8.3 Nomenclature and Stability of Alkenes
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the four basic steps for naming alkanes and alkyl halides?
Identify the parent chain
Identify the substituents
Number the substituents
Arrange the substituents alphabetically
Are the same four steps used to name alkenes?
Yes, with a few additional rules
What change is made to the parent name when naming an alkene?
Replace “-ane” with “-ene”
What does the ending “-ene” indicate?
The compound contains a C=C double bond
What is the parent name for an alkane with five carbons?
Pentane

What is the parent name for an alkene with five carbons?
Pentene

How do you choose the parent chain when naming alkanes?
Choose the longest continuous carbon chain; if there’s a tie, choose the one with more substituents
What additonal rule applies when choosing the parent chain for an alkene?
The parent chain must include the C=C (π bond)
What do you do if two chains are the same length?
Choose the chain that contains the double bond as the parent
Why must the parent chain include the double bond?
Because the double bond defines the compound as an alkene, not an alkane
What is the parent name of a 6-carbon alkane?
Hexane
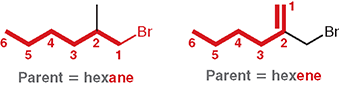
What is the parent name of a 6-carbon alkene with a double bond?
Hexene
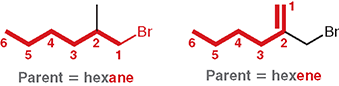
In the given example, why is “hexene” the correct parent?
Because the chosen chain includes π bond, even though another chain without the double bond is the same length
What gets top priority when numbering the parent chain of an alkene?
The π bond (double bond)
How should the parent chain of an alkene be numbered?
From the end closest to the double bond, giving it the lowest possible number
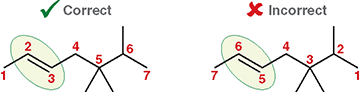
Why is the π bond given the lowest number?
Because the location of the double bond is the most important feature in naming an alkene
What makes the left example correct?
Numbering 1 → 2 → 3 reaches the double bond first, giving it the lowest locant
What makes the right example incorrect?
Numbering from the opposite end gives the double bond a higher number, which is not allowed
What is the general rule for numbering alkenes?
Always number toward the double bond
How do you indicate the position of the double bond in an alkene?
Use a single number showing where the π bond starts
If a double bond is between carbons 2 and 3, which number is used?
2 (because the double bond starts at carbon 2)
Where can the double-bond position number be placed in the name?
Before the parent name (1979 IUPAC)
Before “-ene” (1993 and later IUPAC)
Both are correct
Examples:
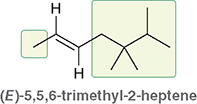
5,5,6-trimethyl-2-heptene
5,5,6-trimethylhept-2-ene
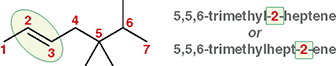
What does the double-bond locant tell you?
The carbon number where the double bond begins
Are both naming formats acceptable on exams?
Yes- both are officially recognized IUPAC names
What does the E configuration mean for a double bond?
The two highest-priority groups on each carbon of the double bond are on opposite sides
What does the Z configuration mean?
The two highest-priority groups are on the same side of the double bond
How do you determine priority around a double bond?
Using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) priority rules
Where is the E/Z stereo descriptor placed in the name?
At the very beginning of the name, in parentheses
Example: What does (E)-5,5,6-trimethyl-2-heptene tell you?
The double bond starts at carbon 2
The higher-priority groups are on opposite sides → (E)
Substituents are on carbons 5, 5, and 6
Why is the stereo descriptor required?
Because E and Z alkenes are different molecules with different shapes and properties
In a cyclic alkene, which carbons automatically get numbers 1 and 2?
The two carbons of the double bond
Do you need to specify the double bond position in simple cyclic alkenes?
No. The double bond is always between C1 and C2
What is the correct parent name for a six-membered ring with a double bond?
Cyclohexene, not 1-cyclohexene
After assigning C1 and C2 to the double bond, how do you number the rest of the ring?
Number in the direction that gives substituents the lowest possible numbers
Why is “3,3-dibromocyclohexene” the correct name in the example?
Because numbering from the double bond toward the substituents givens them the lowest locants (3 and 3)
What makes the incorrect examples wrong?
They number in the wrong direction, giving substituents higher and incorrect numbers (like 1,2 or 1,3)

