Ch 3 - Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
sequence
function from the whole number to the real number
arithmetic sequence
a(n) = a(0) + dn
common difference
a(n) = a(k) + d(n - k)
geometric sequence
g(n) = g(0) * r^h
common ratio
g(n) = g(k) * r^(h-k)
arithmetic creates _______ while geometric create ________
linear functions; exponential functions
linear function based on table bc
equal length input value intervals have output values of function change at a constant rate
exponential
consistent ration that is multiplied between equa distant input intervals
rate of change is increasing when
concave up (quadratic) or going up (exponential)
rate of change is decreasing when
concave down (quadratic) or going near asymptote (exponential)
exponential function parts
f(x) = a * b ^(x - c) + d
a = vertical stretch or compression
b = base
c = horizontal shift
d = vertical shift
reflect over x-axis when (-) negative is in front of
a
reflect over y-axis when (-) negative is in front of
x
increasing at an increasing rate
f(x) = e^x
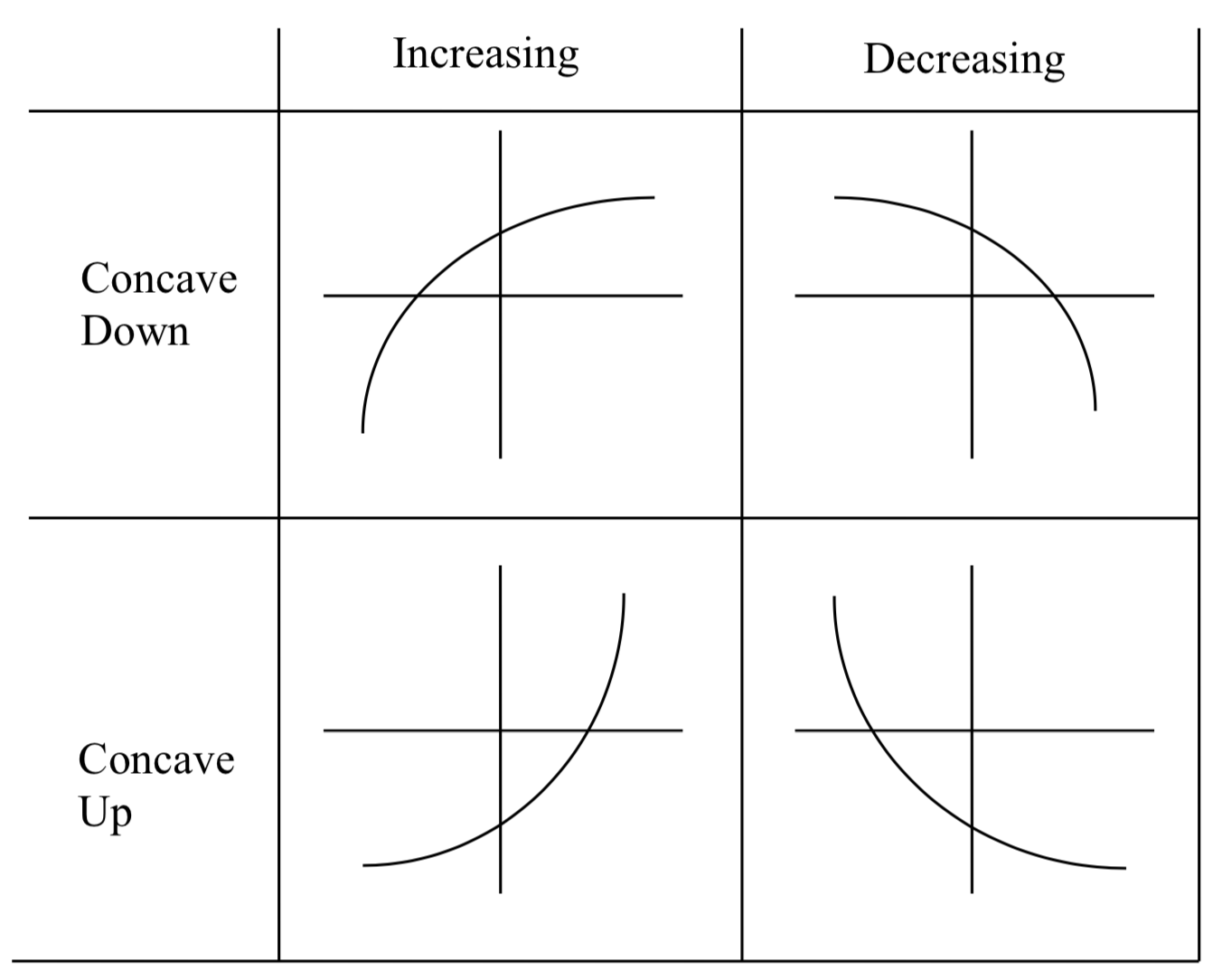
increasing at a decreasing rate
f(x) = e^-x
