White Lesions
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
what is a Flat, solid, raised area of the skin or mucosa > 1 cm in diameter?
plaque
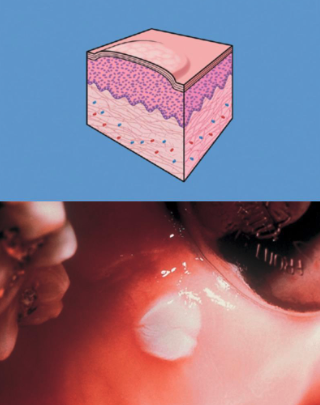
(> 1 cm in diameter)
plaque
what is a Solid mass of tissue > 1 cm in diameter?
tumor
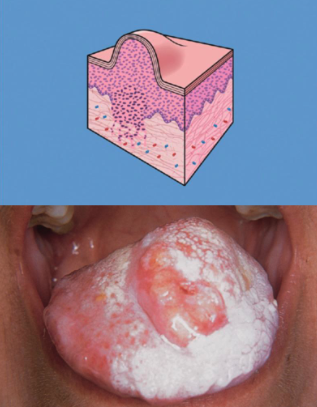
(Solid mass of tissue > 1 cm in diameter)
tumor
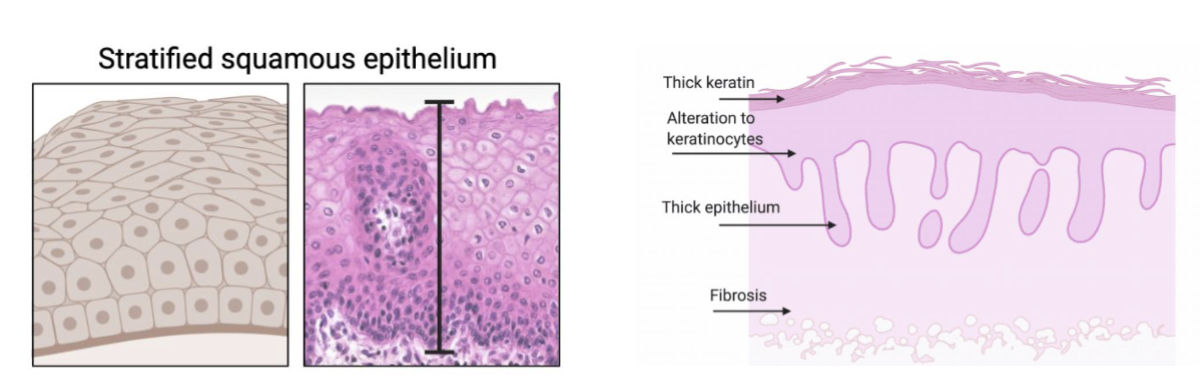
what makes the oral mucosa look white?
could be due to:
thick keratin
alteration to keratinocytes
thick epithelium
fibrosis
what acronym can we use to remember etiologies/types of white lesions?
HIDE MAN
hereditary
infectious
developmental
environmental/reactive
metabolic/medication-induced
autoimmune/allergic/immune
neoplastic
• White sponge nevus
• Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
• Darier disease/Warty dyskeratoma
• Dyskeratosis congenita
Are what category of white lesions?
hereditary
how is White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease) passed down
rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis
White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease) is caused by a mutation in…?
keratin 4 and 13
White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease) is the defective _______ of oral mucosa
keratinization
the following are clinical features of:
• Appears at birth or early childhood
• Asymptomatic, bilateral and symmetrical, thickened, white, corrugated or velvety, diffuse plaques of the buccal mucosa
• Other oral mucosal sites
• Extra oral mucosal sites less common
White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease)
what treatment is indicated for White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease)?
• No treatment required
White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease)
white, symmetrical, waxy plaques
could be mistaken for pseudomembranous candidiasis
White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease) histopathologically presents with prominent __________ and marked acanthosis with clearing of the cytoplasm of the cells in the _______ layer
hyperparakeratosis; spinous
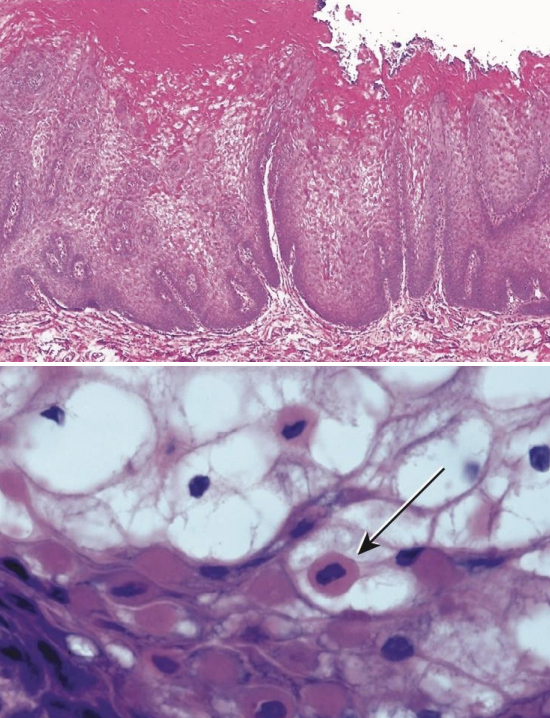
Perinuclear condensation of keratin tonofilaments found in White Sponge Nevus (Cannon disease)
how is Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis passed down?
rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis
Descendants of Native Americans who originally lived in North Carolina
Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis is caused by the duplication of chromosome _____
4q35
the following are clinical features of what white lesion?
