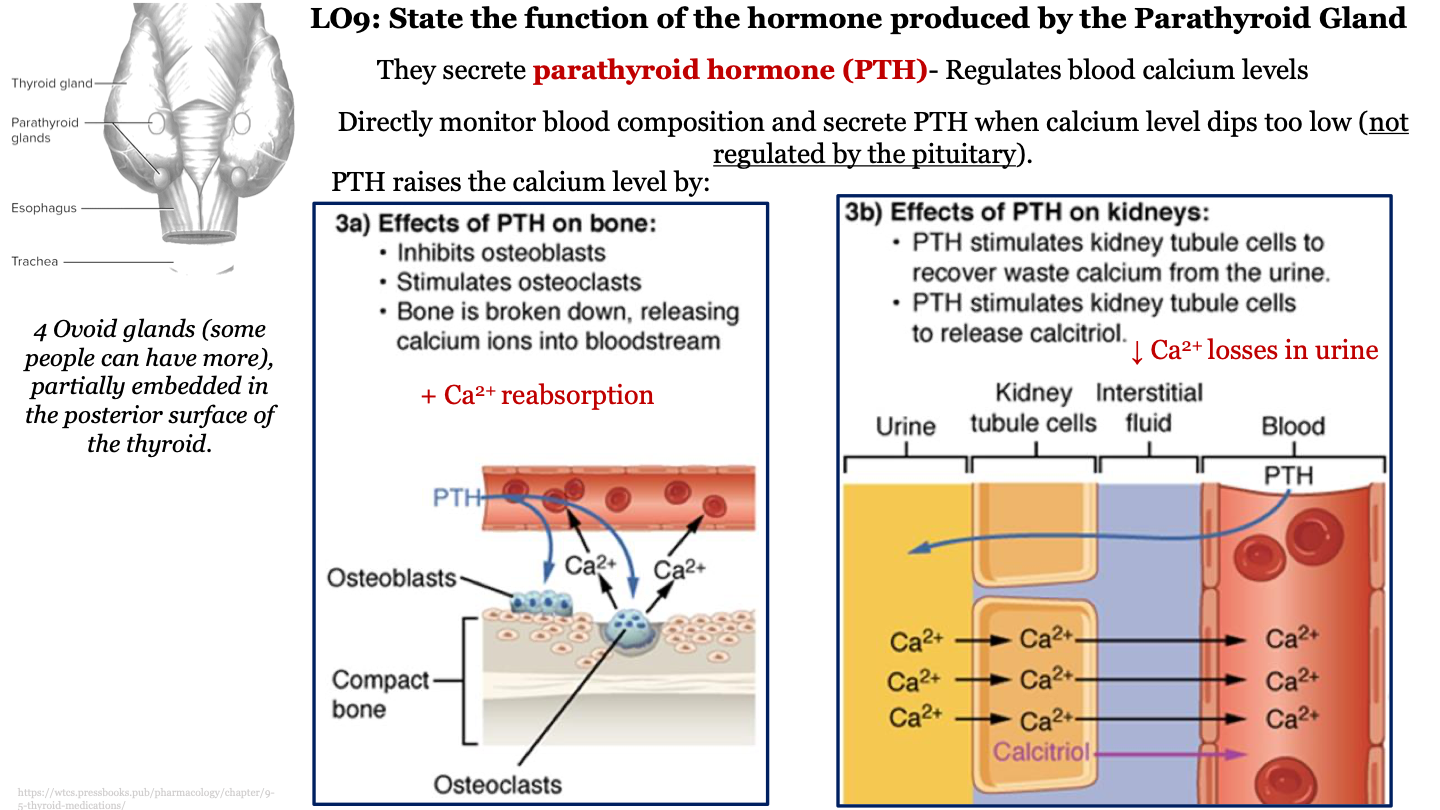
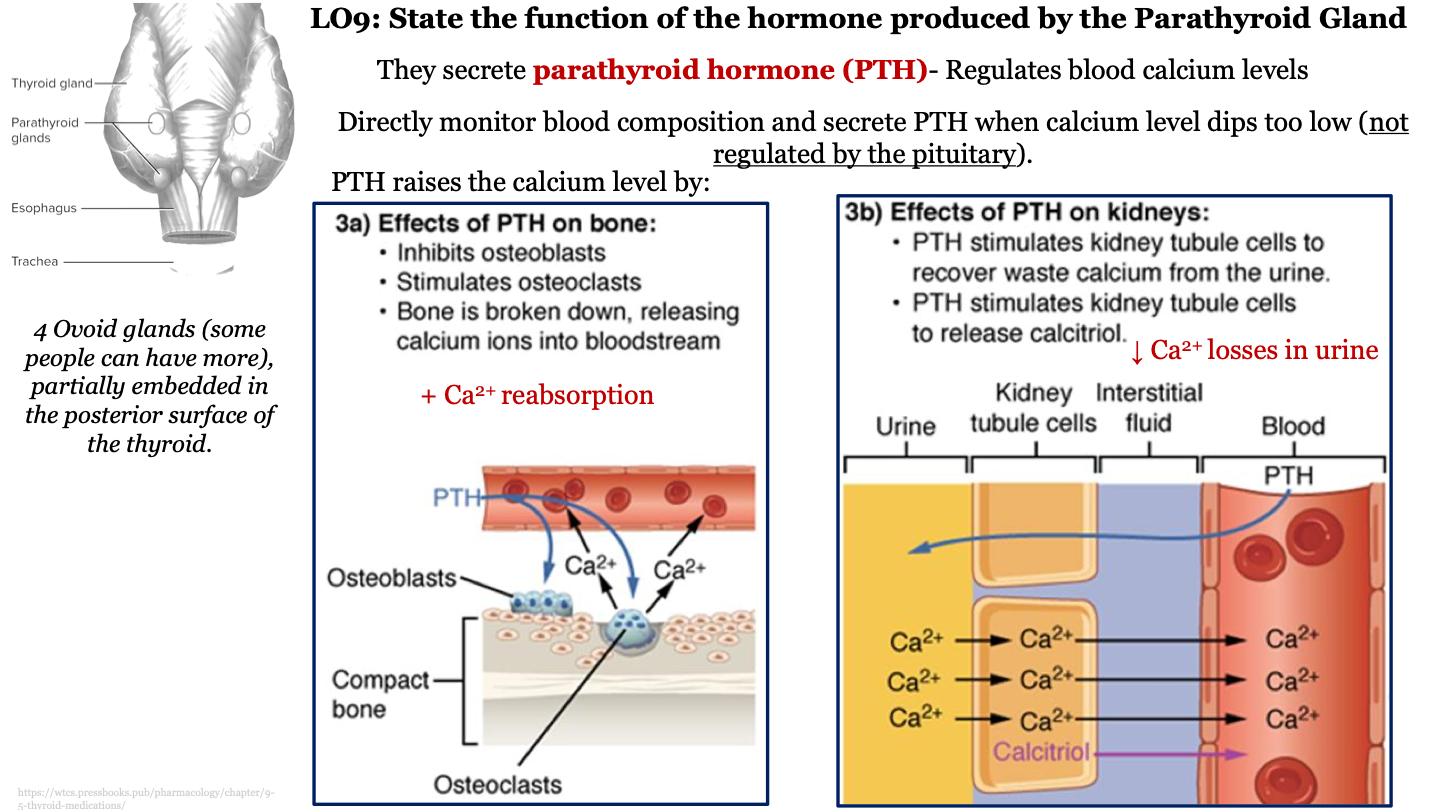
function of parathyroid gland
secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates calcium level in the blood; directly monitors blood composition and secretes PTH when calcium level dips too low (not regulated by the pituitary)
69
New cards
effects of PTH on bone
-inhibits osteoblasts
-stimulates osteoclasts
-bone is broken down, releasing calcium ions into bloodstream (calcium resorption)
-stimulates osteoclasts
-bone is broken down, releasing calcium ions into bloodstream (calcium resorption)
70
New cards
structure of parathyroid gland
4 ovoid glands (some people can have more), partially embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid
71
New cards
effects of PTH on kidneys
-PTH stimulates kidney tubule cells to recover waste calcium from the urine (decrease calcium loss from urine)
-PTH stimulates kidney tubule cells to release calcitriol
-PTH stimulates kidney tubule cells to release calcitriol
72
New cards
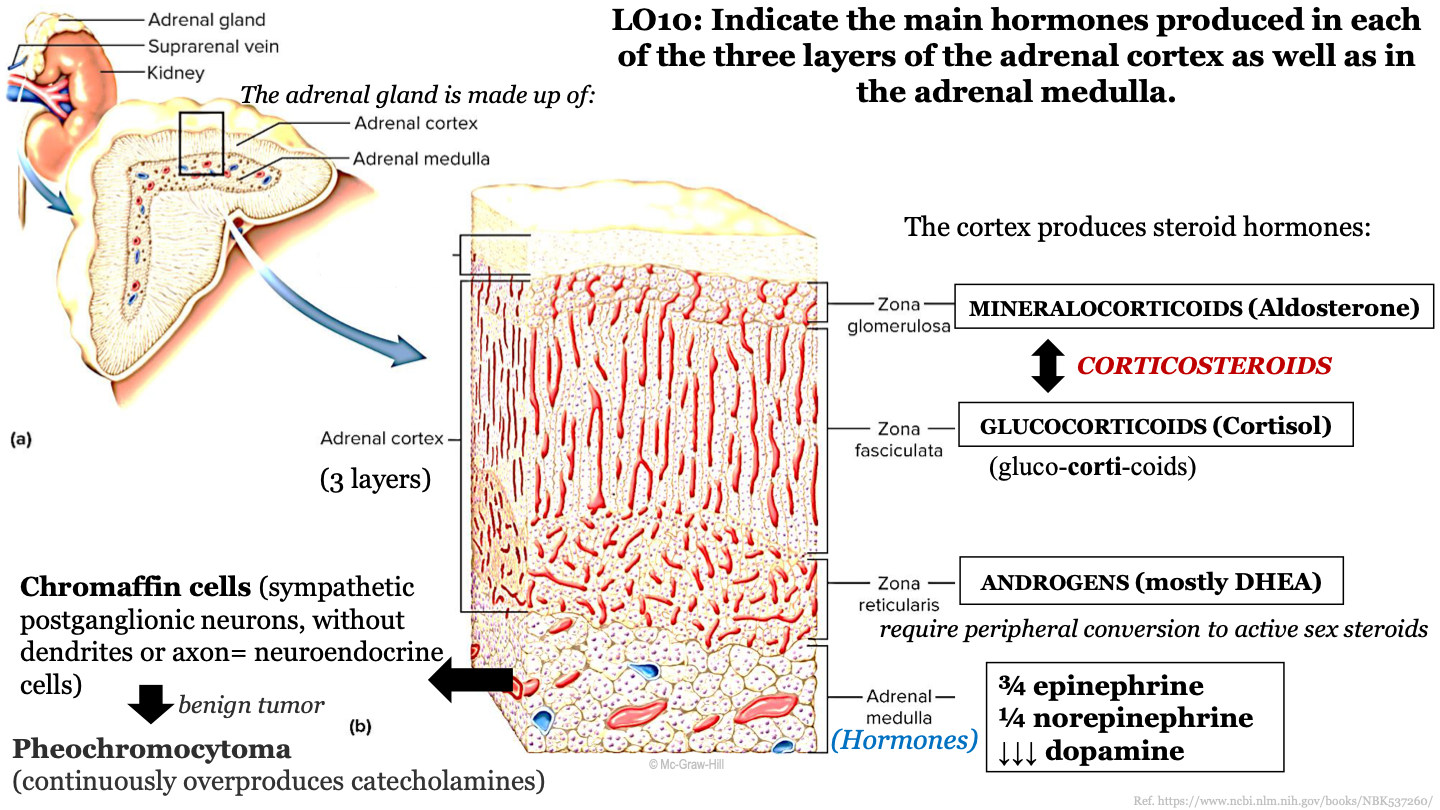
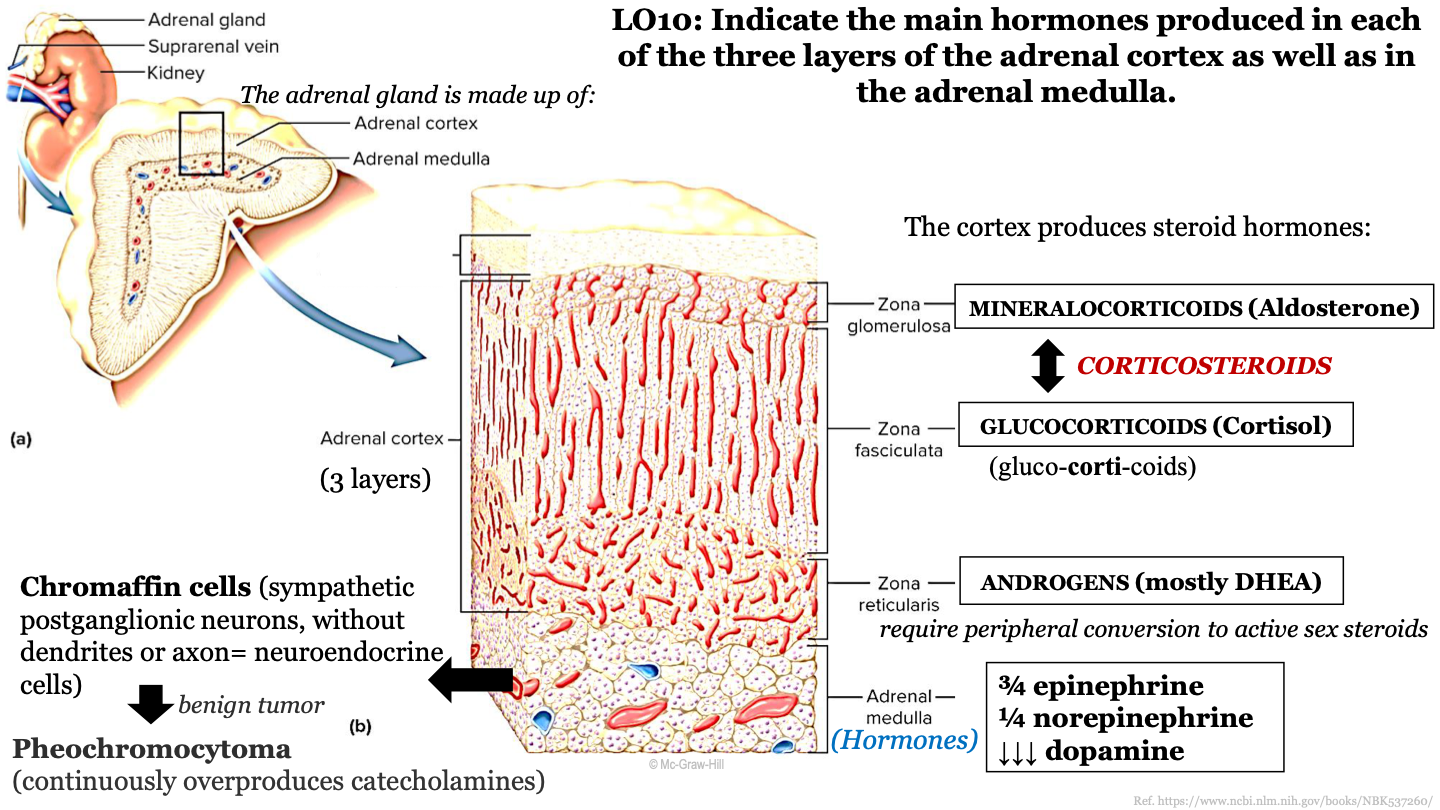
what structures make up the adrenal gland?
the adrenal cortex (superficial) and the adrenal medulla (deep)
73
New cards
what are the 3 zones of the adrenal cortex (from superficial to deep)?
