Anatomy 18.2 Heart Homestasis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Two conditions severely weaken heart:
-Incompetent Valve
-Valvular stenosis
Valvular stenosis
Stiff flaps that constrict opening
Heart needs to exert more force to pump blood
Defective valve can be replaced with
mechanical, animal, or cadaver (from another human)valve
Incompetent valve
Blood backflows so heart repumps same blood over and over
angina pectrois
-Thoracic pain caused by fleeting deficiency in blood delivery to myocardium
-cells are weakened
Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
-prolonged coronary blockage
-areas of cell death are reapired with noncontractile scar tissue
The heart relies mostly on
aerobic respiration (a chemical process that uses oxygen to convert glucose into energy, carbon dioxide, and water)
Cardiac muscle has more mitochondria than skeletal muscle so has greater dependence on
oxygen
-cannot function without it
-skeletal musclecan go through fermentation if without it
Both types of tissues can use other fuel sources including
-lactic acid (must have oxygen)
coordinated heartbeat is a function of
-Presence of gap junctions
-intrinsic cardiac conduction system (network of algorithmic (non-contractile) cells)
arrhythmias
-irregular heart rhythms
—uncoordinated atrial and ventricular contractions
Fibrillation
-rapid, irregular contractions
-heart becomes useless for pumping blood, causing circulation to cease, brain death
Fibrillation treatment
-defibrillation interrupts chaotic twitching, giving heart a “clean slate” to start regular, normal depolarizations
Changes in patterns or timing of ECG may reveal
-diseased or damaged hear
- problems with heart’s conduction system
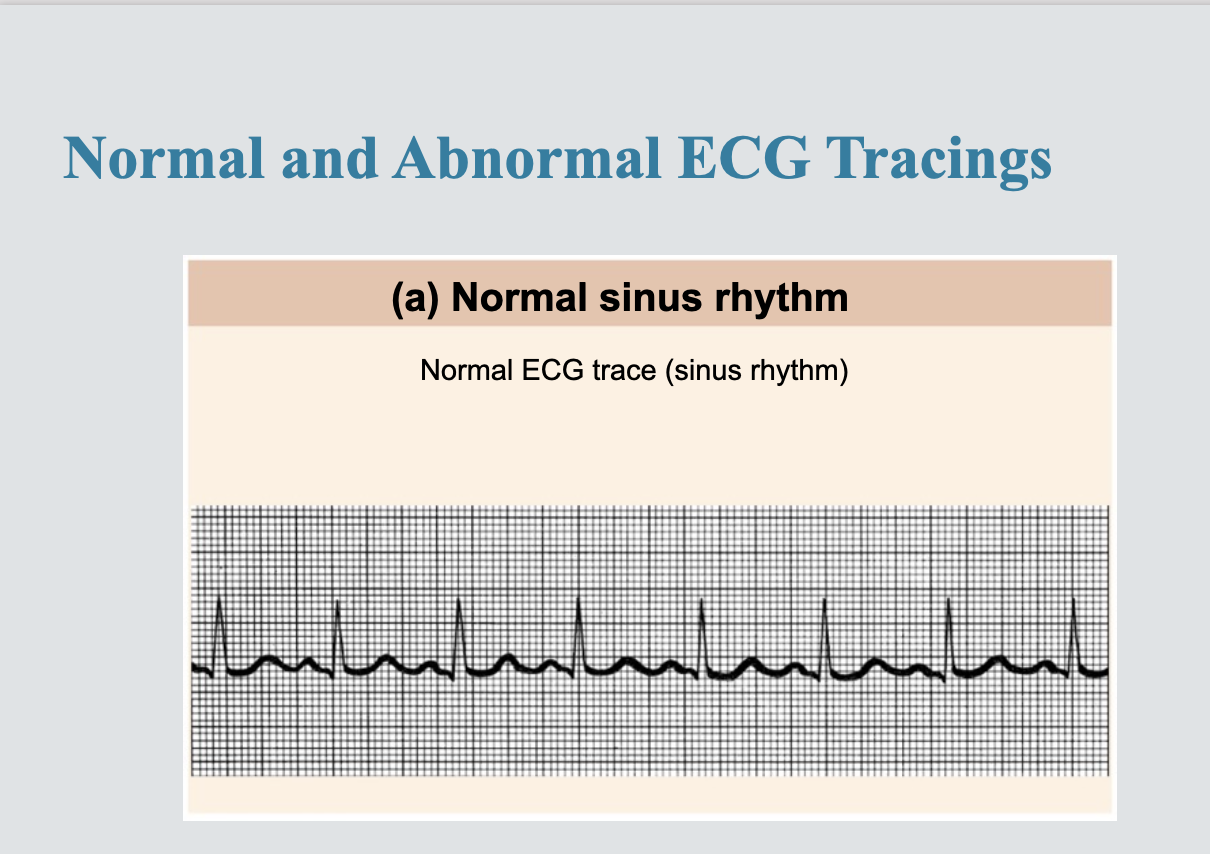
problems that can be detected in the ECG pattern are
-enlarged R waves - can indiacte enlarged ventricles
-elevated or depressed S-t segment- indicates cardiac ischemia
Heart murmurs
abnormal heart sounds heard when blood hits obstructions
-indicates valve problems
Stetnotic valve during heart murmur
Fails to open completely, restricting blood flow through valve
Causes: high- pitched sound or clicking as blood is forced through narrow valve
imcompetent valve during heart murmur
Valve fails to close completetly, allowing backflow of blood
Causes: swishing sound as blood regurgitates backward from ventricle into atria
Tachycadia
abnormally fast heart rate
-if persistent can lead to fibrillation
bradycardia-
heart rate slower than 60 beats / min
-may lead to grossly inadequate blood circulation in nonathletes
congestive heart failure
-Progressive condition; CO is so low that blood circulation is inadequate to meet tissue needs
congestive heart failure is caused by
coronary atherosclerosis
-Clogged arteries from fat buildup, impairs oxygen delivery to cardiac cells
-heart becomes hypoxic
caused by blood pressure
Multiple myocardial infracts
heart becomes weak as contractile cells are replaced w/ scar tissue
-Drug toxicity or chronic inflammation may play a role
Left sided congestive heart failure results in
in pulmonary congestion
-blood backs up in lungs
Right- sided congestive heart failure results in
peripheral congestion
-blood pools in body organs, causing edema
Failure to either side of heart can
weaken the other side
-leads to decompensated, seriously weakened heart
Treatment for congestive heart failure:
Removal of fluid
-drugs to reduce afterload and increase contractility