CISC260 Study Info
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
ldr xRegister, =label
Loads the address of a variable/string into a register.
ldr xRegister, [xRegister]
Loads the value stored at the memory address inside a register.
mov x8, 0x40
write!
mov x8, 0×3f
read!
mov x8, #93
exit!
What does w0 represent in ARM?
the lower 32 bits of register x0
What does x0 represent in ARM?
a 64-bit register
What is the decimal representation of the non-negative integer represented in binary as 0101 1010?
90
What is the hexadecimal representation of the unsigned integer represented in binary as 0101 1010?
5A
Write the decimal value 117 in hexadecimal.
75
Enter the 8-bit binary value for 0xF4.
11110100
Enter the decimal value of 0xF4 assuming the use of two's complement in eight bits.
-12
Enter the 8-bit binary equivalent of the decimal value 117
01110101
Which of the following types of code could be made to run on different CPU architectures?
Question 5Answer
a. C code
b. Assembly code
c. Python code
d. Machine code
a. C code
c. Python code
Which tools and files in order in which they are used to turn a C source file into something the computer can execute.
a. executable file → object code → assembler → assembly code → compiler → C source file
b. C source file → compiler → assembly code → assembler → Object code → linker → executable file
c. C source file → assembly code → assembler → object file → linker → compiler → executable file
b. C source file → compiler → assembly code → assembler → Object code → linker → executable file
Assuming two's-complement is being used, what is the sign-inversion of 10101000? Express your answer as an eight-bit binary value.
01011000
Which of the following sums will produce a carry-out to the fifth bit? Note: all values are written using standard 4-bit binary notation.
Question 8Answer
a. 0111 + 0100
b. 1100 + 0111
c. 1000 + 1000
d. 0000 + 1000
e. 1111 + 0001
f. 1010 + 0101
b. 1100 + 0111
c. 1000 + 1000
e. 1111 + 0001
Enter the binary equivalent to the decimal value -42 in eight bits using two's complement.
11010110
Consider the following 8-bit addition:
1101 1011
+0110 1000Select all the below that apply:
a. Neither overflow nor carryout occurs when the values are interpreted as unsigned integers.
b. Carry-out occurs when the values are interpreted as signed integers.
c. Neither overflow nor carryout occurs when the values are interpreted as signed integers.
d. Overflow occurs when the values are interpreted as unsigned integers.
e. Overflow occurs when the values are interpreted as signed integers.
f. Carry-out occurs when the values are interpreted as unsigned integers.
b. Carry-out occurs when the values are interpreted as signed integers.
d. Overflow occurs when the values are interpreted as unsigned integers.
f. Carry-out occurs when the values are interpreted as unsigned integers.
Match the below one-bit sums with the associated sum "S" and carry "C"
0 + 1 + 0
Sum 1 Carry 0
Match the below one-bit sums with the associated sum "S" and carry "C"
0 + 0 + 0
Sum 0 Carry 0
Match the below one-bit sums with the associated sum "S" and carry "C"
1 + 1 + 0
Sum 0 Carry 1
Match the below one-bit sums with the associated sum "S" and carry "C"
1 + 1 + 1
Sum 1 Carry 1
Express the following 8-bit signed value as a signed 16-bit binary value:
1110 00111111111111100011
What is the ASR (arithmetic shift right) by two of the eight bit value:
1010 1101
11101011
What's the smallest 8-bit unsigned integer value that will cause overflow when added to
0101 1101 (considered to be an unsigned integer).
(you might want to use subtraction).