-zona glomerulosa
-zona fasciculata
-zona reticularis
-zona fasciculata
-zona reticularis
74
New cards
what steroid hormone does the zona glomerulosa produce?
mineralcorticoids (Aldosterone)
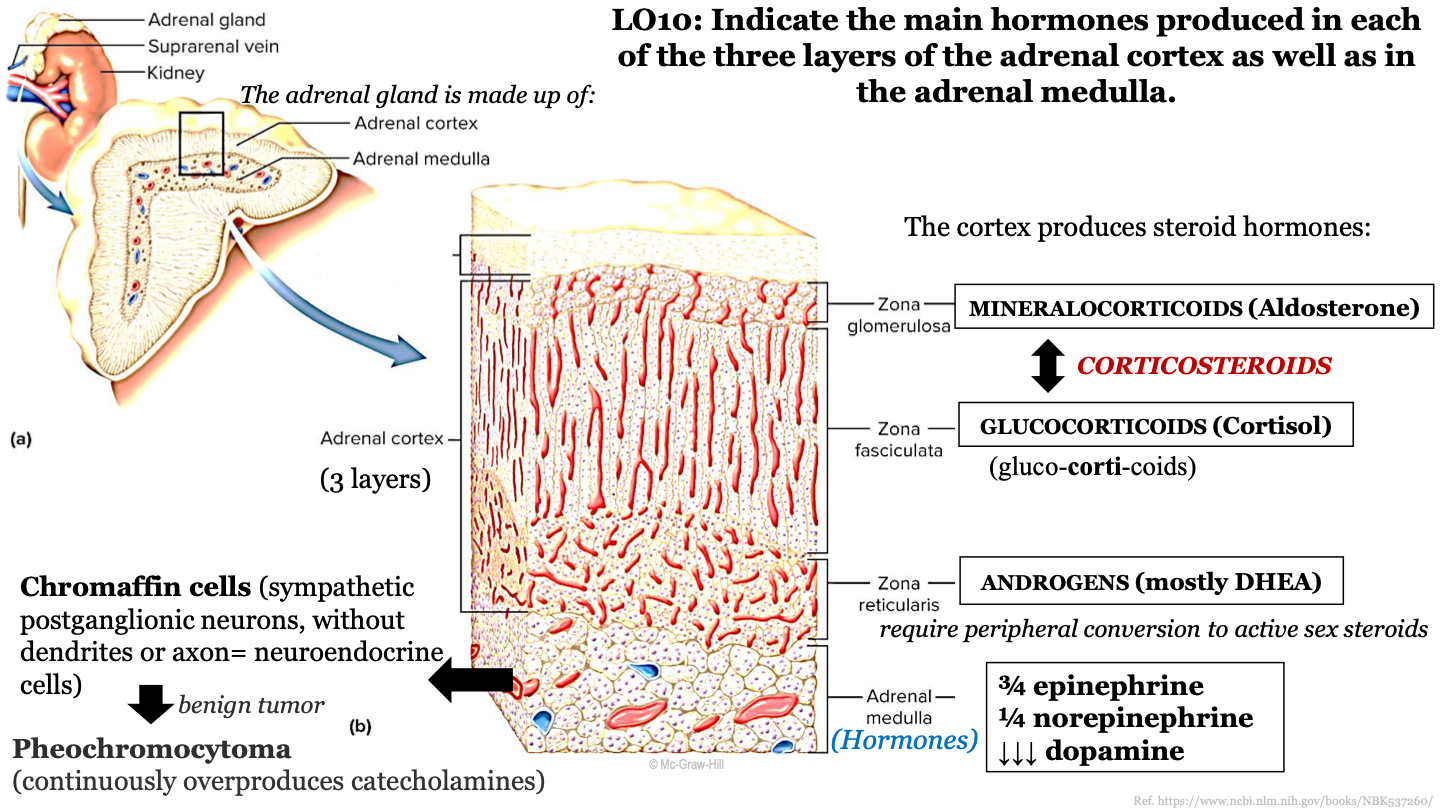
75
New cards
what steroid hormone does the zona fasciculata produce?
glucocorticoids (cortisol)
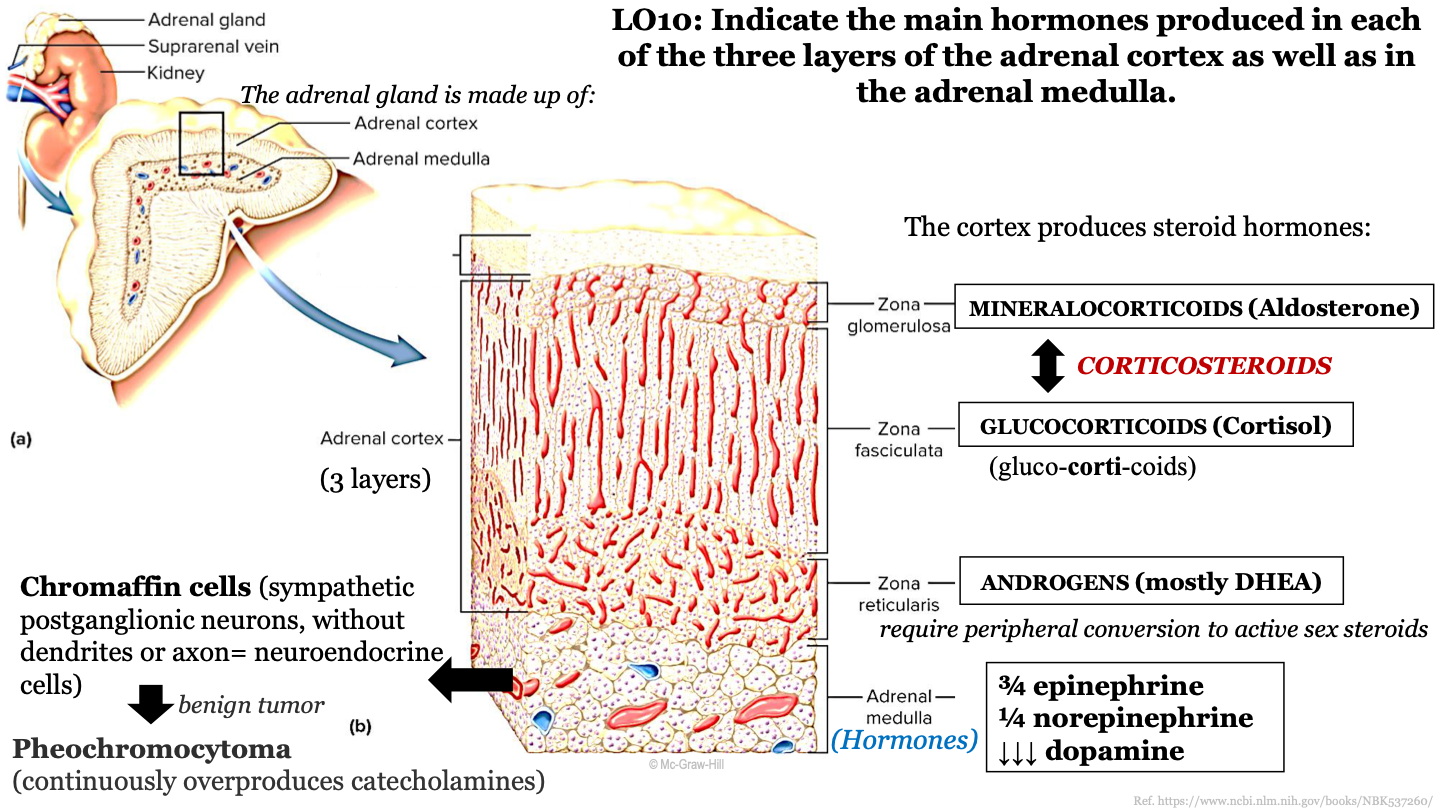
76
New cards
what steroid hormone does the zona reticularis produce?
androgens (mostly DHEA)
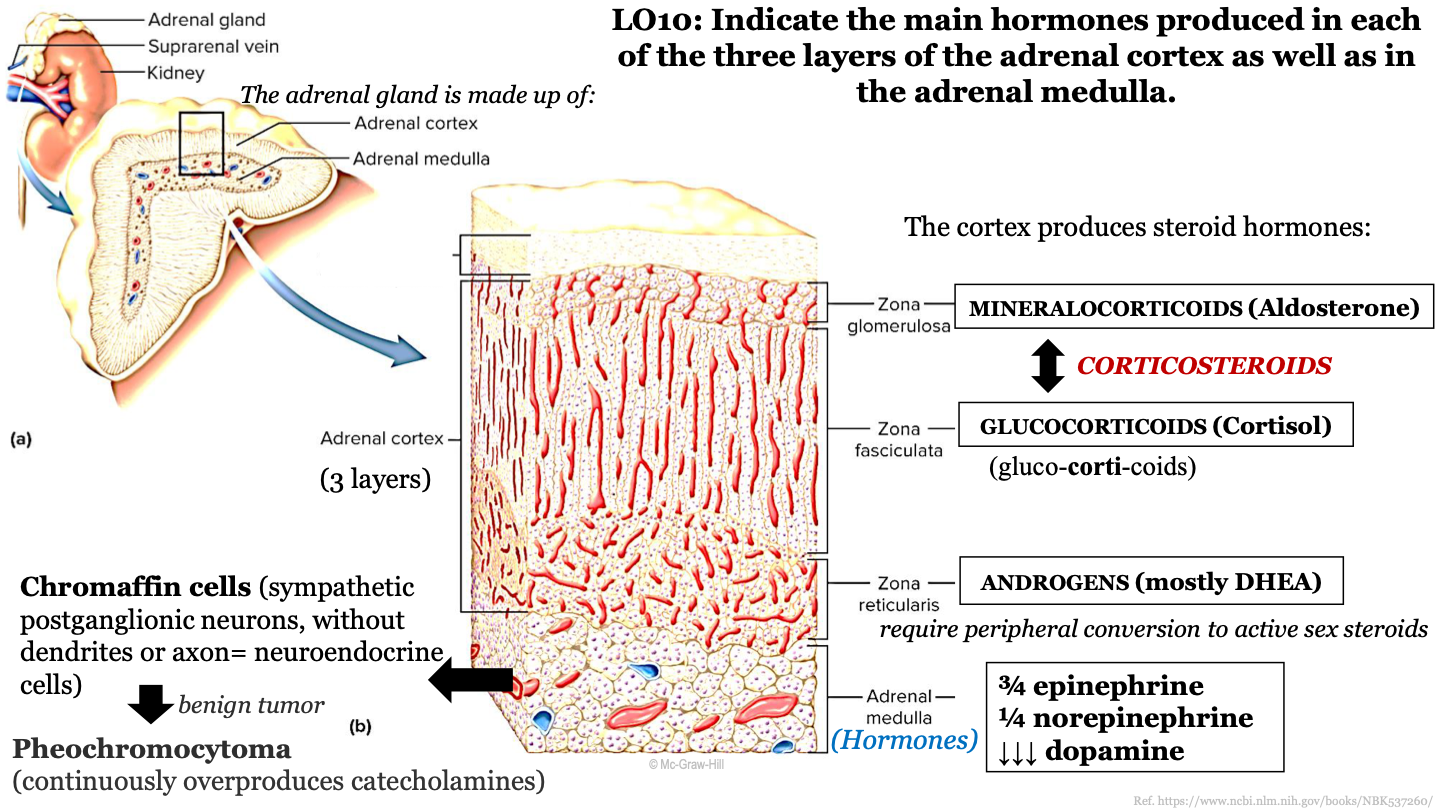
77
New cards
which steroid hormones are known as corticosteroids?
