Teas 7 Chemistry Study Guide
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Solid to Liquid
Melting (absorbs energy)
Liquid to Solid
Freezing, (releases energy)
Liquid to Gas
vaporization/absorbs energy
Gast to Liquid
condensation/ release energy
Gas to Solid
deposition/ release energy
Solid to Gas
sublimation
Matter
Anything that takes up space
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
How Does Matter Change?
Matter usually changes state when you add or take away heat, which changes the temperature of the matter
Substance
A single kind of matter that is pure and has a specific set of properties.
examples of substances
1. Water
2. Alcohol
3. Oil
4. Food coloring
Solids
The particles in solids are tightly packed, least compressible
Liquids
Liquids are also a condensed phase, however, in contrast to solids, the particles have some translational kinetic energy, which means they have freedom to move
gas phase
the phase of matter in which atoms or molecules can move essentially independently of one another, most compressible
Which state(s) of matter take the shape of their container?
Liquids and gases take the shape of their containers since, they do not have definite shape and volume. Only solids have definite shape and volume.
SOLIDS
have a definite shape and volume
LIQUIDS
have a definite volume, but can take the shape of their container
GASES
have neither a definite shape nor volume
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Solids have a definite shape and definite volume.
(b) Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape.
(c) Gases have a definite volume but no definite shape.
(d) Liquids have both definite shape and definite volume.
(a) Solids have definite shape and definite volume.
(b) Liquids have definite volume but no definite shape.
The higher the temperature?
the more energy the molecules have (move particles of matter apart) and the more space they take up
The higher the pressure?
the more the molecules are forced together
Which state of matter has atoms that move freely?
Gas
Which state of matter has atoms that can slide past each other?
Liquid
Which state of matter has atoms that vibrate in place?
Solid
Plasma
often found in the stars, a gas that is ionized, meaning that electrons have been stripped from the atoms
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
(sugar is the most comment solute)
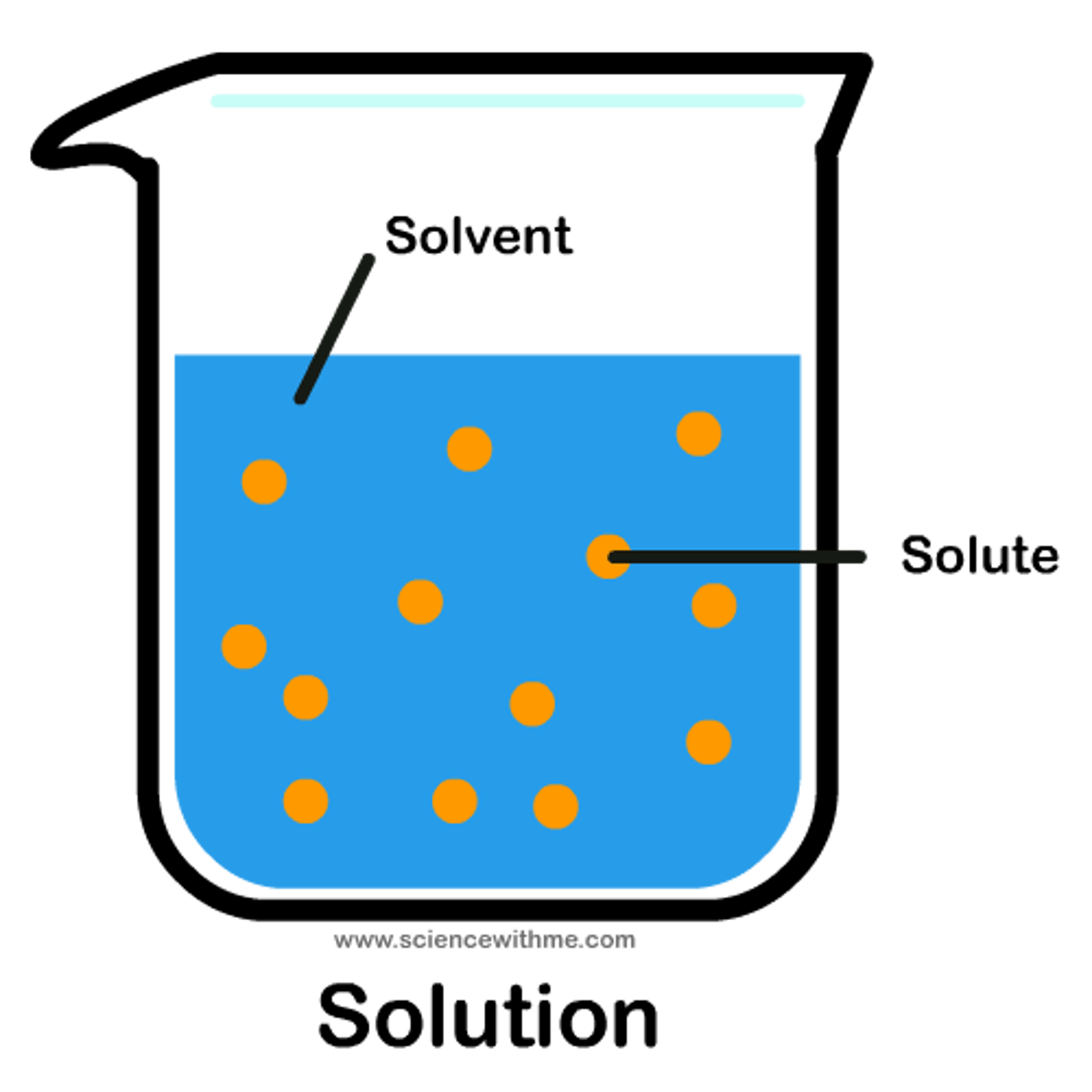
Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
(water is the universal solvent)

Hydrophilic
water loving solute
(ex: salt with water)
Hydrophobic
water fearing solute
(ex: oil with water)
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances

Solubility
the ability of a solute to dissolve in a solvent
Solubility limit
the amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent
Dilution
process of adding solvent to a solution to decrease the concentration of the solution
Molarity
the concentration of a solute in a solution
(mol/L) (moles of solution/ liters of solution)
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, (high to low, passive)
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Cohesion
process of similar molecule surrounding and binding to another molecule
ex: water is going to attract water
Adhesion
process of dissimilar molecules binding to another molecule
ex: water is the universal solvent because of its polarity, many substances can dissolve in water
Atom
The smallest component and the most basic part of matter that still retains its identity
Atomic structure
Atoms have a nucleus and electrons. Its nucleus contains protons and neutrons
Nucleus
The part of the atom that houses the protons and the neutrons
Protons
positively charged subatomic particles
Neutrons
the particles of the nucleus that have no charge. they are neutral and without a positive or negative electrical charge; the part of the atom that gives the atom its isotope identity.
Electrons
The part of the atom that has a negative (-) charge
Ion
An electrically charged atom
Cation
A positively charged ion, lost one or more electrons
Anion
A negatively charged ion, gained one or more electrons
Plasma
Plasma is not naturally found in nature on our earth. Instead, plasma is produced artificially or it is found beyond our atmosphere and universe.