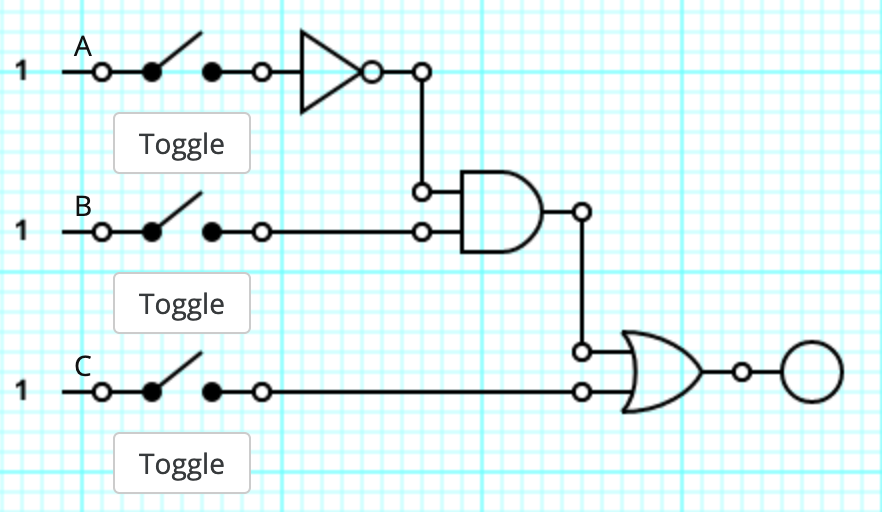
Which of the following expressions correctly represents the following logic gate circuit?
a. (~A&B)|C
b. (~A&B)&C
c. (~A|B)&C
d. ~A&(B|C)
e. ~(A&B)|C
(~A&B)|C
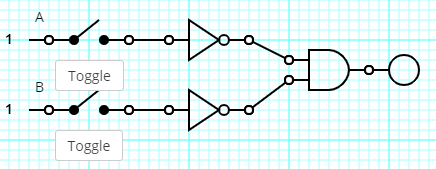
Which of the following expressions is equivalent to the below logic gate circuit?
a. ~A | ~B
b. ~A|B
c. ~(A|B)
d. None of these expressions are equivalent to the circuit
e. ~A&B
~(A|B)
Consider the following logic-gate circuit:
Fill in the truth table for the Boolean expression
~(A&B)
a.
A 0 0 0 0
B 0 0 0 0
O 0 0 0 0
b.
A 0 1 0 0
B 0 0 1 0
O 0 0 1 1
c.
A 1 1 1 1
B 1 1 1 1
O 1 1 1 1
a.
A 0 0 0 0
B 0 0 0 0
O 0 0 0 0
What purpose does X1 have in the following instruction:
sub X0, X2, X1
a. It stores the value being subtracted
b. It's where the answer of X0-X2 is stored
c. It stores the value being subtracted from
d. It is changed to a negative value.
e. It contains bits representing a number using two's-complement
a. It stores the value being subtracted
What is the relationship between X0 and W0 in ARMv8? (See 9.1.2 in the text)
a. X0 is a "virtual" register that uses only the lower 32-bits of W0.
b. W0 is a 32-bit register and X0 a similarly-named, but otherwise unrelated, 64-bit register
c. X0 and W0 are simply different names for the same register
d. W0 is used for memory addresses, while X0 is used for values
e. W0 is a "virtual" register that uses only the lower 32-bits of X0.
W0 is a "virtual" register that uses only the lower 32-bits of X0.
What is the ASR (arithmetic shift right) by two of the eight bit value:
1010 1101
a. 1110 1011
b. 1010 1101
c. 1011 1111
a. 1110 1011
What is the ASR by two of the eight-bit value:
0101 0110
a. 0000 0111
b. 0001 0101
c. 1010 1011
b. 0001 0101
What is 0x0303 represented as a two-byte binary value?
0000 0011 0000 0011
Create a truth table that represents the following Boolean expression
(p & q & ~r) | (r | ~p)
where p, q and r are Boolean variables (so they each represent a 0 or a 1, an on or off switch, or True and False.)
Select all that apply to your truth table:
a. The only time the result is 0 is when p is 0, and q and r are 1.
b. The only time the result is 0 is when p is 1, and q and r are 0.
c. There is no combination of p, q, and r where the output is 0
d. There are 4 different combinations for the truth table.
e. There are 8 different combinations for the truth table.
f. The output is always 1 when p is 0
b. The only time the result is 0 is when p is 1, and q and r are 0.
e. There are 8 different combinations for the truth table.
