Chapter 29 - Chromatography + Spectroscopy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Rf value equation
distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent
thin layer chromatography (TLC)
adsorption = process by which silica holds substance to its surface by hydrogen bonds
stationary phase = solid adsorbant substance coated on glass sheet e.g. silica
mobile phase = suitable solvent
Rf value for TLC
-different substances have different adsorptions = stronger adsorption, substance moves slower, lower Rf value
e.g. phenylamine will travel further than tetrachloromethane as it can form hydrogen bonds
how to make colourless components visible?
-view under UV light
-dried chromatogram sprayed with ninhydrin which turns them purple
gas chromatography (GC)
-used to separate volatile organic compounds in a mixture
stationary phase = column containing high boiling point liquid adsorbed onto solid
mobile phase = inert gas that carries components
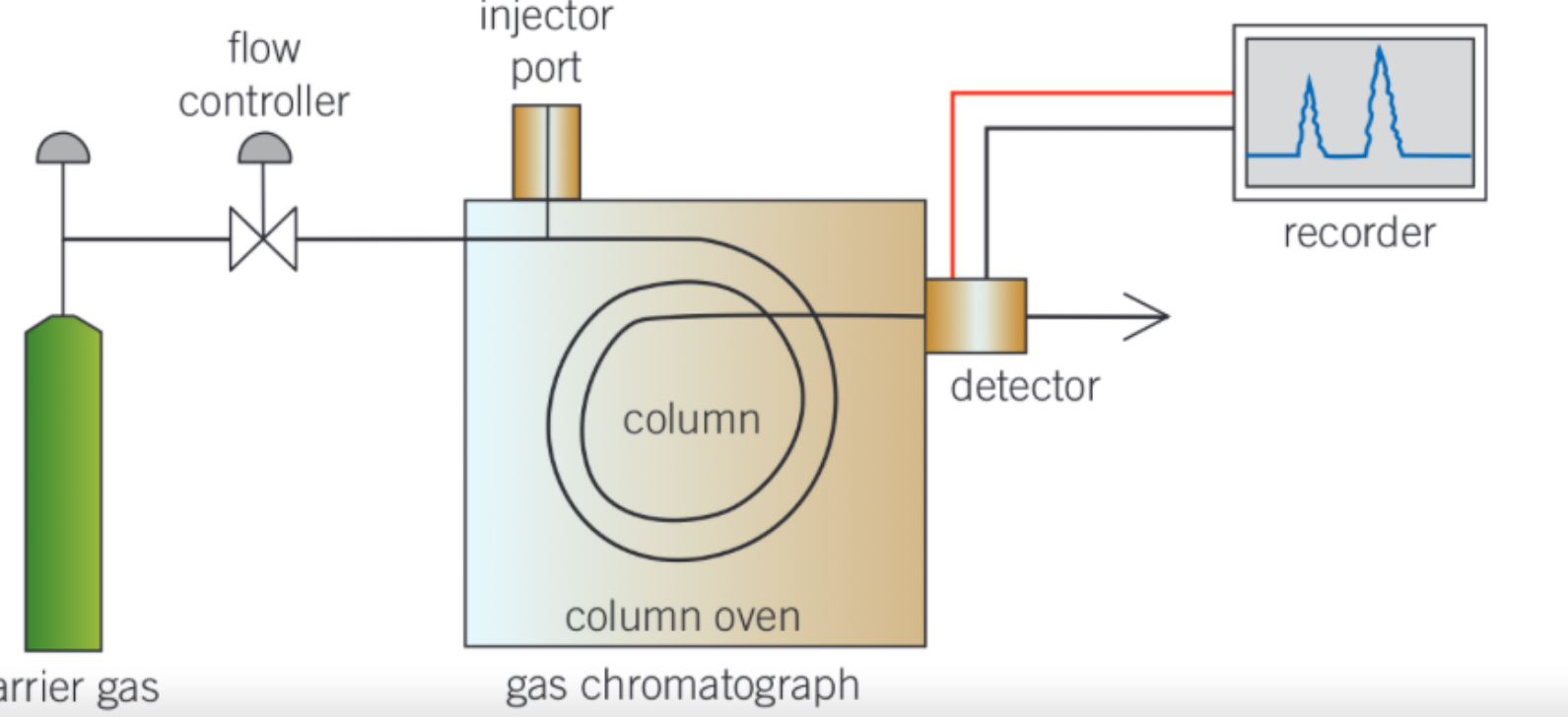
order that components leave column
from most volatile to least volatile
-most volatile = less soluble in liquid stationary phase so less interaction so faster travel in column so less time taken
info from gas chromatogram
-retention time = time taken to travel - identify components
-peak integration area = identify concentration of each component
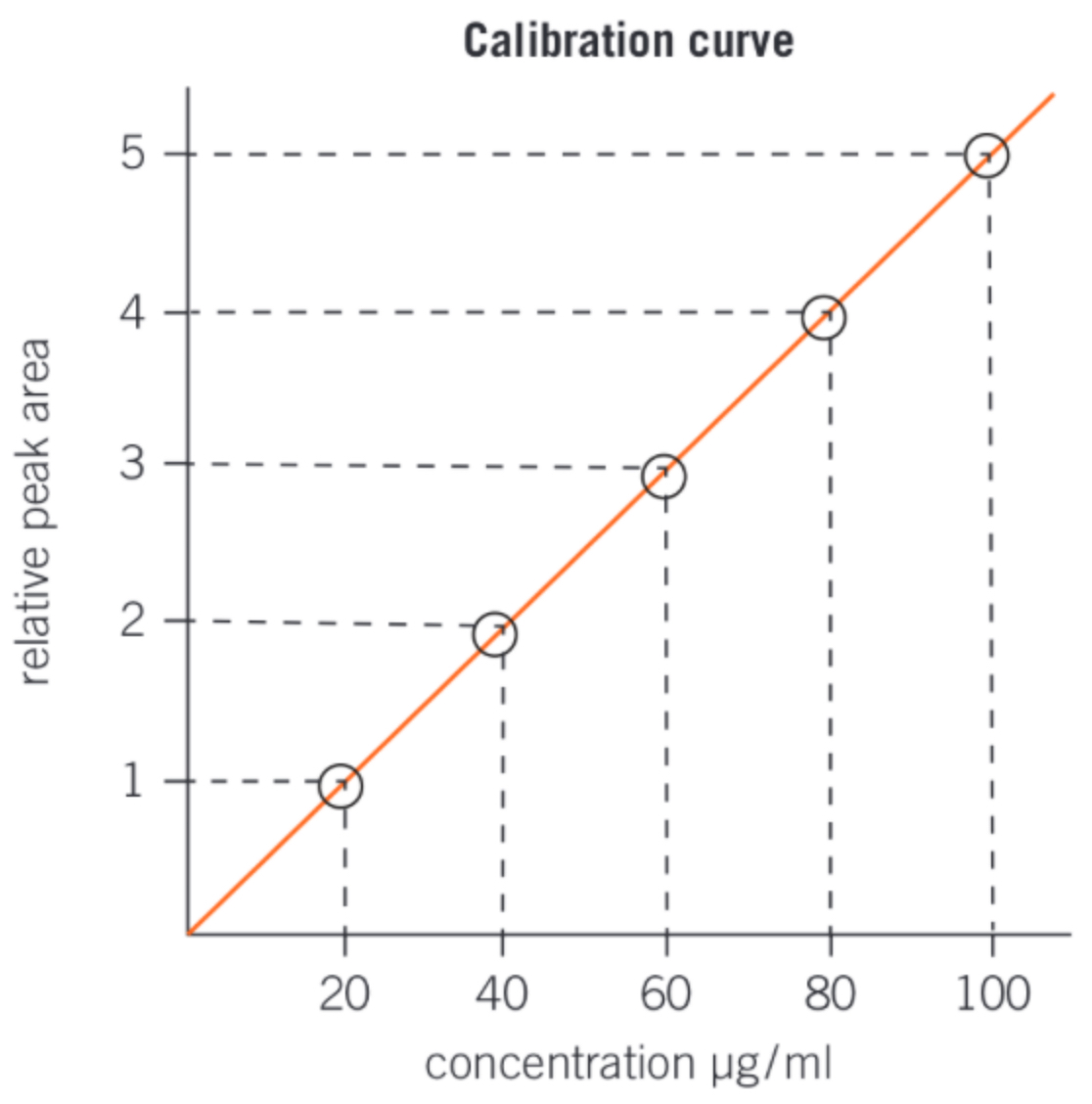
