Germanic Kingdoms: Military History and Notable Events
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes both Frankish (Merovingian and Carolingian) and Anglo-Saxon (Heptarchy) Kingdoms as well as other Germanic Kingdoms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
113 BCE - 101 BCE - Cimbrian War (All Facts)
War in which the two large namesake Celtic groups were ultimately defeated by Gaius Marius and Quintus Catulus and the Romans
War which
Began when the the namesake Celtic subtribe and the Teutones, another Celtic subtribe, left their homes at the time and went looking for new homes in Southern Gaul / northern Italy
The Romans sent several armies north to deal with them
In 109 BCE, the namesake subtribe and Teutones requested land to settle on in exchange for military service
However, Rome refused their offer and thus took a loss at one of its armies being destroyed as a result and then another army later on
War which marked the end of the Germanic threat to the Roman Republic
113 BCE - Battle of Noreia (All Facts)
Battle in which the Romans were defeated by the Cimbri and Teutones, it began the Cimbrian War
105 BCE - Battle of Arausio (All Facts)
Battle in which the Romans were defeated by the Cimbri, Teutones, and Ambrones, during the Cimbrian War
Battle regarded as the worst defeat in the history of ancient Rome surpassing the Battle of Cannae, in terms of Romans killed
102 BCE - Battle of Aquae Sextiae (All Facts)
Battle in which Gaius Marius and the Romans defeated the Teutones and Cimbri, subtribes of Celts that were advancing into Italy and southern Gaul, during the Cimbrian War
200K Teutones were killed
90K Teutones were taken prisoner
101 BCE - Battle of Vercellae (All Facts)
Battle in which Gaius Marius and Quintus Catulus and the Romans defeated the Cimbri and Teutones, subtribes of Celts that were advancing into Italy and southern Gaul, thus ending the Cimbrian War
140K Cimbri were killed
Many Teutones women were enslaved after this battle
Thus, the invincible barbarians from the north who had Italy at their mercy were invincible no more when faced, for the first time, with the toughened Volunteer Army of Marius
Battle which marked the end of the Germanic threat and defeat of the Cimbri to the Roman Republic
9 CE - Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (All Facts)
Battle in which Varus and the Romans were defeated by Arminius and the Cherusci tribe of the Germans, also known as the “Varian Disaster”
Was caused by the need to pacify a region that was neglected to revolts elsewhere
Varus had trusted Arminius’s loyalty to Rome, which he was initially loyal to despite being German
However, he was led into an ambush where he and three Roman legions were slaughtered, hemmed in by forests and marshes
Varus, who had deluded himself into thinking the tribesmen were grateful for Roman rule, killed himself with his sword after which his head was cut off and sent to Rome by the victorious Germans
Battle which thus proved to be a damaging blow to Roman prestige and its hold in Germany
Emperor Augustus was so overcome by the defeat that he
Refused to cut his beard or hair for several months
Abandoned the attempted conquest of Germany
16 - Battle of the Weser River (All Facts)
Battle in which Germanicus and the Romans defeated Arminius and the Germans
Battle which was the latest victory in a series of campaigns organized by Rome to avenge Varus and themselves for the crushing defeat they suffered at the hands of the Germans in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
Battle which made Germanicus popular, so much so that it aroused jealousy in Tiberius who had him recalled to Rome so he could keep a close watch of him
16 - Battle of the Angrivarian Wall (All Facts)
Battle in which Germanicus and the Romans defeated Arminius and the Germans
Battle which was the latest victory in a series of campaigns organized by Rome to avenge Varus and themselves for the crushing defeat they suffered at the hands of the Germans in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
