APES Chapter 4
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
What landforms form at divergent plate boundaries?
Volcanoes, ridges, seafloor spreading, rift valley, possible earthquakes
What landforms form at convergent plate boundaries?
Volcanoes, mountains, earthquakes, island arcs, trenches
What landforms form at transform plate boundaries?
Earthquakes, tsunamis
What does the lithosphere consist of?
Crust and upper solid mantle
What is important about the asthenosphere?
It allows techtonic plate movement
How does subduction cause volcanoes?
One plate slides under the other and melts, which brings magma up to the surface
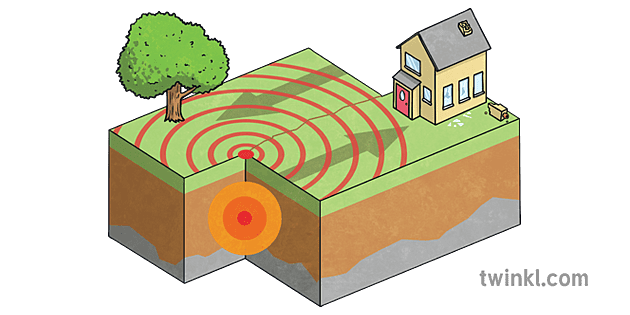
Label the focus and epicenter
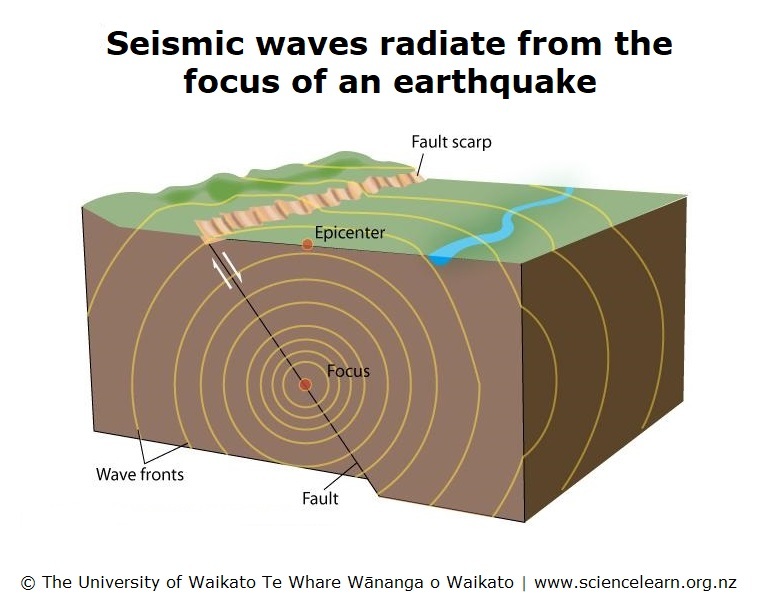
How does a trasform boundary cause earthquakes?
The plates lock up as they are sliding past each other, building up stress and energy. The plates suddenly slide past each other, releasing the large amount of energy.
Is oceanic or continental plate more dense?
Oceanic
How do earthquakes cause tsunamis?
When an earthquake is underwater and close to shore, its energy can cause the ocean floor to suddenly move up or down, which displaces water, creating a tsunami
Subduction
When one plate slides beneath the other
Another term for transform boundary
Strike-Slip
Negative impacts of tsunamis
Loss of habitat, flooding brings in saltwater, species can drown
O soil layer
Organic; Layer of organic matter
A soil layer
Surface/topsoil; Layer of humus and minerals
E soil layer
Layer of clay, sand, and silt
B soil layer
Subsoil; layer of minerals, clay, and less organic matter than above
C soil layer
Substra; Layer of weathered rock, most closely resembles parent material
R soil layer
Bedrock
Which biomes don’t typically have O soil layer?
Deserts
Which biomes typically have E soil layer?
Forests
Soil layers from top to bottom
OAEBCR
How is soil formed from the bottom?
Weathering of parent material produces small fragments that make up the inorganic part of soil
How is soil formed from the top?
Breakdown of organic matter adds humus to soil; Erosion deposits soil particles from other areas
Weathering and the types
The breaking down of rock into small pieces that form soil; Physical (wind and rain), biological (tree roots crack rocks), chemical (acid).
Erosion
The transportation of weathered rock by wind or rain
Deposition
When soil is deposited at new location
How does climate impact soil formation? (2 types)
Warmer weather makes organic matter break down faster. More rain leads to more weathering, erosion, and deposition.
What is topography and how does it impact soil?
The shape and length of a slope; Impacts the drainage and erosion
What causes topsoil loss and what is the effect?
