2.3 role and importance of stakeholders
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
internal stakeholders
employees
managers
shareholders
external stakeholders
customer
supplier
government
local community
pressure groups
competitors
trade unions
primary stakeholder
affected directly by actions of the business - usually financially
secondary stakeholders
not directly affected by actions of the business
uses of stakeholder mapping
help avoid resistance to change when making decisions
help inform decision making
informs managers of the importance of each stakeholder group - how involved they should be in decision making
failure to involve stakeholders may become a negative influence
stakeholder map
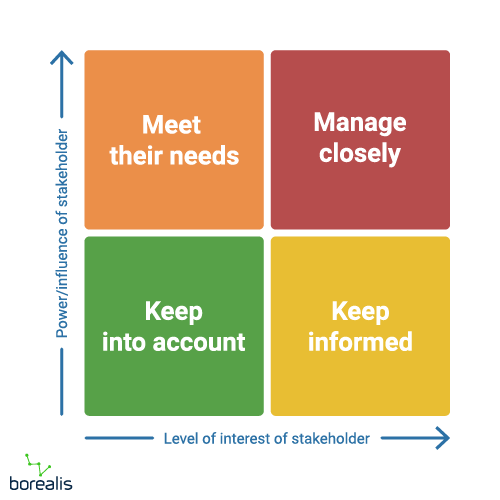
issues with stakeholder mapping
power and interests could change
not always obvious
opinion based
stakeholder engagement (managing relationship)
communication
consultation - finding out views
participation - involve them in decision making
partnership - working together
stakeholder conflict of needs
shareholders - maximization of profits and returns on investment (ROI), concerned with the long-term financial health of the business
employees - fair compensation, job security, career development, and a safe and healthy working environment
Customers - quality products/services, good customer service, fair pricing, and reliability
Suppliers - fair payment terms, long-term business relationships, and predictable demand for their products/services
Government - compliance with laws and regulations, including tax laws, environmental standards, and labor laws, want businesses to operate ethically
Local Communities- environmental responsibility, employment opportunities, and corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Managers- achievement of business goals, team development, efficient processes, and a healthy culture
divorce between ownership and control
a situation where the owners of a company do not have direct control over the company's operations and management
role of shaeholders’s
provide capital - shareholders invest money into the company, helping it fund operations, expansion
influence decisions - through voting rights, shareholders can influence key decisions
benefit from profit: shareholders receive dividends (a share of the company’s profits) and/or can benefit from an increase in the company’s share price
reason for buying shares
capital Gains- shareholders hope to sell their shares at a higher price than they bought them for, making a profit.
dividends -investors may buy shares in companies that pay regular dividends
ownership & influence - some investors buy shares to have ownership in a company and to potentially influence its management or direction, particularly in smaller companies