• Develops during childhood
• Thick, corrugated white plaques, buccal and labial mucosa
• Other oral mucosal sites
• Ocular involvement → Thick, opaque, gelatinous plaques affecting the bulbar conjunctiva adjacent to the cornea
Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis
what treatment is indicated for Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis?
• No treatment required
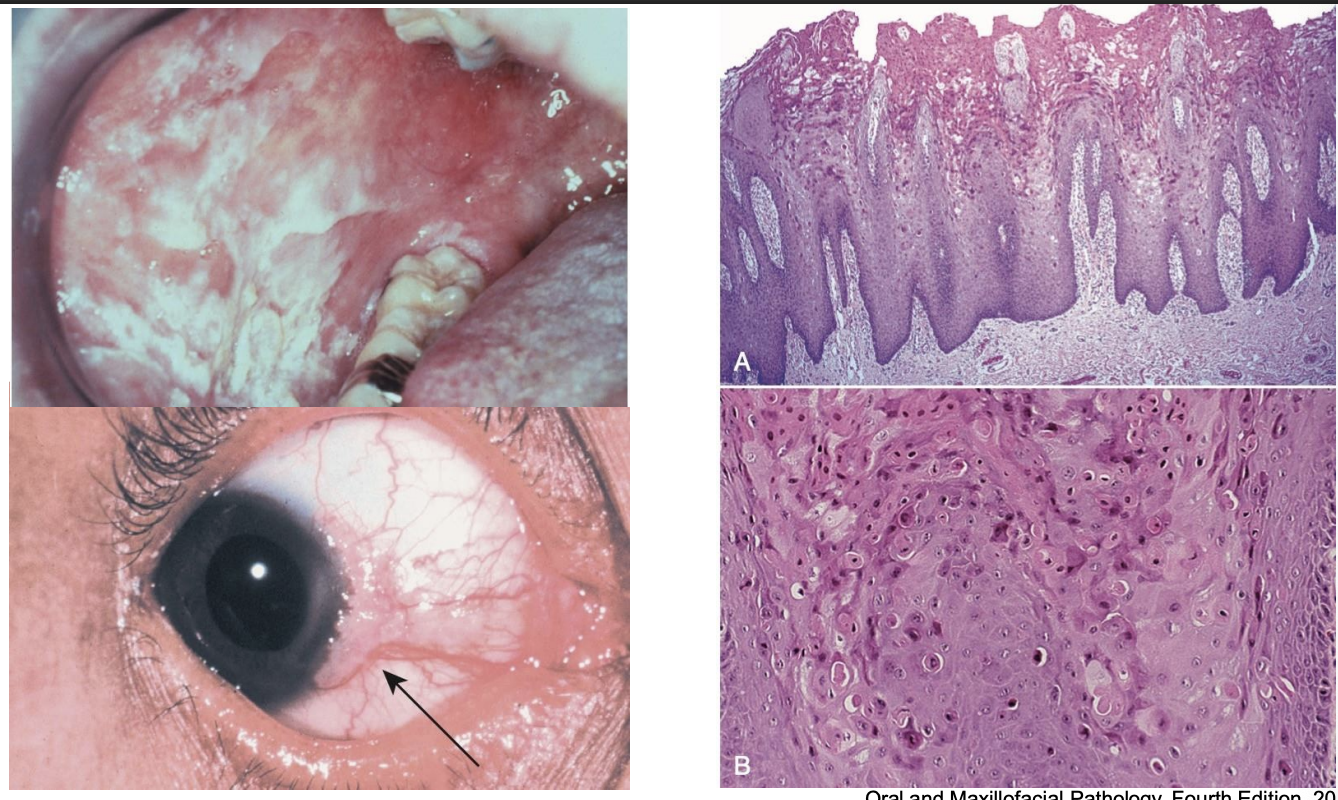
Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis
how is Keratosis Follicularis (Darier disease) passed down?
Autosomal dominant disorder
Keratosis Follicularis (Darier disease) is caused by a mutation in ______ gene
ATP2A2 (alters normal function of desmosomes and keratin)
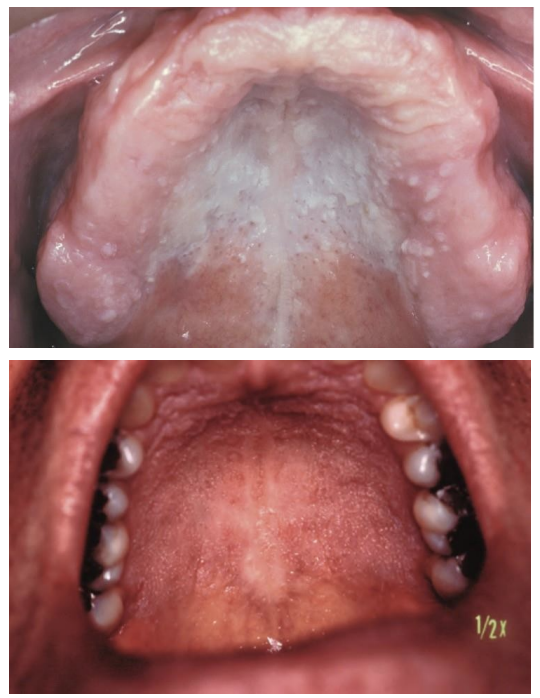
the following are clinical features of what white lesion?