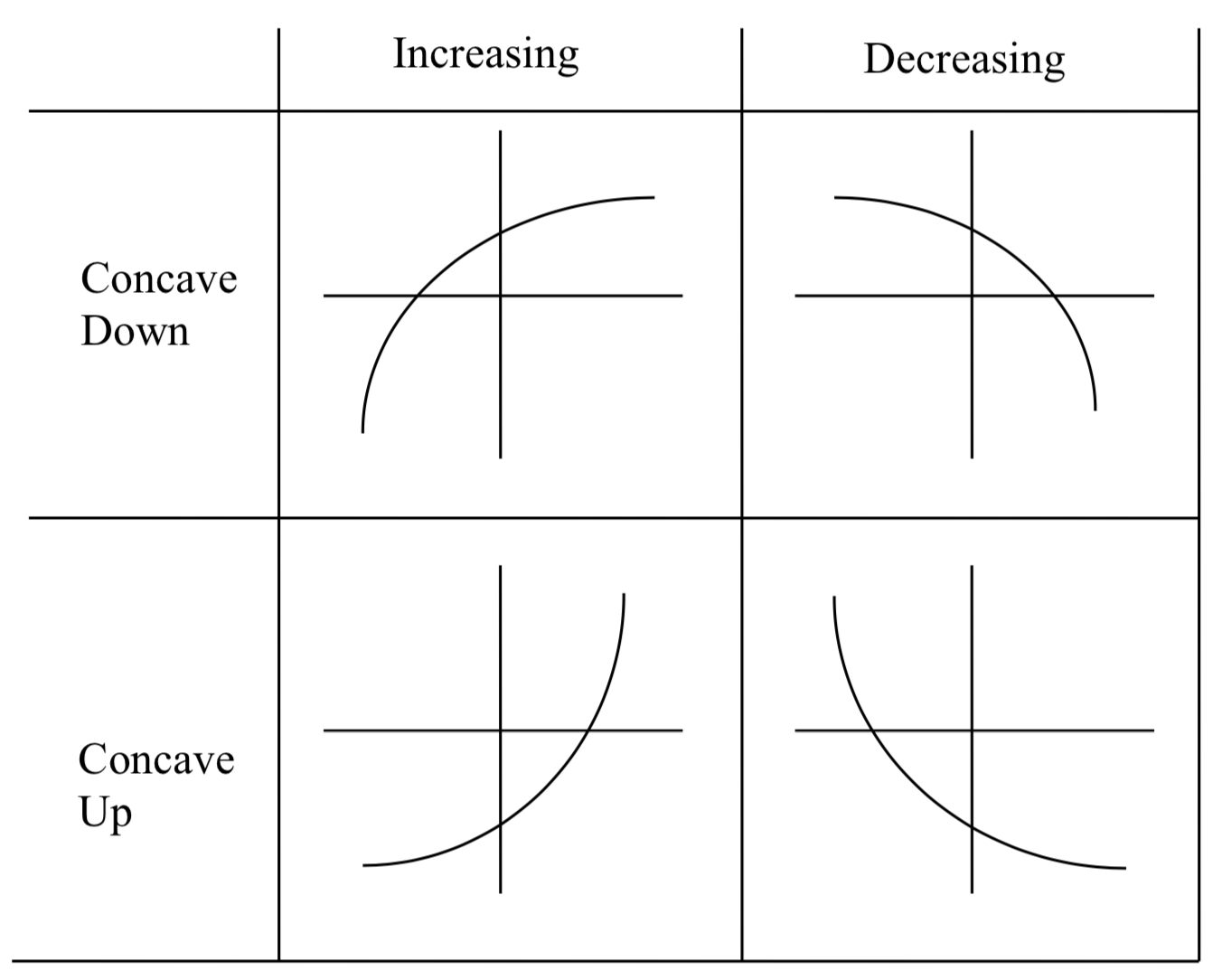
decreasing at a decreasing rate
f(x) = -e^x
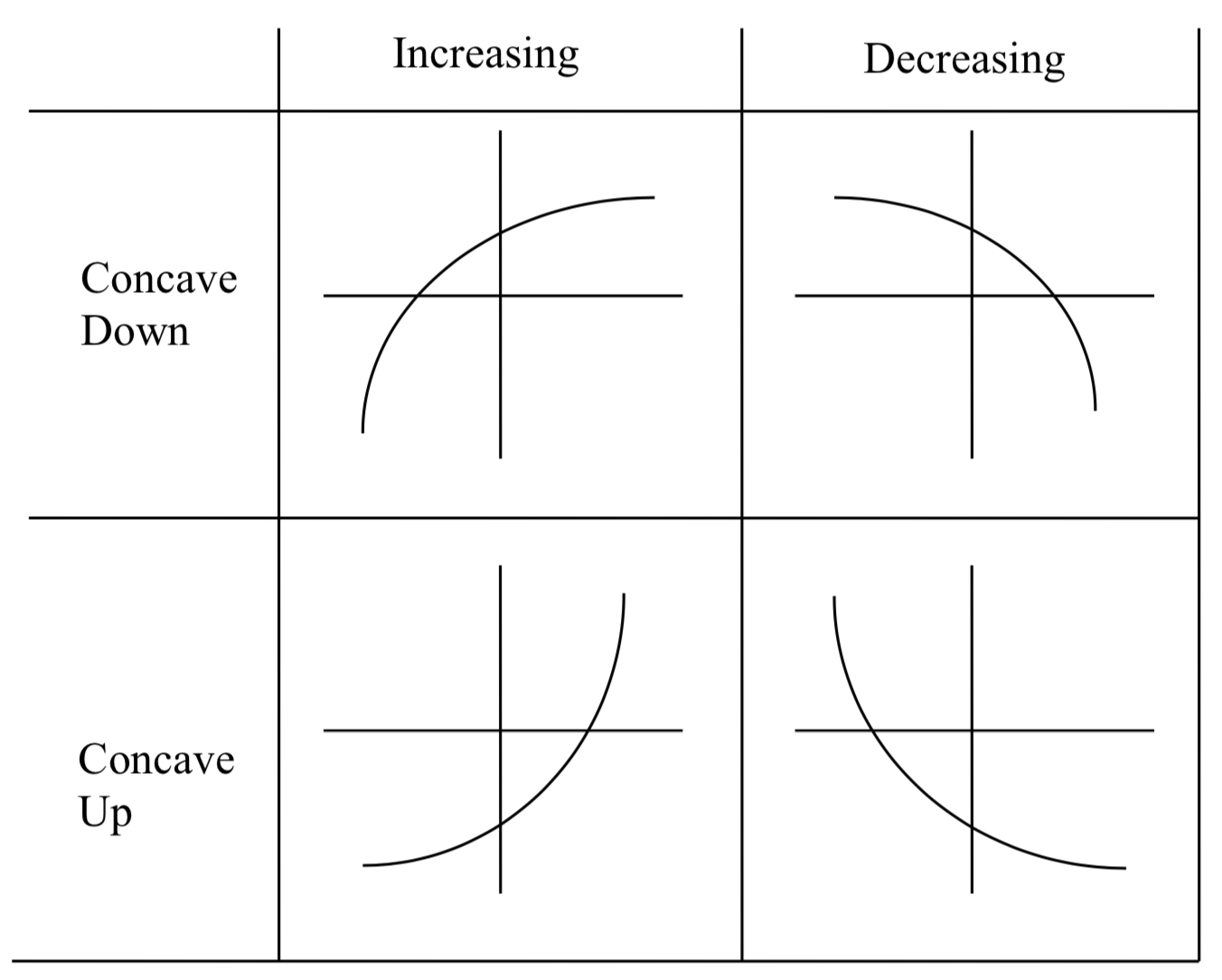
decreasing at an increasing rate
f(x) = -e^-x
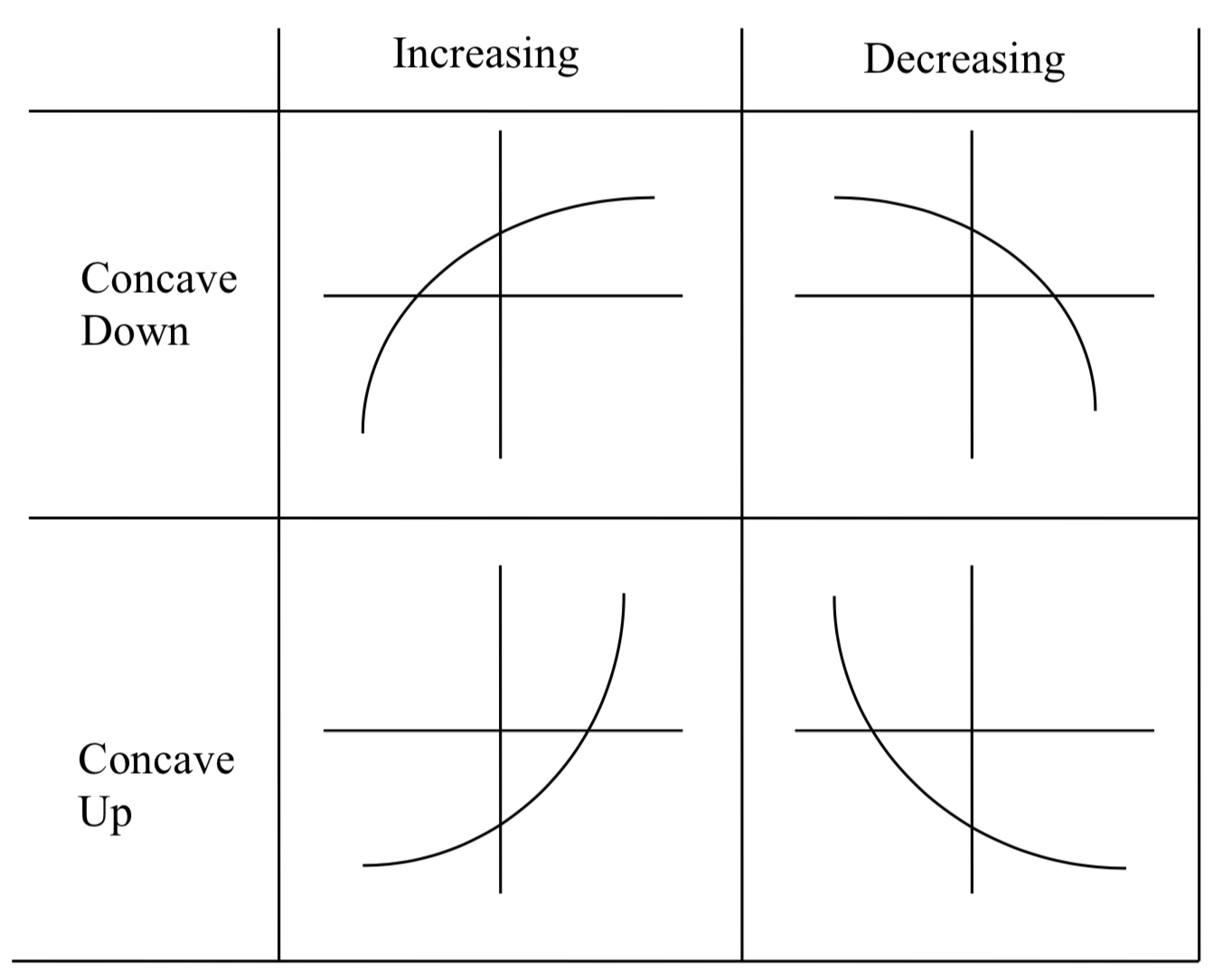
vertical stretch or compression
stretch = a > 1
compress/shrink = 0 < a < 1
half life formula
A = P (1/2) ^ t/h
compound interest
A = P (1 + r/n) ^ nt
compound continuous
A = Per^rt
logarithmic function
y = log(b) * (x - h) + k; vertical asymptote = h
log(a) 1 = 0 means
a^0 = 1
log(a) a = 1 means
a^1 = a
inverse property
log(a) a^x = x means a^log(a)x = x
one to one property