calibration curves
-area under peak is proportional to concentration of substance in mixture
-peak area is compared with peak areas from different standard solutions (different known concentrations)
NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
-nucleus has nuclear spin that is significant if odd number of electrons
-electron + nucleus have 2 different spin states with different energies
-used in MRI body scanners
13C NMR
-number of peaks = number of different carbon environments (what carbon is bonded to)
-can have several carbons in same carbon environments = lines of symmetry
-chemical shift = type of carbon environment (in data sheet)
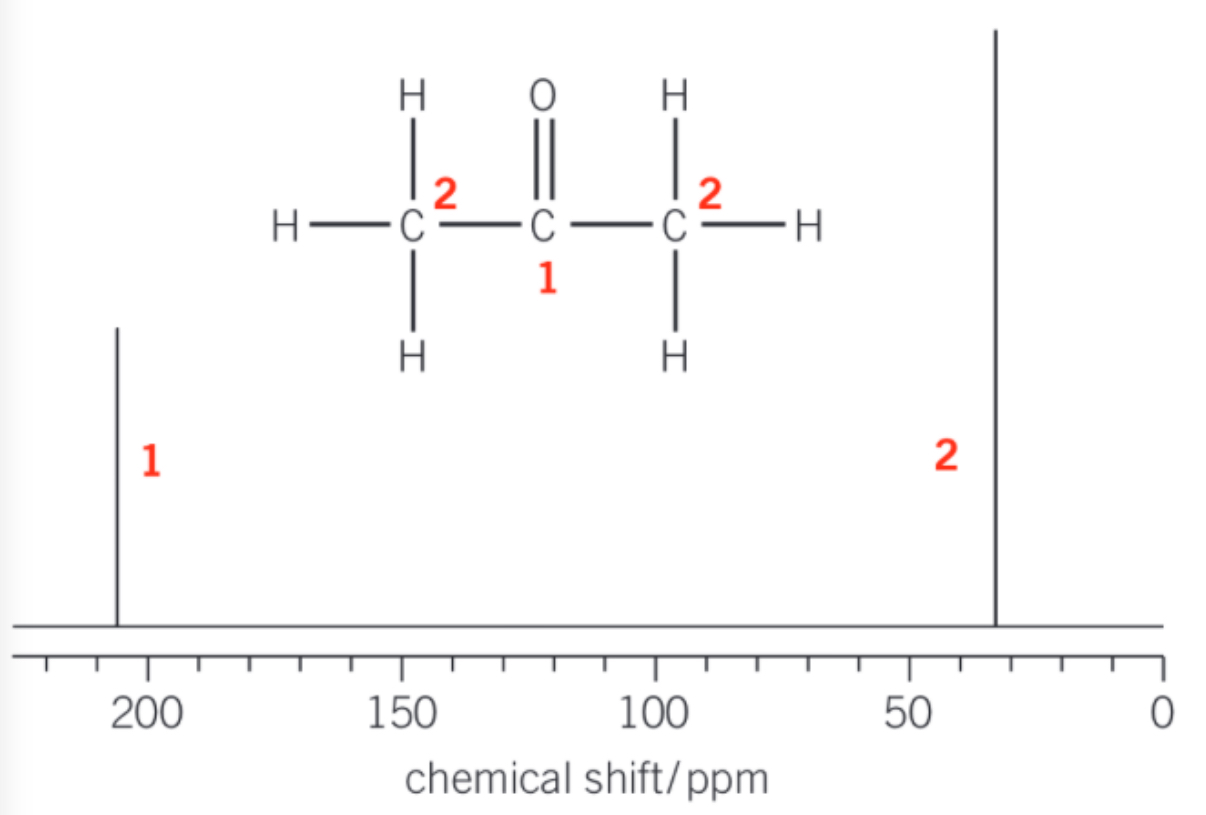
chemical shift + TMS