• White, painless, keratotic papules or plaques, and cobblestoning of the oral mucosa
• 1/3 parotid or submandibular swelling
• Erythematous, papules on the skin of the trunk and the scalp
Keratosis Follicularis (Darier disease)
what treatment is indicated for Keratosis Follicularis (Darier disease)?
topical steroids
how is Dyskeratosis Congenita passed down?
Rare X-linked recessive genodermatosis
Dyskeratosis Congenita is caused by a mutation in _____ gene
DKC1 (other mutations have also been identified)
Dyskeratosis Congenita is caused by gene mutations that disrupt the normal maintenance of ________-
telomerase
Dyskeratosis Congenita presents an increased risk of …?
oral cancer and aplastic anemia
the following are clinical features of…?
• Apparent during first decade (super young patients)
• Nail dystrophy
• Oral leukoplakia
• Abnormal skin pigmentation
Dyskeratosis Congenita
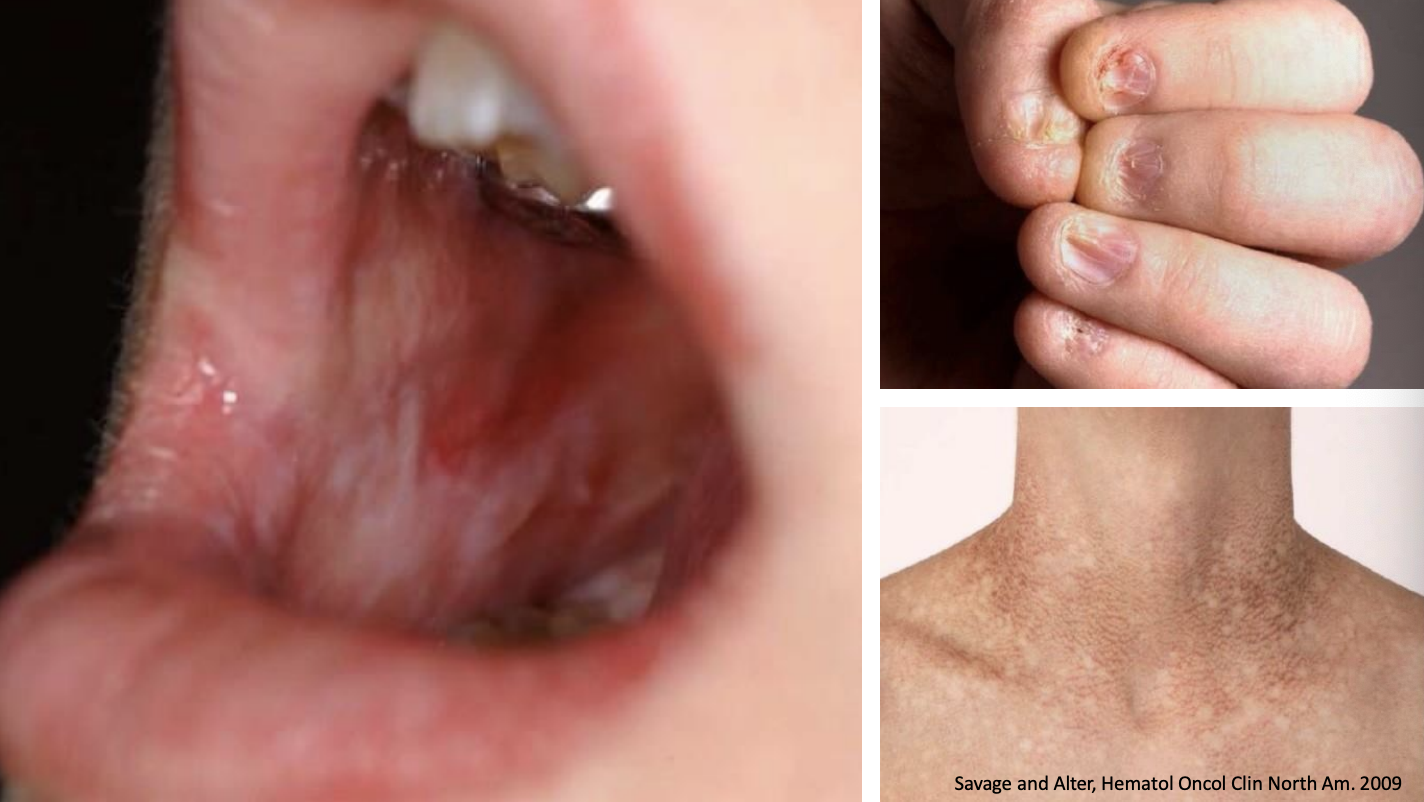
Dyskeratosis Congenita
what category of white lesion are the following?
• Oral candidiasis
• Oral Hairy leukoplakia
infectious
what are some causes of oral candidiasis?