The Properties of Substances
The unique and distinctive properties of substances differentiate them from other substances with their own unique and distinctive properties.
Density
mass/volume
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
Boiling point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
Conductivity
The ability of an object to transfer heat or electricity to another object.
Heat capacity
the number of heat units needed to raise the temperature of a body by one degree.
Malleability
the ability of a substance to be hammered or beaten into thin sheets
What is a physical property?
a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance
What is cellular transport?
the movement of molecules in/out of cells to keep cells alive and maintain homeostasis
Cellular transport is split into two categories
a. Active transport
b. Passive transport
What is active transport?
the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. ACTIVE=ENERGY
What is passive transport?
The movement of materials across the cell membrane without using cellular energy. PASSIVE=NO ENERGY
What is diffusion?
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What is an example of Diffusion?
For example, when you add a drop of food coloring to water, immediately, the food coloring begins to spread (or diffuse) throughout the water, eventually reaching equilibrium where all areas have the same concentration of coloring:
What is a concentration gradient?
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
What is Kinetic Energy?
the energy an object has due to its motion.

An example of kinetic energy is
running water
Catalysts
speed up reactions
Activation Energy
the minimum amount of energy that is needed for a chemical reaction to occur
Enzymes
proteins that act as catalysts, specific to the reaction that the catalyze and are usually named after the substrate that they act upon
Endothermic reactions
absorb heat
ex: temperature increases when cooking an egg (heat is absorbed from the pan to cook the egg)
Exothermic reactions
release heat
ex: concentration of reactants causing combustion or rain condensation of water vapor into rain releasing energy in the form of heat
Equilibrium
rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse action
Dynamic equilibrium
the forward and reverse reactions are occurring simultaneously
ex: carbon dioxide is dissolved into the liquid form of soda at the same rate as the lqiuid form is being covered into gas (soda bubbles/fiz)
Static equilibrium
concentrations of the reactants and products are not changing
ex: the weight of the body does not change when repositioned because the gravitational constant is the same for all objects
KCl is an example of which type of bond?
ionic
What is an ionic compound?
Ionic compounds are compounds made up of ions that form charged particles when an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses electrons. A cation is an ion charged positively; an anion is an ion charged negatively.
What is an ionic bond?
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Which of the following is exchanged between two or more atoms that undergo ionic bonding?
Valence electrons
What is an ion?
Ions are formed when an atom gains or loses electrons
What is a negative ion?
A negative ion is created when an atom gains electrons. Electrons have a negative charge.
What is a positive ion?
A positive ion is created when an atom loses electrons. Electrons have a negative charge.
What is a chemical bound?
1. Atoms of the same element may bond together to form molecules or crystalline solids.
2. involves atoms combining to form chemical compounds and bring stability to the resulting product. I
What is a valence electrons?
electrons in the outermost shell
How do you find the number of protons?
Look at the atomic number it is the same.
How do you find the number of electrons?
same as the number of protons.
How to find the number of neutrons in an atom?
To find the number of neutrons, you will need to subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Remember that the atomic number is the same as the number of protons, which you have already identified
Where can I find the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number is located above the element symbol.