mineralcorticoids (Aldosterone) and glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
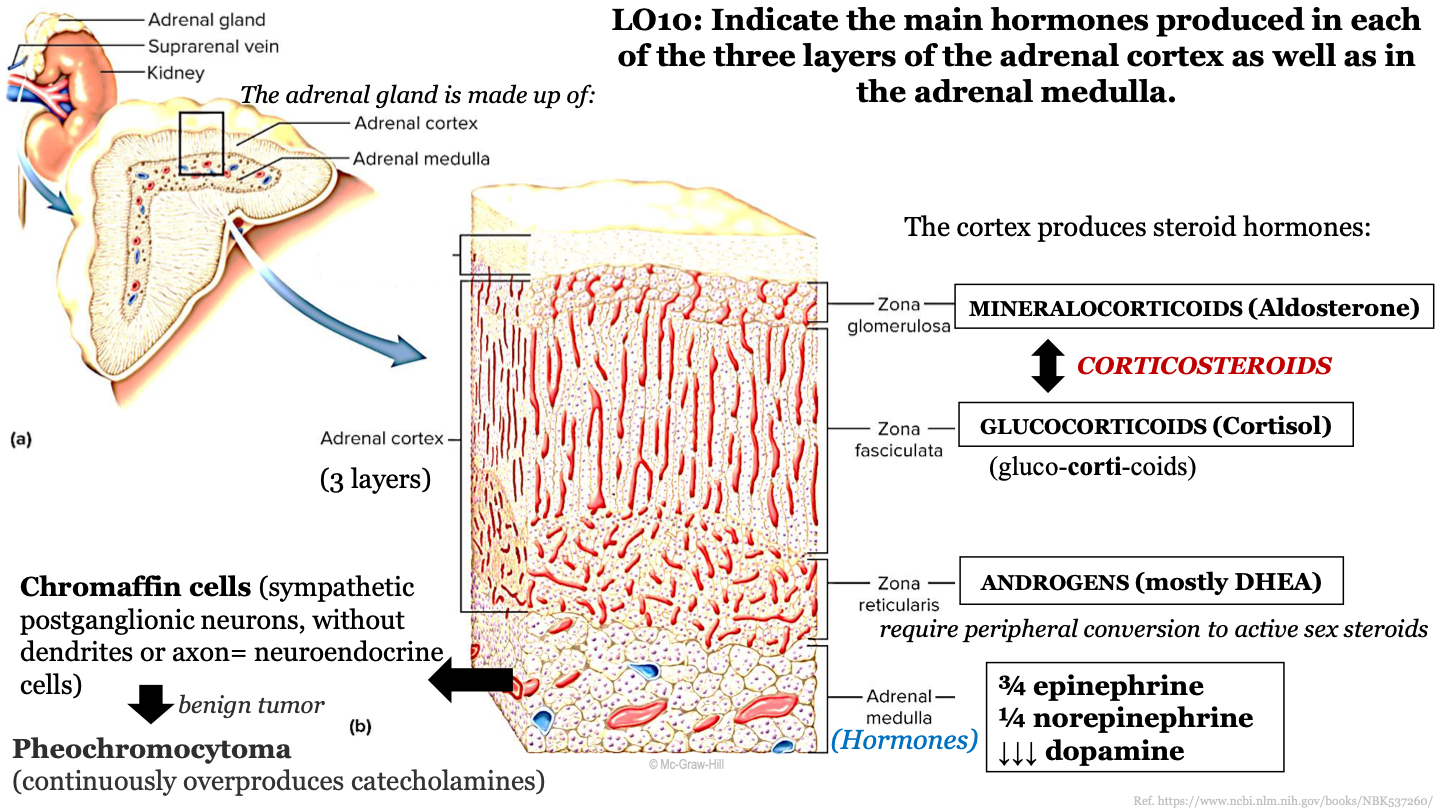
78
New cards
what do androgens (mostly DHEA) require to activate sex steroids?
peripheral conversion
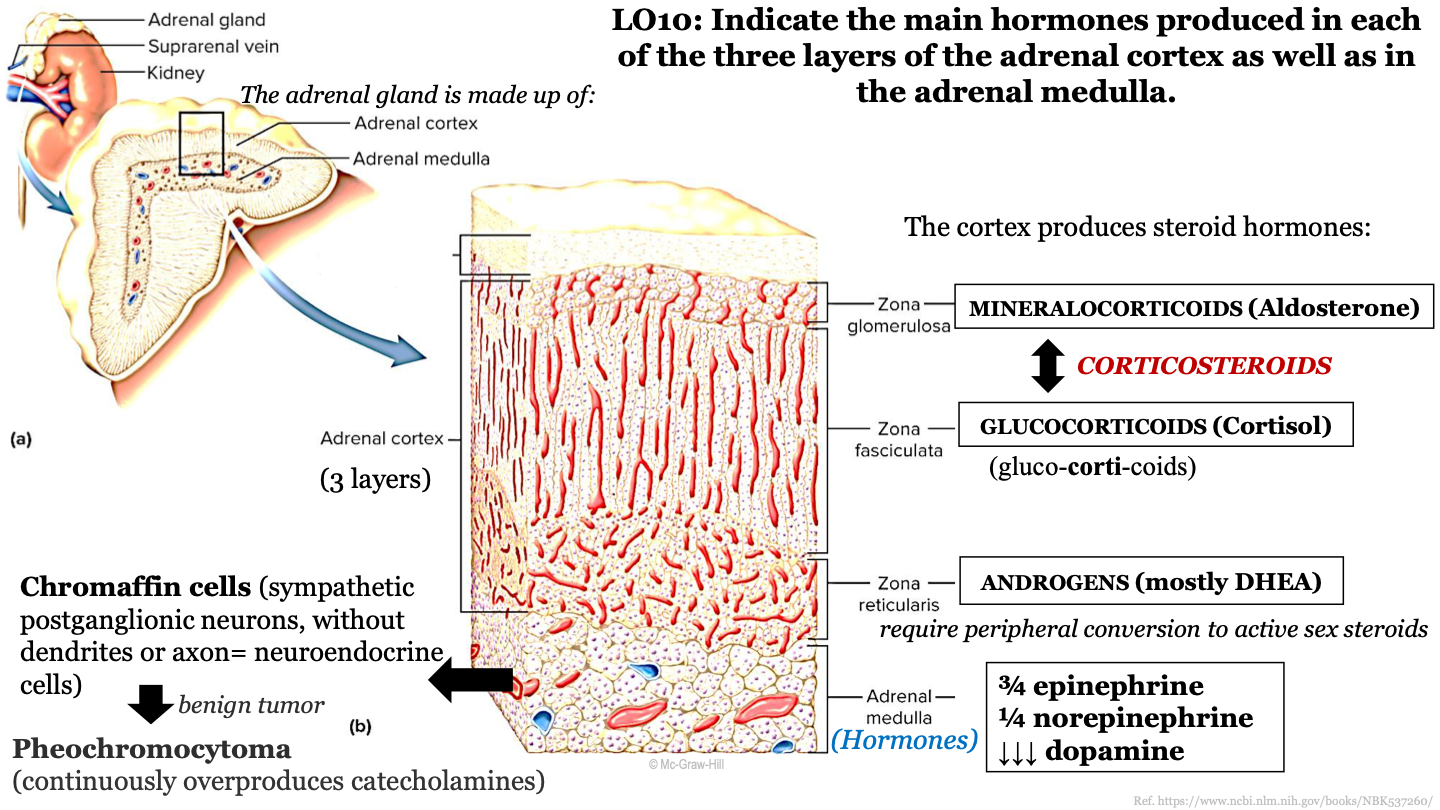
79
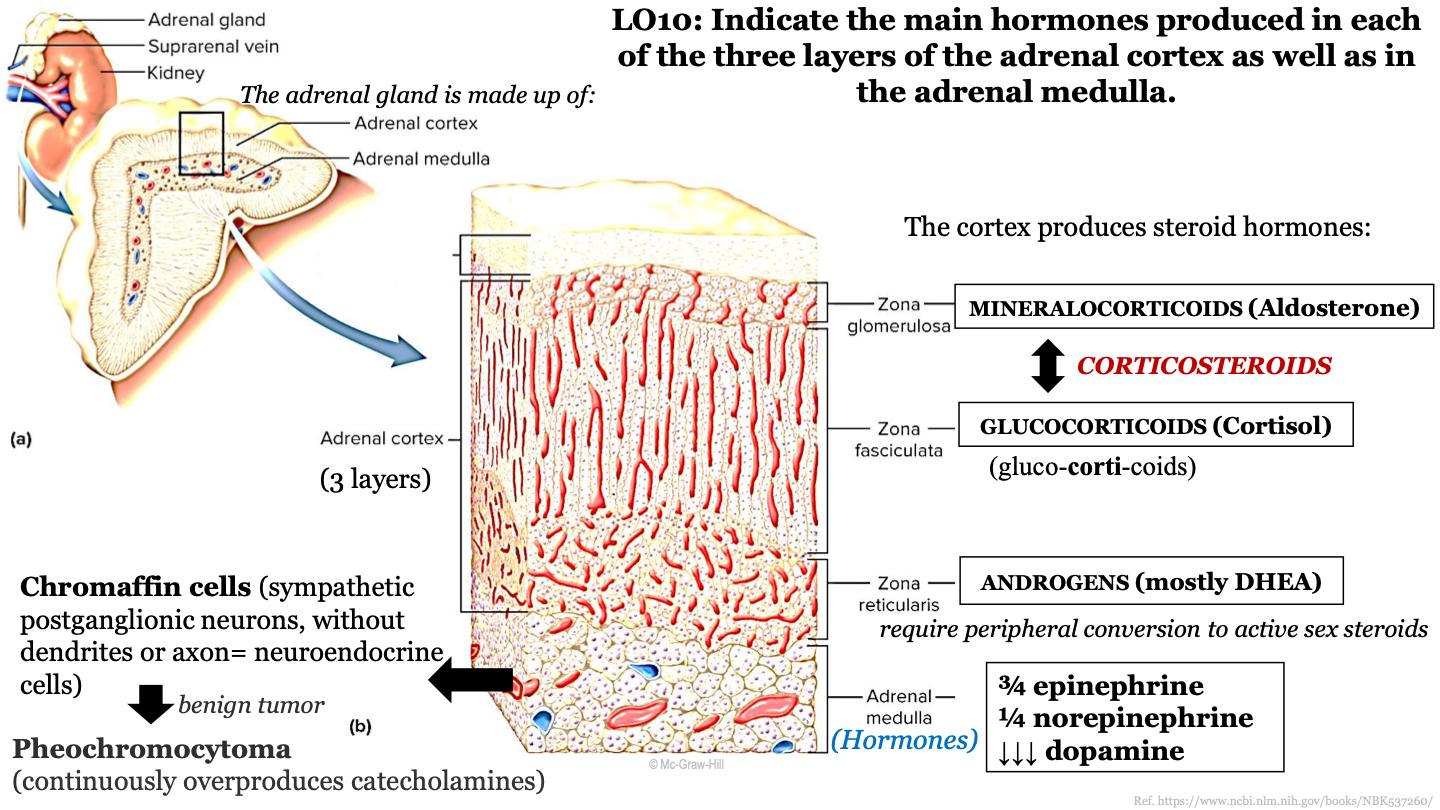
New cards
chromaffin cells
sympathetic postganglionic neurons, without dendrites or axons; these are neuroendocrine cells; they release epinephrine and noepinephrine (catecholamines); found in adrenal medulla
80
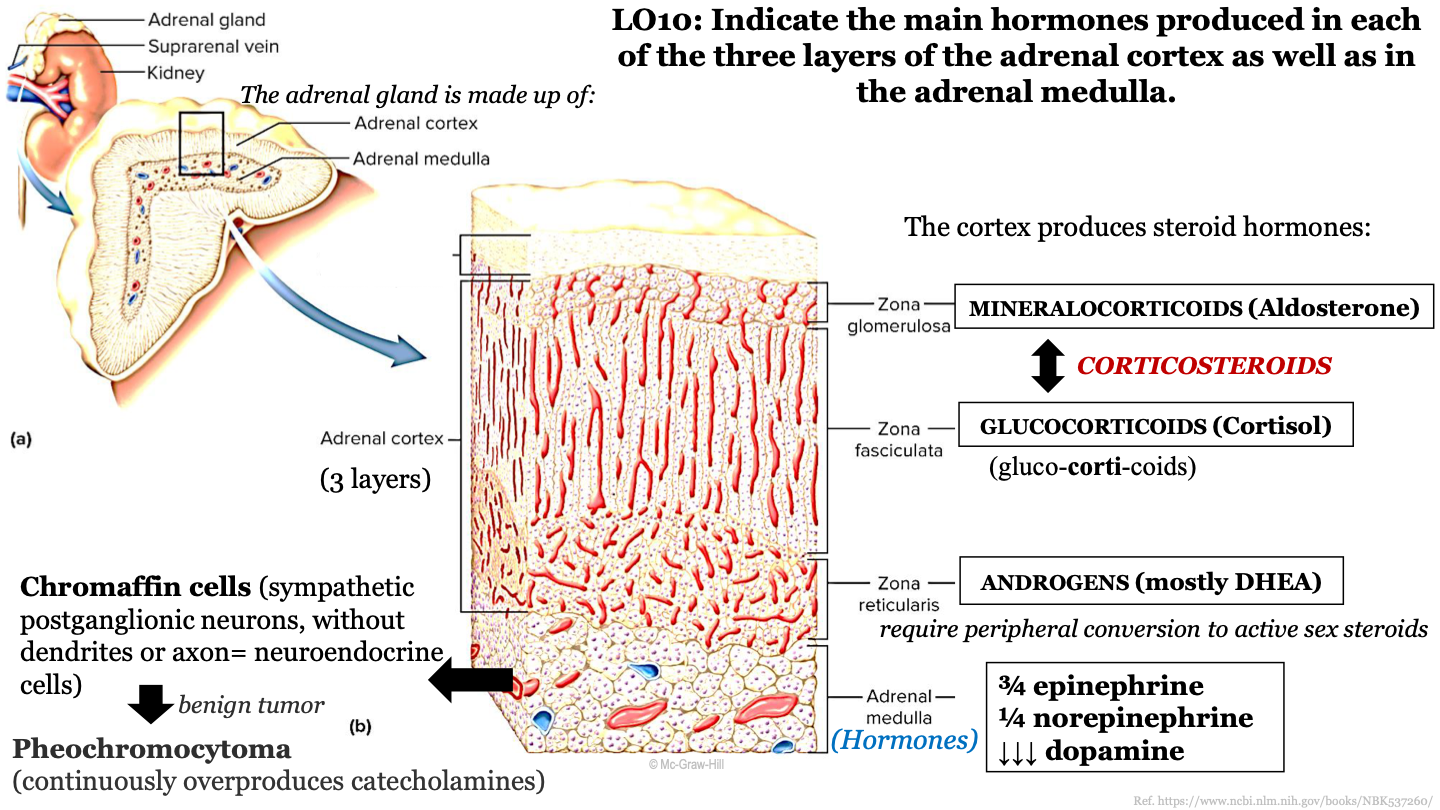
New cards
what is a benign tumor of the chromaffin cells in the adrenal gland called?