Antibiotics, inhaled/topical steroids, immunosuppression, dry mouth, denture
t/f: oral candidiasis is an opportunistic fungal infection
true
the following are clinical features of what white lesion?
• Pseudomembraneous
• Erythematous
• Hyperplastic
oral candidiasis
what treatment is indicated for oral candidiasis?
• Nystatin suspension
• Clotrimazole troches
• Fluconazole
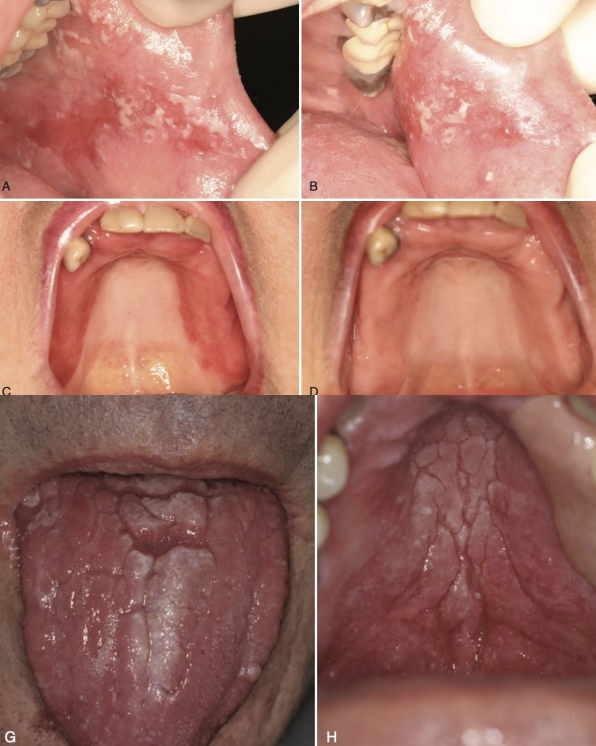
oral candidiasis
how is oral candidiasis diagnosed?
clinically and in laboratory
what causes oral hairy leukoplakia?
Epstein-Barr virus
t/f: oral hairy leukoplakia is a premalignant lesion
true
the following are clinical features of…?
white, vertical, linear lesion or plaque on lateral border of tongue
oral hairy leukoplakia
what treatment is indicated for oral hairy leukoplakia?
topical antivirals
Adjustment of HIV medications and systemic immunosuppressants
what patients populations are affected by oral hairy leukoplakia?
HIV/AIDS with low CD4 counts
immunocompromised
topical steroids
healthy individuals
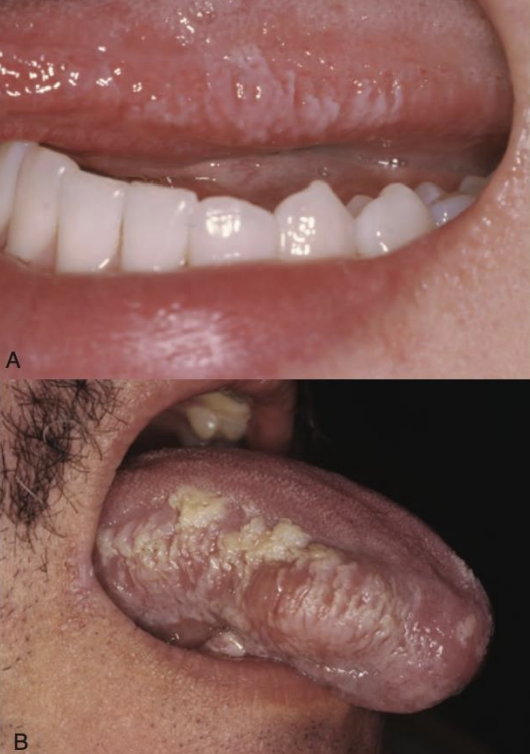
oral hairy leukoplakia
the following are what cateogory of white lesions?
• Leukoedema
• Contact desquamation
• Hairy tongue
• Frictional keratosis
• Benign alveolar ridge keratosis
• Nicotine stomatitis
• Smokeless tobacco keratosis
environmental/reactive
the following are clinical features of Leukoedema?
• Delicate lacy, gray-white lines on the buccal mucosa or ventral tongue
• Disappears on stretching the mucosa
• Very common
leukodema
what are causes of leukodema?
Mildly irritating substances
Smoke from tobacco products or marijuana
caustic oral rinses, or toothpaste
Traumatic, parafunctional habit such as mucosal sucking
what treatment is indicated for leukodema?
no treatment required
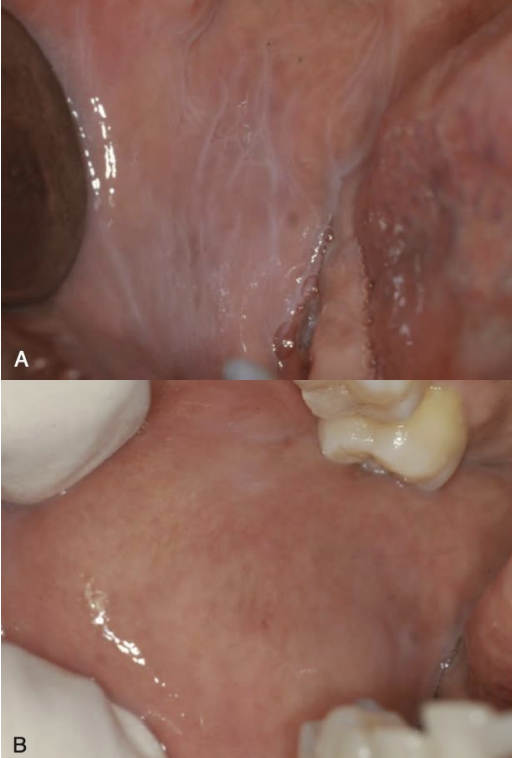
leukodema
the following are clinical features of what white lesion?
