APK2100C Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:19 PM on 9/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
253 Terms
1
New cards
anatomy
study of structures of the body
2
New cards
physiology
study of the functions of the body
3
New cards
functional anatomy
anatomy which emphasizes structural characteristics of a body part that contribute to its function
\
ie the knee and its joints
\
ie the knee and its joints
4
New cards
subdisciplines of anatomy
gross, regional, systemic, surface, microscopic
5
New cards
gross anatomy
dissection; can see structures with naked eye
6
New cards
regional anatomy
one specific area of the body ie structures with arm
7
New cards
systemic anatomy
organ systems ie digestive
8
New cards
surface anatomy
landmarks ie bony bump, vein
9
New cards
microscopic anatomy
requires microscope to see structure
\
2 subdisciplines
histology which evaluates structures ie tissues and cells
physiological/disease
\
\
2 subdisciplines
histology which evaluates structures ie tissues and cells
physiological/disease
\
10
New cards
hierarchy of structural organization
chemical level-cellular level-tissue level-organ level-organ system-organismal level
11
New cards
organ systems (11)
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
12
New cards
integumentary system
skin, external layers of body and accessory organs ie hair and glands
13
New cards
skeletal system
framework that allows movement of muscles or protects…
14
New cards
muscular system
muscles that allow movement and facial expression
15
New cards
nervous system
communication via electrical impulses (fast)
16
New cards
endocrine system
communication via chemical messengers ie hormones (Slow)
17
New cards
cardiovascular system
heart/blood vessels → transporting blood
18
New cards
lymphatic system
immune response
19
New cards
respiratory system
bring air in and remove waste ie CO2
20
New cards
digestive system
breaking down food into absorbable energy
21
New cards
urinary system
filters blood, waste, water content
22
New cards
reproductive system
embryo formation → cells
23
New cards
anatomical terminology
standardized terminology by med professionals and scientists; derived from greek and latin
\
ie osteoperosis
osteo= bone in greek porus= holes in greek- osis= greek condition for disease
\
ie osteoperosis
osteo= bone in greek porus= holes in greek- osis= greek condition for disease
24
New cards
anatomical position
body upright, standing erect facing observer, head and eyes facing forward, feet are flat on floor and forward, upper limbs to sides, palms turned forward
25
New cards
midline
line that moves down middle of body
26
New cards
medial/lateral
closer to midline/moving away from midline
27
New cards
left/right
from patients view, not viewer
28
New cards
superior/inferior
“above” towards head/ “below” towards feet
29
New cards
proximal/distal
close to point of attachment/ away from point of attachment
\
ie. leg closer to hip/
\
ie. leg closer to hip/
30
New cards
anterior/posterior
toward front(ventral)/ towards back (dorsal)
31
New cards
directional terminology
describing position of one structure relative to another structures
32
New cards
superficial/deep
closer to surface of body/more internal to body
33
New cards
ipsilateral/contralateral
structures on same side of body/ opposite of body
\
ie right hand and right leg/ right hand and left leg
\
ie right hand and right leg/ right hand and left leg
34
New cards
regional terminology
terms describing specific ….