pheochromocytoma; continuously overproduces catecholamines
81
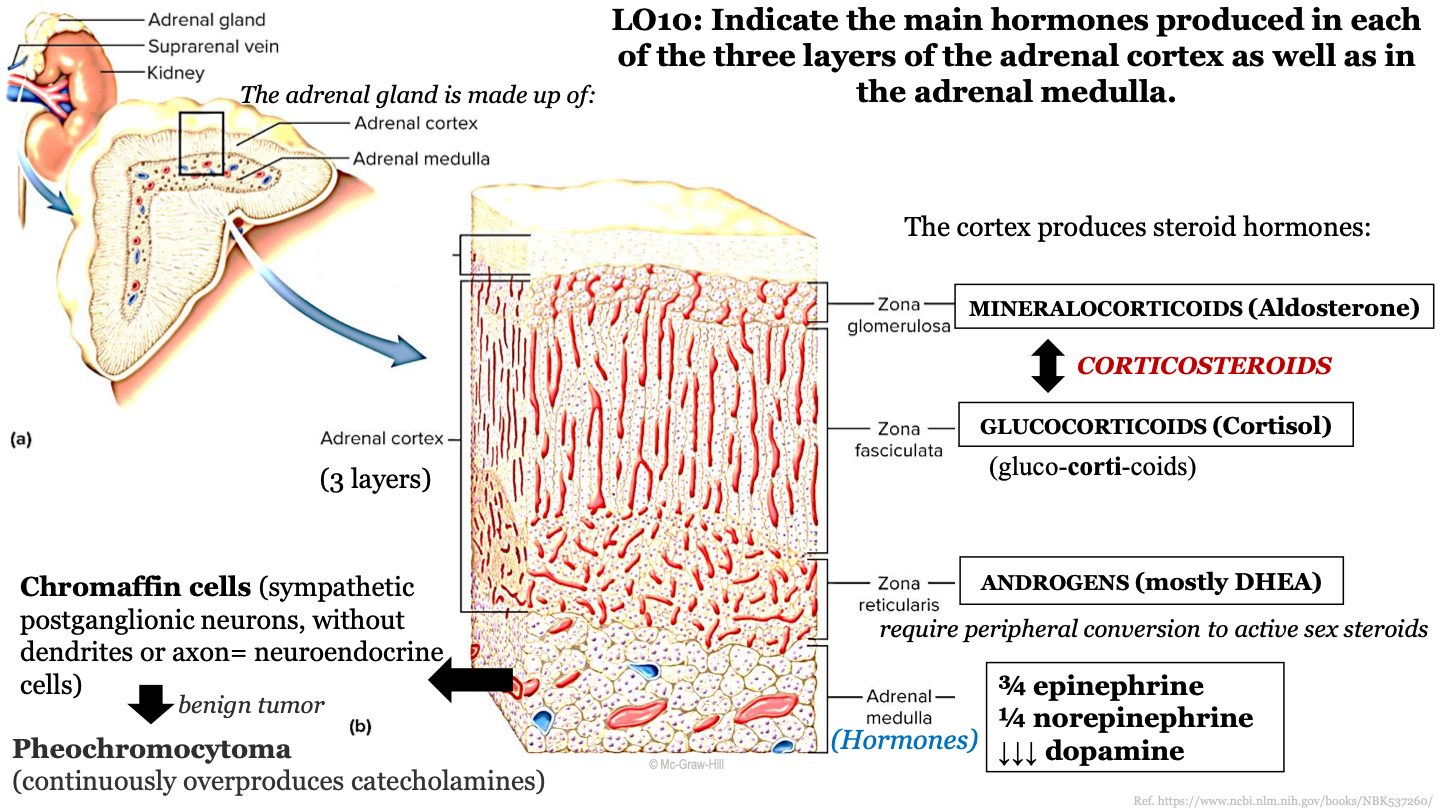
New cards
adrenal medulla function
releases hormones into the bloodstream; produces 3/4 epinephrine, 1/4 noepinephrine, and dopamine
82
New cards
main function of aldosterone
stimulates kidneys to retain sodium; water is retained with it by osmosis; this increases the circulating volume and therefore increases BP
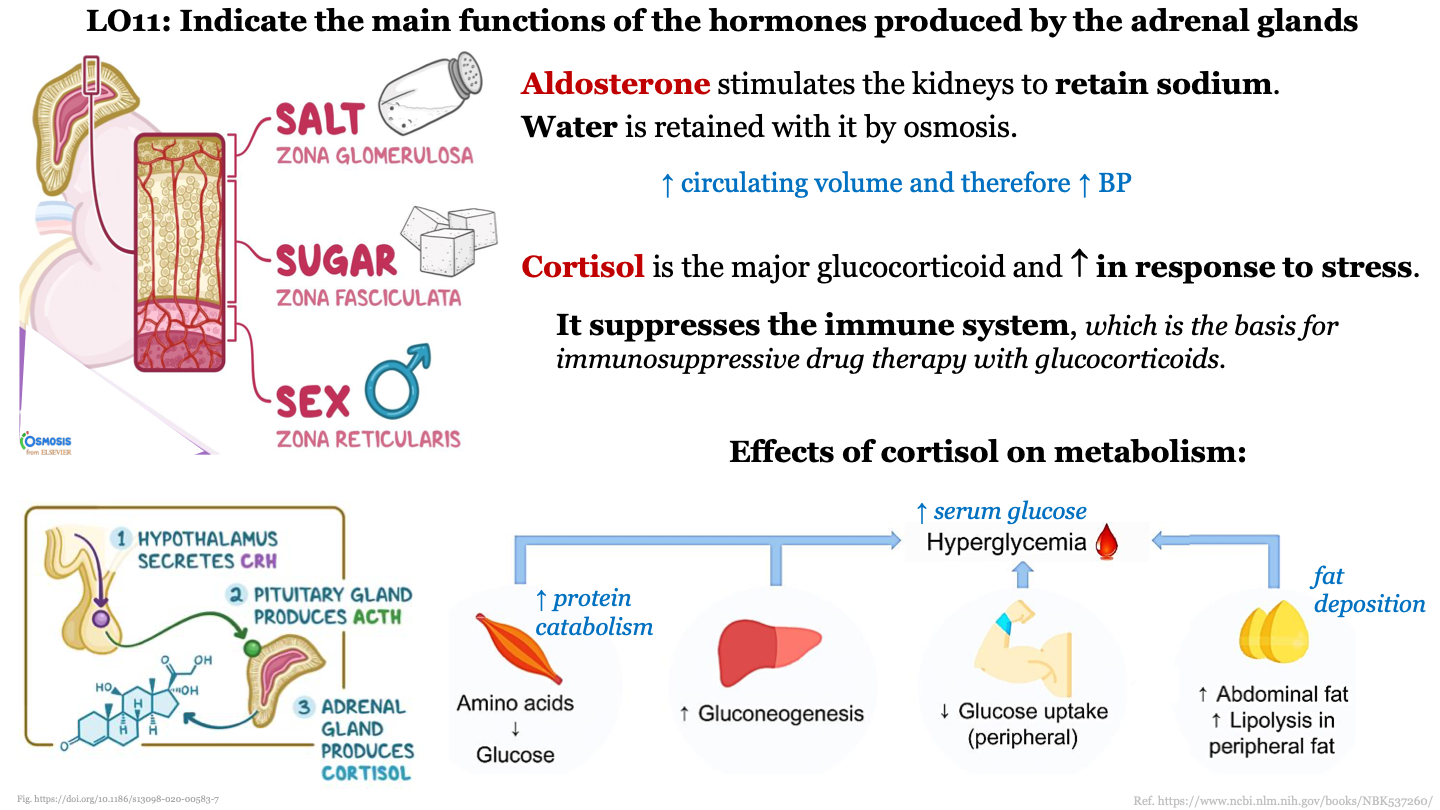
83
New cards
main function of cortisol
it is the major glucocorticoid and increases in response to stress; it suppresses the immune system (basis for immunosuppressive drug therapy with glucocorticoids)
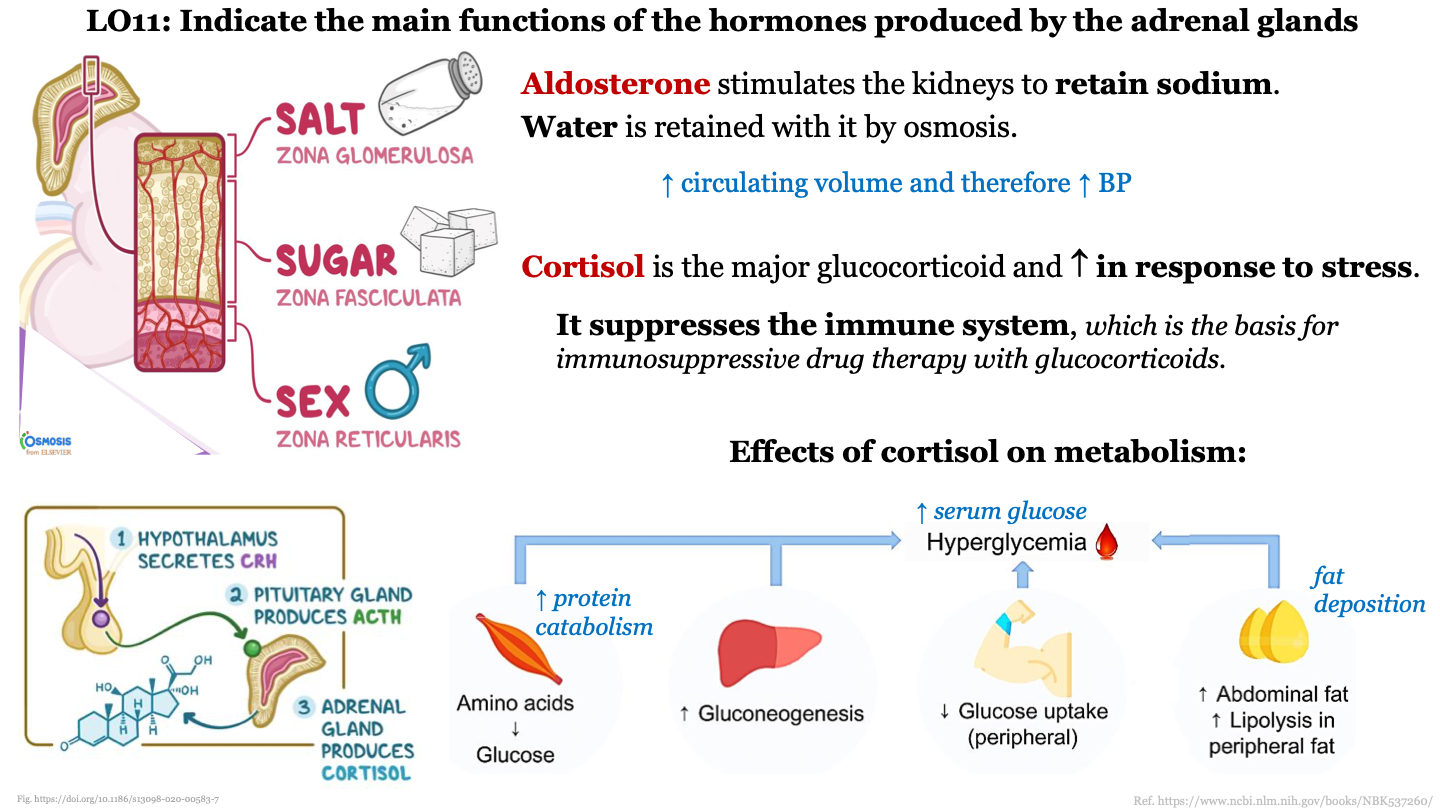
84
New cards
effects of cortisol on metabolism
-increases protein catabolism by breaking amino acids into glucose