• Painless, thready white tissue on the mucosa, peels off leaving normal mucosa
Contact Desquamation
what causes Contact Desquamation?
• Caustic mouth washes high in alcohol content
• Strong toothpastes (whitening)
• Other contactants that are irritants to the mucosa
what treatment is indicated for Contact Desquamation?
Discontinuation of offending agent
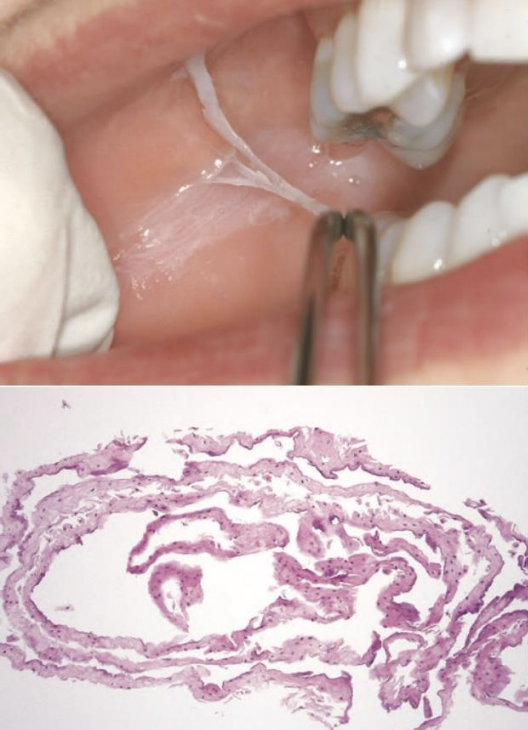
Contact Desquamation
coated tongue is also known as…?
hairy tongue
the following are clinical features of what condition?
• Elongated filiform papillae on the dorsal surface of the tongue
• Yellowish white, can be discolored
coated tongue
what are some causes of coated tongue?
heavy smoking
poor PO intake
dehydration
poor oral hygiene
do not confuse hairy tongue with what other condition?
hairy leukoplakia
what treatment is indicated for coated tongue?
none (benign, esthetic concerns)
brushing tongue, improving oral hygiene
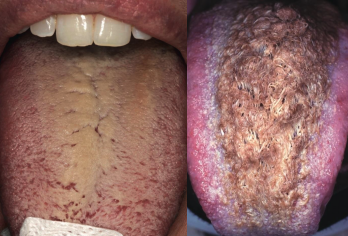
coated tongue
what treatment is inidcated for frictional keratosis?
none. biopsy is rarely indicated
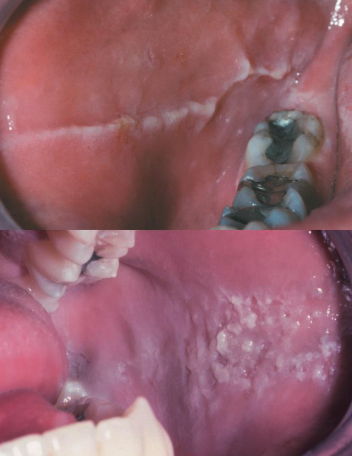
frictional keratosis
above = linea alba
below = morsicatio mucosae oris
what are 2 types of frictional keratosis?
linea alba (buccal mucosa)
morsicatio mucosae oris (chronic chewing of oral mucosa)
Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis is oftren confused with ________
leukoplakia
what treatment is indicated for Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis?
none
what white lesion is a poorly demarcated, rought white plaque of keratinized mucosa caused by friction with food?
Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis
t/f; Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis is essentially a callous in the oral mucosa
`true
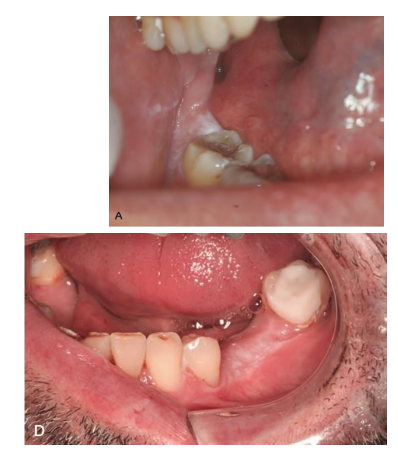
Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis
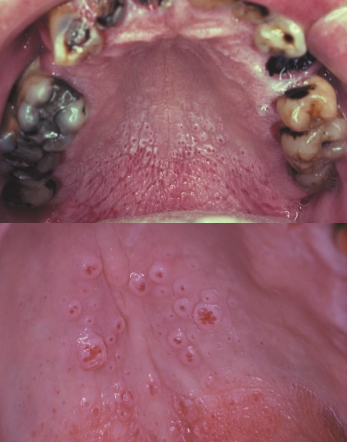
what condition is a leathery, white change of the hard palatal mucosa in long term smokers?