35
New cards
anterior regional terminology
front of body
36
New cards
axial region
midline of body; ax is of body (head,neck,trunk)
37
New cards
appendicular region
everything not in axial
38
New cards
cephalic
general head region
39
New cards
frontal
forehead
40
New cards
orbital
eyes
41
New cards
nasal
nose
42
New cards
oral
mouth
43
New cards
mental
chin
44
New cards
cervical
neck
45
New cards
thoracic region
sternal= sternum. axillary= armpit, mammary= chest
46
New cards
abdominal region
umbilical=belly button ; pelvic region below
47
New cards
inguinal region (groin)
pubic= genitalia
48
New cards
appendicular
extremities= upper and lower limbs
49
New cards
anterior upper limb
acromial= shoulder, brachial= upper arm (shoulder to elbow), antecubital= crook of elbow, antebrachial= forearm, carpal= wrist
50
New cards
anterior hand
hand= manus, pollex= thumb, palmar= palm, digital= pther fingers
51
New cards
anterior lower limb
coxal= hip, femoral= thigh, patellar= knee cap, crural= leg, fibular, outside of leg
52
New cards
anterior pedal
tarsal= ankle, metatarsal= foot, digital= all toes, hallux= big toe
53
New cards
posterior cephallic
otic= ears, occipital= back of head (cervical underneath)
54
New cards
posterior dorsal
scapular= shoulder blade, vertebral- along middle of back, lumbar= lower back, sacral= between low back and butt, gluteal= buttox, perineal= btwn anus and external genitalia
55
New cards
posterior upper limb
acrhomial, brachial, olecranial= back of elbow, antebrachial= forearm
56
New cards
posterior manus
metacarpal and sital
57
New cards
posterior lower limb
femoral= thigh, poiteal= back of knee, sural= calf, fibural or peroneal= outside of leg
58
New cards
posterior pedal
calcaneal= heel, plantar= sole of foot
