Chemistry- Unit 5: Atomic Theory
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Democritus
Matter is made up of indestructable, indivisible, solid particles
John Dalton
1) Matter is composed of atoms: indivisible, indestructable, solid spheres
2) Atoms of same element: identical properties
Atoms of different element: different properties
3) Atoms can't be created, destroyed, or changed
4) Chemical rxn is rearrangement of atoms
Law of Multiple Proportions
2 elements form 1+ compound, ratio of masses will be small whole numbers
Tomson and Crookes
Discovered the electron
- Crooke's Tube
- Plum Pudding Model: atom is fully positive with negative embedded in it
Rutherford
Most particles went through gold foil BUT SOME BOUNCED BACK - when (+) alpha particles collided with + nucleas
# of electrons (in a neutral atom) =
# of protons
# of electrons (in a positve ion)
# of protons - charge #
# of electrons (in a negative ion)
# of protons + charge #
# of protons =
atomic #
# of neutrons =
mass # - atomic #
atomic mass =
(isotope mass x %) + (isotope mass x %) ...
to find frequency or wavelength
C= λv
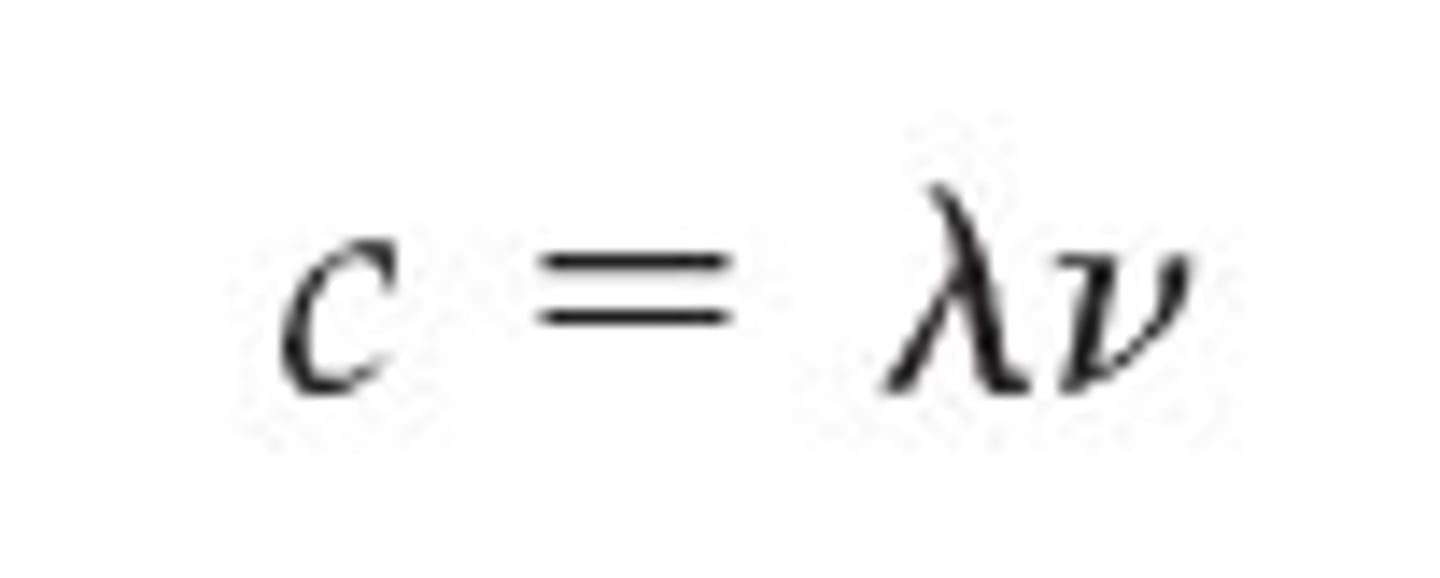
to find energy or frequency (plancks hypothesis)
E = hv
Bohr atomic model
• Electrons orbit only at certain allowed orbits or specific energy level
How is bright-light spectrum formed?
1) ground state: lowest possible energy level
2) atom absorbs NRG (light, electricity, heat, collisions..)
3) excied state: electron moves to higher energy state
4) electron falls back to ground state and releases NRG as photons of light
photon/nucleon
a particle of light