NURS 400: Module 9: Skin Disorders
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
stage 1 pressure ulcer
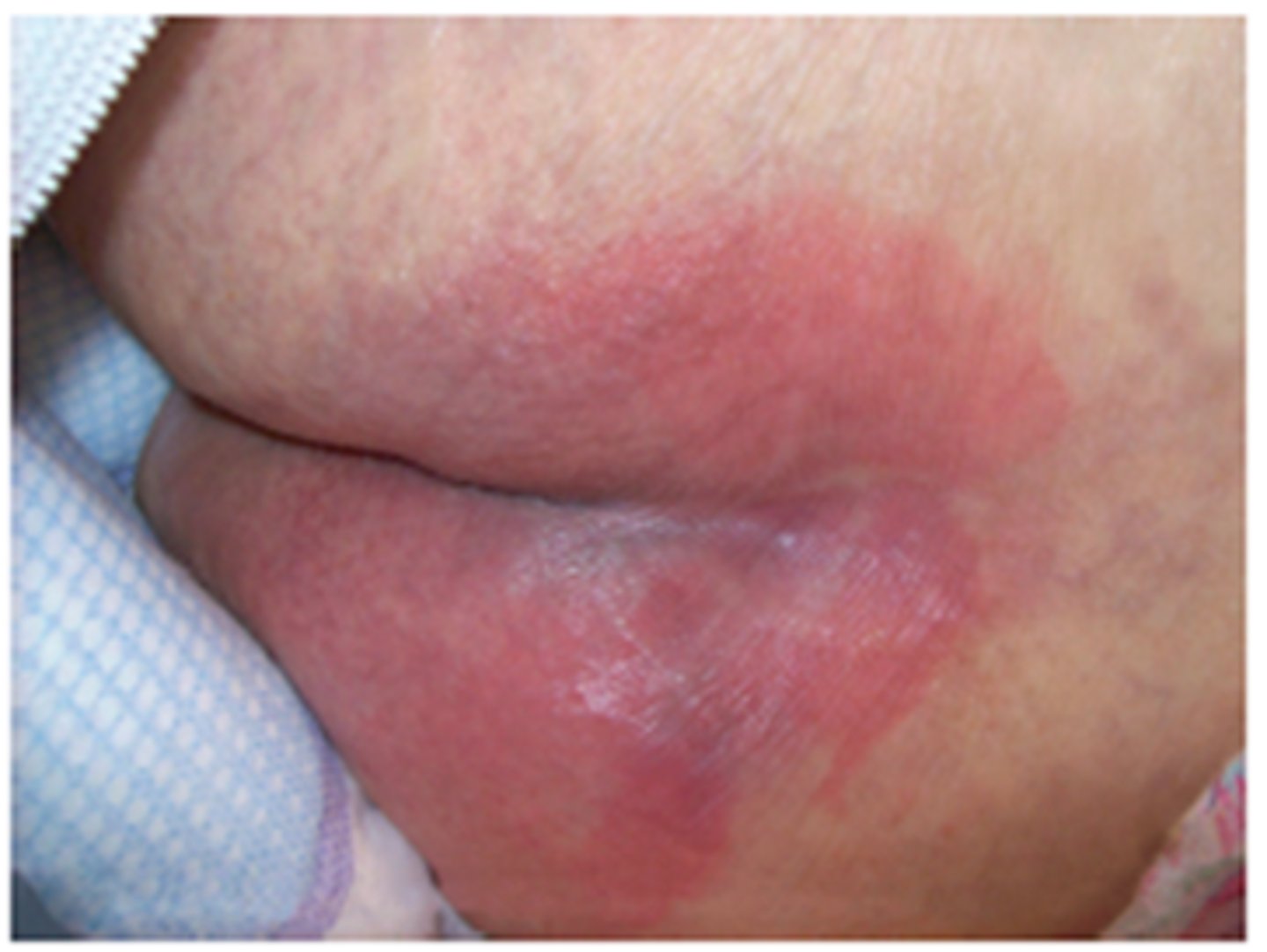
stage 1 pressure ulcer description
-Intact skin with localized area of non-blanchable erythema (may appear differently in skin with darker pigmentation)
-May be preceded by changes in sensation, temp, or firmness
-Color changes are not purple or maroon
stage 2 pressure ulcer
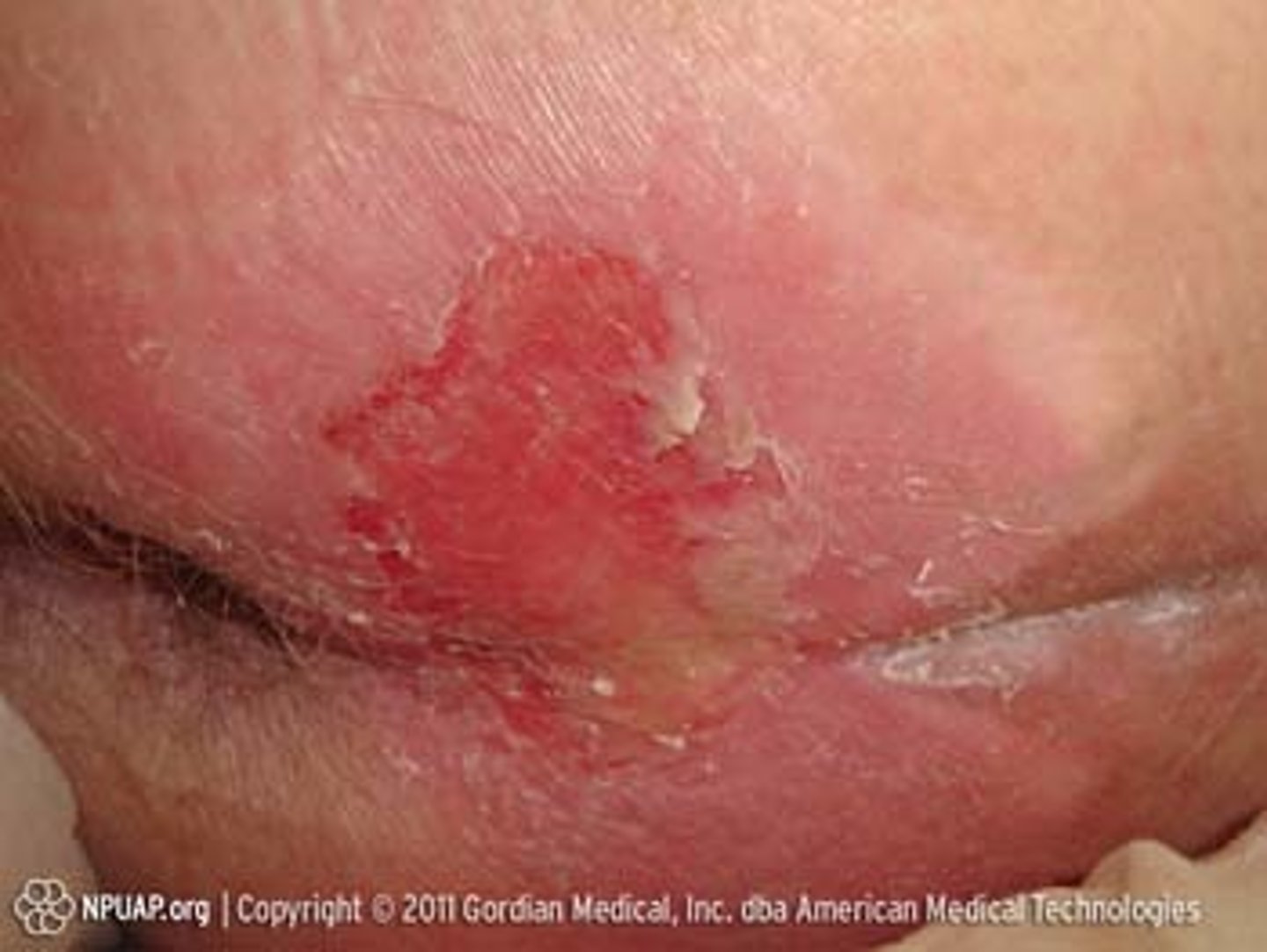
stage 2 pressure ulcer description
-partial thickness loss of skin with exposed dermis
-wound bed is viable, pink/red, and moist
-may look like intact or ruptured serum-filled blister
stage 3 pressure ulcer
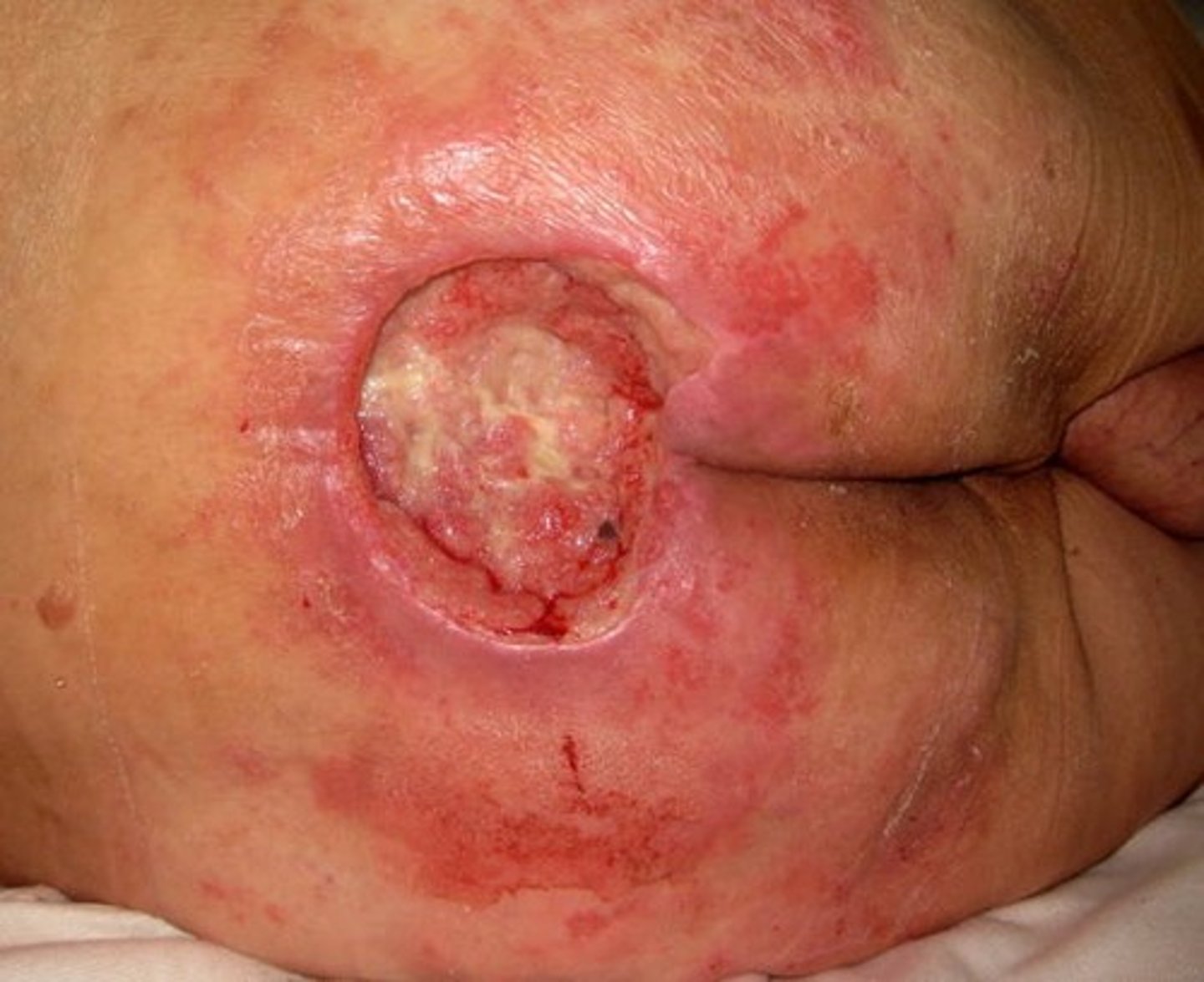
what is stage 3 pressure ulcer
-full-thickness skin loss with adipose visible in the ulcer
-granulation tissue and rolled wound edges are often present
-slough/eschar may be present
-subQ tissues may be damaged/necrotic
stage 4 pressure ulcer
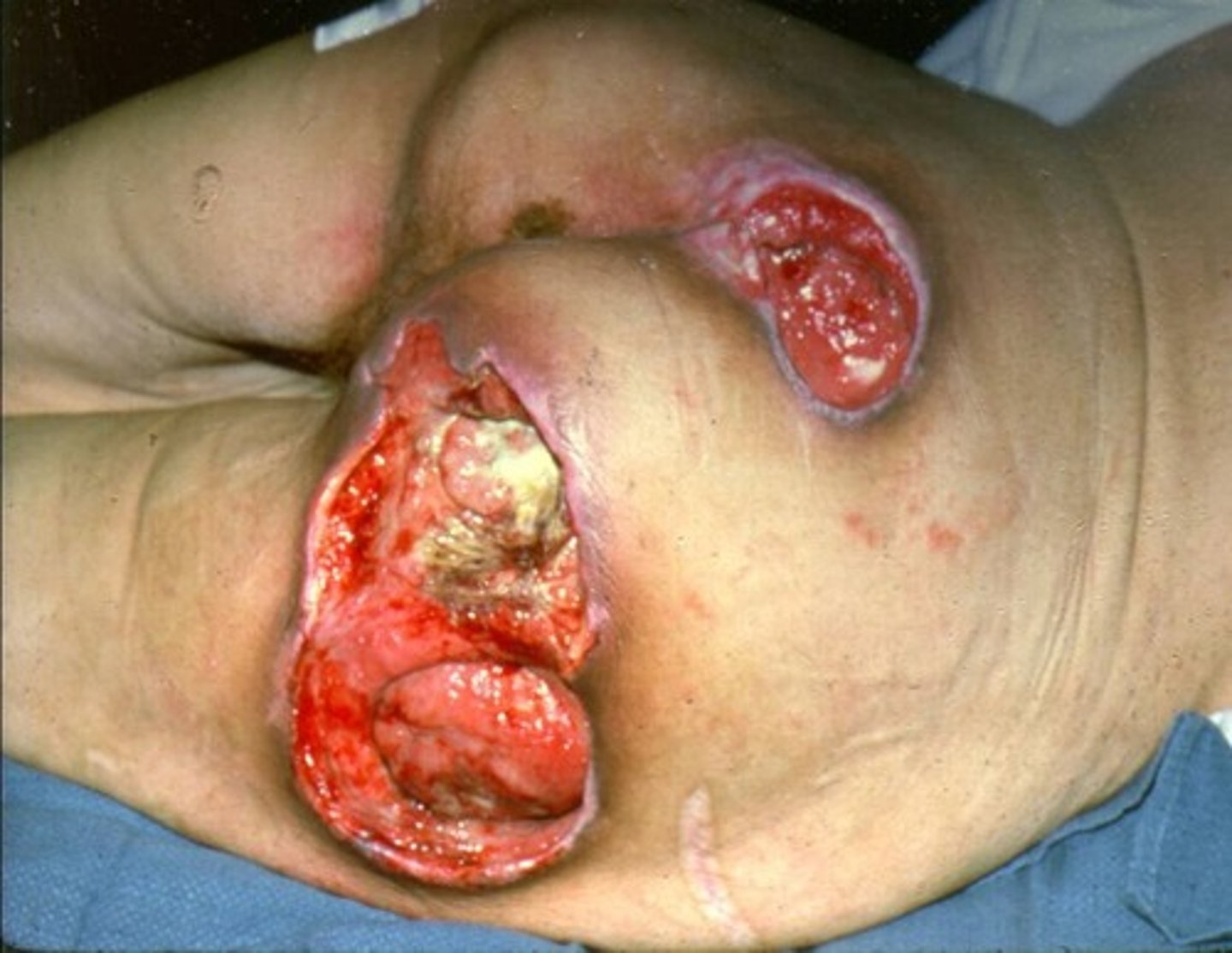
stage 4 pressure ulcer description
-full thickness skin loss with exposed or palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage, or bone
-may have slough/eschar
