Exam #2
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
which research method is colorimetric assay to measure the concentration of a specific ligand?
ELISA
which of the following is a disadvantage of cell culture experimentation?
the cells are isolated from the rest of the brain
which is not an example of a challenge with studying humans?
there aren’t enough differences between people to study them
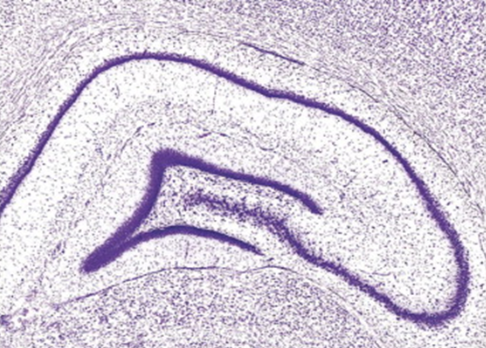
what experimental technique was used in this image?
immunohistochemistry
which of the following techniques measures gross brain activity?
EEG
which task test for language abilities?
token task
you are interested to see how mice will perform in a maze task if they do not have a specific gene (gene X23); what type of mice are you most likely going to use?
knock out mice
which of the following is false about stereotaxic surgery?
if you write down the coordinates you used, there is no need to verify (postmortem) that you hit the correct area of the brain
sleep spindles are seen in stage ___ sleep and K complexes are seen in stage ___ sleep:
2; 2
just before sleep, ___ waves appear:
alpha
the EEG for REM sleep most closely resembles which EEG?
alert wakefulness
which sleep theory is summarized by “being awake disturbs homeostasis and sleep is required to restore it”?
recuperating theory
which theory of dreaming says that our dreams are simulations of everything that prepare us to respond to situations better in real life?
hobson’s protoconsciousness hypothesis
if the ___ region of the brain is damaged, a person will not experience any visual imagery in their dreams:
medial occipital lobe
why is sleep deprivation so difficult to study?
people who are sleep deprived also experience high levels of stress
in the reticular formation, high levels of activity lead to ___; in the reticular formation, low levels of activity lead to ___:
wakefulness; sleep
melatonin is best categorized into which drug class?
circadian rhythm drugs
this condition is caused by the lack of muscle atonia during REM:
REM-sleep behavior disorder
select all of the statements about narcolepsy that are true:
a characteristic symptom of narcolepsy is cataplexy, where muscle tone is lost while awake, often resulting in falls
EEG
a test that measures electrical activity in the brain using small, metal discs
EOG
a measure of eye movement
EMG
a record of muscle tension
frequency
number of peaks/unit time; number of cortical neurons generating EPSPs
amplitude
height of the wave; number of EPSPs that occur at the same point in time and number of neurons firing in synchrony
alpha waves
high frequency and high amplitude
sleep spindle
high frequency and low amplitude; involved in memory consolidation and cortical development
k complex
single, large negative wave followed by a single, large positive wave; suppresses cortisol arousal
delta wave
low frequency and high amplitude
adaptation theories of sleep
sleep evolved to protect organisms from predation, accidents, and to conserve energy - not to fulfill a physiological need
hobson’s activation-synthesis hypothesis
many brain stem circuits are active
the cortex is bombarded with signals
information from signals are largely random
dreams are the brain trying to make sense of the random signals
revonsuo’s evolutionary theory of dreams
dreams serve an important evolutionary function
dreams simulate threatening events
these simulations help us better predict and respond to threats in real life
hobson’s protoconsciousness hypothesis
dreams simulate everything
dreams as a training mechanism
each dream represents a real-life scenario
no dreams in:
temporo-parieto junction + medial prefrontal cortex
no visual imagery in dreams:
medial occipital lobe
jet lag
a mismatch between a person’s normal daily rhythms and a new time zone
shift work
workers are forced to adjust their natural sleep-wake cycles in order to meet the demands of changing work schedules
anterior hypothalamus
promotes sleep
posterior hypothalamus
promotes wakefulness
reticular formation - low levels
produce sleep
reticular formation - high levels
produce wakefulness
caudal reticular formation
production of REM sleep
hypnotic drug
drugs that promote or increase sleep
anti-hypnotic drug
drugs that inhibit or reduce sleep
circadian rhythm drugs
drugs that alter circadian rhythms
benzodiazepines
GABA agonists with anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and sedative properties
chronic use of benzodiazepines:
tolerance, insomnia after stopping, distort normal sleep patterns, next day drowsiness, reduce life expectancy
cocaine/amphetamine derived + tricyclic antidepressants
these promote wakefulness by increasing the activity of catecholamines - dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
side effects of anti-hypnotics:
anxiety, tremors, dependency, reduced appetite, disrupted sleeping patterns, and masking because of sleepiness
melatonin
hormone synthesized from serotonin in the pineal gland
insomnia
sleep disorder that can make it hard to fall asleep, hard to stay asleep, or cause you to wake up too early and not be able to fall back asleep
causes of insomnia
medications, sleep apnea, disorders that cause limb movement (restless leg syndrome)
narcolepsy
severe daytime sleepiness; repeated brief (10-15 minutes) daytime sleep episodes
cataplexy
recurring losses of muscle tone during wakefulness
sleep paralysis
inability to move just as one is falling asleep or waking up
hypnagogic hallucinations
dreamlike experiences during wakefulness
REM-sleep behavior disorders
REM sleep without core-muscle atonia; people can then act out their dreams
system variable
what are you trying to regulate?
