FSHN 265 Energy Metabolism
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what is metabolism?
the sum of all chemical reactions in the body
what are metabolic pathways?
interconnected pathways within energy metabolism where compounds are converted into new compounds
where is energy stored?
in the bonds of the molecules that make up carbs, proteins, fats
what are the major metabolic pathways?
Stage 1: Glycolysis
Stage 2: Pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Stage 3: TCA cycle
Stae 4: Electron transport chain
describe glycolysis
an anaerobic stage of metabolism occurring in the cytosol that splits a 6C glucose molecule into two 3C pyruvate molecules (+ 2 ATP and hydrogen ions)
what other monosaccharides (besides glucose) can be used in glycolysis to produce ATP? How many metabolic steps do they have to go through before entering glycolysis?
fructose can enter glycolysis after going through 7 metabolic steps. Galactose enters glycolysis after going through 4 metabolic steps.
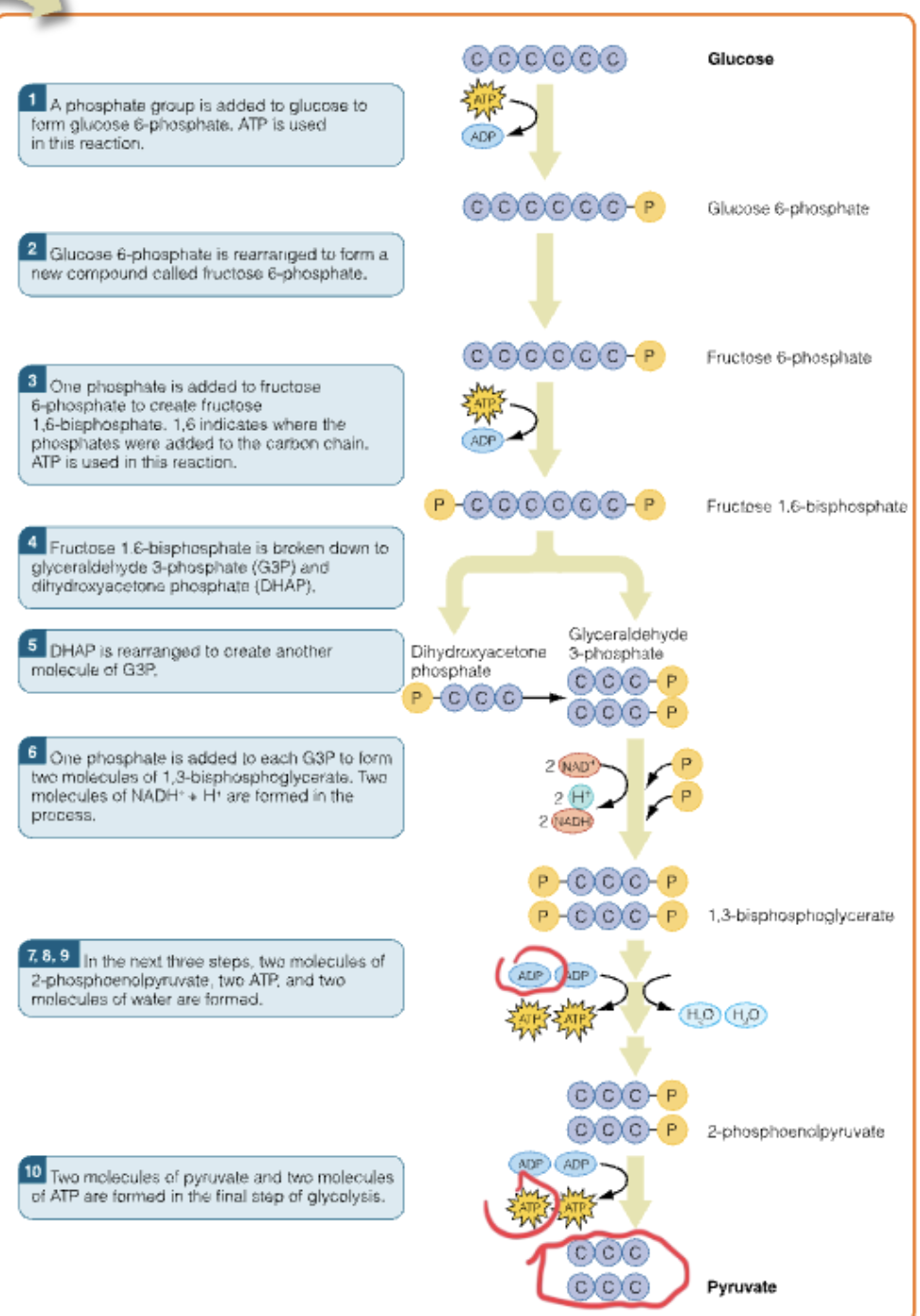
Summarize the specific steps of glycolysis
Phosphate group added to glucose to form glucose 6-phosphate.