Nicotine Stomatitis
what treatment is indicated for Nicotine Stomatitis?
none (reversible after smoking cessation)
Nicotine Stomatitis is a mucosal response to ______
heat
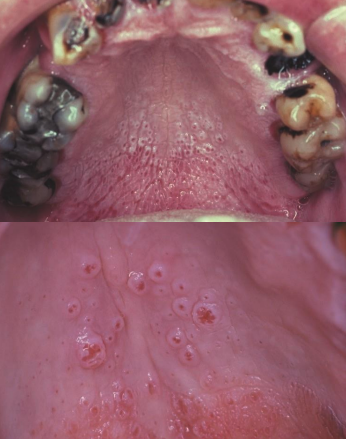
Nicotine Stomatitis
Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis is caused by contact with caustic agents within ______
tobacco
how does early stage of Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis present?
grayish-white wrinkles and parallel ridges and fissures in the area where tobacco is placed
*reversible
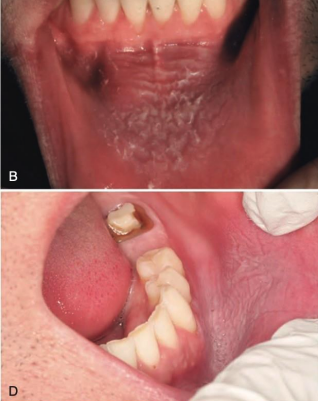
how does advanced stage of Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis present?
well-demarcated keratotic plaques
must biopsy for evaluation of dysplasia
regular follow up
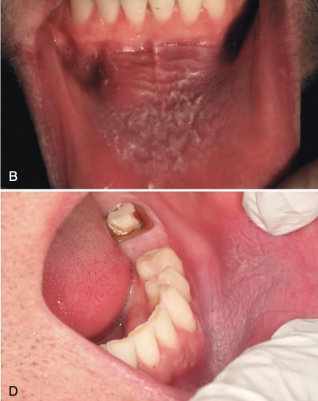
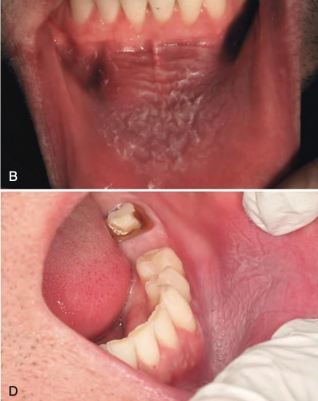
smokeless tobacco keratosis
what category of white lesions are the following?
• Oral lichen planus
• Lupus erythematosus
• Oral graft-versus-host disease
autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic
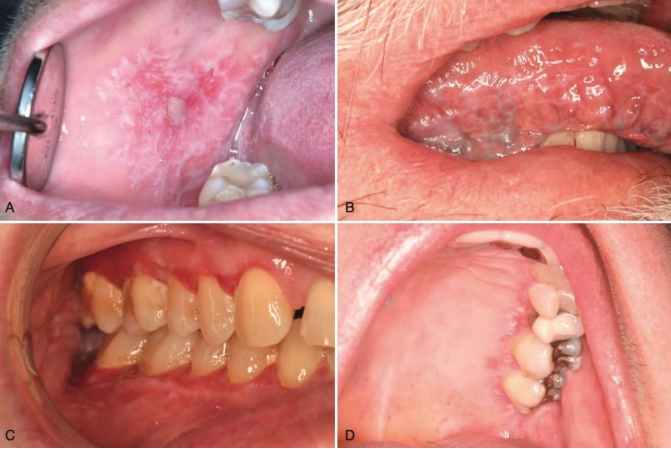
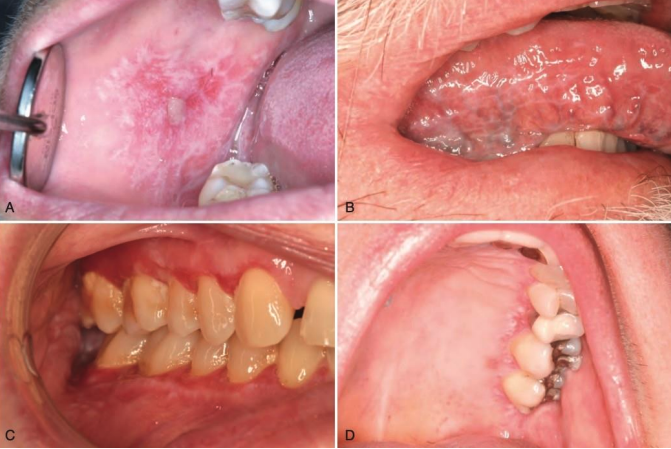
the following are clinical features of what condition?