-increases gluconeogenesis (process that transforms non carbohydrate substances into glucose)
-decreases glucose uptake (peripheral)
-increases fat deposition (increased abdominal fat and lipolysis in peripheral fat)
*all of these effects contribute to hyperglycemia
-increases gluconeogenesis (process that transforms non carbohydrate substances into glucose)
-decreases glucose uptake (peripheral)
-increases fat deposition (increased abdominal fat and lipolysis in peripheral fat)
*all of these effects contribute to hyperglycemia
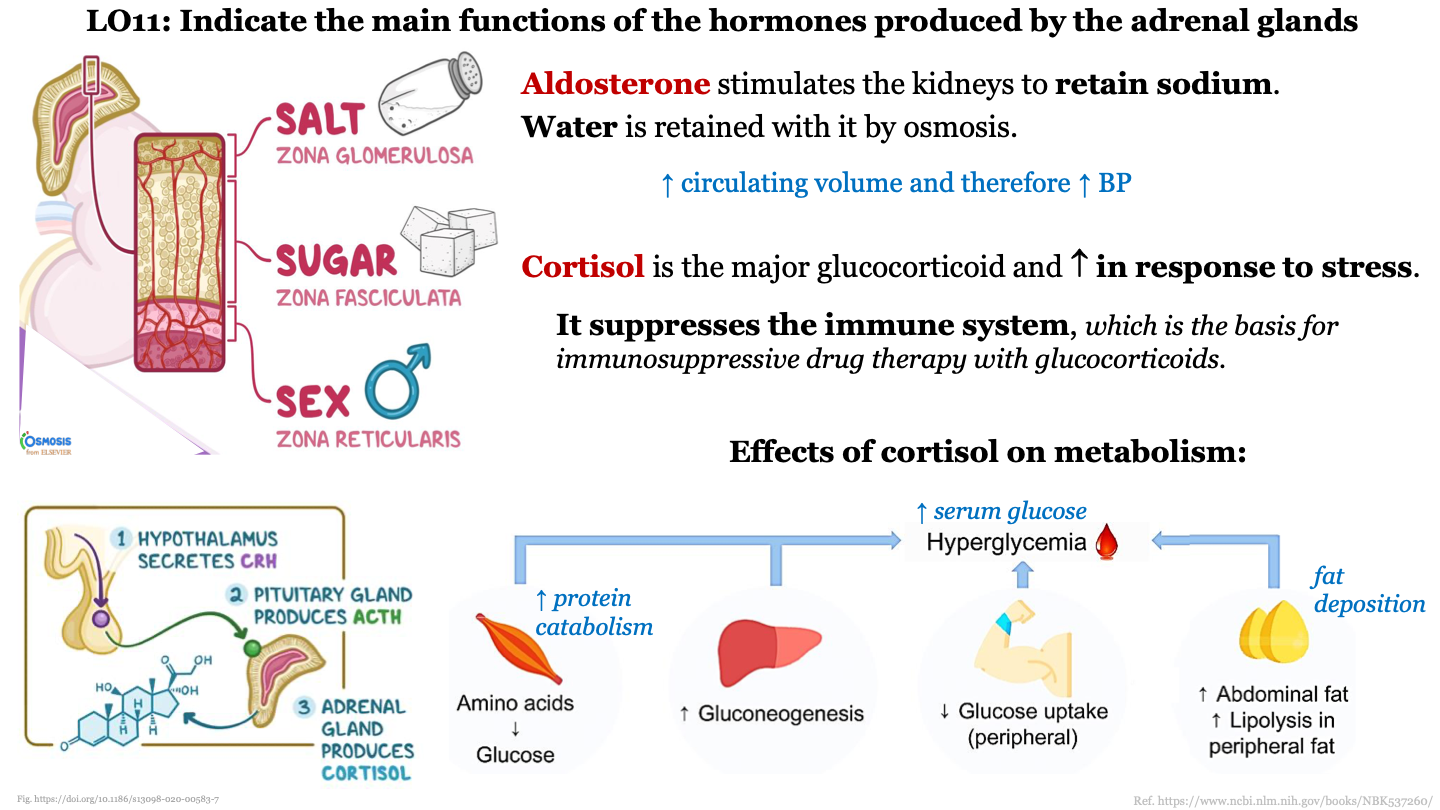
85
New cards
main function of zona glomerulosa
aldosterone retains sodium; SALT
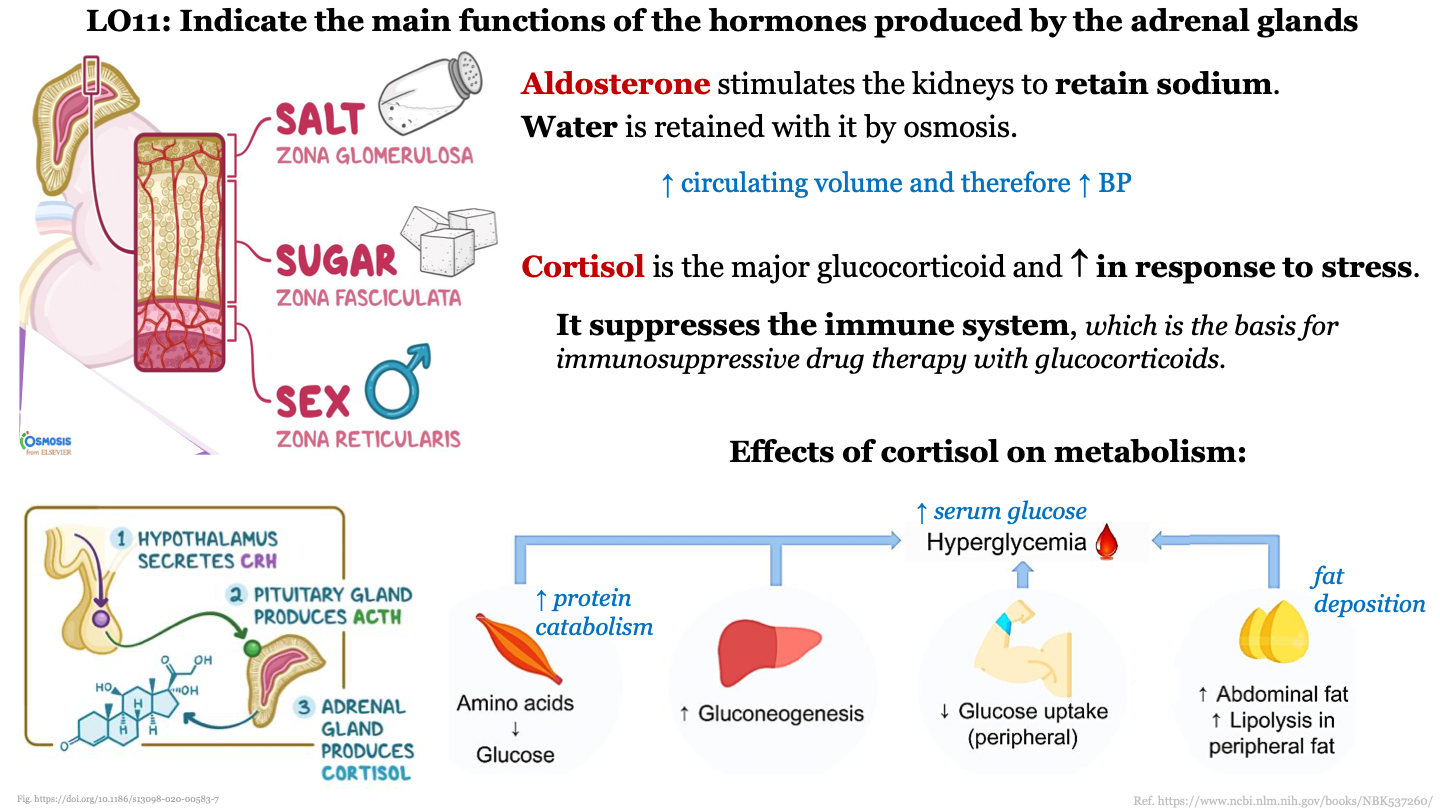
86
New cards
main function of zona fasciculata
produces cortisol which causes glucose release into bloodstream and can lead to hyperglycemia; SUGAR
