Heritability and Genetics in Behavioral Science
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Heritability
Estimates the proportion of variance in a trait within a population that can be attributed to genetic differences. It is population-specific, not individual-specific.
Heritability Range
Range from 0 (no genetic contribution) to 1 (entirely genetic).
0.5 suggests ~50% variability due to genetics.
Heritability Calculation
Calculated using twin studies: Heritability ≈ 2(rMZ - rDZ),
Where MZ twins share 100% of genes and DZ twins share ~50%.
Vp Formula
Vp = A² + C² + E²,
A² = Additive genetic influence,
C² = Shared environment,
E² = Non-shared environment.
High Heritability Misconception
High heritability does not mean a trait is immutable or unaffected by the environment.
Heritability other misconceptions
Estimates vary across time, populations, and methods.
Heritability says nothing about causation in individuals.
Environmental Variability and Heritability
Heritability increases if environmental variability decreases (e.g., schooling is equal).
Flynn's Multiplier Effect
Small genetic differences may influence environments that reinforce these differences
Mendelian Inheritance - basic principle
Inheritance is based on discrete units (genes), where traits are determined by alleles.
Traits can be dominant or recessive.
Genotype
Genetic makeup (e.g., GG, Gg, gg).
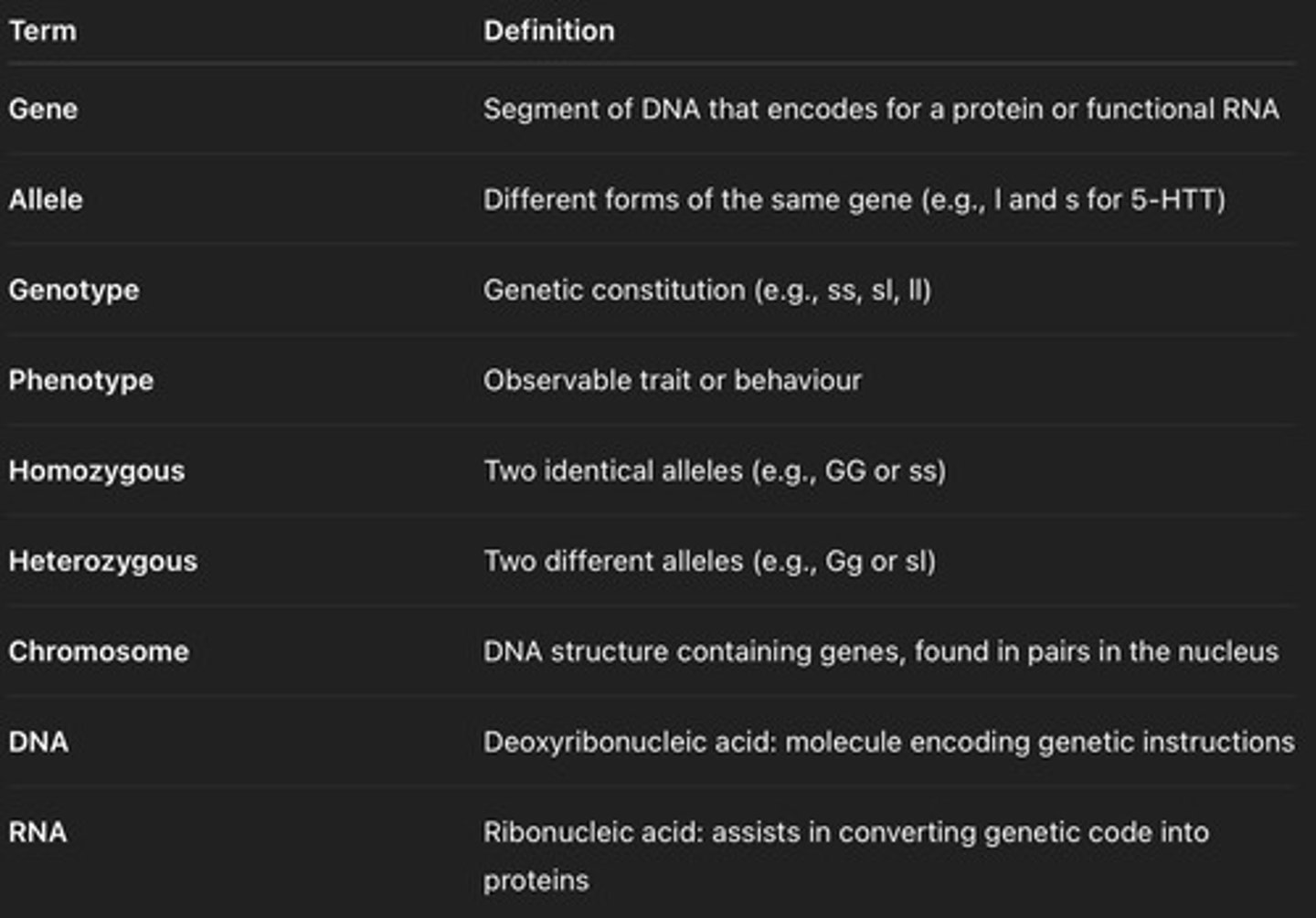
Phenotype
Observed traits (e.g., green or yellow peas).
Punnett Squares
Predict outcomes of genetic crosses.
Heterozygous Cross Phenotypic Ratio
A heterozygous cross (Gg × Gg) yields a 3:1 phenotypic ratio (dominant:recessive).
Serotonin Transporter Gene
Has two alleles: long (l) and short (s).
Effects are additive, not strictly dominant/recessive.
Gene Transcription Function
Replication - copying for new cells or offspring; Protein Synthesis - via transcription and translation.
Transcription Process
DNA → mRNA in the nucleus; RNA polymerase reads DNA and synthesizes complementary RNA.
mRNA Function
mRNA leaves the nucleus and is translated into proteins in the ribosome.
Tryptophan Hydroxylase
Genes transcribed into enzymes like tryptophan hydroxylase (involved in serotonin production).
Caspi et al. (2003) Study
Key Finding: Short allele (especially ss) associated with increased risk of depression only when combined with life stress.
No direct effect of gene or stress alone — but a significant gene-environment interaction (G×E).
Zhang et al. (2005) Study - Tryptophan Hydroxylase Gene
Finding: Mutant form associated with lower serotonin production in vitro.
Higher prevalence in depressed individuals, but not all depressed people have it → other factors involved.
DAT1: Dopamine transporter gene
linked to ADHD, cocaine addiction, schizophrenia
GABRA2: GABA receptor gene
linked to conduct disorder, epilepsy;
CHRNA5-A3-B4 cluster: Nicotinic receptor gene
linked to smoking and nicotine addiction.
Polygenic Influences
Single genes rarely cause psychiatric conditions.
Environmental Context
Environmental context matters: E.g., stress, parenting, peer groups.
Replication Problems
Not all studies consistently replicate associations.