59
New cards
body planes and sections
coronal/frontal, horizontal/transverse, sagittal
60
New cards
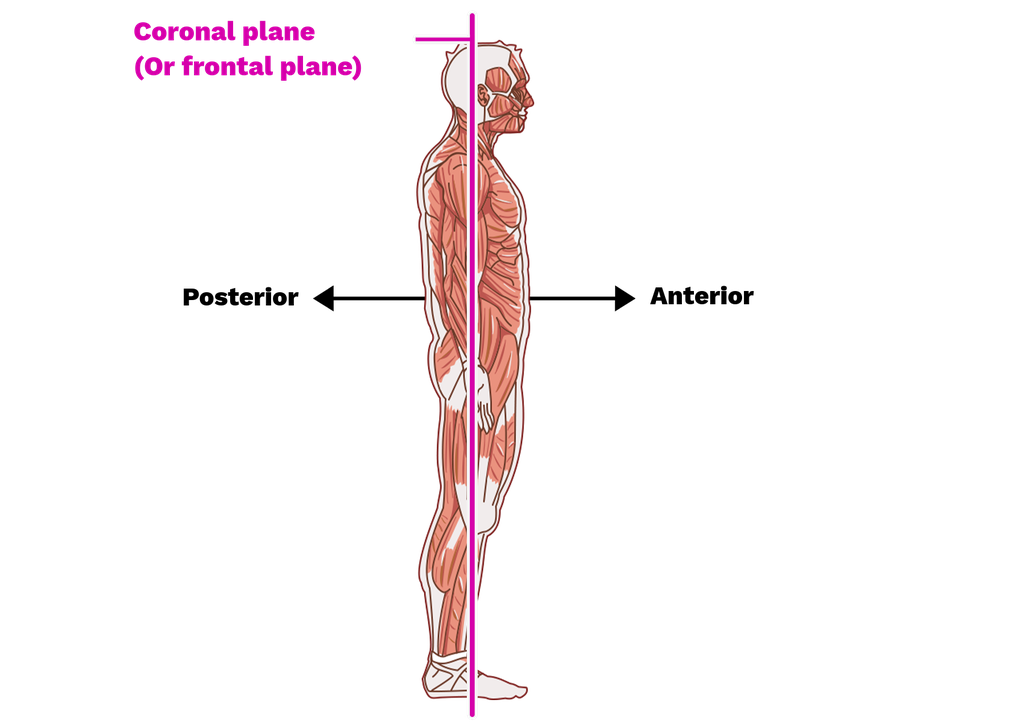
coronal plane
divides body/organ into anterior and posterior
61
New cards
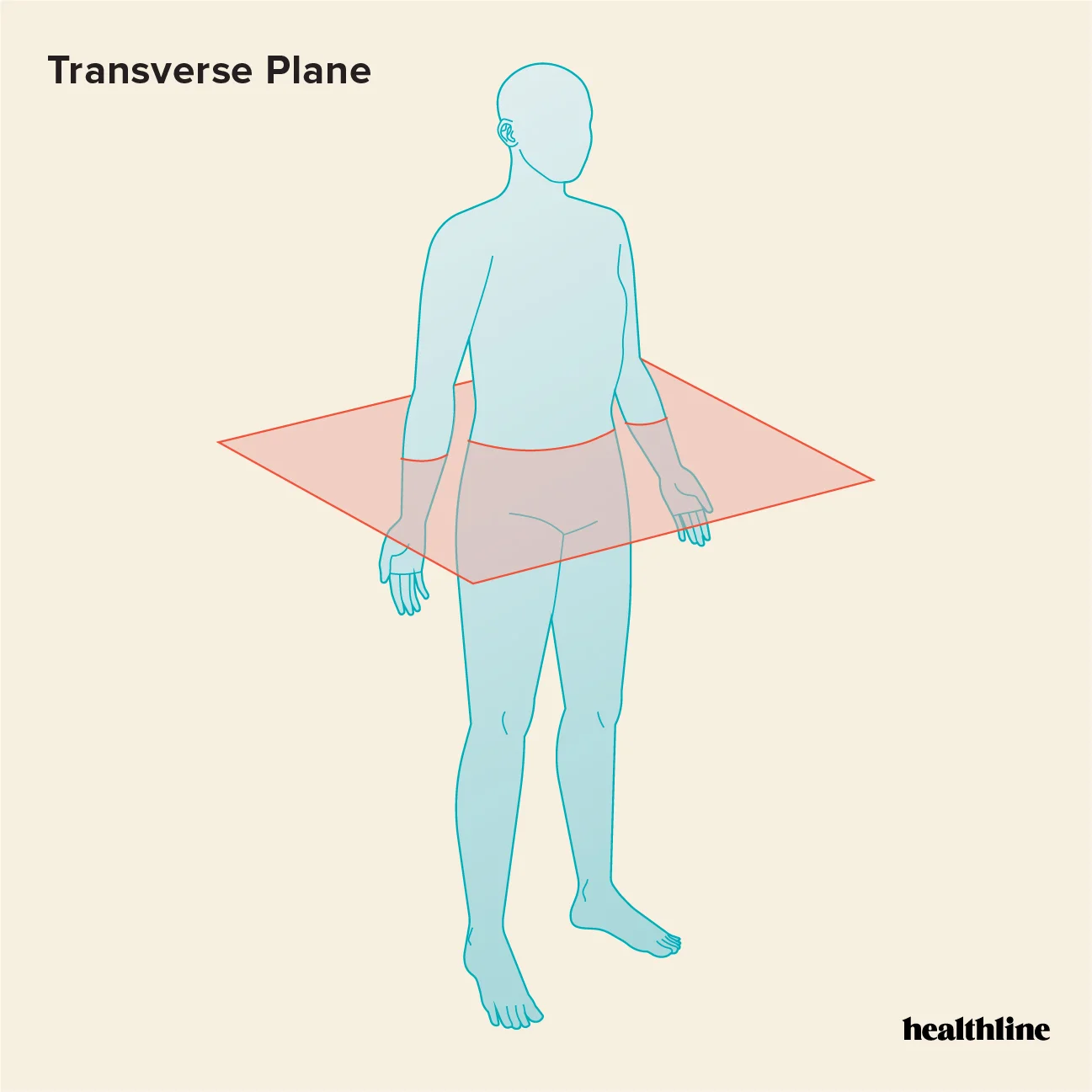
horizontal/transverse plane
divides body/organs into superior and inferior half
62
New cards
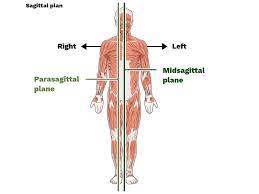
sagittal plane
vertical plane that divides body into right and left, can be equal (midsagittal) or unequal (parasagittal)
63
New cards
body cavities
spaces within body that separate, protect, and support internal organs
64
New cards
dorsal body cavities
associated with back (cranial and verterbal cavity)
65
New cards
ventral body cavity
thoracic and abdominopelvic
66
New cards
cranial cavity
formed by cranial bones and contains and protects brain
67
New cards
verterbral canal
formed by bones of verterbral column and protects spinal cord
68
New cards
meninges
layers of protective tissues that the line the cranial and verterbral canal
69
New cards
thoracic cavity
made of pleural cavity and Mediastinum
70
New cards
Mediastinum
region that has many structures
71
New cards
pleural cavity
reference to lungs; on right and left
72
New cards
abdominopelvic cavity
made of abdominal and pelvic cavity, closed cavities
73
New cards
mucous membranes
lines cavities that are open to outside environment, cells secrete mucous, ie oral and nasal cavities, vagina, anus
74
New cards
serous membranes
lines cavities that are closed to outside environment, cells secrete serous fluid as lubricant, thoracic and abdominal cavities found withinl 2 layers are continous with one another
\
visceral layer: touches organ, pariteal layer touches body wall
\
balloon example!!!