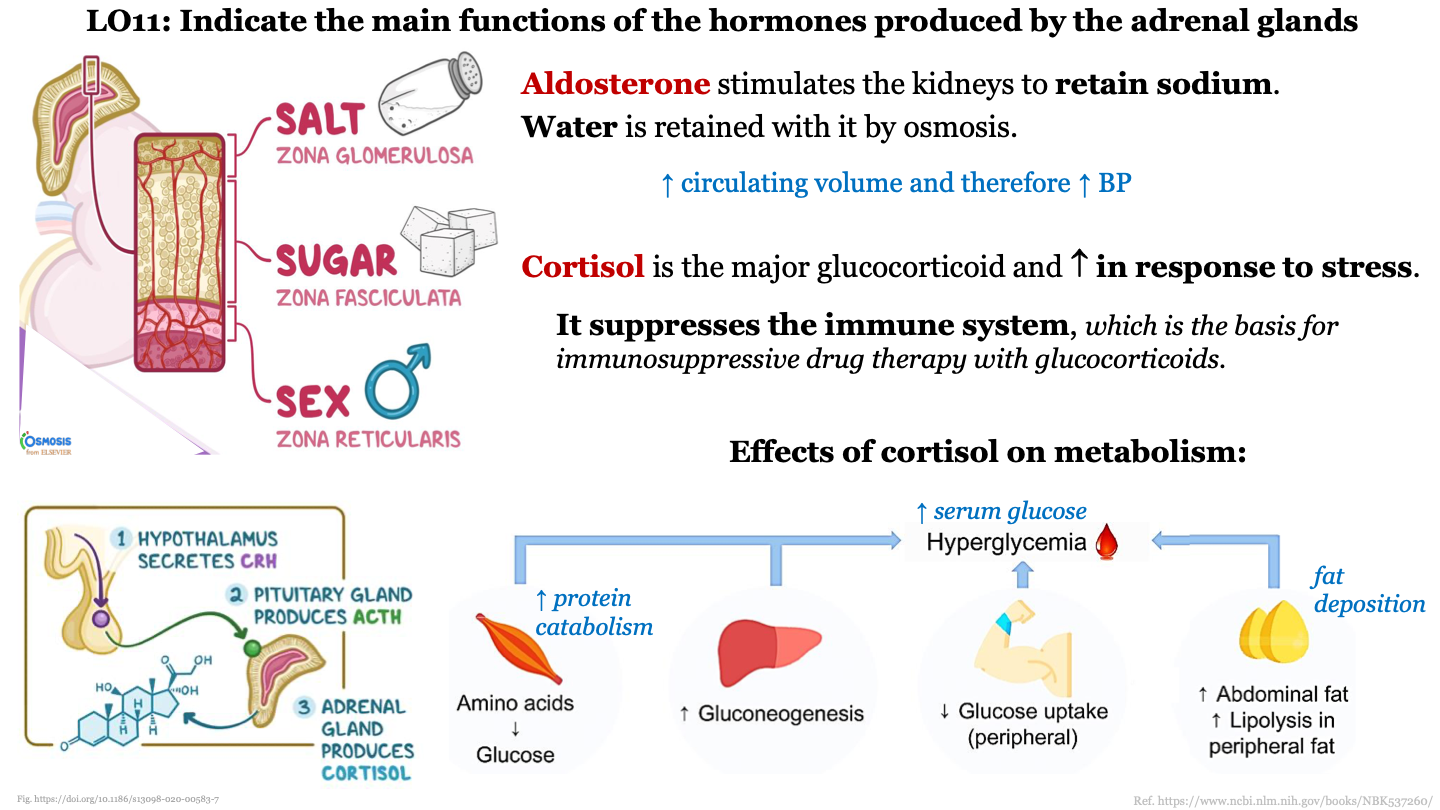
87
New cards
main function of zona reticularis
produces androgens; SEX
88
New cards
3 steps in cortisol production
1. hypothalamus secretes CRH
2. pituitary gland produces ACTH
3. adrenal gland produces cortisol
2. pituitary gland produces ACTH
3. adrenal gland produces cortisol
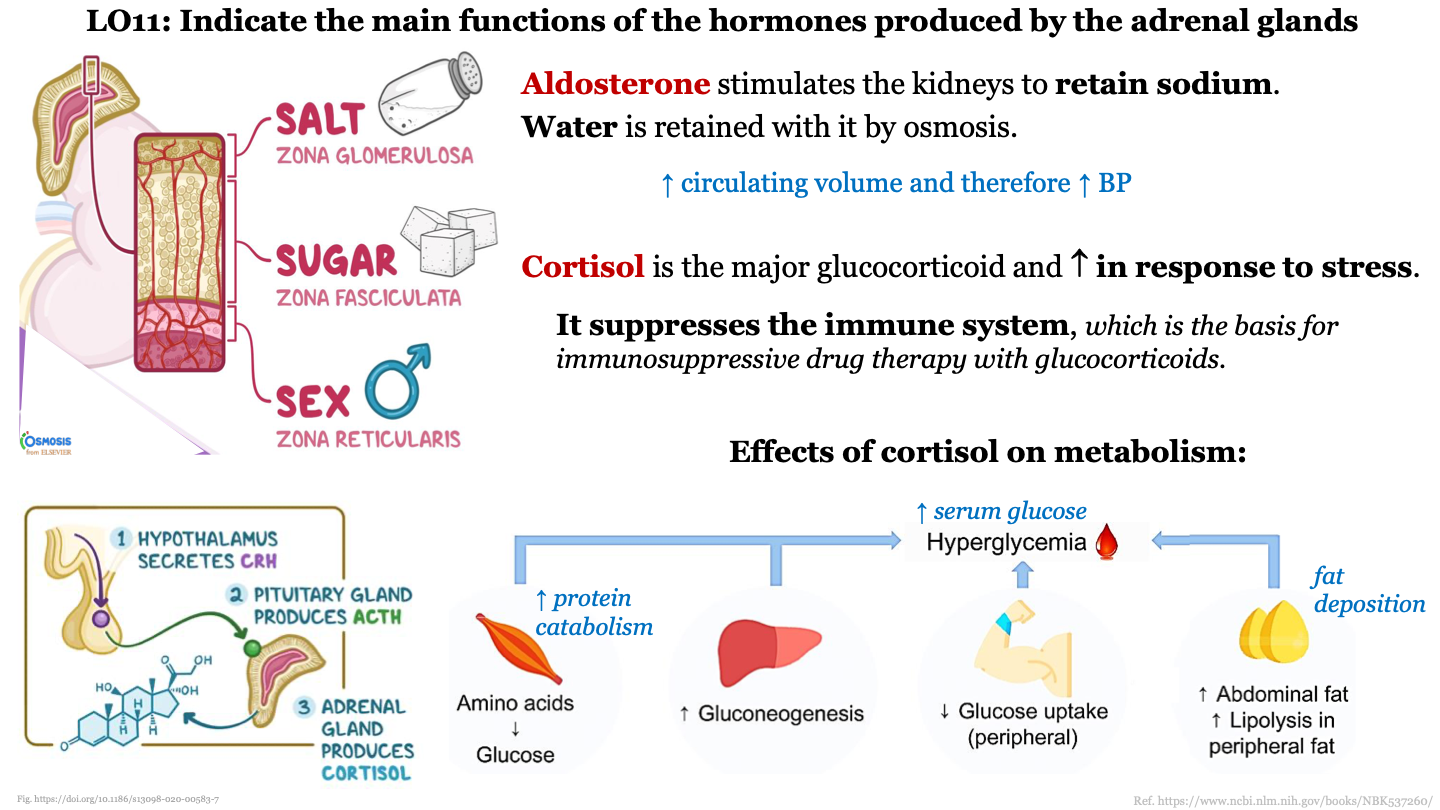
89
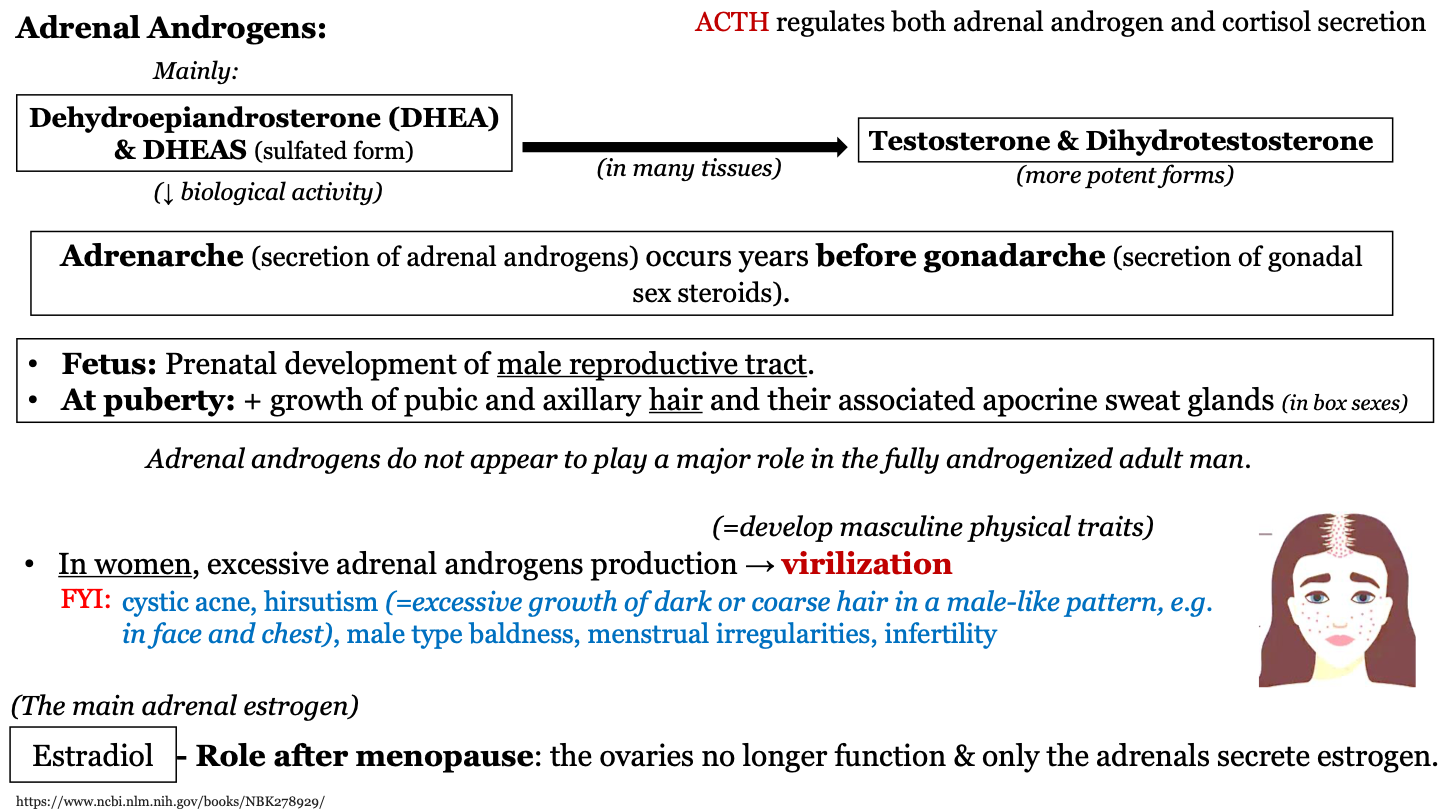
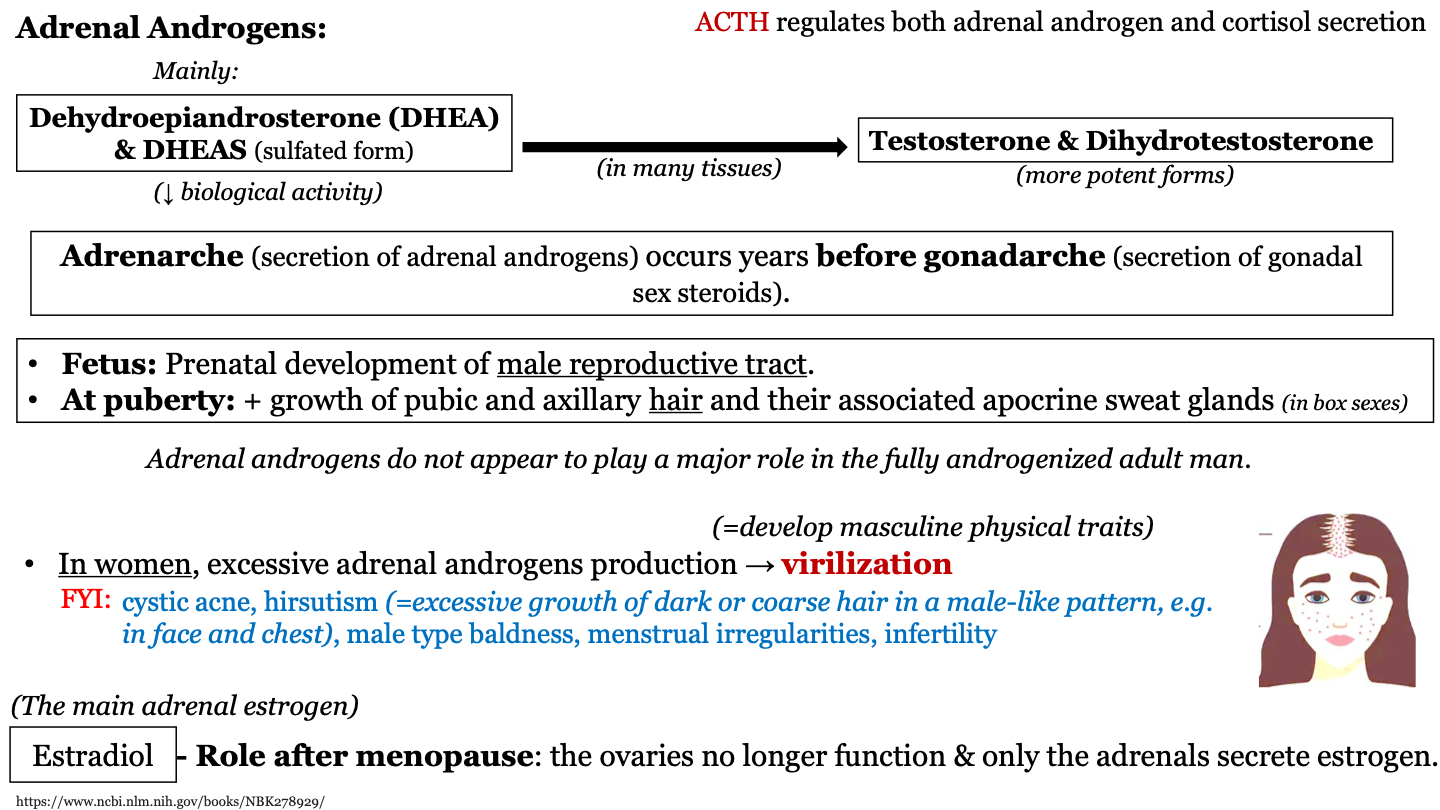
New cards
_________ regulates both adrenal androgen and cortisol secretion
ACTH
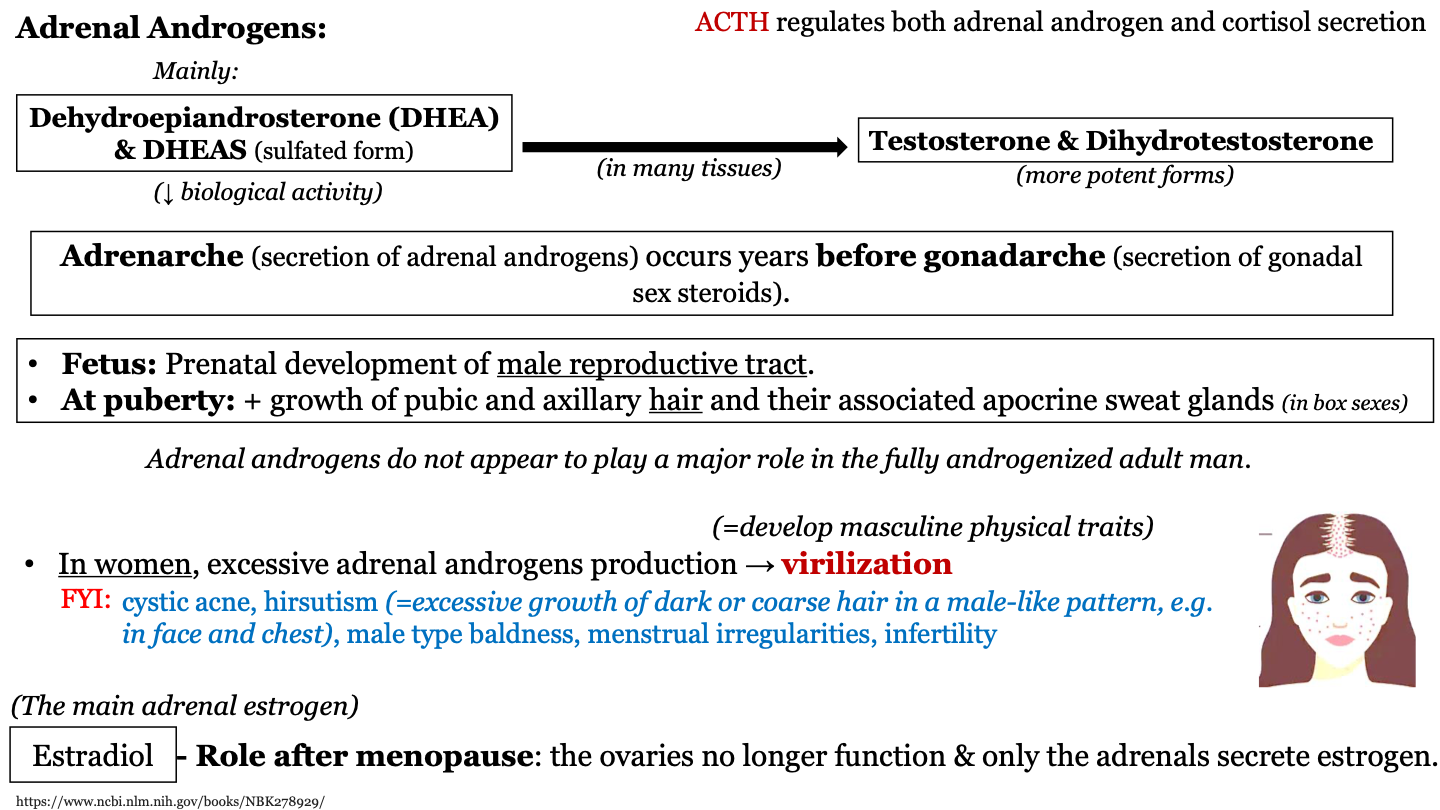
90
New cards
functions of DHEA - fetus
prenatal development of male reproductive tract
91
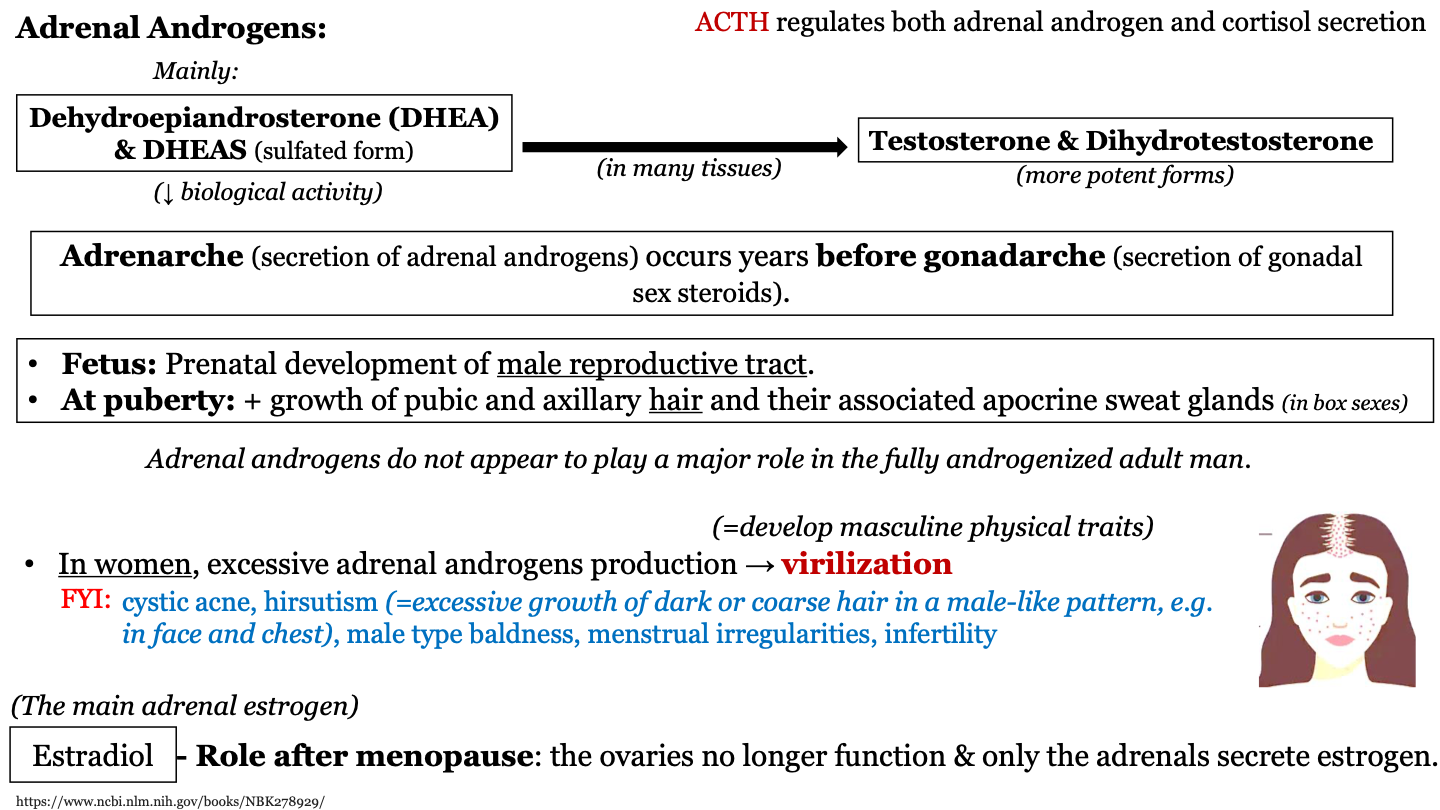
New cards
functions of DHEA - at puberty
