Unit 1 COLLEGE biology (introductory) (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/207
Last updated 9:16 PM on 6/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
1
New cards
gene expression
The process of turning on a gene to produce RNA and protein, leads to speciation
2
New cards
why gene expression is necessary
if there is no gene expression, will make every gene (protein) all the time, using lots of resources + space
3
New cards
transcription (DNA to RNA)
where most gene regulation occurs in prokaryotes
4
New cards
simultaneously
when does transcription and translation happen in prokaryotic cells
5
New cards
repressors
proteins that suppress transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus
6
New cards
activators
proteins that increase the transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus, multiple of these= enhancers
7
New cards
inducers
small molecules that either activate or repress transcription depending on the needs of the cell and the availability of substrate
8
New cards
operons
Proteins that are needed for a specific function are encoded together in blocks
9
New cards
Jacob and Monod
the first to show the organization of bacterial genes into operons through the lac operon
10
New cards
transcription factors
proteins encoded by regulatory genes
11
New cards
RNA polymerase
makes mRNA strand
12
New cards
operator
regulatory region located between the RNA polymerase binding site of the promoter and the transcriptional start site of the first structural gene
13
New cards
sequence of an operon
promoter, operator, structural genes (in that order)
14
New cards
the 3 regulators
activator, repressor, inducer
15
New cards
constitutively expressed
Gene products that are needed consistently are ________ in prokaryotes.
16
New cards
enhancers
regions that help increase or enhance the transcription of a distant gene, made up of activators
17
New cards
splicing
when original DNA or RNA sequence is split up to only leave what needs to be turned into a protein
18
New cards
exons
The regions of DNA or RNA that code for protein
19
New cards
introns
a segment that doesn’t code for a protein + interrupts sequence
20
New cards
miRNA (microRNA)
short single-stranded RNA molecules that are only 21–24 nucleotides in length. Like transcription factors and RBPs, mature miRNAs recognize a specific sequence and bind to the RNA to degrade the target mRNA. They rapidly destroy the RNA molecule.
21
New cards
poly-A tail
long chain of adenine nucleotides added to mRNA to increase stability
22
New cards
5’ cap
placed on 5’ end of mRNA to keep it from degrading when attached to poly-A tail (mRNA)
23
New cards
3’ cap
placed on 3’ end of poly-A tail to keep from degrading when attached to mRNA (POLY-A TAIL)
24
New cards
5’ end
phosphate
25
New cards
3’ end
sugar
26
New cards
RNA stability
the rate an RNA molecule decays at, it’s lifespan
27
New cards
nuclear pore complex
holes in the nucleus that mRNA can come out of
28
New cards
RNA splicing, RNA shuttling, RNA stability
the 3 versions of post-transcriptional control, if only one of these is not completed a protein can’t be synthesized
29
New cards
histones
the proteins DNA wraps around to make chromatin
30
New cards
nucleosome
DNA wrapped around a histone to control what parts of DNA can be accessed by proteins.
31
New cards
epigenetic regulation
regulation due to histones making DNA accessible or inaccessible in eukaryotes
32
New cards
sympatric speciation
when speciation happens even though they are not geographically seperated
33
New cards
allopatric speciation
speciation caused by a geographical barrier
34
New cards
promoter
where RNA polymerase and the transcription factors bind
35
New cards
DNA bending protein
brings an enhancer into contact with transcription factors so it can increase transcription
36
New cards
pea plant
Pisum Sativum, what Mendel used
37
New cards
trait
a variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic
38
New cards
law of segregation
each gamete only gets one copy of a gene
39
New cards
blending theory of inheritance
What Lamarck believed (the giraffe guy)
40
New cards
continuous variation
like polygenic traits, have a continuous number of phenotypes
41
New cards
discontinuous variation
monohybrid traits, dihybrid traits, non-polygenic traits; limited number of phenotypes
42
New cards
model system
models that represent biological circumstances to run experiments on
43
New cards
incomplete dominance
traits mix, neither is completely expressed
44
New cards
codominance
spots, both traits are present
45
New cards
autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
46
New cards
hemizygous
when you only have 1 copy of a chromosome (males are hemizygous for x chromosomes)
47
New cards
wild type
the most common geno/phenotype found in the wild, usually abbreviated with a +
48
New cards
variants
any other geno/phenotype that is not most commonly found in the wild (like albinism)
49
New cards
pleiotropic gene
a gene that affects multiple characteristics. inherited like single trait alleles
50
New cards
multifactorial characteristics
Characteristics that are influenced by environmental as well as genes
51
New cards
H.M.S Beagle
the ship Darwin traveled the world on
52
New cards
convergent evolution
what makes vestigial structures, two organisms with similar traits but evolved seperately
53
New cards
human economic pressures
One of the foundational concepts of natural selection was an essay on ________.
