Clemson Plant Bio Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:23 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
1
New cards
Apical Meristem
area of new cell generation that go on to differentiate into 1 of 3 primary meristems
2
New cards
Name the Primary meristems produced from the Apical meristem
Ground meristem
Protoderm
Procambium
Protoderm
Procambium
3
New cards
What tissue system does the Ground Meristem produce
Ground tissue system
4
New cards
What tissue system does the protoderm produce
Dermal tissue system
5
New cards
What tissue system does the procambium produce
Vascular tissue system
6
New cards
Simple tissue
Tissues comprised of only 1 cell type
\-Collenchyma
\-Collenchyma
7
New cards
complex tissue
Tissues comprised of multiple cell types
\-phloem
\-phloem
8
New cards
Tissue
Groups of cells that are structurally or functionally distinct
9
New cards
Tissue system
Groups of tissues organized into a structural or functional unit
10
New cards
Plant tissue systems
Dermal tissue system
Ground tissue system
Vascular tissue system
Ground tissue system
Vascular tissue system
11
New cards
What tissues make up the Dermal tissue system
Epidermis
Periderm
Periderm
12
New cards
What tissues make up the Ground tissue system
Parenchyma
collenchyma
sclerenchyma
collenchyma
sclerenchyma
13
New cards
What tissues make up the Vascular tissue system
xylem
phloem
phloem
14
New cards
Parenchyma
\-Most numerous cells in plant body
\-Alive at maturity
\-have thin primary walls
\-Function in photosynthesis, storage, secretion, and regeneration
\-Alive at maturity
\-have thin primary walls
\-Function in photosynthesis, storage, secretion, and regeneration
15
New cards
Parenchyma cells in plant body and their function
* Cortex & pith of stems and roots
* used for storage
* Mesophyll of leaves
* photosynthesis
* Flesh of fruit
* Vertical strands in primary Xylem and phloem
* Rays in secondary xylem
* Transfer cells
* used for storage
* Mesophyll of leaves
* photosynthesis
* Flesh of fruit
* Vertical strands in primary Xylem and phloem
* Rays in secondary xylem
* Transfer cells
16
New cards
Collenchyma
Supports young growing organs
* Mainly found just under epidermis
* Have cellulose primary walls with thickened corners
* Usually NOT found in roots or in monocot stems and leaves
* Mainly found just under epidermis
* Have cellulose primary walls with thickened corners
* Usually NOT found in roots or in monocot stems and leaves
17
New cards
Where won’t you generally find Collenchyma cells?
* Roots
* Monocot stems and leaves
* Monocot stems and leaves
18
New cards
Sclerenchyma
Strengthens and supports plant parts that are no longer elongating
* Dead at maturity
* Thick secondary wall of lignin
* Made up of fibers and sclereids
* Dead at maturity
* Thick secondary wall of lignin
* Made up of fibers and sclereids
19
New cards
Fibers
Long, thin cells that occur in strands or bundles
20
New cards
Sclereids
Irregularly-shaped individual cells; occur singly or in aggregates
21
New cards
Phloem
Transport of sugars and many other compounds
* Sieve cells in gymnosperms
* Sieve-tube elements in angiosperms
* Sieve elements in everything else
* Living
* Sieve cells in gymnosperms
* Sieve-tube elements in angiosperms
* Sieve elements in everything else
* Living
22
New cards
Xylem
Transport of water and minerals
* Tracheary elements
* tracheids
* vessel elements
* Dead at maturity
* Tracheary elements
* tracheids
* vessel elements
* Dead at maturity
23
New cards
Stele
Central cylinder of the root or stem where xylem and phloem are located; may also contain pith
24
New cards
mesophyll cells
Chloroplast-containing, photosynthetic parenchyma cells found in leaves
25
New cards
pith
Central column of ground tissue in the center of the stele
26
New cards
Epidermis
Outer layer of cells on a plant’s body used for protection
* Cells closely packed
* Secretes waxy cuticle
* Contains specialized cells:
* Trichomes
* Guard cells
* Cells closely packed
* Secretes waxy cuticle
* Contains specialized cells:
* Trichomes
* Guard cells
27
New cards
Specialized cels of Epidermis
Trichomes
Guard cells
Guard cells
28
New cards
Trichomes
Hair-like projections on epidermis
29
New cards
Guard cells
Control stomatal opening
30
New cards
What does the epidermis secrete to prevent water loss?
Cutin
31
New cards
Tracheids
Single, elongated cells used in water transport
32
New cards
Vessel elements
Present in many angiosperms in combination with tracheids
33
New cards
2 components that make up phloem
Sieve cells
Sieve tube elements
Sieve tube elements
34
New cards
5 main functions of roots
1. Anchors
2. Absorbs water
3. Conducts water and minerals
4. Cundicts hormones and secondary metabolites
5. Clonal regeneration
35
New cards
Name of first root to develop
Radicle
36
New cards
Tap root system
One main, deep penetrating root with lateral roots branching off it
* Taproot born from radicle
* Taproot born from radicle
37
New cards
Fibrous root system
No main taproot; no one root is more prominent
* Roots are stem born; **adventitious roots**
* Do not penetrate as far as taproot
* Roots are stem born; **adventitious roots**
* Do not penetrate as far as taproot
38
New cards
Where are most roots located
underground
39
New cards
Where does most water and mineral absorption happen in the roots?