increased growth of pubic and axillary hair and their associated apocrine sweat glands (in both sexes)
92
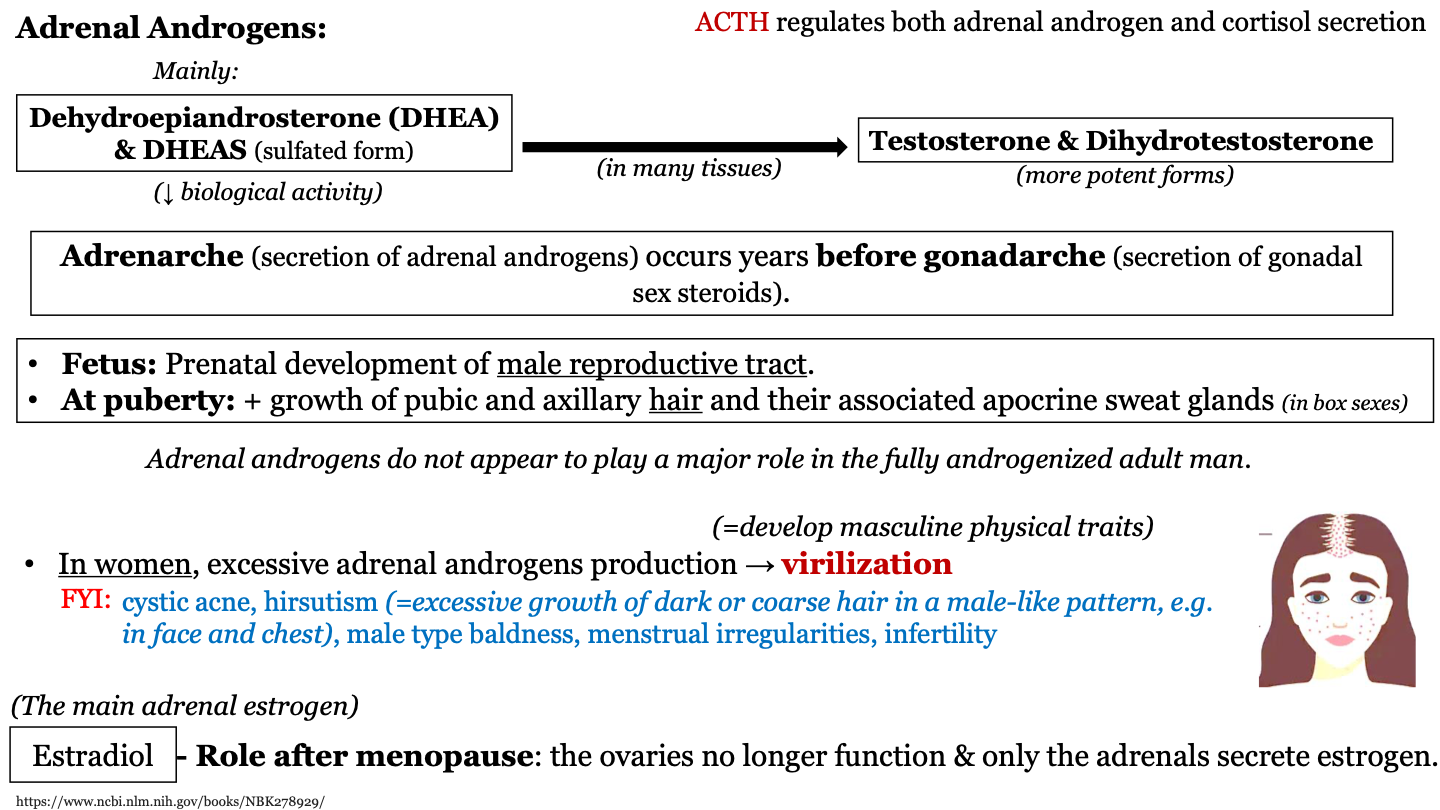
New cards
____________ occurs years before ___________
adrenarche; gonadarche
93
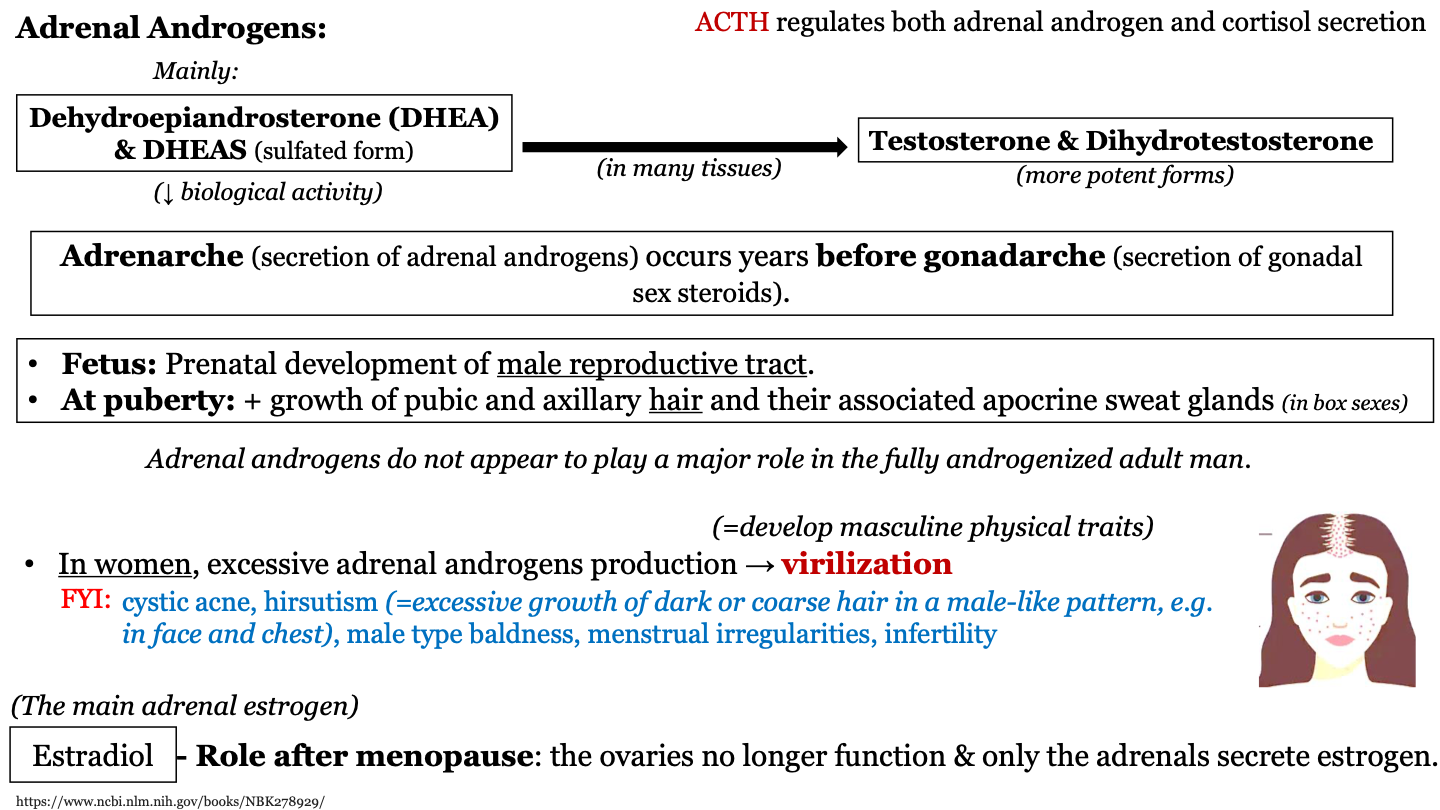
New cards
what is adrenarche?
secretion of adrenal androgens
94
New cards
what is gonadarche?
secretion of gonadal sex steroids
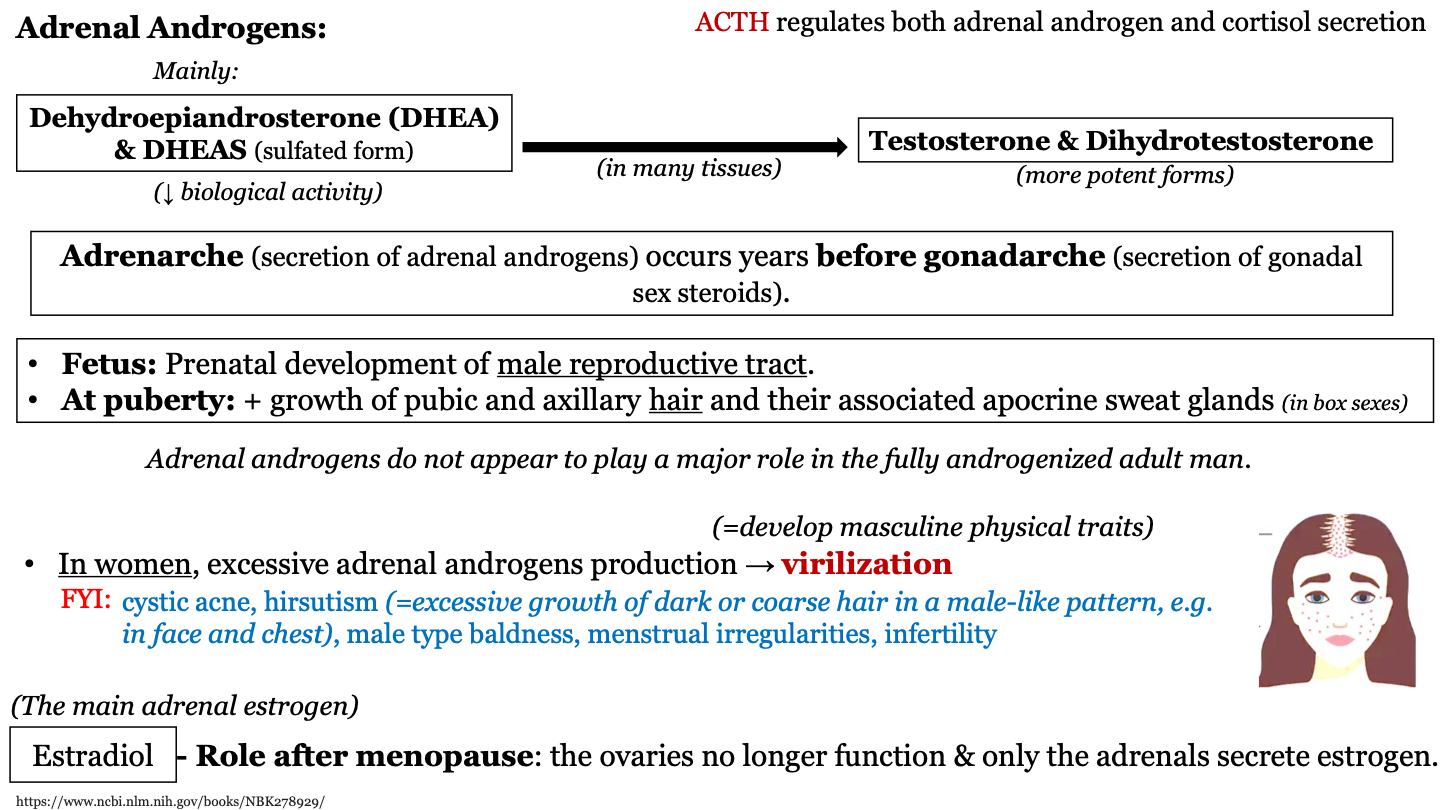
95
New cards
T or F: Adrenal androgens seem to play a major role in the fully androgenized adult man
F: Adrenal androgens don't seem to play a major role in the fully androgenized adult man
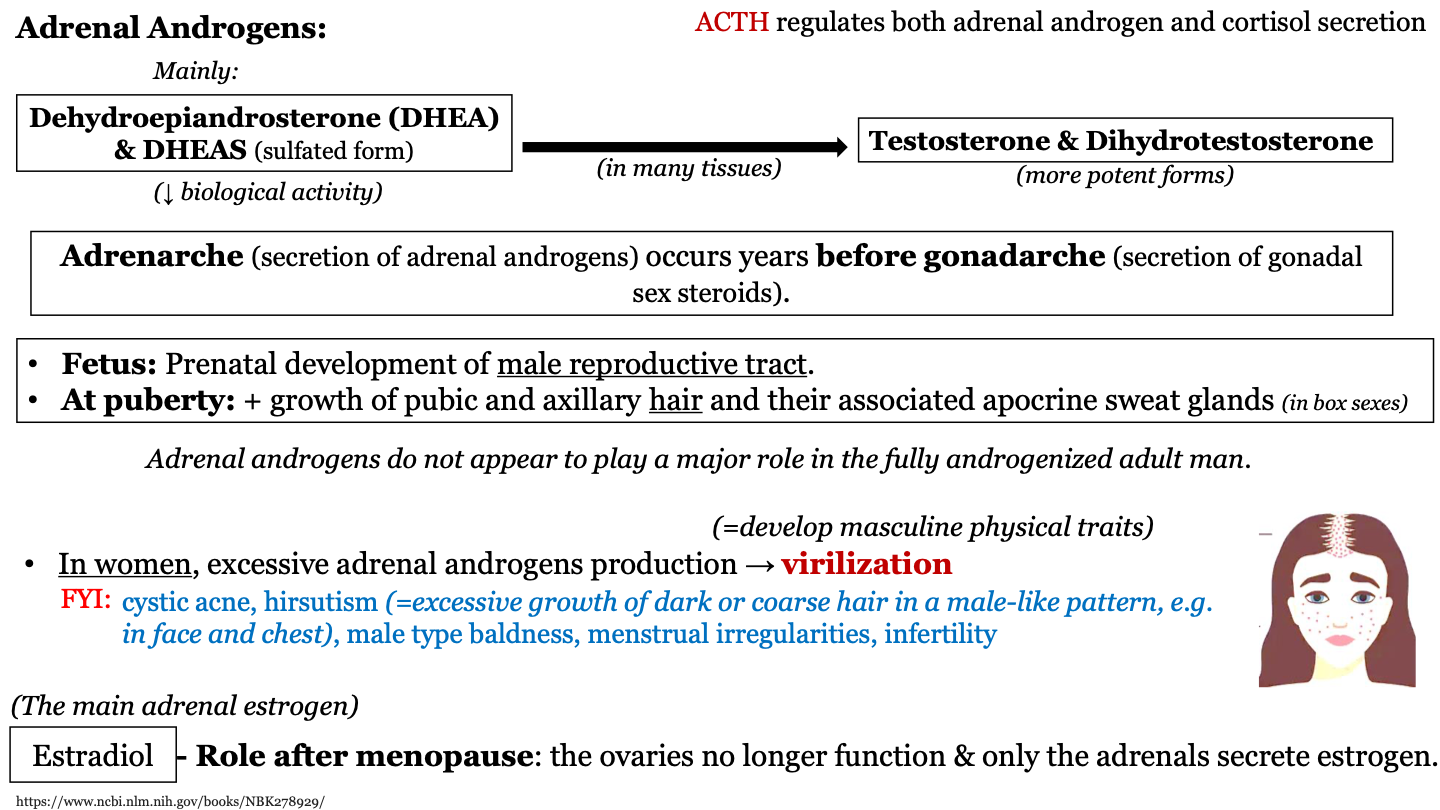
96
New cards
what are the main adrenal androgens
dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEAS (which have low biological activity); these are converted to their more potent forms testosterone and dihydrotestosterone