Battle which made Germanicus popular, so much so that it aroused jealousy in Tiberius who had him recalled to Rome so he could keep a close watch of him
69 - Batavian Revolt / Revolt of the Batavi (All Facts)
Revolt in which Quintus Cerialis (a general under Vespasian) and the Roman legions defeated Gaius Julius Civilis and his Germanic army
Sometimes referred to as the “War of Liberation”
It began under the pretext of providing support for Vespasian, and was joined by Gallic tribes such as the Treveri and the Lingones
166 - 180 - Marcomannic Wars (All Facts)
Series of wars in which Marcus Aurelius and the Romans fought the namesake Germanic tribe and the Quadi and Sarmatian Iazyges
166 - German tribes poured across the upper and lower Danube River and invaded northern Italy
167 - Claudius Pompeianus and the Romans halted the German invaders in Pannonia
168 - At Aquileia, Aurelius and Verus reach peace terms with the German invaders who entered northern Italy in 166, in which the region is freed from foreign interference
169 - The namesake tribe and the Quadi get as far as the plains of north Italy, in which they cause panic in Rome
172 - Aurelius imposed a peace on the namesake tribe and the Quadi, in which a strip of land almost five miles wide to the north of the Danube River became forbidden to them
173 - Avidius Cassius crushed the insurrections of the shepherd brigands known as the Boukoloi
175 - Aurelius imposed a peace on the Sarmatian Iazyges in the Danubian region
177 - The namesake tribe and the Quadi declare war on the Roman Empire again
179 - Tarrutenius Paternus and the Romans won against the Marcomanni on the Danube River in the Battle of Vindobona
180 - Commodus, after consolidating his power and retaining the sole emperorship, abandons plans for Roman conquest of the German tribes’ lands and makes peace with the namesake before returning to Rome
212 - 305 - Barbarian Invasions of the Third Century (All Facts)
Uninterrupted period of raids within the borders of the Roman Empire, conducted for purposes of plunder and booty, by armed peoples belonging to various populations
Notable Raids include
233 / 235 - The Alamanni raided the frontier of the upper Rhine and an area called the Agri Decumates
They withdrew after they were bribed or paid tribute by the Romans
238 - The Goths and the Carpi took possession of land north of the Black Sea, crossed the Danube River and invaded the province of Moesia
Despite the Romans paying them tribute, they could not persuade these two groups to withdraw from the province of Moesia
250 - The Carpi invade Dacia
250 / 251 - The Goths invade Moesia, penetrating Dacia
253 - The Franks invaded Gaul
253 - The Alamanni invaded Gaul
260 - The Franks invaded Gaul again, having swept into Spain
260 - The Goths and Vandals invaded Italy and Greece
260 - The Berbers attacked Roman land in Africa
267 - The Goths pillage Thrace, Macedonia, and Greece
271 - Romans are forced to evacuate Dacia
275 - The Franks pillaged Gaul
275 - The Alamanni pillaged Gaul
This period roughly corresponds with the “Crisis of the Third Century”
251 - Battle of Abrittus (All Facts)
Battle in which Cniva and the Goths and Scythians defeated Decius and his son and led to Gallus’s emperorship
Battle which began as a result of the disloyalty of Gallus, the governor of Moesia
357 - Battle of Strasbourg (All Facts)
Battle in which King Chnodomar and the Alamanni were defeated by Emperor Julian and the Romans in which they were driven back behind the Rhine River after initially crossing it
378 - Battle of Adrianople (All Facts)
Battle in which King Fritigern of the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths (their calvary) and the Alans (of Iran) defeated Emperor Valens and the Romans
Battle in which
Emperor Valens did not wait for Gratian and the Western Roman army, and was wounded and carried into a house which the Visigoths and Ostrogoths had then burned down shortly afterwards, burning him alive and killing him along with it