Fine roots
40
New cards
In a fibrous root system, the primary root is _________ lived
Short
41
New cards
Root cap
Mass of living parenchyma cells that protects the root apical meristem
42
New cards
Quiescent center
Pool of stem cells (initials) within the root apical meristem
43
New cards
Promeristem
Area with small, many-sided initial cells, base of the apical meristem where it meets the root cap
44
New cards
The promeristem goes on to form what structure?
quiescent center
45
New cards
How is the root cap able to sense and respond to gravity?
Statolith cells act like free pebbles that “roll around” in response to gravity
\-Auxin hormone stimulates growth on one side of root in response to statolith position
\-Auxin hormone stimulates growth on one side of root in response to statolith position
46
New cards
Statoliths
“stationary stone”
Pebbles in a jar; respond to gravity; how plants figure out where “down” is
Pebbles in a jar; respond to gravity; how plants figure out where “down” is
47
New cards
Auxins
Growth hormone used in various parts of plant
\-In root, its produced on one side of root in response to statolith position
\-In root, its produced on one side of root in response to statolith position
48
New cards
3 Root zones
* Zone of cell division
* Zone of elongation
* Zone of maturation
* Zone of elongation
* Zone of maturation
49
New cards
Casparian strip
Gives the plant greater control over what comes into the plant body and is moved by the vascular tissue
* Attach tightly to the plasma membrane of cells forcing water to move symplastically through the living components of the cell
* Attach tightly to the plasma membrane of cells forcing water to move symplastically through the living components of the cell
50
New cards
Cortex
Ground tissue; mostly parenchyma
51
New cards
Endodermis
Innermost cell layer of cortex
* barrier to apoplastic movement of water and solutes with aid of casparian strip
* barrier to apoplastic movement of water and solutes with aid of casparian strip
52
New cards
Vascular cylinder
Innermost part of root where the vascular tissue is located
53
New cards
Pericycle
surrounds the vascular cylinder – lateral roots arise from it
54
New cards
What role does the casparian strip play in water movement?
Allows plant to regulate what fluid does and doesnt pass into/out of vascular cylinder
55
New cards
Where do lateral roots arise from (be able to label this)
Pericycle
56
New cards
3 types of specialized roots
* Adventitious roots
* Pneumatophores
* Storage roots
* Pneumatophores
* Storage roots
57
New cards
Adventitious roots
roots arising from stem
58
New cards
Pneumatophores
“air roots”
59
New cards
Storage roots
tubers and the like
60
New cards
Bulbs
Modified leaf for food storage
61
New cards
Corms
Modified stem for food storage
62
New cards
Phytomere
* Node
* Leave
* Internode
* Bud
* Leave
* Internode
* Bud
63
New cards
Shoot
Leaf + stem
64
New cards
node
area of stem where leaf sprouts out just below the bud
65
New cards
internode
area between nodes
66
New cards
Leaf primordia
protects shoot apical meristem
67
New cards
Tunica
Outermost layer(s) of cells on shoot apical meristem
68
New cards
Corpus
beneath the tunica layer
69
New cards
Anticlinal Division
perpendicular division; cells divide side by side
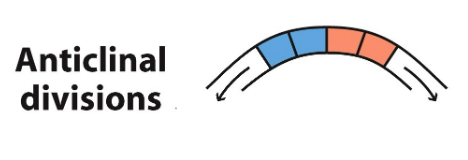
70
New cards
Periclinal division
Parallel division; cells divide on top of each other
* adds bulk
* adds bulk
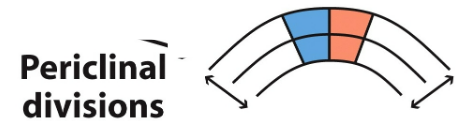
71
New cards
what kind of cell division gives rise to the tunica?
Anticlinal
72
New cards
what kind of cell division gives rise to the corpus?