-rolled edges, undermining, or tunneling may be present
unstageable and suspected deep-tissue injury
eschar covering

pressure injury interventions
-improving tissue integrity
-surgical management
-preventing infection
s/s of infection in a pressure injury
-sudden deterioration of the wound, with increase in the size or depth of the lesion
-changes in skin color or texture of the granulation tissue
-changes in quality, color, or odor of exudate
-report changes to primary HCP
-maintain safe environment
what is SJS
rare disorder of skin and mucous membranes
-cell death causes epidermis to separate from dermis
-milder form of toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
etiology of SJS
-medications
-infectious causes
-delayed hypersensitive rxn
symptoms of SJS
-flu like symptoms occur several days before rash appears
-symmetric burning rash: begins on face/upper part of torso
-spreads within hours to days
what is skin like in SJS
-painful
-looks burned (peeling, blistered hives)
-lesions (cutaneous, appearance of target, red/purple coloration)
-core lesion surrounded by macular erythema later
tx in SJS
-dont cover
-stopping all non-essential meds
-fluid replacement, nutrition, wound and eye care
-pain meds, antihistamines, abx, topical steroids
-no baths
-administer morphine, clindamycin, diphenhydramine
what is cellulitis
diffuse painful inflammation of skin and subQ layers
who is most at risk for cellulitis
-athletes
-children
-men who have sex with men
-military recruits
-prisoners
-residents of LTC facilities
-IV drug users
-prior MRSA exposure
patho of cellulitis
-break in skin from injury
-most common bacteria (streptococcus/staphylococcus, MRSA)
manifestations of cellulitis
-painful, red swollen area of skin, hot, tender to touch
-fever/chills
-vesicles, bullae, plaques (with staph)
-tachycardia, hypotension, confusion, HA
-lymphadentitis and lyphangitis
cellulitis tx
abx- to kill infection and prevent sepsis
what is urticaria
-hives and welts on skin that itch
-vary in size
-may join together to form one large welt
types of urticaria
-acute hives
-chronic hives
-angioedema
what are acute hives
-may appear and go away within 24 hours
-may last for less than 6 weeks
what are chronic hives
last more than 6 weeks
what is angioedema
hives that occur deep under skin; acute episodes often involve lips, eyes, and face