set point
optimal value
detector
monitors system variable
correctional mechanism
return to setpoint; water, nutrients
negative feedback
regulates activity
osmosis
movement of water thru a semipermeable membrane form to high solute concentration
osmoreceptors
firing rate determined by hydration; shrinking cells changes firing and signal the brain
what part of your regulatory mechanism returns your system to its optimal value?
correctional mechanism
true or false - too much water in red blood cells means they are hypertonic, and they will burst:
false
what is the first step of digestion?
chewing breaks down food in the mouth
which four organ systems are involved in maintaining homeostasis?
circulatory, urinary, gastro-intestinal, and respiratory
in short term energy storage, ___ from the food is converted into ___ and stored in the ___:
glucose, glycogen, liver and muscle cells
this phase of metabolism is the preparatory phase that sets the body up to be able to accept the influx of food:
cephalic phase
which stage of metabolism has low levels of insulin and high levels of glucagon?
fasting phase
energy metabolism
the chemical changes by which energy is made available for an organism’s use
cephalic metabolism
prepares the body for the food it needs to absorb
absorptive metabolism
energy is absorbed into the bloodstream and meets the body’s immediate demands for energy
fasting phase
all unstored energy from the previous meal has been used and the body is drawing from its reserves to meet the body’s next cephalic phase
environmental satiety factors
taste, people, portions, time of day, food presentation
sensory satiety factors
appearance/odor/taste/texture/temperature, tasting and swallowing vs. feeding tube, age related losses
liver satiety factors
first to know food is being received from the intestines; sends a satiety signal to the brain in response to nutrients
which side of the light-dark box will a rat spend more time in if they are displaying anxiety-like behaviors?
dark
most studies that use mazes (radial arm, T maze, plus maze, water maze) are trying to study which phenomenon?
memory
which of the following is not one of the considerations for using a specific species in a research study?
if the research has the animal as a pet
cell culture
removing cells from their natural environment and growing them in an artificial, but favorable environment
advantages of cell culture
extreme level of experimental control, cell type, high throughput, ethical consideration
disadvantages of cell culture
cells in isolation, artificial environment, generational concerns
slice culture
extraction and growth of portions of intact brain regions; allows for cellular and synaptic integrity
elisa (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay)
colorimetric assay to measure the presence of a specific ligand in a sample
immunohistochemistry
use of stain and visualize specific cellular components such as proteins and other macromolecules
selecting the best animal to study
goal: learn something about human condition, disease, or behavior; considerations: behaviors, species limitations, size, cost, existing literature, similarity to humans
knock out model
organisms bred to lack a specific gene
knock in model
replacing a gene with another or adding in a new one that doesn’t exist typically in that organism
transgenic model
putting genes from one species into another
deep brain stimulation (dbs)
for chronic pain, personality disorders, epilepsy, ocd, depression
cerebral angiography
injection of dye that will differ in x-ray absorbance into blood vessel into vertebral artery; shows cerebral vasculature and abnormalities
pet scan
injection of radioactive sugar into carotid artery; gets taken up like glucose but can’t be metabolized → radioactive sugar accumulates
mri
measures the waves emitted by activated hydrogen atoms
mri: diffuse tensor imaging
based on movement of water molecules; shows major tracts of the brain (tract: bundle of axons)
fmri (functional mri)
measures increases in oxygenated blood flow
transcranial magnetic stimulation
use of magnets near the skull to turn on (stimulate) or turn off a region of the cortex
intelligence behavioral tasks
wechsler adult intelligence scale (wais), verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, processing speed
memory behavioral task
digit span test
language behavioral task
token test