Panic was caused in Constantinople that led to the massacring of many Gothic troops that had served in the Roman army as a precautionary measure lest the join the Goths again
Battle that was considered the worst Roman defeat at the hands of the Goths since the Battle of Teutoburg Forest in 9 CE
382 - Roman-Gothic Treaty of 382 (All Facts)
Treaty signed between the Visigoths and Emperor Theodosius the Great of Rome which
Provided the Visigoths land and political autonomy
Provided Rome with military service by the Visigoths
This was the first time in Roman history and Theodosius was the first Roman Emperor to accept undefeated barbarians (Germanic Tribes) into the empire and recruit them into the army for Roman military service
402 - Siege of Asti (All Facts)
Battle in which Alaric and the Visigoths invade northern Italy from the Balkans and take the namesake city from the Romans
402 - Battle of Verona (All Facts)
Battle in which Alaric and the Visigoths were defeated by Stilicho and the Romans
Battle in which Alaric and the Visigoths were forced out of Italy by Stilicho and the Romans
406 - Battle of Fiesole (All Facts)
Battle in which Radagaisus and the Vandals and Goths were defeated by Stilicho and the Romans after Radagaisus and the Vandals and Goths had pillaged the namesake city near Florence, Italy
406 - Crossing of the Rhine River (All Facts)
Action taken by hordes of Vandals, Burgundians, Suebi, and Alani in which the tribes took advantage of the freezing cold winter to perform the namesake action while the namesake place was frozen and expose the final frontier of the Romans
Event which was the beginning of the end for Western Rome and is considered to have contributed significantly to the decline and sack of Rome by the Germanic Kingdoms
From the Rhine River, they pillaged in
406 - Gaul
409 - Spain
410 - First Sack of Rome (All Facts)
Event in which Alaric and the Visigoths defeated the Romans and take the namesake heart of the Roman Empire, burning and pillaging it
Event which marked the first time in 800+ years that Rome had fallen to a foreign enemy
Event triggered by Emperor Honorius refusing Alaric’s demands for gold and honors, including the “Master of Soldiers” honor
Event in which Emperor Honorius’s sister, Galla Placidia, was taken hostage by Alaric and the Visigoths and eventually married Athaulf
Event whose psychological destruction was of far greater detriment to the Roman Empire than the material destruction
Although the capital of the empire was moved by Emperor Honorius to Ravenna, its sack was quite significant despite Roman optimists pointing out that it was not militaristically significant, but was rather spiritually significant
Throughout the empire, there were many who blamed Christianity and the neglect of the old gods for Rome’s decline and weakness, however realists knew that Romans had abdicated responsibility for defending themselves, transferring the position to the Goths fighting for them, with them, and/or against them on their frontiers
As a result of this event, Emperor Honorius ceded Aquitania, the Roman province in modern-day southwestern France to the Visigoths, from which they soon established their own independent “successor” kingdom
430 - 431 - Siege of Hippo (All Facts)
Battle in which King Gaiseric and the Vandals seize and capture the namesake Roman city from Bonifatius and the Romans
439 - 442 - Vandal War (All Facts)
War in which King Gaiseric and the Vandals defeated Flavius Aetius and the Romans, in which they took Carthage and North Africa from Rome
War which ended when King Gaiseric and the Vandals signed a peace treaty with Valentinian III and the Romans, with the approval of Theodosius II
It granted Gaiseric full rights to be an independent ruler over most of the Roman province of Africa (Tunisia and Western Libya), leading to the formation of the Vandal Kingdom
In exchange, Gaiseric and the Vandals agreed to give Sicily, Numidia, and Mauretania (Morocco and Algeria) back to Valentinian III and the Roman Empire
