OZ 6 The CFC story
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
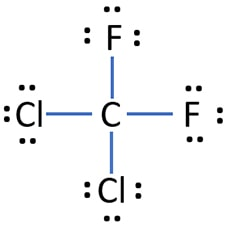
dichlorodifluoromethane
CCl₂F₂
Uses of CFCs
Refrigerants
Air conditioning
Aerosol propellants
Blowing agents
Dry cleaning solvents
Carbon- halogen bonds is
polar
Polar boding occurs when two atoms with
different electronegativities form a covalent bond
dipole
charge separation
The atom with the __________ _____________ pulls the shared electrons closer, becoming slightly ______ , while the other atom becomes slightly ________. This creates a _________ within the molecule.
higher electronegativity
negative δ⁻
positive δ⁺
dipole
_________ molecules dissolve in water
polar
_________ molecules do not dissolve in water
non-polar
OH bond is
polar
Electronegativity
relative tendency of an atom in a covalent bond in a molecule to attract electrons in a covalent bond to itself
Name 4 of the most electronegative atoms
F, O, N, Cl
Electronegativity __________ across a period
increases
Why does electronegativity increase across a period?
number of protons increases
atomic radius decreases- electrons in the same shell are pulled in more
Electronegativity _________ down a group
decreases
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group?
distance between nucleus and outer electrons increases
shielding of inner electrons increases
What kind of compounds are purely covalent?
elements of similar electronegativity- small electronegativity difference
All haloalkanes are _______ with water
immiscible
The _______ the halogen atom in a haloalkane and the _______ halogen atoms there are, the __________ bpt
bigger
more
higher
longer molecules have ________ intermolecular bonds
stronger
Why do straight chain alkanes have higher bpt?
more contact between molecules
more opportunities for intermolecular bonds to form
Why does the bpt of noble gases increase down the group?
Atoms get bigger
more electrons
stronger id-id bonds
more energy to break
dipole
charge separation
When does a polar covalent bond form?
elements in bond have different electronegativities
When are dipoles formed in a polar covalent bond?
bond has unequal distribution of electrons producing a charge separation
When are compounds ionic?
very different electronegativities and large electronegativity difference
Why does instantaneous dipoles occur?
electrons are in constant and random motion
electron density can fluctuate
parts of molecule become more or less negative
When do induced dipoles form?
a dipoles cause dipoles to form in a neighbouring molecule
induced dipole has the ______ charge to a temporary/permanent dipole
opposite
How does the number of electrons affect the size of id-id bonds?
more electrons
higher chance of temporary dipoles
id-id bonds stronger
higher bpt
The boiling point of halogen________ down the group
increases
Why does the bpt of halogen increase down the group?
bigger molecules have more electrons
bigger id-id bonds
more energy needed to break bonds
Why does the bpt of alkane homologous series increase down the series?
bigger molecules have more electrons
bigger id-id bonds
more energy needed to break bonds
The boiling point of alkanes ___________ across the series
increases
Why do long chain alkanes have a high bpt?
larger surface area of contact between molecules
more induced dipole- instantaneous dipole interactions
When do induced dipoles occur?
when an unpolarised molecule is next to a dipole
When do permanent dipoles occur?
between polar molecules
Order the dipoles from weakest to strongest
instantaneous dipole- induced dipole
permanent dipole- permanent dipole
permanent dipole- induced dipole
When is the molecules non-polar even if it has permanent dipoles?
symmetrical
Reaction for methane removing chlorine radicals in stratosphere
CH₄ + Cl → CH₃ + HCl