log(a) x = log(a) = y means x= y
for logs and ln, what must x always be
x > 0
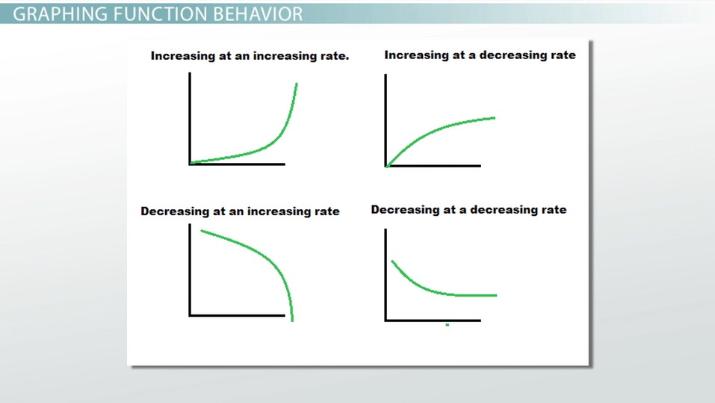
increasing at a decreasing rate
f(x) = -ln(x)
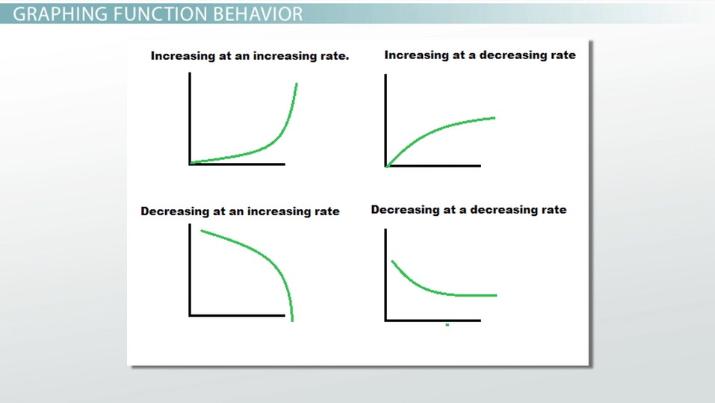
decreasing at an increasing rate
f(x) = ln (-x)
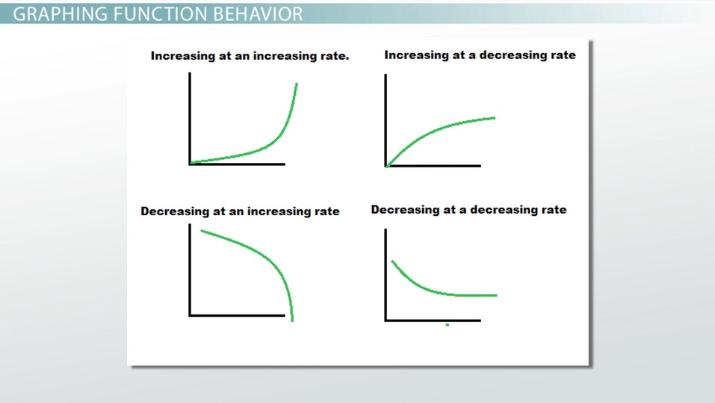
increasing at an increasing rate
f(x) = -ln (-x)
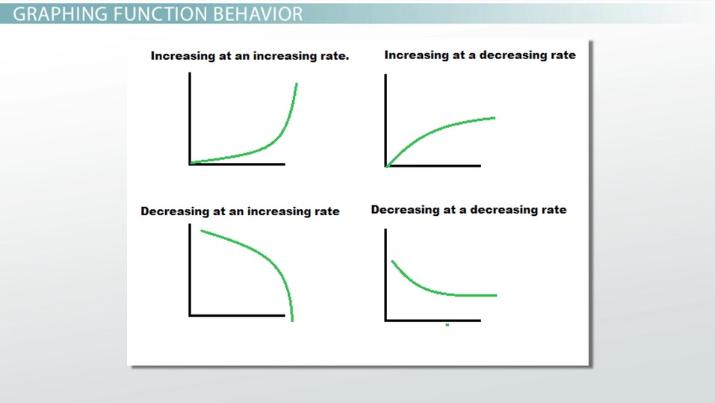
decreasing at a increasing rate
f(x) = ln (x)
ln (-x+3)
reflect across the y-axis at x = 3
-x +3 > 0 = x < 3
change of base formula
log (a) x = log x / log a
product property of logs
log (a) uv = log (a) u + log (a) v
quotient property of logs
log (a) u/v = log (a) u - log (a) v
log power property
log (a) u^v = v log (a) u
gaussian model
y = ae^-(x-b)² / c
logistic model
y = a/ 1 + be^-rx
exponential model regression
y = a * b^x
coefficient of determination
r² ; measure that provides information about goodness of fit of a model; closer to 0.99 is best fit
correlation coefficient
r ; defined correlation between independent and depend variables between -1 and + 1;
power model regression
y = a * x^b
LnReg - Logarithmic Model
y = a + b ln x
LinReg - Linear Model
y = ax + b