-chemical shift - units = ppm
-TMS = tetramethylsilane (CH3)4Si - used as standard reference - value = 0 ppm
deuterated solvents
-used in which 1H atoms have been replaced by 2H atoms (deuterium D) so has neutron in nucleus
-produces no NMR signal as it has even number of electrons
2 solvents used = CDCl3 used as solvent, D2O used to identify -OH or -NH protons
proton NMR
-number of peaks = number of proton environments (what hydrogen is bonded to)
-chemical shift = type of hydrogen environment
-relative peak area = number of protons in environment - given as ratio with numbers next to or as integration trace
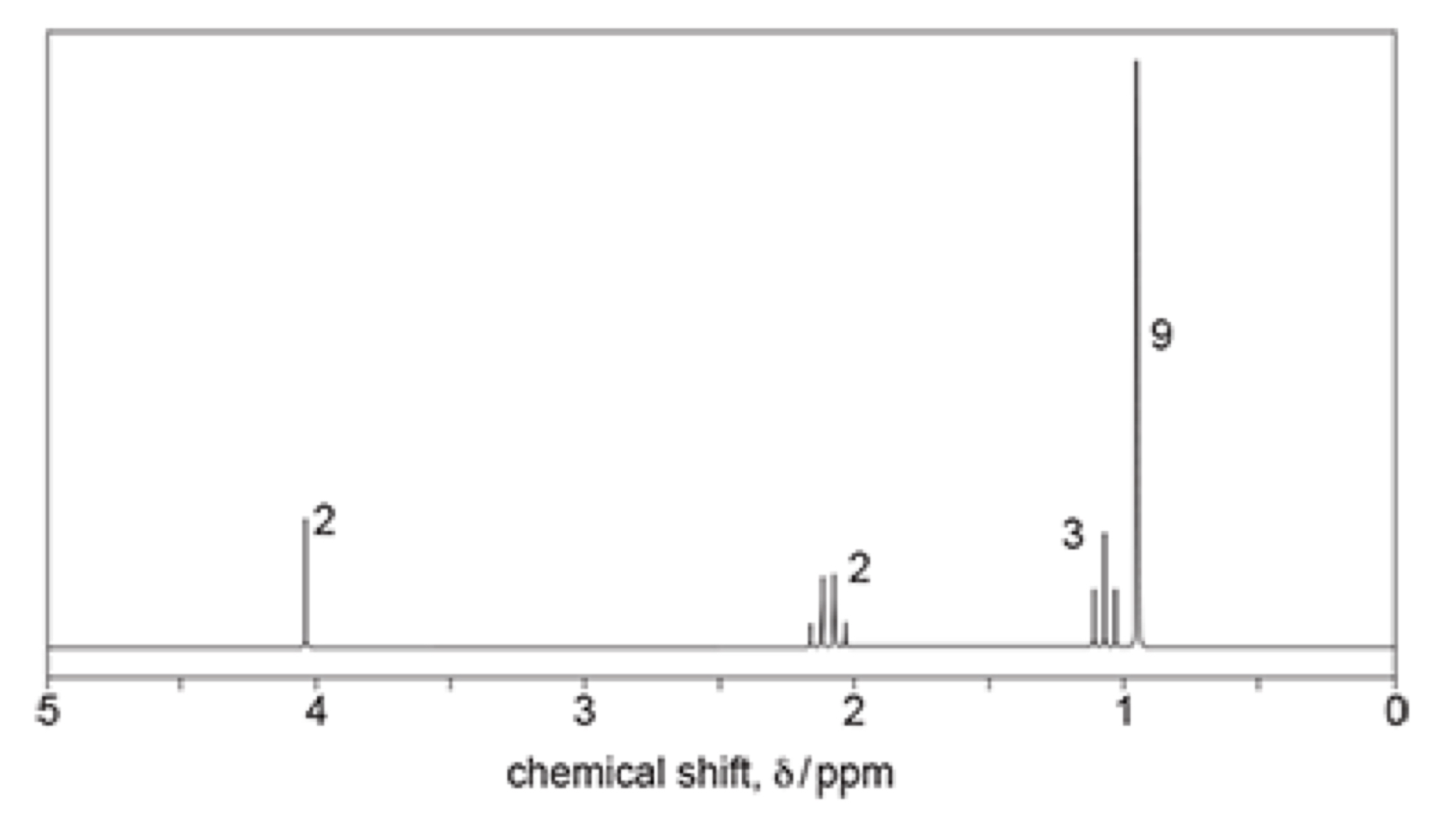
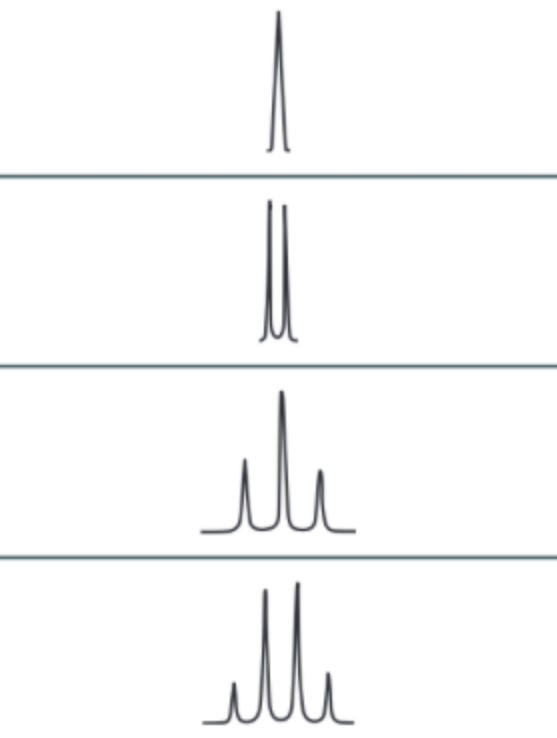