Glucose 6-phosphate is rearranged to be fructose 6-phosphate (phosphofructokinase —PFK)
fructose-6-phosphate —> fructose 1,6-biphosphate (one phosphate is added)
fructose 1,6-biphosphate broken down to G3P and DHAP
DHAP is rearranged so there are 2 molecules of G3P
2 G3P —> 2 1,3-biphosphoglycerate (NADH+ and H+ formed too)
8,9: 92 molecules of 2-phosphoenolpyruvate, 2 ATp, and 2 H2O are formed
Final step of glycolysis forms 2 pyruvate and 2 ATP
What happens to pyruvate during anaerobic metabolism?
if there is not enough oxygen, pyruvate is reduced to lactate, which diffuses out of the muscle cell and enters the liver through the bloodstream. The liver converts lactate —> pyruvate —> glucose (gluconeogenesis) via the Cori cycle.
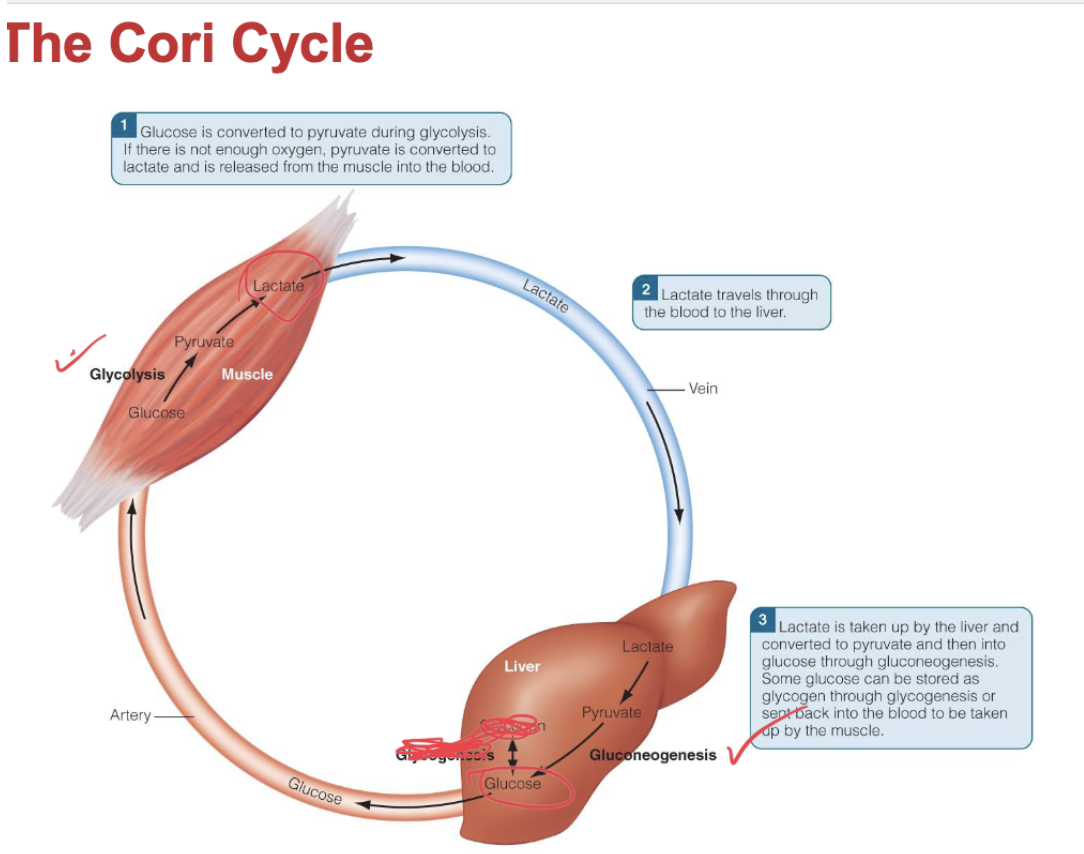
what is the cycle called the converts lactate to glucose?
the Cori cycle
What happens to pyruvate during aerobic metabolism?
in the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA in the mitochondria.