Periclinal
73
New cards
3 zones of shoot apical meristem
Rib Zone
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Central zone
Peripheral zone
74
New cards
3 layers of shoot apical meristem
2 Tunica; One Corpus
75
New cards
Rib zone
Gives rise to internal tissues of stem
76
New cards
Central zone
Replenishes peripheral and rib zones
77
New cards
peripheral zone
gives rise to leaf primordia
78
New cards
Most eudicots have shoot apical meristems with 3 layers; 2 _____ layers, and 1 _____ layer
Tunical; Corpus
79
New cards
Layer 1 (L1)
* Anticlinal division
* Gives rise to Epidermis
* Gives rise to Epidermis
80
New cards
Layer 2 (L2)
* Anticlinal division
* Gives rise to internal tissues
* Gives rise to internal tissues
81
New cards
Layer 3 (L3)
* Periclinal division
* Gives rise to internal tissues
* Gives rise to internal tissues
82
New cards
components of the vascular bundle in eudicots
* Bundle cap
* parenchyma
* sclerenchyma
* Primary phloem
* Vascular Cambium
* Primary xylem
* parenchyma
* sclerenchyma
* Primary phloem
* Vascular Cambium
* Primary xylem
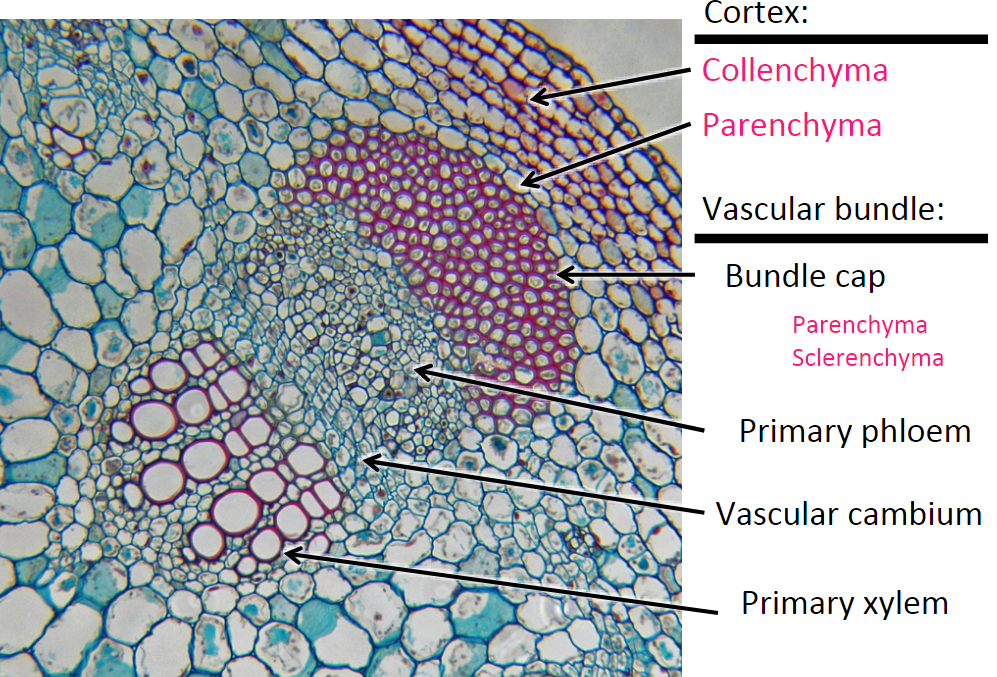
83
New cards
How are vascular bundles arranged in eudicots?
In a ring
84
New cards
How are vascular bundles arranged in monocots?
Randomly arranged
85
New cards
3 main stem types
Siphonostele-like eustele
Eustele with discrete bundles
Monocot stem
Eustele with discrete bundles
Monocot stem
86
New cards
Describe a Siphonostele-like eustele
Vascular cylinder is near-fully connected around pith
* narrow interfascicular region
* narrow interfascicular region
87
New cards
Describe a Eustele with discrete bundles
Vascular bundles arranged in a cylinder, but not connect
* Wide interfascicular regions
* Cortex and pith are distinct, but connected
* Wide interfascicular regions
* Cortex and pith are distinct, but connected
88
New cards
Describe a monocot stem
The vascular bundles occur in multiple rings of bundles OR scattered throughout the ground tissue
* Ground tissue is NOT separated into cortex and pith
* Ground tissue is NOT separated into cortex and pith
89
New cards
What is the most common stem type for eudicots?
Eustele with discrete bundles
90
New cards
Herb
* Herbaceous
* Stems not persistent
* Dies back to the ground at the end of the growing season
* Little to no secondary growth
* Stems not persistent
* Dies back to the ground at the end of the growing season
* Little to no secondary growth
91
New cards
Vine
* Herbaceous
* Stem climbing (tendrils, holdfast, or adventitious roots) or twining
* Little to no secondary growth
* Stem climbing (tendrils, holdfast, or adventitious roots) or twining
* Little to no secondary growth
92
New cards
Shrub
* woody
* several stems from the base
* less than 25' tall.
* Secondary growth
* several stems from the base
* less than 25' tall.
* Secondary growth
93
New cards
tree
* woody
* usually one main stem
* usually more than 25' tall
* much secondary growth
* usually one main stem
* usually more than 25' tall
* much secondary growth
94
New cards
in shrubs and trees, secondary growth results in the production of what?
woody tissue
95
New cards
Where does secondary growth in the stem take place
vascular and cork cambium
96
New cards
Annual plant
Lives for 1 yr/season
97
New cards
Biennial plant
Lives for 2 yrs/season
98
New cards
Perennial plant
lives for several to many years/seasons
99
New cards
Deciduous plant
Leaves die off in cold season
100
New cards
evergreen plant
Leaves persist for 2+ seasons