54
New cards
divergent evolution
2 species that evolved similar traits due to a common ancestor
55
New cards
evidence for evolution
fossil record, embryology, comparative anatomy, biogeography, molecular biology
56
New cards
microevolution
change of alleles over generations
57
New cards
macroevolution
creation of new species
58
New cards
population genetics
The field of biology that studies allele frequencies in populations and how they change over time
59
New cards
adaptive evolution
increasing the frequency of beneficial traits
60
New cards
frequency-dependent selection
there are 3 different lizards. Like a game of rock-paper-scissors, orange beats blue, blue beats yellow, and yellow beats orange in the competition for females. THE FREQUENCY OF ONE TRAIT IS DEPENDENT ON ANOTHER.
61
New cards
sexual dimorphisms
differences between males and females of a species
62
New cards
handicap principle
some sexual adaptations can put members of species at risk. (like a bright tail) this is the idea that the more risk, the more fit an individual is, since they can handle that risk
63
New cards
good genes hypothesis
the idea that males have ornamental sexual traits because it corresponds with better genes
64
New cards
honest signal
the idea that ornamental sexual traits on males mean they are actually superior and are not a “trick”
65
New cards
perfect organism
natural selection will never create a ______.
66
New cards
bottleneck effect
type of genetic drift where lots of alleles are taken out by a catastrophic event
67
New cards
founder effect
type of genetic drift where a small group separates and creates own population with their set of alleles
68
New cards
gene flow
flow of alleles in and out of a population due to migration
69
New cards
phylogeny
the evolutionary history and relationship of an organism or group of organisms
70
New cards
phylogenetic tree
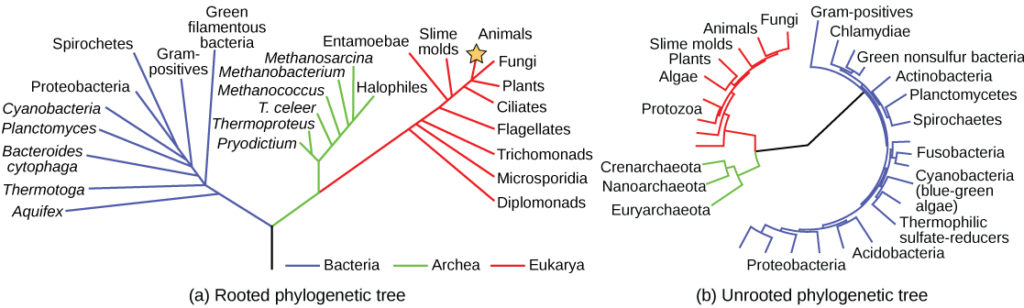
71
New cards
taxonomy
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
72
New cards
binomial nomenclature
the two-word scientific name of a species. ex: *Canis lupus*
73
New cards
taxon
the names of each level of taxonomy (domain, kingdom, etc)
74
New cards
unrooted phylogenetic tree
shows relationships but not time
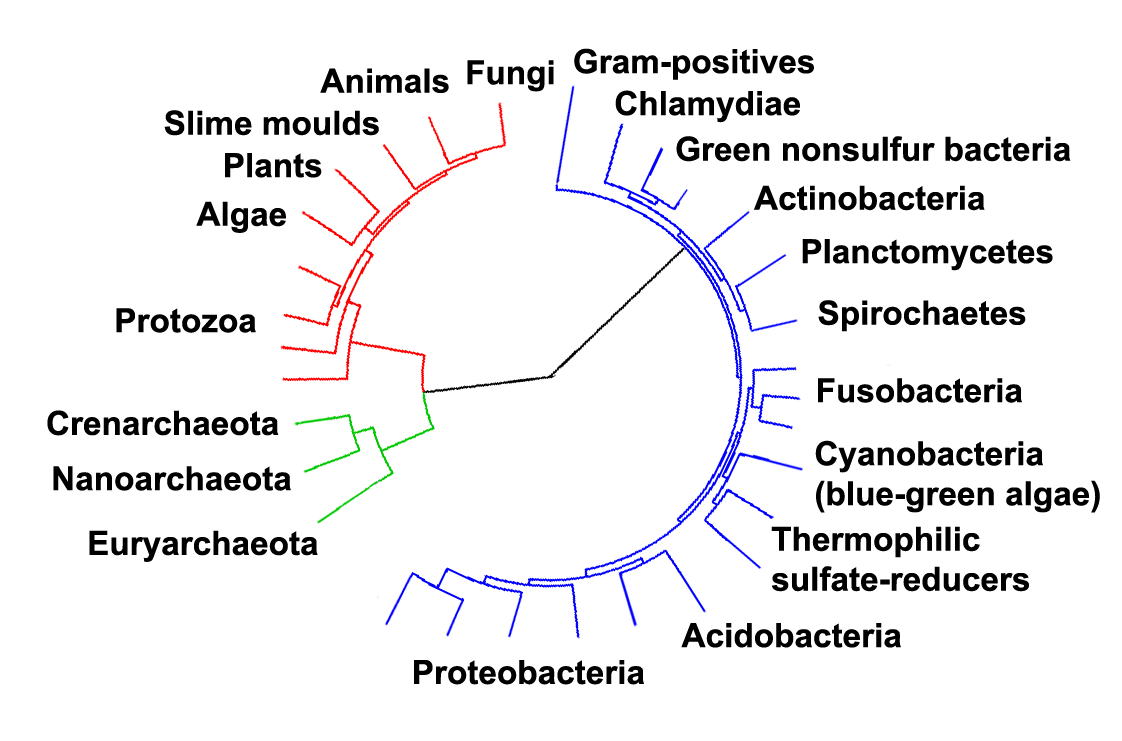
75
New cards
rooted phylogenetic tree
shows relationships and time