451 - Battle of the Catalaunian Fields (All Facts)
Battle in which Flavius Aetius led a coalition of Romans, Visigoths, Burgundians, and Franks and defeated Atilla and the Huns
Battle which definitively prevented Atilla and the Huns from conquering Gaul
Battle in which Aetius allowed Attila to retreat to Pannonia (Hungary)
Battle which began when Atilla the Hun demanded that he marry Emperor Valentinian III’s sister Honoria (who was willing to marry him) but Valentinian III denied his request so Atilla invaded Gaul in response
Battle in which Theodoric, 5th King of the Visigoths, died heroically
454 - Battle of Nedao (All Facts)
Battle in which King Ardaric and the Gepids, alongside other peoples that were in the Hunnic Empire, revolted against and defeated the sons of Atilla the Hun and their allies in Pannonia, leading to the dissolution of the Hunnic Empire
455 - Second Sack of Rome (All Facts)
Event in which Gaiseric and the Vandals defeated the Romans and take the namesake heart of the Roman Empire, pillaging it for two weeks straight, upon the death of Valentinian III
Gaiseric and the Vandals agreed not to burn Rome after Pope Leo pleaded them not to
Event in which Gaiseric and the Vandals seized
The remainder of Roman North Africa
Sardinia and Corsica
Spoils taken by Titus from Jerusalem back in 70 CE
Thousands of captives
Empress Eudoxia and her daughters
Event in which Gaiseric and the Vandals took Rome due to their powerful fleet
Despite being his ally, Gaiseric took Valentinian III’s murder as a sign that all treaty obligations with him were nullified
After this event, the fleet roamed freely throughout the western Mediterranean ready to take more land and booty
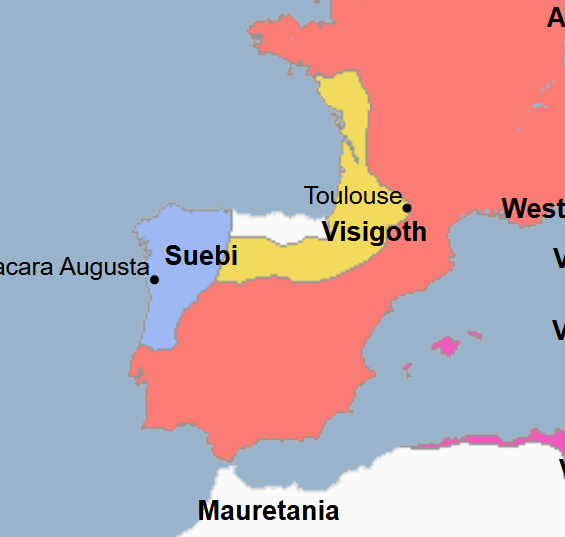
456 - Gothic War in Spain (All Facts)
War which Emperor Avitus and the Roman Empire instigates in which Theodoric II and the Visigoths fought against and defeated King Rechiarus and the Suebi
They are assisted by Romans, Franks, and Burgundians
As a result, Theodoric II and the Visigoths seized parts of modern-day Spain to be added to the Visigothic Kingdom
486 - Battle of Soissons (All Facts)
Battle in which Clovis and the Franks defeated Syagrius and the Romans and conquered northern Gaul, which led to the foundation of the Frankish Kingdom
489 - Battle of Verona (All Facts)
Battle in which Theodoric the Great and the Ostrogoths defeated King Odoacer of Italy
Odoacer fled to Ravenna
490 - 493 - Siege of Ravenna (All Facts)
Event in which Theodoric the Great and the Ostrogoths besieged Odoacer and his forces in the namesake city
Event which ended when the two men agreed to peace, in which Theodoric persuaded Odoacer to surrender by offering him a share of the government
However, shortly afterwards, Theodoric the Great murdered Odoacer at a banquet
Event which led to the Ostrogothic control of Italy and the start of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
496 - Battle of Tolbiac (All Facts)
Battle in which Clovis and the Franks defeated the Alamanni near the Rhine River, in which they were driven back beyond the river
507 - Battle of Vouille (All Facts)
Battle in which Clovis and the Franks, with help from Gundobad and the Burgundians, defeated Alaric II and the Visigoths
Battle in which the Franks
Took Aquitaine
Pushed the Visigoths back into Spain
Killed Alaric II
Battle which Clovis was “theologically justified” in waging against the Visigoths because of their Arianism and denial of the Trinity as he was a recently converted Nicene Christian
Battle which led to Clovis and the Franks’ control of all of Gaul except for southeastern Gaul
Battle which took place 10 miles from Poitiers
524 - Battle of Vezeronce (All Facts)
Battle in which Godomar II and the Burgundians defeated Chlodomer and the Franks
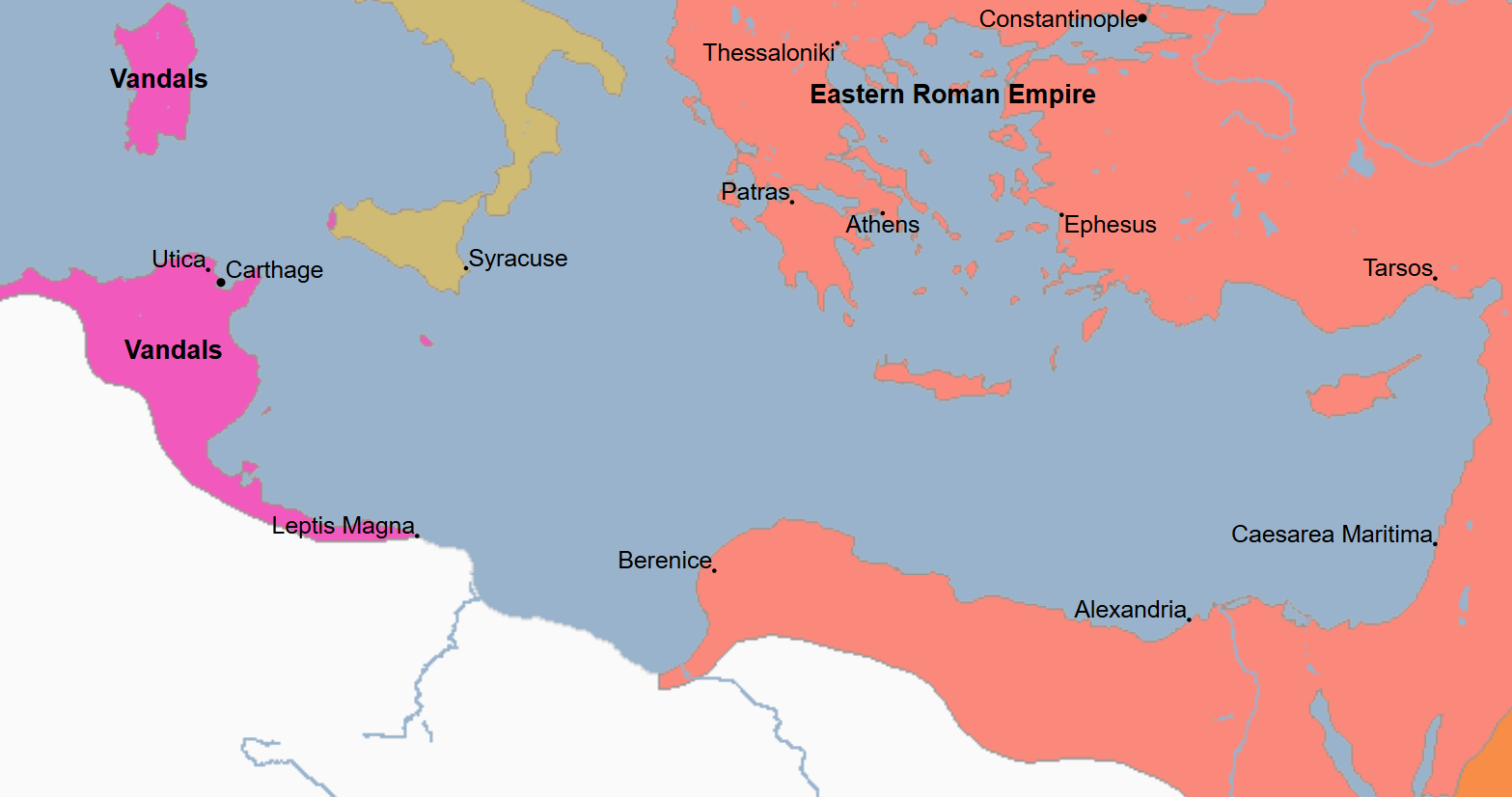
533 - 534 - Vandalic War (All Facts)
War in which Gelimer and the Vandals were defeated nu Justinian, Belisarius, and the Byzantines, who retook North Africa (Tunisia) from them