• Typically, bilateral and symmetrical
• Reticular/keratotic (Wickham striae)
• Ulcerative
• Erythematous/erosive
Oral Lichen Planus (OLP)
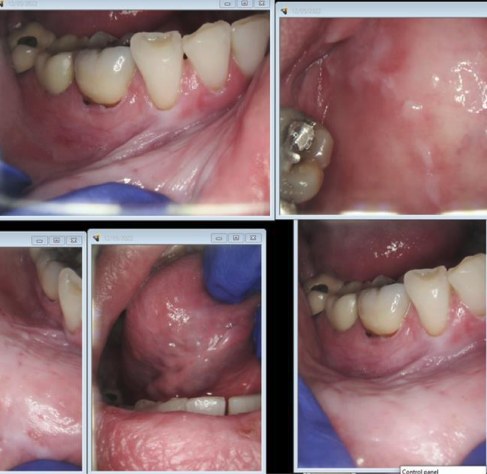
smokeless tobacco lesion
what treatment is indicated for oral lichen planus (OLP)?
• Topical and systemic steroids or steroid-sparing agents
• Replacing amalgam restorations
what demographics are affected by oral lichen planus?
1-2% of middle-aged patients
2/3 : 1 female predominance
what are some causes of oral lichen planus (OLP)?
idiopathic
medication-induced
hepatitis C virus
what is the MOA of oral lichen planus (OLP)?
T cell destruction of basal cells
oral lichen planus (OLP) can occur as contact lichenoid reactions to dental _________
amalgams
oral lichen planus (OLP) show malignant transformation potential of %
0.1-1% of cases
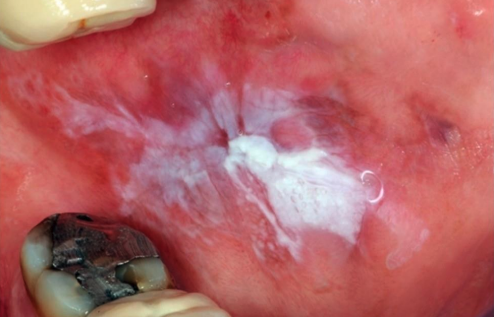
Lichenoid reaction associated with amalgam restoration
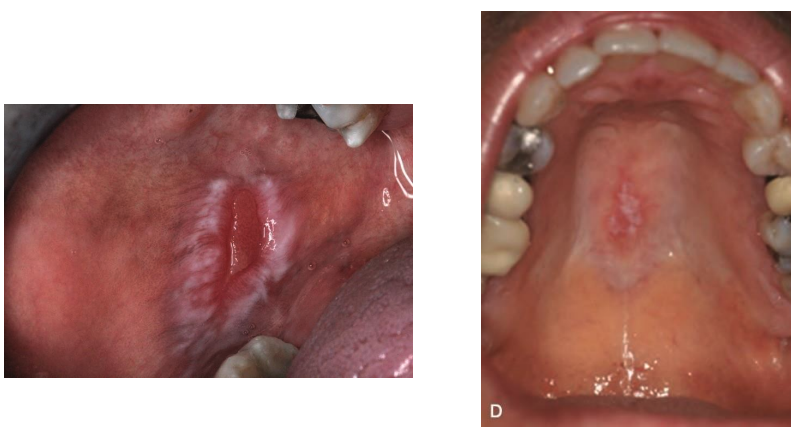
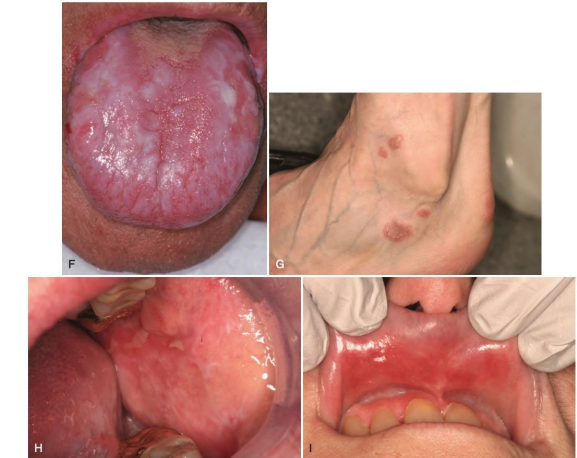
the following are clinical features of what condition?