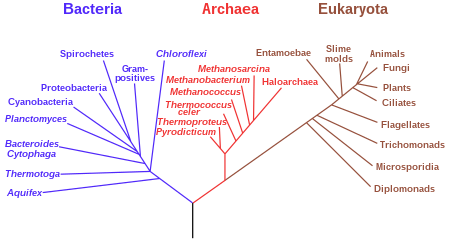
76
New cards
carriers
2 parents can never both be _____.
77
New cards
biosphere
collection of all ecosystems
78
New cards
order of the biosphere
organism, populations, communites, ecosystems, biosphere (OPCEB)
79
New cards
Order (Property of Life)
made of cells
80
New cards
Regulation (Property of Life)
the way body temp, blood pressure, energy usage, etc. is regulated
81
New cards
Homeostasis (Property of Life)
variables in body have to be at a “set point”
82
New cards
Order, Stimuli, Reproduction, Growth, Regulation, Homeostasis, Energy processing (OSRGRHE)
The properties of life
83
New cards
community
a group of organisms interacting together
84
New cards
ecosystem
a community and the abiotic (nonliving) factors that impact them
85
New cards
population
a group of organisms of the same species
86
New cards
alpha diversity
diversity within a particular area, community or ecosystem, compare total # of taxa in each area
87
New cards
beta diversity
diversity between ecosystems; compare # of taxa unique to each area
88
New cards
gamma diversity
a measurement of the overall diversity for different ecosystems within a region
89
New cards
capitalized genus + lowercase species
format of binomial nomenclature
90
New cards
animal
heterotroph (eats for energy), eukaryotic + mulitcellular, most are able to move + produce sexually
91
New cards
exctant
died off, extinct
92
New cards
body plan
a group of structural characteristics used to identify a taxon
93
New cards
parazoa
a taxonomic subkingdom within the kingdom Animalia; the sponges
94
New cards
Eumetazoa
a taxonomic subkingdom, within kingdom Animalia; all animals except the sponges
95
New cards
epithelial tissue
one of the four basic types of animal tissue, which line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands
96
New cards
metamorphasis
a change in the form and often habits of an animal after the embryonic stage during normal development
97
New cards
hox gene
genes responsible for determining the general body plan, such as the number of body segments of an animal
98
New cards
blastula
a 6-32-celled hollow structure that is formed after a zygote undergoes cell division
99
New cards
radial symmetry (body plan)
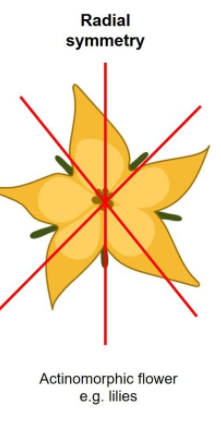
100
New cards
bilateral symmetry (body plan)