It was the first in a series of wars instigated by Justinian to try and reconquer Western Rome
War in which Belisarius led a small force of about 18K troops, 1K of which were Barbarian allies and Belisarius’s own bodyguard, carried in 500 ships
They landed in Byzacenum
Within a month, the imperial force crushed a large Vandal army at Ad Decinum and the gates of Carthage were opened back up to the Byzantine Empire
Belisarius was helped in his attack on the Vandals by the initial absence of their king, Gelimer, who was putting down a revolt in Sardinia
When Gelimer returned to North Africa, he blockaded Carthage in the process, but his armies were defeated within an hour of meeting the imperial army at Tricamarum
Gelimer fled
The empire recovered all of its lost possessions in the imperial province of Africa (Tunisia)
Justinian awarded himself the title “Vandalicus” (conqueror of the Vandals) as a result of the Byzantine victory in this war
535 - 554 - Gothic War (All Facts)
War in which the Ostrogoths were defeated by the Byzantines, thus having ended the Ostrogoth Kingdom
War in which
535 - Theodahad of the Ostrogoths has his wife and daughter of his predecessor Amalasuntha strangled, which gave Justinian a pretext for invading Ostrogothic Italy
535 - Belisarius captures Sicily
536 - Belisarius captures Rome and Naples
537 - Vitiges and the Ostrogoths besiege Rome
538 - Vitiges and the Ostrogoths abandon their siege of Rome
539 - Vitiges and the Ostrogoths capture and destroy Milan, massacring its men and enslaving its women
540 - Belisarius tricks Vitiges into surrendering to him, and takes possession of Ravena, thoroughly reconquering Italy south of the Po River and takes Vitiges with him back to Constantinople
543 - Totila and the Ostrogoths besiege and recaptures Naples, forcing Belisarius to return to Italy
546 - Totila and the Ostrogoths besiege and recapture Rome, in which all but 500 of its inhabitants flee from the city
547 - Belisarius reoccupies and repairs the defenses of the deserted city of Rome
550 - Belisarius is recalled from Italy back to Constantinople due to lack of imperial money and reinforcements, and Totila takes advantage and recaptures and reconquers Rome
551 - Totila and the Ostrogoths recapture almost all of Italy
552 - Narses and the Byzantines defeated Totila and the Ostrogoths, killing Totila, in the Battle of Taginae
553 - Narses and the Byzantines defeated Teias and the Ostrogoths in the Battle of Vesuvius, having (almost) completely reconquered Italy and ending the Ostrogoth Kingdom
537 - 538 - Siege of Rome (All Facts)
Battle in which Vitiges and the Ostrogoths moved onto Rome during the Gothic War
Within a year, however, Vitiges abandoned it
Battle which played a significant role in the early development of the Gothic War
539 - Siege of Milan (All Facts)
Battle in which Vitiges and the Ostrogoths moved onto Milan during the Gothic War
After the battle, Vitiges and the Ostrogoths massacred all of Milan’s men and enslaved all of Milan’s women
539 - 540 - Siege of Ravenna (All Facts)
Battle in which Vitiges and the Ostrogoths were defeated by Belisarius and the Byzantines during the Gothic War
Battle in which Belisarius tricked Vitiges into surrendering to him
After this battle, Belisarius took Vitiges back with him to Rome, forcing the Ostrogoths to elect a new king to succeed him
542 - 543 - Siege of Naples (All Facts)
Battle in which Totila and the Ostrogoths defeated the Byzantines during the Gothic War, forcing Belisarius to return to Italy from Constantinople
546 - Sack of Rome (All Facts)
Battle in which Totila and the Ostrogoths took the namesake city during the Gothic War, in which all but 500 of its inhabitants to flee
One year after the battle, Belisarius returned to the namesake city to reoccupy it and repair its defenses
549 - 550 - Siege of Rome (All Facts)