What two pathways can Acetyl CoA enter?
the TCA cycle (limited ATP)
converted to fatty acids and stored as fat (ample ATP)
how are fatty acids converted to acetyl CoA?
Lipolysis occurs (hydrolysis of triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol)
Beta-oxidation occurs: coenzyme A is added to the carboxylic end of the fatty acid chain. This activates the fatty acid and it can cross into the mitochondria, where it can be converted to acetyl CoA and enter TCA/Krebs cycle.
what enzyme catalyzes lipolysis in adipose tissue?
hormone-sensitive lipase
what state is hormone-sensitive lipase more active in?
it is most active in the fasted state, when it is activated by glucagon (insulin is low)
what hormone stimulates hormone-sensitive lipase?
glucagon stimulates hormone sensitive lipase to catalyze the hydrolysis of triglycerides into 3 fatty acids + glycerol
what does beta oxidation do?
it disassembles fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules in the mitochondria
what is the most metabolically active organ in the body?
the liver converts monosaccharides, amino acids, glycerol, and fatty acids into energy, new compounds, or storage for future use
anabolic vs catabolic reactions
anabolic: absorb energy
combine simple molecules to form larger molecules
catabolic reactions: release energy (ATP or heat)
break down large molecules into simpler molecules
what kind of reaction is glucose —> glycogen?
anabolic reaction
what kind of reaction is glycogen —> glucose?
catabolic reaction
In general, how are anabolic and catabolic reactions regulated?
by hormones
what type of reaction does insulin stimulate?
anabolic reaction, stimulating synthesis of glycogen, protein, etc.
what kind of reaction does glucagon stimulate?
catabolic reactions — breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis and lipids (lipolysis)
what is ATP? What is it composed of?
a high energy molecule composed of adenine, ribose ,and 3 phosphate molecules. It is the cell’s direct energy source
aerobic vs anaerobic metabolism:
Anaerobic:
produces more ATP per min
provides 1-1.5 min of maximal activity
high intensity, short duration activities
Aerobic:
produces less ATP per min
can produce ATP indefinitely
involved in low intensity, long duration activities
what molecule enters the TCA cycle?
Acetyl CoA
What molecules enter the electron transport chain?
NADH + H+, FADH2
what metabolic pathway produces the majority of ATP?
the electron transport chain
what does glucogenic mean?
can be converted into glucose during metabolism
how many amino acids are glucogenic?
18 out of 20 amino acids can be transformed into pyruvate and other TCA cycle intermediates that enter gluconeogenesis and produce glucose
What is the entry point into metabolism for 6 of the 18 glucogenic amino acids (alanine, serine, glycine, etc.)?
pyruvate
what is the entry point into metabolism for the other 12 glucogenic amino acids?
points along the TCA cycle (keto acids)
what are ketogenic amino acids?
amino acids that are converted to Acetyl CoA, which can either be transformed into fatty acids and stored as triglycerides or enters TCA cycle
What can fatty acids be used to form?
ketone bodies (alternative energy source for when glucose is low)
what are the steps of beta oxidation?
2 carbons at the end of the fatty acid are removed and joined with CoA to form acetyl CoA
process repeats
hydrogen and electrons are released as each pair of carbons is cleaved off
what is the beta oxidation pathway?
a metabolic pathway that breaks down fatty acids to acetyl CoA to enter the TCA cycle
where does the TCA cycle occur?
the mitochondrial matrix
what kinds of molecules does the TCA cycle release?
high energy electrons and hydrogen ions
what do NADH + H+ and FADH2 after they are produced by the TCA cycle?
they deliver high energy electrons and hydrogen ions to the inner mitochondrial membrane for use in the electron transport chain.
