3 - Blood Pressure
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What should prompt you to make blood pressure a staple in your entrance testing?
HTN
Renal conditions
CVD
Obesity
Physical inactivity
Heavy alcohol intake
Smoking
Family history of: HTN or CVD
According to The American Heart Association (AHA), how prevalent is high blood pressure (HBP) among American adults?
Nearly 50% American adults have ↑BP (many don’t know they have it)
Define systolic BP. What does it correlate to?
→ blood is pumped out of the heart and into the arteries to enter the peripheral circulation
max BP
correlates to heart’s pumping efficiency + elasticity of arterial walls
Define diastolic BP. What does it correlate to?
→ occurs when the ventricles are relaxed & filling with blood
correlates to PVR
What is the primary way HBP causes harm to the arteries and heart?
↑ workload of heart and blood vessels & forcing them to work less efficiently
How does HBP lead to the start of atherosclerosis?
Force and friction of ↑BP damages the delicate tissues inside the arteries
LDL (bad) cholesterol forms plaque along tiny tears in the artery walls
How does plaque buildup exacerbate hypertension?
↑ plaque + damage → narrow artery diameter → ↑ BP
this can further lead to arrhythmia or heart attack
What is Primary Hypertension caused by? How prevalent is it?
Cause: none
can be familial (involving environmental & genetic factors)
-make up 90–95% of HTN cases
↑ prevalance w/ age
What is Secondary Hypertension caused by? How prevalent is it?
Cause: conditions affecting the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system OR may occur during pregnancy
occurs as a result of a pre-existing condition
makes up 5–10% of HTN cases
What are the typical symptoms of hypertension?
Asymptomatic
Note: Symptoms occur when it’s too late (Stage 4 HTN)
What are the symptoms associated with Acute ER cases of hypertension (>180/120mmHg)?
Headaches (suboccipital pulsating headaches during early AM)
Confusion
Visual disturbance
Nausea
Vomiting
List non-pathological sources of elevated BP.
Anger
Stress/Anxiety
Weight gain
BP increases during exercise
BP increases after meals/caffeine
White coat reaction
List the systemic conditions (ROS) reported by a patient in their case history, which indicate the need to take their blood pressure.
HTN
Hyperlipidemia
CAD
Carotid artery disease
Congestive heart failure
Renal failure
DM
MI
Stroke
What information must be recorded when measuring BP?
Systolic and Diastolic measurement in mmHg
Right or Left arm
Patient’s position
Time
Cuff Size
Draw the table showing the BP categories, with their corresponding Systolic and Diastolic BP.

List the most common errors when measuring BP.
Using the wrong size cuff
Using an incorrect arm position
Wrong diaphragm placement
Not setting stethoscope to the ‘on’ position
Releasing air too quickly/slowly
When do you do the Carotid Artery assessment?
When patient reports transient vision loss (“amaurosis fugax”)
Define Amaurosis fugax.
→ sudden vision loss in one eye that feels like a “curtain coming down over the vision”
lasts more than 1 min
painless
Amaurosis fugax, combined with which systemic factors (ROS), indicates a higher risk of Carotid Artery Disease?
HTN
Hyperlipidemia
DM
CAD
Stroke
Smoking
What does the assessment of the carotid arteries include?
Listening for a systolic bruit
What is a bruit?
→ “whoosh" sound
sound of turbulence in blood flow when the normal laminar flow is disrupted by the narrowing (stenosis) of the artery
If a bruit is audible, what % of patients have been shown to have significant stenosis on angiography?
77%
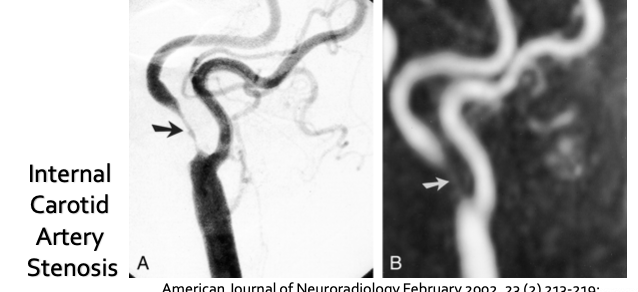
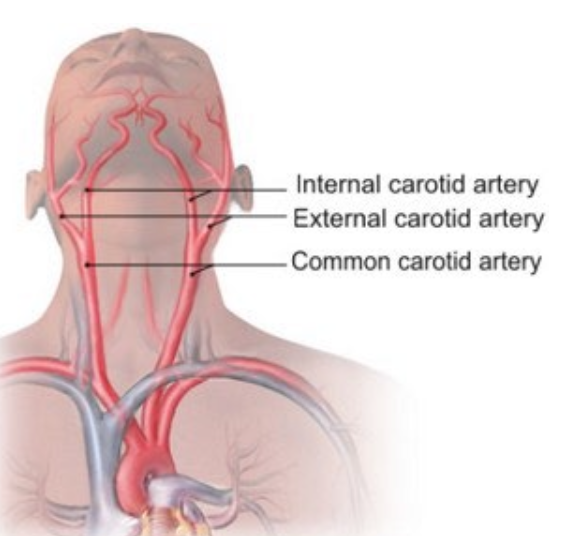
What is the order where the stethescope is placed intially and then repositioned?
Common carotid artery (approximately 2.5 cm above the clavicle bone)
Bifurcation of the common carotid
Internal carotid artery
What are the Most Common Errors in Carotid Artery Assessment?
Not being an experienced practitioner
Using too much pressure holding the bell → this can cause a bruit to be heard when there’s isn’t actually one present
Why is palpating the carotid arteries generally discouraged for non-experienced practitioners?
can dislodge a plaque → stroke