Battle in which Totila and the Ostrogoths recaptured and reconquered the namesake city during the Gothic War, undoing the repair done by Belisarius previously and wreaking havoc on the male population there
Battle which was prompted by Totila taking advantage of a situation in which Belisarius was recalled from Italy back to Constantinople due to lack of imperial money and reinforcements
552 - Battle of Taginae (All Facts)
Battle in which Totila and the Ostrogoths were defeated by Narses and the Byzantines during the Gothic War
Battle in which Totila is killed, forcing the Ostrogoths to elect a new king to succeed him
553 - Battle of Vesuvius (All Facts)
Battle in which Teias and the Ostrogoths were defeated by Narses and the Byzantines
Battle which marked
the (almost) complete reconquest of Italy
the end to the Ostrogoth Kingdom
the end to the Gothic War
569 - Siege of Pavia (All Facts)
Battle in which Alboin and the Lombards besieged the namesake city and overran (northern) Italy, which led to the foundation of the Lombard Kingdom in Italy
603 - Battle of Degsastan (All Facts)
Battle in which King Aethelfrith of Bernicia defeated Aedan and the Gaels of Dál Riada
633 - Battle of Hatfield Chase (All Facts)
Battle in which Cadwallon ap Cadfan of the Gwynedd Kingdom and Penda of the Mercian Kingdom defeated and killed Edwin and the Northumbrian Kingdom, the latter of whom was venerated as a result and due to his baptism
642 - Battle of Maserfield (All Facts)
Battle in which Penda and the pagan Mercians defeated the Nicene Christian Oswald and the Northumbrians
655 - Battle of the Winwaed River (All Facts)
Battle in which Oswy and the Nicene Christian Northumbrians defeated and killed Penda and the Arian Christian Mercians
685 - Battle of Dun Nechtain (All Facts)
Battle in which Ecgfrith and the Northumbrians were defeated and killed by Bridei III and the Picts
Battle in which the Northumbrians were forced to flee from conquered Pictish territory
Battle in which Ecgfrith was tricked by Bridei into chasing him into a remote valley in Angus before he sprang a reinforced ambushed
Battle in which Ecgfrith’s body lied in a monastery unmolested because both the Picts and Northumbrians had recently converted to Christianity due to the efforts of the missionary Columba
Battle which ended 30 years of Northumbrian dominance over the Pictish Kingdom
687 - Battle of Tertry (All Facts)
Battle in which Pepin of Herstal and the Austrasians defeated and conquered the Neustrians, uniting the Franks under one king and one mayor
711 - Battle of Guadalete (All Facts)
Battle in which Roderic and the Visigoths were defeated by Tariq ibn Ziyad and the Umayyad Caliphate
Battle in which much of Visigothic Spain was given over to the Umayyad Caliphate
716 - Battle of Ambleve (All Facts)
Battle in which Charles Martel, mayor of Austrasia at the time, defeated King Chilperic II of the Franks at Neustria, in order to consolidate his own power
Battle which demonstrated Martel’s military genius for the first time, which would characterize the remainder of his military career
721 - Battle of Toulouse (All Facts)
Battle in which Duke Odo the Great and the Franks defeated al-Sanh ibn Malik and the Umayyad Caliphate, preventing an Arab Muslim invasion of Gaul
722 - Battle of Covadonga (All Facts)
Battle in which Pelagius and the Visigoths defeated the Arab Muslims of the Umayyad Caliphate after leading a rebellion against them in Visigothic Spain, marking the start of the Spanish Reconquest of Spain from the Umayyad Caliphate and the founding of the tiny independent Christian kingdom of the Asturias in northern Spain by Pelagius
732 - Battle of Tours (All Facts)
Battle in which Charles Martel and the Franks defeated Abd al-Rahman and the Umayyad Caliphate, essentially preventing further Arab Muslim invasions into Europe
756 - Donation of Pepin (All Facts)
Treaty between Pepin the Short of the Franks and Pope Stephen II in which
Pepin the Short vowed to give 23 towns in central and northern Italy to Pope Stephen II
Pepin the Short promised Pope Stephen II he would invade Italy and take those towns from King Aistulf of the Lombards, who held them
