Pathology of the Aorta (Part 1)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is an aneurysm?
a permanent localized dilation of an artery, with an increase in diameter > 1.5 times the normal diameter
AAA is
> 3 cm or greater than 1.5 times the superior aorta
Primary risk factors for a patient with AAA:
Dissection and rupture
What puts a patient at risk fro AAA
Smoking
HTN
Cardiovascular disease
COPD
Family history of AAA
Genetic conditions
Men that are ________ have a 5-10% increase risk of AAA
> 65
How does an US determine AAA
Measures diameter, length and looks at extent of involvement of branches
Once they compare diameter of abnormal area vs the normal vessel (Sup and Inf) they can…
make a diagnosis
What is the most common cause of AAA
Arteriosclerosis
Where is it most common to see AAA
infrarenal
Who is it more common to see AAA in
men
AAA ____ extend into iliac arteries
may
AAA may involve
ascending and descending aorta
a PA will do a physical exam where they check
Pulsatile abdominal mass
Slightly to left of midline
Between xyphoid & umbilicus
Will listen for a bruit
Clinical Symptoms and Indications of AAA not at rupture:
May vary
Most are asymptomatic
Pulsatile abdominal mass
Abdominal pain
Impinge on adjacent structures
Occlusion of vessel by direct pressure or thrombus
Abdominal bruit
Clinical symptoms and indication of AAA at rupture:
intense back pain and drop in hematocrit
Grey Turner’s syndrome
AAA treatment for < 4cm
follow up in 6 months
AAA treatments when size is 4-5 cm
surgery or endovascular repair; if in good health
AAA treatments when size is 5-6cm
surgery or endovascular repair
AAA treatments when size is >6cm
surgery
AAA size that has the highest risk of rupture
> 6cm
What needs to be measured to AAA
Exact location of AAA
Measurements
AP of AAA
Width of AAA
Length of AAA
AP of lumen
Width of lumen
Relationship to Renal Arteries (infrarenal neck)
Extent (Branches &/or Iliac arteries)
What doppler do we use for AAA
color and spectral
What does this image show
Pseudoaneurysm
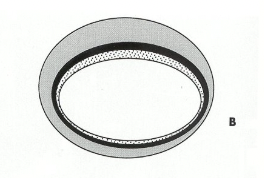
What does this image show
True aneurysm
In a true aneurysm ______________ of the vessel wall are intact but STRETCHED
all 3 layers
In a true aneurysm there is ____________ and localized dilation of the arterial wall
focal weakening
Over time a true aneurysm may
enlarge or even tear
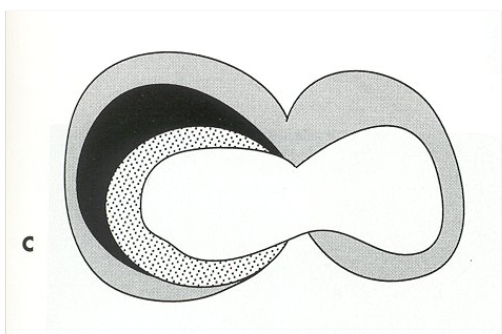
Fusiform and Saccular aneurysm are:
true aneurysms
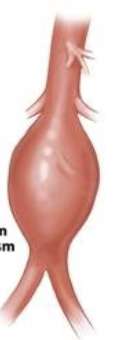
What aneurysm is this
Fusiform
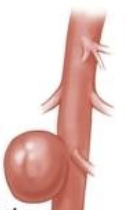
What aneurysm is this
Saccular
Grey Turner’s Syndrome
when aneurysm ruptures they will have bruising at flanks bc blood is pooling at abdomen