Acetyl CoA binds with _____ to form citrate in the first step of the TCA cycle.
oxaloacetate
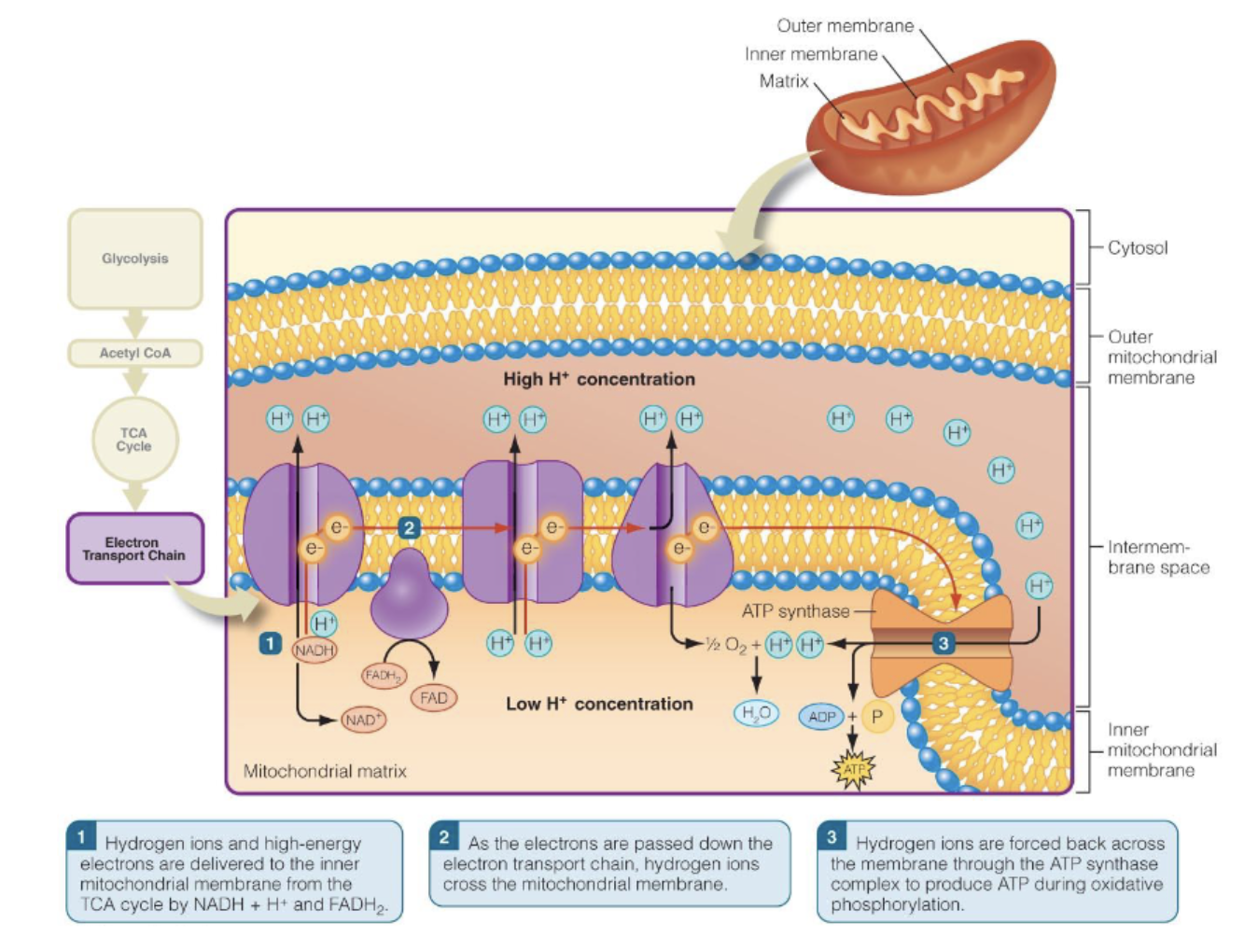
summarize the steps of the electron transport chain
high energy electrons and hydrogen ions are delivered to the inner mitochondrial membrane by NADH + H+ and FADH2
Electrons are passed down electron transport chain. Hydrogen ions cross mitochondrial membrane.