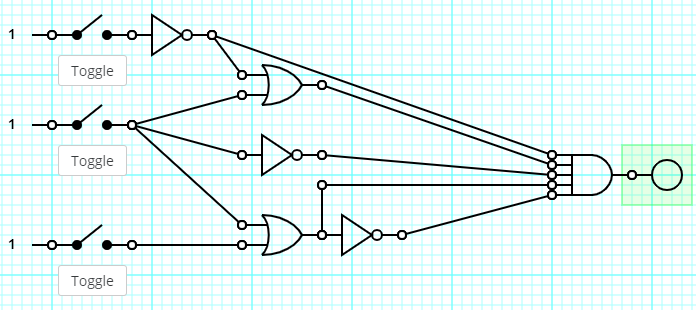
If we label the toggles a, b, and c from top to bottom (with a closed toggle being True), select the abc combinations below which result in a True output on the right.
a. TTT
b. FFF
c. FFT
d. TFF
e. TFT
f. FTF
g. No combination will make this True
No combination will make this True
Consider the following truth table, where X, Y, and Z are Boolean variable inputs and W is a Boolean-valued result:
X | Y | Z | W |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Write an expression for the above table using ~&|.
(~X & ~Y & ~Z) | (~X & ~Y & Z) | (X & ~Y & ~Z) | (X & Y & Z)
Using C, define a function called "func(int x0, int x1, int x2)" that duplicates the actions of the following assembly code and prints the final values of x0, x1, and x2. (Initial values for x0, x1, and x2 will be provided to your function as arguments).
_start:
mov X2, X0.L0:
cmp X1, X0
b.lt .L1
sub X1, X1, 4
add X0, X0, 2
add X2, X0, X1
b .L0
.L1:void func(int x0, int x1, int x2) {
/* your code here */
x2 = x0;
while(x1 >= x0){
x1 = x1 - 4;
x0 = x0 + 2;
x2 = x0 + x1;
}
printf("X0=%d, X1=%d, and X2=%d", x0, x1, x2);
}
What will happen when this instruction is executed if X1 holds the value of 0x50? (Choose all that apply). LDR W3, [W1, #16]
a. This will load sixteen bytes stored at address 0x50 into W3.
b.The value of W1 will NOT be modified
c.W3 will get the value stored at the memory address 16 bytes before the address stored in X1.
d. The value of W1 will be modified.
e. This will load the value stored at address 0x60 into W3
f. W3 will get the value stored at the memory address 16 bytes after the address stored in X1.
b.The value of W1 will NOT be modified
e. This will load the value stored at address 0x60 into W3
f. W3 will get the value stored at the memory address 16 bytes after the address stored in X1.
Assume that register X0 stores an unsigned integer value. Write ARMv8 assembly code so that X1 contains the value 1 if X0 is odd and 0 if X0 is even. Leave X0 unchanged!
and X1, X0, #1
Assume that registers X0 and X1 store an unsigned integer values. Drag the labels and instructions into an order so that X2 becomes the product of X0 and X1 (i.e. X2 = X0*X1) after they execute.

Select whether the statements represent a half-adder, full-adder, or both.
Has 3 input bits and 2 output bits
Full-adder
Select whether the statements represent a half-adder, full-adder, or both.
Used for adding binary numbers
Both
Select whether the statements represent a half-adder, full-adder, or both.
Has 2 input bits and 2 output bits
Half -Adder
Select whether the statements represent a half-adder, full-adder, or both.
A combinational circuit used for arithmetic operation
Both
Select whether the statements represent a half-adder, full-adder, or both.
Includes gates for processing a carry bit
Full-adder
What will be the results of applying the following logical operations to the 4 bits: 1100?
Logical right shift
0110
What will be the results of applying the following logical operations to the 4 bits: 1100?