s/s of urticaria
-appears as vascular rxn of skin
-characterized by sudden eruption of pale wheals or papules that cause severe itching
-some have burning/itching
presentation of urticaria
-wheals
-swellings
signs that med treatment is necessary in urticaria
-stridor
-wheezing
-other resp problems
-angioedema
tx for urticaria
-determine cause
-avoid to prevent future episodes
-OTC tx usually effective
what do we use to tx itching in urticaria
-calamine lotion
-cortisone cream
how do we dry the skin in urticaria
-topical emollients
-aluminum acetate
how do we ease discomfort in urticaria
-wet dressings
-oatmeal baths
what do ticks do in tick-bites
-blood sucking arachnids (parasites)
-embed head into skin and grow as they feed
patho of tick bites
can cause acute and chronic skin conditions
clinical manifestations of tick bites
-usual allergic rxn
-associated diseases: flu-like symptoms, rash over entire body, neck stiffness, swollen lymph nodes
lymes disease
-red bump with ringed red rash resembling bulls-eye
-fever
-HA/fatigue
-erythema migrans
etiology of squamous cell carcinoma
cumulative UV light exposure
patho of squamous cell carcinoma
-arises from damaged, unrepaired DNA in the nucleus of squamous cells of the epidermis
-UV radiation triggers cancerous keratinocyte transformation
-impaired keratinocytes extend into dermis
manifestations of squamous cell carcinoma
-Firm, smooth, or hyperkeratotic papules or plaques with ulcer in the center on sun-exposed skin
-Often presents as nonhealing sore that bleeds easily
-May present as large wart, cutaneous horn, or slow-growing, scaly, red plaque
-typically occurs in sun-exposed areas
-may also occur in body regions that are no sun exposed
types of burns
-superficial
-superficial partial thickness
-deep partial thickness
-full thickness
what are superficial burns
-reddened skin-painful
what are superficial partial thickness burns
-burned epidermis and papillary dermis
-blistering
-dermis is red and moist-painful
what is deep partial thickness burns
-damage to epidermis, papillary dermis, and reticular layer of the dermis
-injury to hair follicles
-blistering
-no pain
what is full thickness burns
-damage to epidermal, all dermal layers and structures and subQ tissue
-skin is charred and pale
-painless
-leathery skin appearance