Lecture 6
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from the Infrastructure lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Infrastructure Equity
A sub-asset class of Alternative Investments, positioned between Private Equity and Real Estate, offering attractive returns, stable cashflows, and diversified portfolios.
Key Trends in Infrastructure
Increasing popularity, private capital for public projects, shifts in telecommunication and power supply, increasing importance of ESG, and adjustments of regulatory requirements.
Project Financing
Can be structured as Infrastructure Equity or Debt, involving equity investors and debt investors with loan repayments from project cash flow.
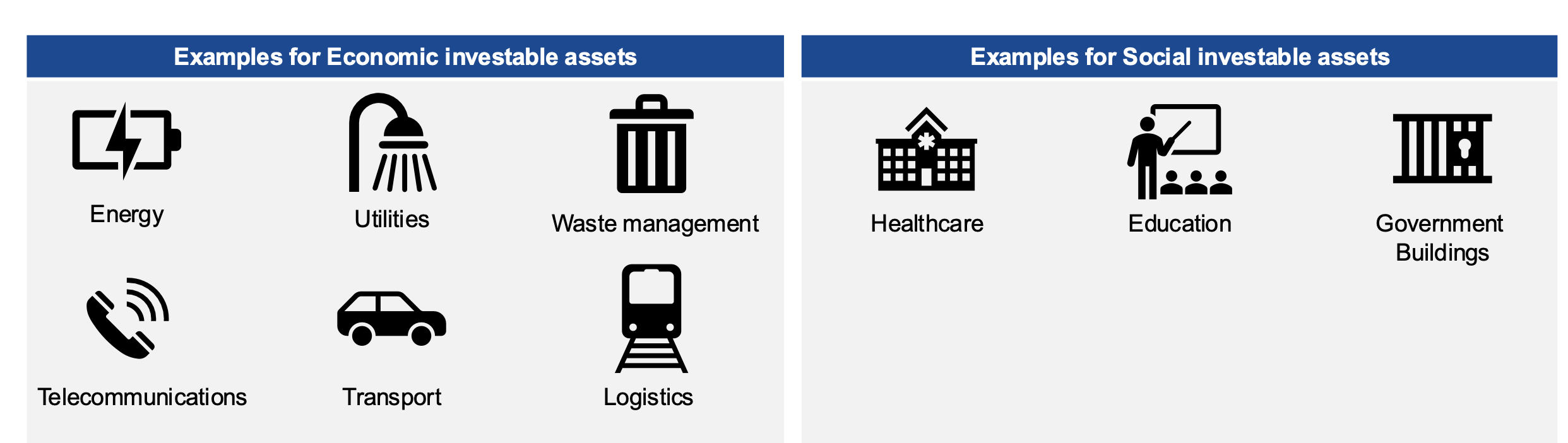
Economic Infrastructure Sectors
Transport, Utility, Communication, and Renewable Energies which are essential for economic development.
Social Infrastructure Sectors
Economic (energy, unitilies, waste management, telecommunications, transport, logistics) ; social (education, healthcare, government bulding)
Core Infrastructure Investments
Long-term contractual agreements with governmental support, very predictable cashflows, mature infrastructure with limited operational risk.
Greenfield Assets
Assets not yet existing, come with cost overrun and construction delay risks, but earn a premium above brownfield assets.

Brownfield Assets
Existing, operating assets that already generate income, without construction risks, allowing for direct investment of money.

Fund Structure
Involves Limited Partners (LPs) providing capital, General Partner (GP) responsible for execution, and Asset Manager managing day-to-day business.