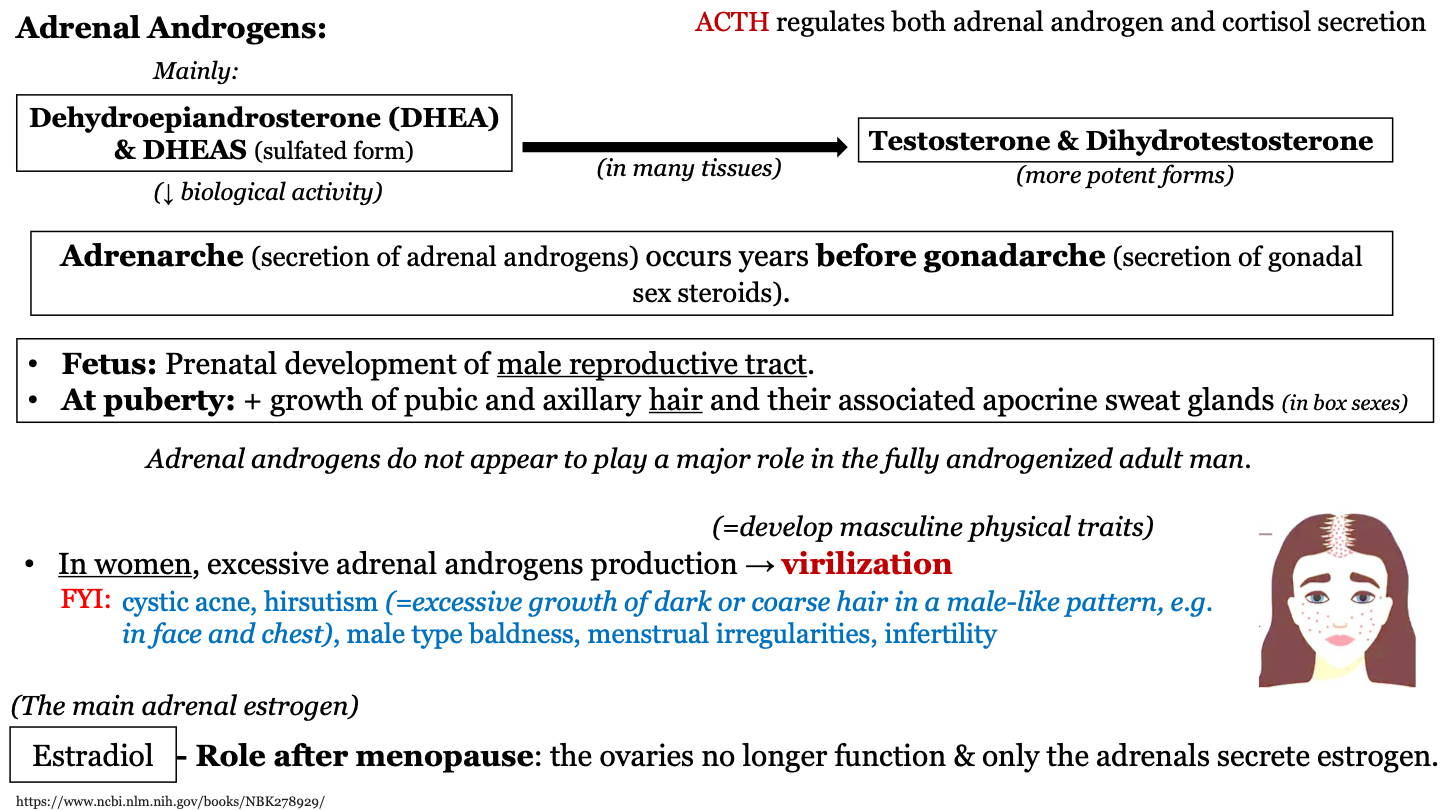
97
New cards
virilization
excessive adrenal androgens production in women; causes them to develop masculine physical traits
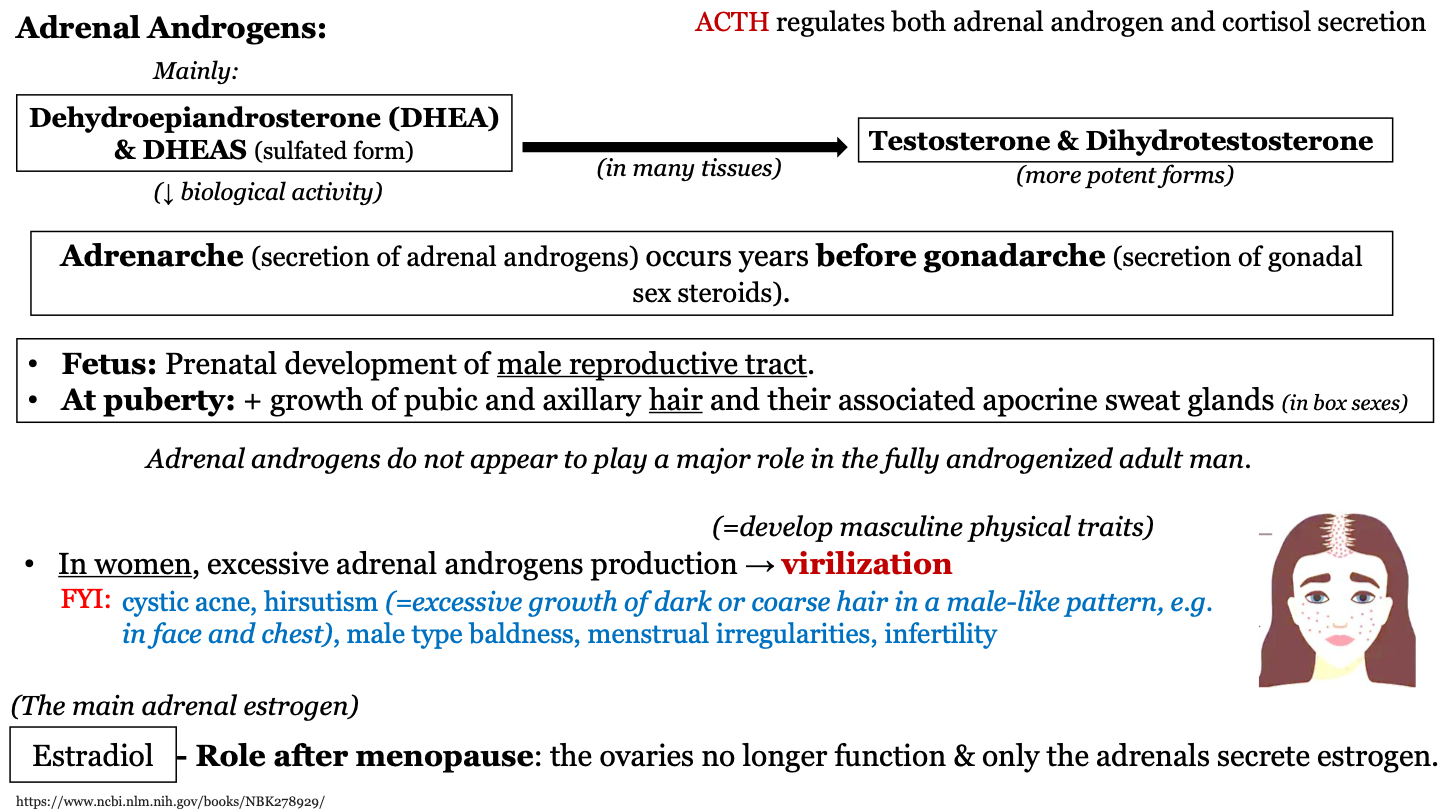
98
New cards
estradiol
the main adrenal estrogen; plays a role after menopause because the ovaries no longer function to produce estrogen so only the adrenals secrete estrogen
99
New cards
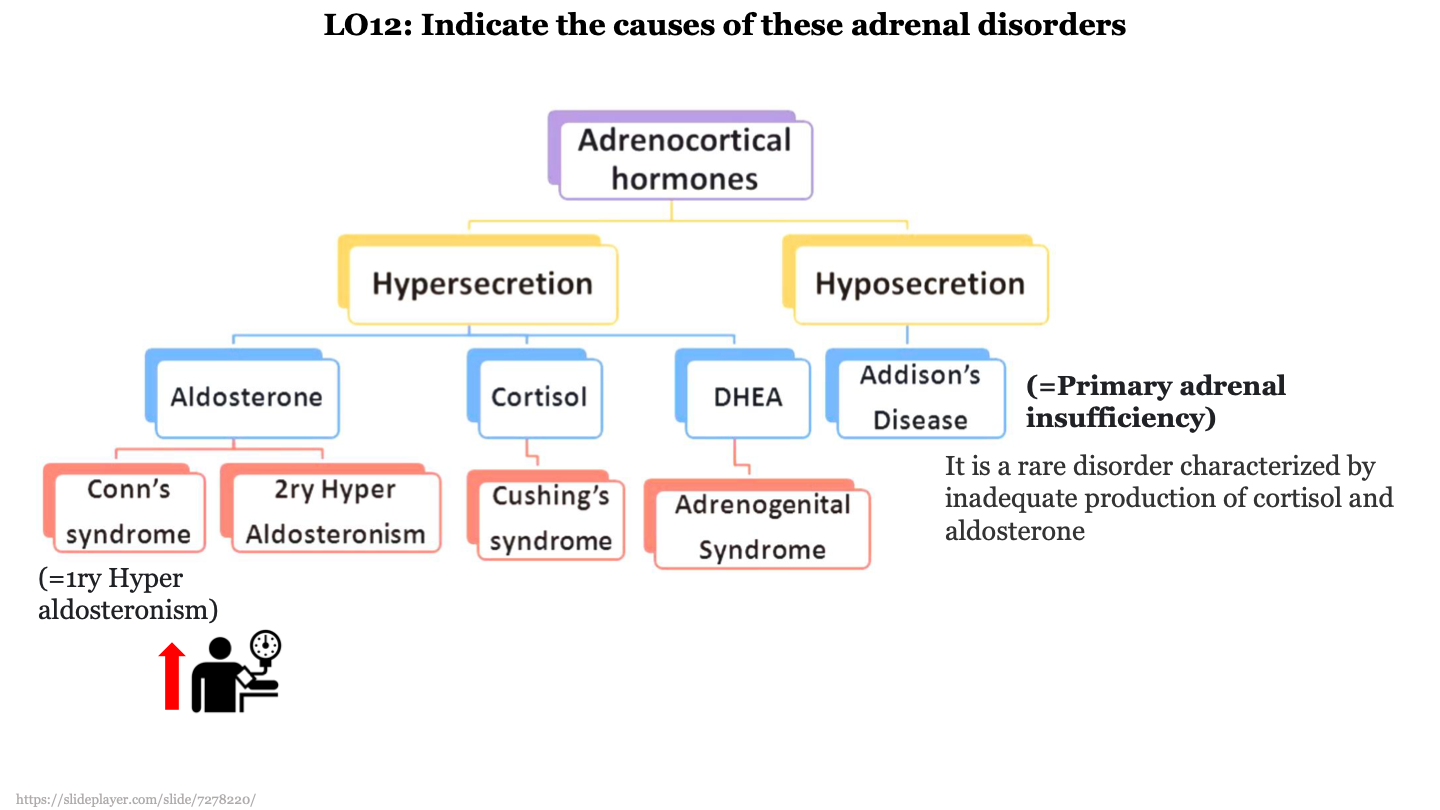
Conn's syndrome (primary hyper aldosteronism)
caused by hypersecretion of the adrenocortical hormone aldosterone; increases BP because more sodium and water are retained in the body
100
New cards
secondary hyper aldosteronism
caused by hypersecretion of the adrenocortical hormone aldosterone