\
examples: serose with lungs, perocardium or abdominal
\
visceral layer: touches organ, pariteal layer touches body wall
\
balloon example!!!
\
examples: serose with lungs, perocardium or abdominal
75
New cards
cells
living units, all living organisms are cellular in nature, smallest living unit in bodies, human has over 200 types of cells
76
New cards
basic cellular function
basic survival function: obtain/use nutrients, dispose of waste, replicate/regenerate/repair; made up of organelles
77
New cards
cytoplasm
fluid environment where organelles are
78
New cards
nucleus
control center of cell
79
New cards
plasma membrane: fluid-mosaic model
fluid-dynamic structure (not permanent in place); mosaic- multiple components associated with membrane; phospholipid bilayer: outward and inward layers, hydrophilic head and hydrophobic fatty acid tail, hydrophobic cholestorol along fatty acid tails
80
New cards
proteins in membrane
intergral: embedded within membrane
peripheral: periphery outside of membrane on ECF OR ICF; loosely associated with membrane and easily separable
peripheral: periphery outside of membrane on ECF OR ICF; loosely associated with membrane and easily separable
81
New cards
integral protein
transmembrane protein if it goes across whole bilayer which is vast majority
82
New cards
glycolipid/glycoprotein
carbohydrate chains attached to suffix
83
New cards
phospholipids
amphiphatic with dynamic arrangement, creates framework for plasma membrane, make up 3/4 of membrane lipids
84
New cards
membrane lipids
phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids,
85
New cards
cholesterol
fouund among lipid tails of bilayer, only in animal cells, strucutural integrity of plasma membrane; 4 ring structure
86
New cards
glycolipids
only found in layer facing ECF, cellular adhesion and recognition, carb chain attached to lipid
87
New cards
principal functions of plasma membrane
protective barrier, cellular communication via receptor proteins, regulating movement of substances in and out via membrane transport
88
New cards
membrane transports
plasma membrane selectively permeable, some solutes diffuse across lipid bilayer (no proteins or ATP needed) integral proteins acts as transports and channels to assist in entrance of impermeable (Cant cross whatsoever) molecules
carrier= passive
pumps=active
carrier= passive
pumps=active
89
New cards
passive transport
simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
90
New cards
simple diffusion
solutes and small enough molecules can cross membrane on their own (lipid soluble)
91
New cards
osmosis
diffusion of water across lipid bilayer requiring aquaporins
92
New cards
facilitated diffusion
transmembrane protein opens up and acts as channel to allow solutes that are water soluble to cross through
93
New cards
active transport
requires trans protein and ATP against concentration gradient
94
New cards
vesicular membrane transport
endocytosis- bring into cell
exocytosis- bring out of cell
exocytosis- bring out of cell
95
New cards
types of endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis
96
New cards
phagocytosis
“cell eating” bringing larger macromolecule into cell via pseudopods “arms”
97
New cards
pinocytosis
“cell drinking” smaller solutes dissolved within ECF, creates divot/pit
98
New cards
receptor mediated endocytosis
requires ligand (chemical messenger) to bind to receptor which signals creation of vesicle to bring materials in
99
New cards
exocytosis
removing material from cell, vesicle migrates to edge of cell, vesicle made of plasma? so fuses with membrane and liberates content out of cell (Secretory vesicle)
100
New cards
cytosol
jelly like fluid in which all other intracellular elements are suspended ie water, ions, enzymes, site of many chemical reactions