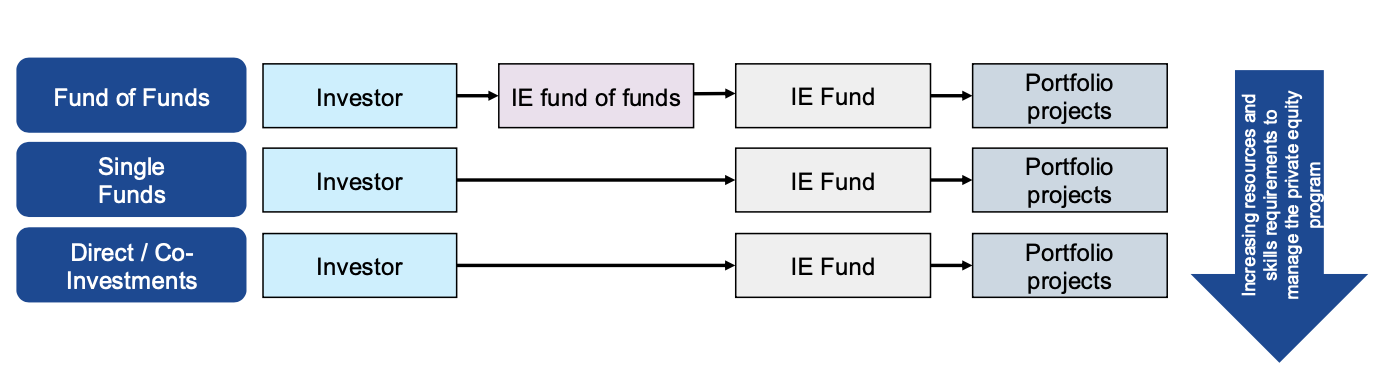
Access to Infrastructure Investments
Can be achieved through Fund of Funds, Direct/Co-Investments, or Single Funds, each requiring increasing resources and skills.
Positive aspects of infrastructure
Positive diversification effect, stable long-term returns, relatively low volatility, good downside protection, and a growing market.
Challenges of infrastructure funds
Booming demand and supply but limited good deals, dropping yields, PE-like cash flow patterns (J-Curve), and strategic decisions required.
Number of risk categories
10 - Technical risk / Demand risk, Political and regulatory risk, Availabilty risk, Operational risk, Leverage risk, Interest rate risk, inflation risk, Deflation risk, Counterparty risk, Refinancing risk
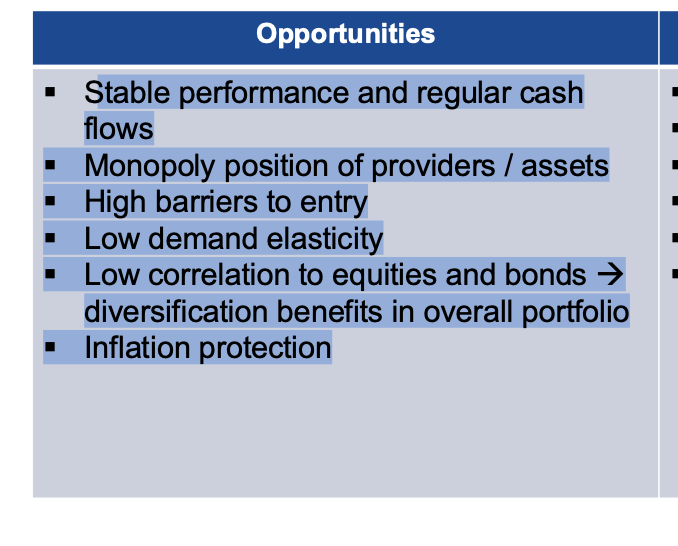
Opportunities
Stable performance and regular cash
flows
▪ Monopoly position of providers / assets
▪ High barriers to entry
▪ Low demand elasticity
▪ Low correlation to equities and bonds →
diversification benefits in overall portfolio
▪ Inflation protection
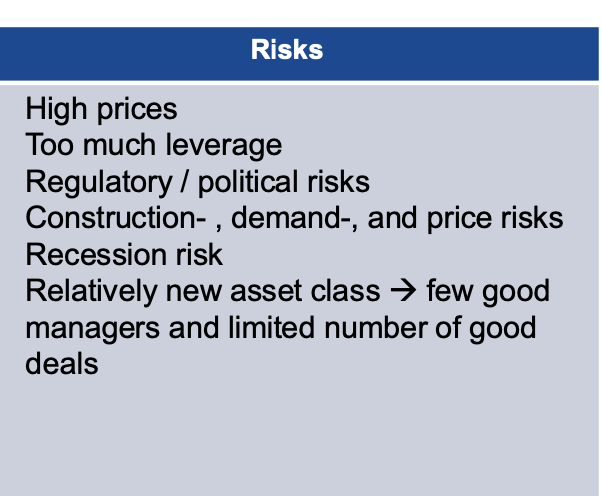
Risks
High prices
▪ Too much leverage
▪ Regulatory / political risks
▪ Construction-
, demand-, and price risks
▪ Recession risk
▪ Relatively new asset class → few good
managers and limited number of good
deals