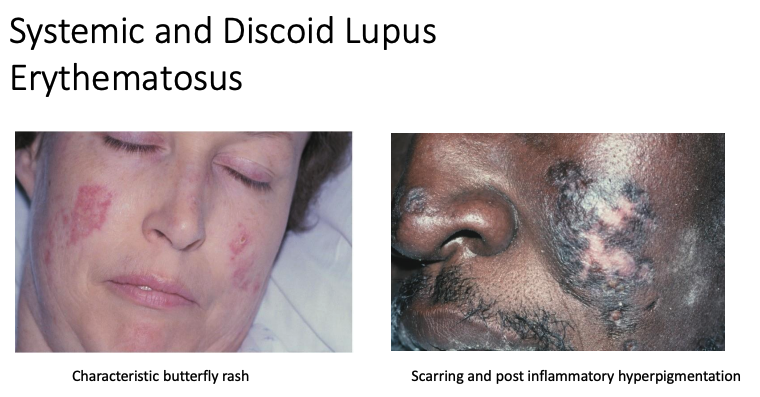
• Autoimmune disease, unknown etiology
• Affects multiple organs
• Oral lesions resemble oral lichen planus (Not always bilateral and symmetrical)
• characteristic butterfly rash, scarring, and post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Lupus Erythematosus
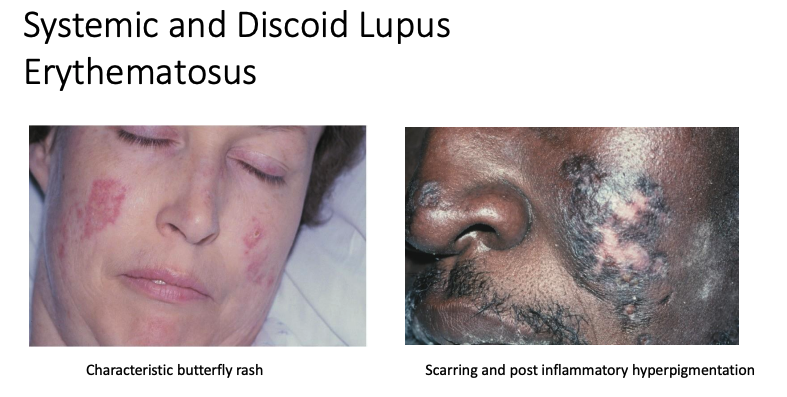
what & of patients with DLE and SLE, respectively, have oral lesions?
20% and 45%
what are some circulating anitbodies in systemic lupus erythematosus?
ANA, anti-Smith, anti–doublestranded DNA, and antiribonucleoprotein
what are 2 forms of lupus erythematosus?
sytemic and discoid
what is a complication that can occur following hematopoietic stem cell transplant for treatment of hematologic malignancies that commonly affects the moutth?
Oral Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD)
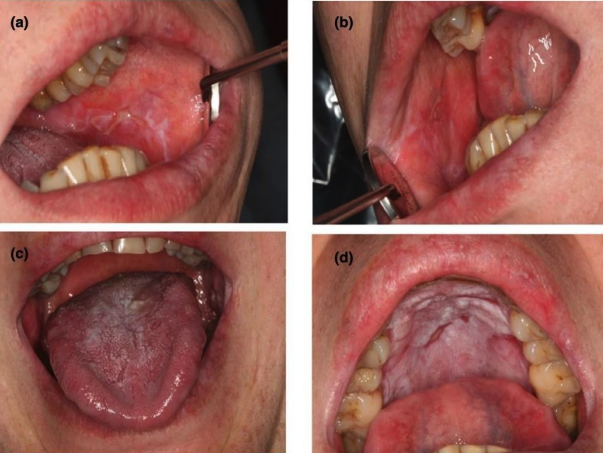
Oral Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) oral mucosal lesions essentailly resemble ___
OLP (and therefore treated similarly)
the following conditions are what category of white lesions?
• Oral leukoplakia
• Oral submucousfibrosis
• Oral squamous cell carcinoma
neoplastic
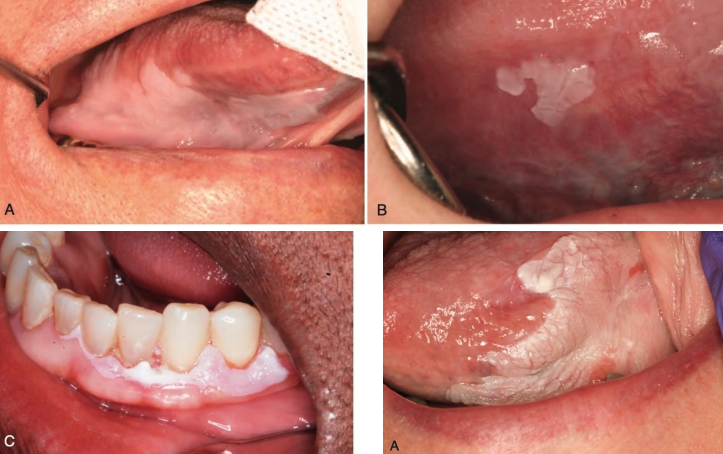
what is a White plaque of questionable risk having excluded other known diseases or disorders that carry no increased risk for cancer?
oral leukoplakia
oral leukoplakia is highly associated with _______ and development of ______.
dysplasia; cancer
what are some high risk sites of oral leukoplakia?
Ventral tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, soft palate, and gingiva
what % of oral leukoplakia represent dysplasia, carcinoma-in-situ, or invasive SCC?
43% to 47%
what are the 3 types of oral leukoplakia?
homogenous (16%)
non-homogenous
proliferative leukoplakia (70-100%)
what are some risk factors for oral leukoplakia?
• Smoking
• Excessive alcohol consumption
• H/o cancer and cancer therapy
• Family h/o cancer
• H/o autoimmune disorder or prolonged immunosuppression
• Areca nut chewing
• Older age
• Human Papilloma Virus
How many of these leukoplakias become/are dysplasia/SCC?
25-47%
Variable malignant transformation
Homogenous: 16%
Proliferative leukoplakia: 70-100%
what treatment is indicated for leukoplakias?
• Surgical excision of small lesions
• Laser ablation
• Novell off label use of topical chemotherapy
• Monitoring
• Clinical trial of immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab) for proliferative leukoplakia