What is the general rule for substituent numbering in cyclic alkenes?
Always start at the double bond (C1-C2) and number toward the nearest substituent
What is a compound with two double bonds called?
A diene
How do you indicate the positions of double bonds in a diene?
Use two numbers, each showing where a double bond starts.
Example: (2Z, 4E)-heptadiene
Where can the numbers for the double bonds be placed?
Either before the parent name (2,4-heptadiene) or before “-diene” (hepta-2,4-diene.) Both are correct.
What is a 10-carbon chain with three double bonds called?
Decatriene
What is an 11-carbon chain with four double bonds called?
Undecatetraene
What does “triene” indicate?
Three double bonds
What does “tetraene” indicate?
Four double bonds
What is the general naming pattern for polyenes?
Parent name + “di-/tri-/tetra-ene”, with numbers showing the position of each C=C bond
What is the common name for ethene (CH2=CH2)?
Ethylene
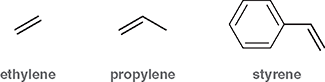
What is the common name for propene (CH2=CH-CH3)?
Propylene
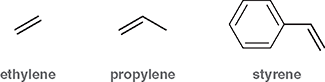
What is stryrene?
A benzene ring attached to a vinyl group (C6H5-CH=CH2)
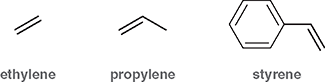
Are ethylene, propylene, and styrene official IUPAC names?
No- they are common names that IUPAC still recognizes due to widespread industrial use
Why are these common names important to know?
They appear frequently in industry, polymer chemistry, and exam problems
What is the mehylene group?
=CH2 as a substituent
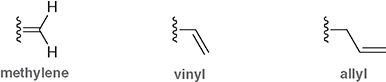
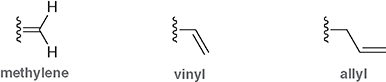
What is the vinyl group?
-CH=CH2 attached to a parent chain
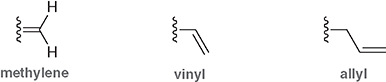
What is the allyl group?
-CH2-CH=CH2 attached to a parent chain
Are these names systemic or common names?
They are common names that IUPAC allows when these groups appear as substituents
Why are these names important?
They show up frequently in synthesis, reactivity, and naming problems
Which substituent contains a double bond directly attached to the parent chain?
The vinyl group
Which substituent has the double bond one carbon away from the parent chain?
The allyl group
What does “degree of substitution” mean for an alkene?
The number of alkyl groups attached directly to the double-bonded carbons
What is a mono-substituted alkene?
The double bond has one alkyl substituent (least stable)
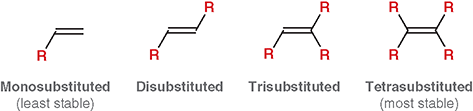
What is disubstituted alkene?
The double bond has two alkyl substituents
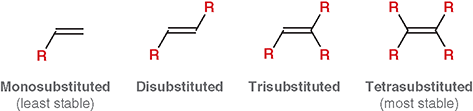
What is trisubstituted alkene?
The double bond has three alkyl substituents
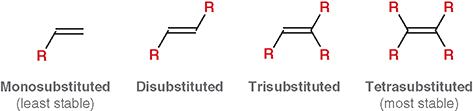
What is a tetra-substituted alkene?
The double bond has four alkyl substituents (most stable)
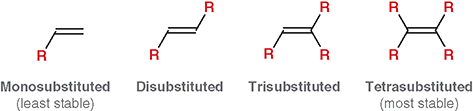
Does “substitution” here refer to substitution reactions from Chapter 7 ?
No. It refers only to how many alkyl groups are bonded to the double bond
Why does more substitution increase stability?
More alkyl groups stabilize the double bond through hyper conjugation and electron donation
What is the main factor that increases alkene stability?
The number of alkyl group attached to the double bond (degree of substitution)
Which is more stable: a more substituted or less substituted alkene?
A more substituted alkene
Why do alkyl groups increase alkene stability?
They donate electron density via hyperconjugation, stabilizing the double bond
Which is more stable: cis or trans alkenes?
Trans alkenes
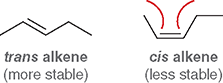
Why are cis alkenes less stable?
They have steric strain, because bulky groups are on the same side of the double bond
What type of strain do cis alkenes experience?
Steric strain (repulsion from groups being too close)
What is the overall stability order cis/trans isomers?
Trans> Cis
Which cycloalkenes cannot have a trans double bond?
Rings with fewer than 7 carbons (cyclopropene → cyclohexene)
What configuration must small cycloalkenes have?
Cis only (trans is impossible)
Why can small rings only have cis double bonds?
The ring is too small to twist into the geometry needed for a trans π bond without severe strain
Why is the configuration not written in names like “cyclohexene”?
The cis configuration is automatically inferred, so no E/Z or cis/trans label is needed
Can cycloheptene have a trans double bond?
In theory yes, but trans-cycloheptene is unstable at room temperature
What is the smallest ring that can stably contain a trans double bond?
Cyclooctene (8-membered ring)
Why can cyclooctene handle a trans double bond?
The ring is large and flexible enough to reduce the strain of opposite-side substituentsThe ring is large and flexible enough to reduce the strain of opposite-side substituents.
What is Bredt’s Rule?
A double bond cannot be placed at a bridgehead position in a small bicyclic system because it will be unstable
What is a bridgehead carbon?
A carbon atom shared by two or more rings in a bicyclic structure
Why is a bridgehead double bond unstable?
Because the bridgehead carbon cannot achieve the required planar geometry for a π bond
What does the red double bond in the example represent?
A trans double bond at a bridgehead- an arrangement that violates Bredt’s Rule
Does Bredt’s Rule apply to all bicyclic systems?
It applies to small bicyclic systems; only large ring systems can support a stable bridgehead alkene
What is required for a stable bridgehead double bond?
A large enough bicyclic system that allows the double-bond carbon atoms to become planar