When these towns were added to Pope Stephen II’s existing lands, they would contribute to the formation of a sizable papal state
The treaty also outlined that security for these papal states would be provided by Pepin the Short
In exchange, Pepin the Short and the Franks received the political and spiritual legitimacy for their reign that they had been craving up to that point
Thus, Pope Stephen II had the last Merovingian King ousted in favor of Pepin the Short
As a result, Pepin the Short and his successors were styled as “Patricians of the Romans”
Treaty which essentially established the temporal authority of the papacy, cutting the link between the papacy and the Byzantine Empire, and establishing a new link between the papacy and Italy
Treaty which contributed to the
Formation of the Papal States
Strong alliance between the Papacy and the Carolingian Empire
Treaty which would have far-reaching effects on the balance of power in northern Europe and which led to war with neighboring states of the Papal States and the Franks
Treaty which thus broke the alliance between the Franks and the Lombards established by Pepin the Short’s predecessor Charles Martel
752 - 759 - Siege of Narbonne (All Facts)
7-year Battle in which Pepin the Short and the Franks defeated the Umayyad Caliphate and defended the namesake city from being taken by the Arab Muslims
Following the battle, they retook control of Septimania from the Umayyad Caliphate as well
760 - 768 - Aquitanian War (All Facts)
Series of conflicts in which Pepin the Short subdue the semi-independent Aquitaine and seized it lands and defeated Waifar of Aquitaine and his army
Feud which ended with the death of both Waifar of Aquitaine and Pepin the Short
Feud which began when Pepin the Short punished Waifar of Aquitaine for defying Frankish authority
Series of conflicts which allowed Pepin the Short and the Carolingian Franks to (finally) establish control over the region, thus initiating the expansion of the Carolingian Empire
772 - 804 - Saxon Wars (All Facts)
Series of conflicts in which Charlemagne and the Carolingian Franks worked to defeat and Christianize the namesake Germanic tribe led by Widukind
The namesake group were either Christianized or mercilessly punished if they resisted Christianization
In 772, Charlemagne and his forces marched to the Weser River and destroyed the column of Irminsul, a tree worshipped by pagans as the tree that supported the world
In 782, Charlemagne annexed the namesake region and made it a Frankish province and imposed the Christian faith on the namesake natives
However, Widukind quickly led a revolt in retaliation and massacred a Frankish army
So, Charlemagne slaughtered rebel prisoners and invaded again
In 785, Widukind was baptized and reconciled to Charlemagne
This forced the namesake group to submit to Charlemagne and the Franks once again
778 - Siege of Zaragoza (All Facts)
Battle in which Charlemagne and the Carolingian Empire was defeated by the Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba
778 - Battle of Roncevaux Pass (All Facts)
Battle in which Roland and the Carolingian Franks were ambushed and defeated by the Basques that took place in the Pyrenees
Many Franks, including Roland himself, were killed
780 - 900 - Carolingian Renaissance (All Facts)
825 - Battle of Ellendun (All Facts)
Battle in which King Egbert of Wessex and the West Saxons defeated King Beornwulf of Mercia and the Mercians
Battle which essentially established West Saxon dominance over Mercia and southern England (the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms south of Northumbria)
840 - 843 - Carolingian Civil War (All Facts)
Series of conflicts over the succession to the Carolingian Empire following the death of Emperor Louis
Caused by the problems caused by the brother’s ambitions and their father and predecessor’s attempt to provide for his young son Charles