Hydrogen ions are forced back across the membrane through ATP synthase complex to produce ATP during oxidative phosphorylation
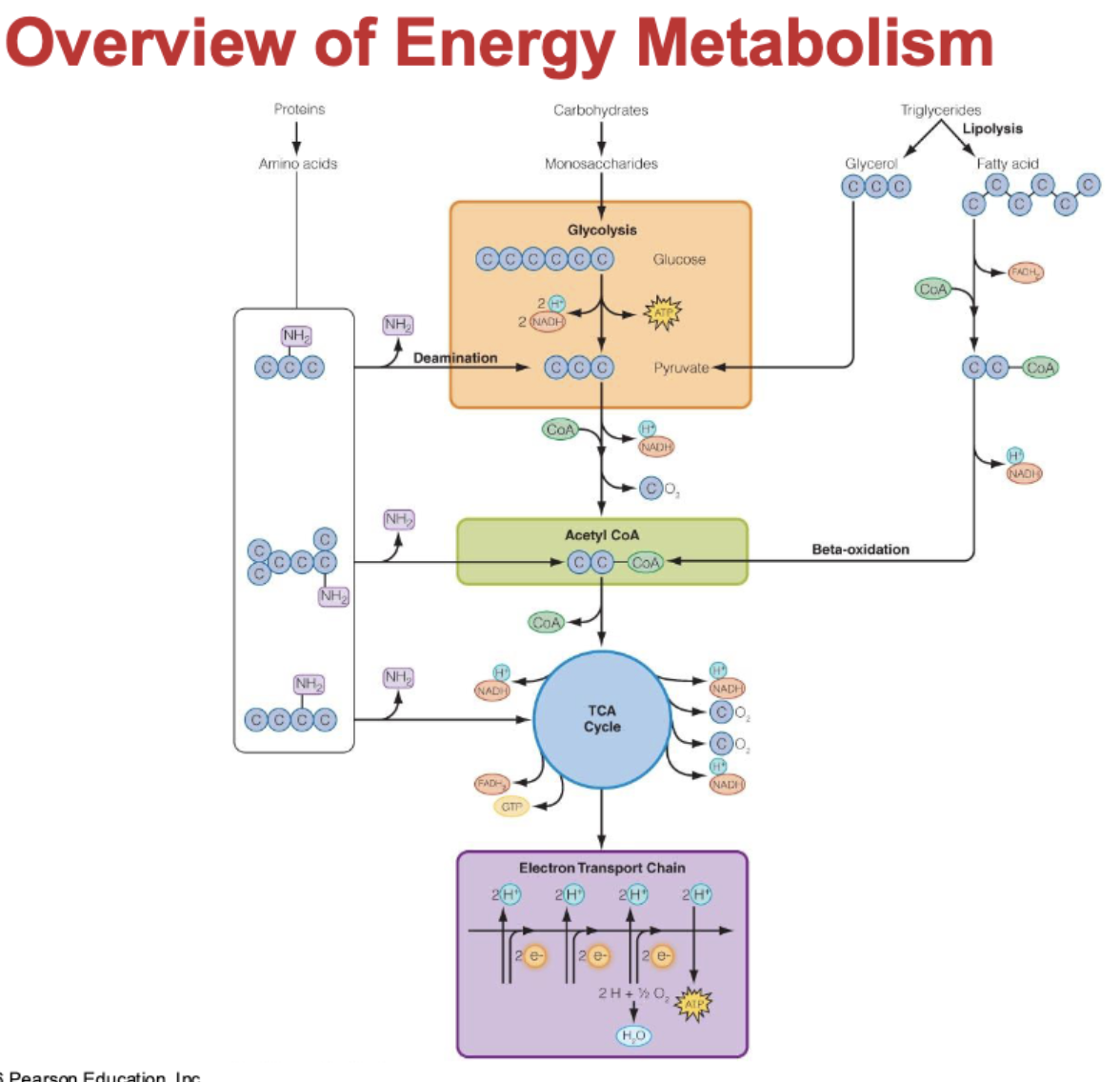
overview of energy metabolism diagram
what is the absorptive (fed) state?
the period within 4 hours after a meal in which anabolic processes are dominant
what is the driving hormone during the absorptive state?
insulin
what is the post-absorptive state?
period of time that is more than 4 hours after eating, when fuel is being removed from storage and catabolic processes are occuring
what is the driving hormone during the postabsorptive state?
glucagon
glucose is the main source of energy for…
red blood cells and the central nervous system
what is liver glycogen?
glucose that is being stored as glycogen. The only form of glucose that can enter the bloodstream is from liver glycogen.
what is muscle glycogen?
glycogen that is being used for energy by the muscle
what happens to excess glucose and excess amino acids?
they are converted into triglycerides via lipogenesis
what is ketogenesis?
the formation of ketone bodies
What does the brain use for fuel when you are fasting and in carbohydrate deficiency?
ketone bodies
what percent of fuel is from ketones during fasting?
30% of fuel is from ketones, 70% is from blood glucose
what is the acute starvation stage characterized by?
when your body is out of liver glycogen
what are the active hormones during the acute starvation stage?
glucagon, cortisol, and epinephrine
what processes do glucagon, epinephrine, and cortisol turn on?
gluconeogenesis and lipolysis