Lecture 3 - Protein Structure and Function
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
How does the pH affect the charge on the side group of an amino acid. For instance, the pKa of the aspartic acid side group is 4.1. What is the charge of aspartic acid at ph7? pH1?
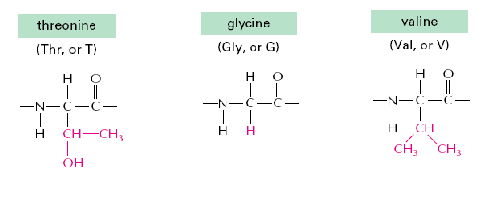
Many proteins have sugar groups attached to the side groups on some of the amino acids (glycoproteins). Which one of the following amino acids is more likely to have a sugar group on?
Threonine is most reactive due to its hydroxyl group.
Neither glycine nor valine are very reactive due to their stable side chains, but glycine is more reactive;
the methyl group-heavy side chain of valine is very non-reactive
Why do hydrophobic groups on amino acids tend to be hidden in the inside of a protein?
Hydrophobic groups want to avoid water, so that the energy of the entire system is minimized. In “free water”, water molecules can fulfill all their needs for hydrogen bonds by interacting with each other, but when a hydrophobic molecule is present, water molecules around cannot have complete hydrogen bonds anymore, which leads to a high-energy surface. Water
molecules will have to align in a specific way around this surface, resulting in decreased entropy, thus, Gibbs’ free energy at this state, a hydrophobic molecule in contact with a water molecule, is positive, and the reaction is not energetically favorable
How can a folded protein be in a lower energy state than an unfolded protein?
Hydrophobic clustering is one of the major forces driving protein folding, and please refer to question 3 for why hydrophobic groups cluster together reduces energy level
Why are alpha helices and beta sheets so common in proteins?
These structures are more stable (hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic
interactions) and allow more side chain groups to be exposed, so proteins can be catalytic
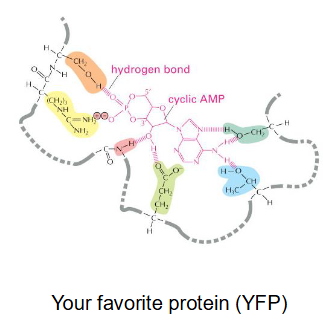
Consider that the image is an actual protein that is reacting with cAMP. If you were asked to make a mutant that has almost exactly the same as WT, but cannot perform the reaction, what would you do?
Mutations should be introduced to regions outside of the catalytic domains
How are alpha helices formed?
A right-handed helix.
3.6 residues per turn.
Hydrogen bonding occurs
between the backbone atoms (N-H to C=O) parallel to the helix axis.
How are beta sheets formed?
hydrogen bonding between the backbone atoms
The ribbons can be parallel or anti-parallel.
the side chains alternate on either side of the sheet
You found that two proteins have the same amino acid composition (same # of different kinds of amino acids), but they have different behavior. What is one of the most obvious reasons why?
The sequence in which the amino acids are arranged in
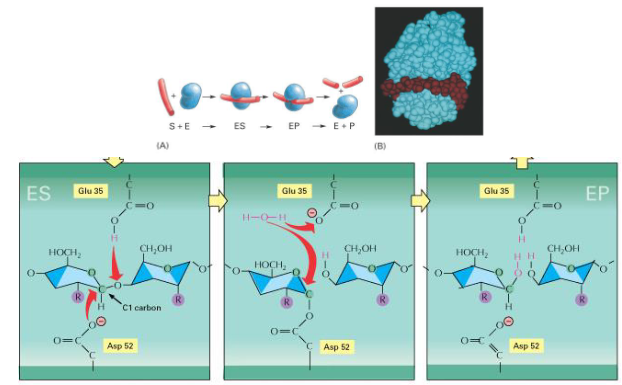
What is happening in this image?