Arithmetic right shift
1110
What will be the results of applying the following logical operations to the 4 bits: 1100?
Logical left shift
1000
Fill in the blanks with the correct terms.
A __________ could be used to signal a particular ____________ location according to a number placed on the address lines of a memory bus. An address ___________ location with ________ inputs can select any of __________ different locations.
A. Decoder; memory location; decoder; n; 2^n
B. Memory location; memory location; decoder; n; 2^n
C. Decoder; memory location; decoder; n; n+n
A. Decoder; memory location; decoder; n; 2^n
What's the minimum number of OPCODE bits needed if the ALU can support 50 different operations?
Question 5Answer
a. 1
b.2
c.3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
g. 7
h. 8
6
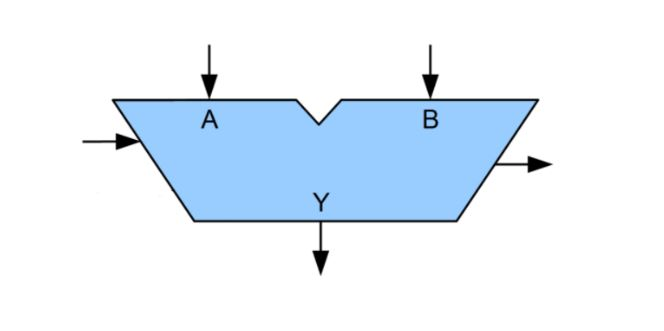
Drag the corresponding labels onto the the correct location of the image.
A: First Operand
B: Second Operand
Y: Result
Left Arrow: OP code
Right arrow: Status flag
Which is true about storage circuits?
a. Storage circuits need a different kind of gate than those in an ALU.
b. A value supplied to a storage circuit is always immediately stored.
c. Storage circuits are combinational.
d. Storage circuits have some kind of feedback loop,
e. There is only one way to design a storage circuit.
Storage circuits have some kind of feedback loop,
What are the caller’s responsibilities in a procedure call?
store arguments
transfer control
What are the callee’s responsibilities in a procedure call?
allocate local storage
execute procedure code
store return value
return control
Which is true about storage circuits?
a. Storage circuits need a different kind of gate than those in an ALU.
b. A value supplied to a storage circuit is always immediately stored.
c. Storage circuits are combinational.
d. Storage circuits have some kind of feedback loop,
e. There is only one way to design a storage circuit.
Storage circuits have some kind of feedback loop
What is the result of the following operation (bitwise exclusive-or)?
1101 1111
^ 1111 01000010 1011
ARMv8 is a "load-store" architecture. This means (select all that apply):
a. Registers can have values loaded directly from memory.
b. ALU results are immediately stored in memory.
c. ALU operations can only be performed on registers and immediates (literals)
d. ALU operations must be performed on values loaded directly from memory
e. Memory addresses range from 1 to 2^39-1
a. Registers can have values loaded directly from memory.
c. ALU operations can only be performed on registers and immediates (literals)
Drag the lines into the following recursive procedure to compute a factorial (the argument should be in X0, and the return value in X1). Note: a 25% penalty will be applied for each incorrect submission.
factorial:
STR LR, [SP,8]
SUB x0,x0,1
CBNZ x0,.gt1
MOV X1,#1
ADD SP,SP,#16
RET
.gt1:
MUL X1,X0,X1
ADD SP,SP,#16
RETSub sp, sp, #16
str x0, [sp]
BL factorial
LDR X0, [SP]
LDR LR, [SP,8]
Match the terms to its corresponding functions or parts of program memory.
Dynamically allocated memory grows as program allocates memory |
heap
Match the terms to its corresponding functions or parts of program memory.
Global variables are stored here.
Data
Match the terms to its corresponding functions or parts of program memory.
The main program that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer program
operating system
Match the terms to its corresponding functions or parts of program memory.
Program instructions stored here.
code
Match the terms to its corresponding functions or parts of program memory.