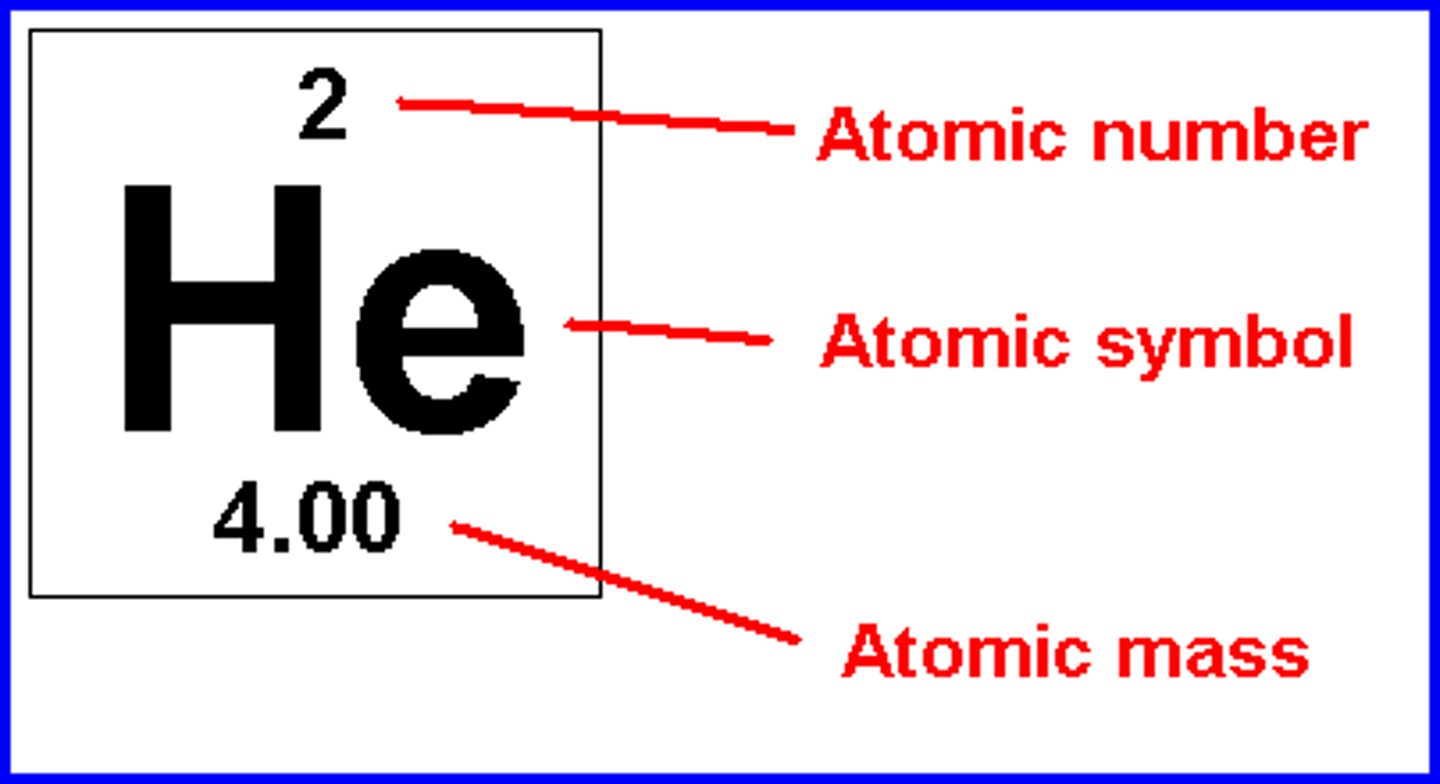
Where can I find the atomic mass of an element?
The atomic mass can be found underneath the symbol for the element.
What is an electrical charge?
For example, if we have an object made up of 14 protons, which are positive, and 12 electrons, which are negative, then we end up with a net charge of positive 2. We simply add 1 for each proton and subtract 1 for each electron. If the resulting number is positive, we have a net positive charge and if the resulting number is negative, we'll have a net negative charge. Note that neutral particles will make no difference in the net charge.
What does combustion produce?
energy, carbon dioxide, and water
Covalent bonds
nonmetal and nonmetal, when atoms share valence electrons
Ionic bounds are found in what elements?
Ionic bonds form only between metals and nonmetals. That's because metals "want" to give up electrons, and nonmetals "want" to gain electrons.
(found in salts)
Hydrogen bounds are found in what elements?
Hydrogen bonding occurs only in molecules where hydrogen is covalently bonded to one of three elements: fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen
(these bonds are weak)
A graduated cylinder is used to measure;
Large amounts of volume
Measuring spoons are used to measure;
Small amounts of liquid
Volumetric pipettes are used to measure;
Used to measure small amounts of water
Volumetric flasks are used to measure;
Large amounts of liquid
What is the equation for 'parts per million"
(amount of solute/amount of solution) x 1.0 x 10^6
Which of the following can change with pressure?
a. Adhesion
b. Boiling Point
c. Luster
d. Cohesion
Water's boiling point depends on the pressure!
Chlorine is a
nonmetal