Louis's eldest son, Emperor Lothar I, laid claim to an undivided empire, while his younger brothers Louis the German and Charles II sought large kingdoms of their own on the basis of previous divisions planned by the late emperor
Civil War in which the Battle of Fontenoy occurred, in which Louis the German and Charles II defeated Lothar I and prevented him from taking control and making himself sole ruler over all of the Carolingian Empire
Series of conflicts which ended with the Treaty of Verdun, which
Divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms ruled by Charles II, Lothair, and Louis the German
Forced Lothair to renounce his kingdom’s sovereignty over the other two kingdoms
841 - Battle of Fontenoy (All Facts)
Battle in which Louis the German and Charles II defeated their elder brother Lothair, preventing Lothair’s sole consolidation and rule of the Carolingian Empire during the Carolingian Civil War
Battle in which Louis the German and Charles II and their armies swore oaths at Strasbourg doing so in local languages, rather than Latin, so that their troops could understand
This was an early transition stage in which early-modern German and early-modern French began to be spoken amongst the emperors
843 - Treaty of Verdun (All Facts)
Treaty which ends the Civil Wars between the sons and successors of Louis the Pious in the Carolingian Empire
Treaty which divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms, ruled by Lothair, Louis the German, and Charles II
Louis the German received “Francia Orientalis” (Bavaria and the other eastern lands in their territory), which became the Kingdom of East Francia / Kingdom of Germany
Charles II received “Francia Occidentialis” (Gaul and the other western lands in their territory), which became the Kingdom of West Francia
Lothair received “Francia Media” (the territory between the other two sons, from Italy to the Channel coast, retaining Aachen, Charlemagne’s capital; and Rome), which became the Middle Frankish Kingdom; along with the title of Emperor
Treaty which recognized Lothair as Emperor, but gave him no power over the kingdoms of his two brothers
It forced Lothair to renounce his kingdom’s sovereignty over the other two kingdoms
871 - Battle of Ashdown (All Facts)
Battle in which King Aethelred, his younger brother, the future King Alfred the Great and the West Saxons defeated Bagsecg, Halfdan, and the Danish Vikings
Despite their victory, however, Aethelred, Alfred the Great, and the West Saxons had to pay tribute to the Danish Vikings
878 - Battle of Edington (All Facts)
Battle in which Alfred the Great and the West Saxons defeated the Danes
After the battle, the Danes agreed to evacuate Wessex
891 - Battle of Leuven (All Facts)
Battle in which King Arnulf and Germany / East Francia (and the Holy Roman Empire) defeated the Vikings near the Dyle River, expelling them from his kingdom
910 - Battle of Tettenhall (All Facts)
Battle in which Edward the Elder, King of Wessex, and the West Saxons defeated the Danes and drove them back, reoccupying previous Danish-occupied territory including the great cities of London and Oxford
911 - Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte (All Facts)
Peace treaty signed between Charles the Simple of France / West Francia and Rollo of Normandy
Peace treaty in which Charles the Simple conceded western territory to Rollo that laid the foundations for the Duchy of Normandy (or “Northmen” or “Normans”), and Rollo
Swore homage to Charles the Simple
Accepted baptism and converted to Christianity
Agreed to defend his kingdom against other Vikings
923 - Battle of Soissons (All Facts)
Battle in which an alliance of Frankish insurgent nobles led by Robert, elected King of West Francia in an assembly the year prior defeated Charles the Simple and his Lotharingian, Norman, and Carolingian forces
Battle after which Charles the Simple was imprisoned
933 - Battle of Merseburg (All Facts)
Battle in which Henry “The Fowler,” King of Germany (East Francia) and his forces defeated the raiding Magyars