splitting patterns
-shows what is on adjacent carbon
n + 1 rule = n is number of hydrogens on adjacent carbon, + 1 is environment
singlet = no hydrogens on adjacent carbon
doublet = 1 hydrogen on adjacent carbon (CH)
triplet = 2 hydrogens on adjacent carbon (CH2)
quartet = 3 hydrogens on adjacent carbon (CH3)
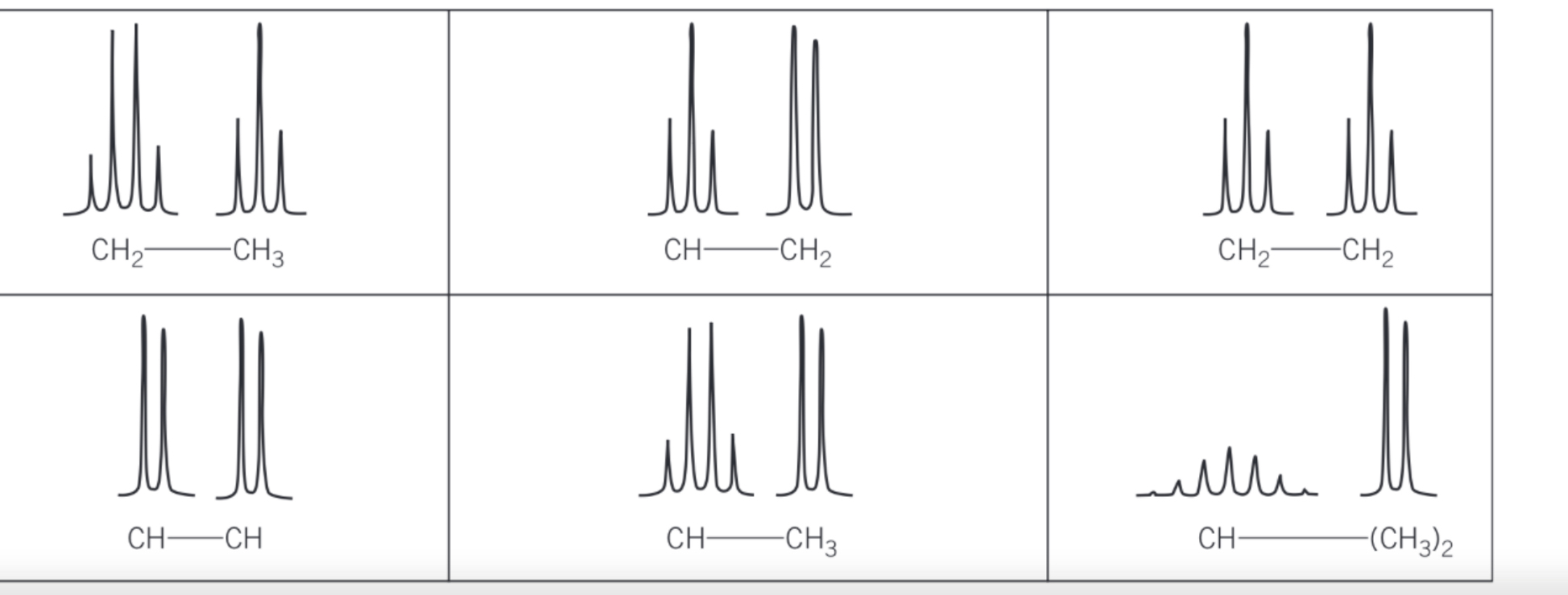
spin-spin coupling pairs
-splitting patterns occur in pairs because each proton splits signal of other
-OH and -NH groups + use of D2O
-D2O used to identify -OH or -NH groups
process: proton NMR run as normal, D2O added to mixture + shaken, D replaces OH and NH protons to form OD or ND
-so peak of OH or NH will disappear as deuterium does not absorb