Turning of soil for agriculture (tilling); dries out soil, removes nutrients, leading to more erosion
What causes soil compaction and what is the effect?
Machines, grazing livestock, humans; reduces soil’s ability to hold moisture, dries soil, leading to more erosion
What causes soil nutrient depletion and what is the effect?
Repeatedly growing crops with the same soil; removes nutrients, reduces the ability to grow crops in the future
Soil parent material
Rock
How does deforestation impact soil?
Lack of roots holding down soil, which leads to more erosion
How does overgrazing impact soil?
Livestock overeats, destroying O horizon and killing roots. Compacts soil. Both lead to increased erosion.
Ways to decrease soil erosion
No till farming, which doesn’t disturb the soil as much and keeps it in tact. Contour farming, where farming is gently sloped to slow water runoff
Oceanic-Oceanic convergent boundary
One plate slides beneath, forcing magma up. Forms volcanoes, island arcs, off-shore trenches
Continental-Continental convergent boundary
Plates push up and create mountains
Continental-Oceanic convergent boundary
Oceanic is more dense so it sinks under, melts into magma. Forces magma up, creating mountains, volcanoes, trenches, tsunamis
Porosity
The amount of pore space a soil has; directly related to permeability
Permeability
how easily water drains in soil; directly related to porosity
Conditions for high water holding capacity
Low porosity/permeability (inversely related)
Factors that increase soil nutrients
Organic matter, humus, decomposers, clay, bases
Factors that decrease soil nutrients
Acid, excessive rain, excessive farming, topsoil erosion
Factors that increase water holding capacity
Aerated soil, humus/organic matter, clay, root structure
Factors that decrease water holding capacity
Compacted soil, topsoil erosion, sand, root loss
Ideal soil for plants and whatnot
Loam: it balances porosity and H20 holding capacity
Chemical soil tests
Nitrogen (nitrates), phosphorus (phosphates), pH (acidity)
Physical soil tests
Soil composition, water holding capacity
Biological soil tests
Earthworms, bacteria
Infiltration
Movement of ions or chemicals through percolation
Percolation
Movement of water into the ground
Humus
Broken down leaves, dead animals, waste
Increases bc warmth of UV rays and ozone
How does temp change as you go up in thermosphere and why
Increases, it is absorbing so much solar radiation
Temperature gradient image
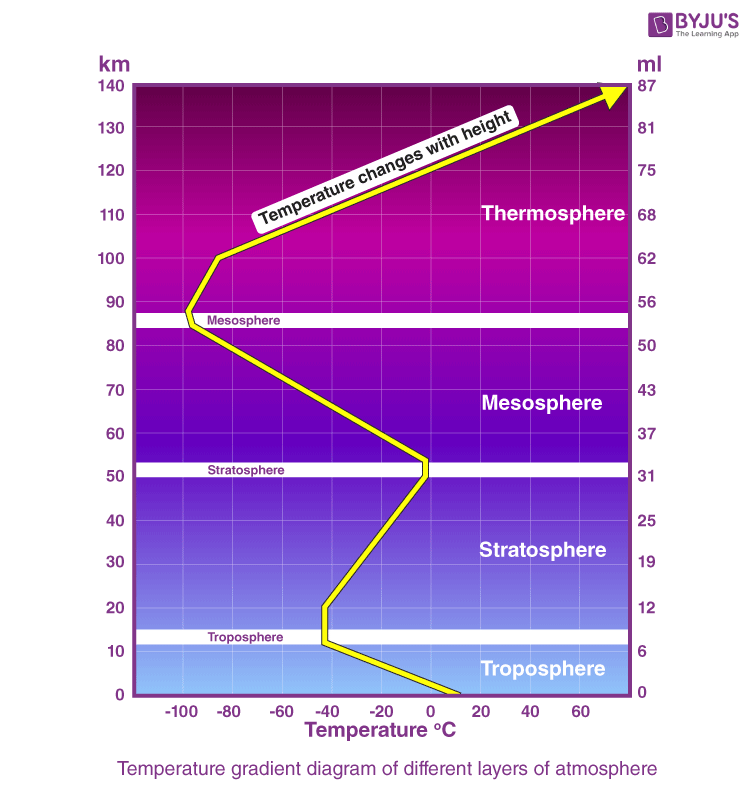
Diagram of wind patterns

filtration
When soil filters water
infiltration
When water goes into the ground
groundwater recharge
When water seeps into the ground and replenishes underwater aquifers
How does latitude determine climate
High latitude-less insolation=cooler, less precipitation
Equator-more intense insolation=higher temp, high precipitation