Local variables, arguments, and other values that need temporary "protection" are stored here. Grows as program calls functions. Shrinks on return from function
stack
Which of the following gates are "universal", in that any logic gate can be constructed from circuits consisting only of them? Choose all that apply
a. nand
b. not
c. nor
d. xor
e. xand
a. nand
c. nor
Match each item to its purpose.
BL
Initiate a procedure call
Match each item to its purpose.
Link register
enables a procedure call to find back to where they were called
Match each item to its purpose.
Program counter
points to the memory address of the current isntruction
Match each item to its purpose.
frame pointer
the largest address the current procedure call may safely modify (often not used)
Match each item to its purpose.
stack pointers
permits procedure to claim memory which can be safely modified
RET
completes a procedure call
Which of the following directly limits the speed of the CPU clock?
a. The execution time of the slowest operation.
b. The size of main memory.
c. The number of operations in the ALU.
d. The execution time of the fastest operation.
e. The number of bits in a register.
The execution time of the slowest operation.
Consider the following assembly code:
.text
.global _start
_start:
ldr x0, =.value
ldr x0,[x0]
mov x8,93
svc 0
.data
.value: .8byte 0xffffffffffffffffConsidered as a signed decimal integer, what value is contained in register x0 when the above code finishes?
-1
What instruction format would be used for the "ret" instruction?
Hint: remember that "ret" means "branch to the address contained in register LR".
a. R
b. I
c. CB
d. B
e. D
R
What instruction format would be used for this instruction:
add x0, x3, #47Question 5Answer
a. CB
b. D
c. B
d. R
e. I
I
Find the binary encoding of this instruction:
adds x0,x12,x12Enter your answer as a hex value.
0xAB0C0180
The first instruction to be executed is indicated by:
a. The _start: label
b. The first memory address
c. The .data directive
d. The .text directive
e. The main: label
a. the _start: label
Express the following 8-bit signed value as a signed 16-bit binary value:
1110 00111111 1111 1110 0011
Consider a variable defined in C like:
int x = 0x12345678;In a little-endian system, what is the value of the byte found at &x?
a. 0x87654321
b. 0x78
c. 0x21
d. 0x87
e. 0x21436587
f. 0x12
g. 0x12345678
b. 0x78
Consider a variable defined in C like:
int x = 0x12345678;In a big-endian system, what is the value of the byte found at &x?
a. 0x12345678
b. 0x21
c. 0x87
d. 0x21436587
e. 0x87654321
f. 0x78
g. 0x12
g. 0x12
What's the format of the ARMv8 instruction with the following hex value:
0x972E1F9Fa. IW-format
b. R-format
c. B-format
d. I-format
e. CB-format
f. D-format
c. B-format
If an ARMv8 machine instruction has the CB Instruction Format, how many 11-bit opcodes refer to that same instruction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 8
c. 8
Select the statements that are true about IEEE754 floating point numbers.
a. The sign of a floating-point number is represented by a single bit.
b. To encode a floating-point number, you need the sign of the expression, the exponent and the value in the range 1.0 to (almost) 2.0
c. Floating-point values are intended to represent extremely small values.
d. The exponent of a floating-point number is stored as an unsigned integer.
e. Floating-point values are intended to represent extremely large values.
a. The sign of a floating-point number is represented by a single bit.
b. To encode a floating-point number, you need the sign of the expression, the exponent and the value in the range 1.0 to (almost) 2.0
Order all the pieces in taking a C program to a running program.
C Program
⇓
__________
⇓
Assembly language program
⇓
_________
⇓
__________
⇓
_________
⇓
Machine-language program
⇓
__________
⇓
__________
compiler
assembler
object code
linker
loader
memory
What is the decimal representation of 0.10101two
0.65625
What is the value of 0.84375 represented in binary?
0.11011
Which of the below is one tenth expressed in binary?
a. 1/10
b. 0.1
c. 0.00011
d. It is not possible to represent one tenth in binary
e. None of the above
e. None of the above