Cariology Lecture 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Where, specifically, do caries typically form?
Plaque stagnation areas; covered, overlapping areas
Where do caries typically form in younger people?
Pits and fissures
Where do caries typically form in older patients?
At interproximal surfaces and at the gingival margin
What is the first clinically visible sign of caries-affected enamel?
White spot lesion
The enamel is dissolving, more pores of the tooth are exposed
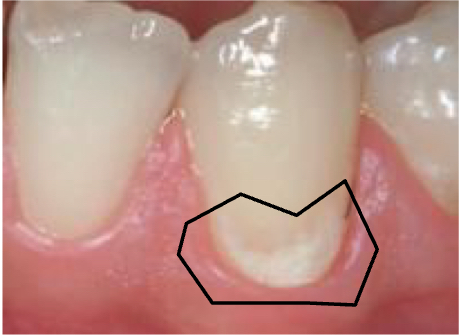
Classical caries zones
Surface zone
Body of the lesion
Dark zone
Translucent zone
When does dentin react to caries?
Before the demineralization process reaches the DEJ (dentin-enamel junction)
What is the first sign of dentin reaction to caries?
Tubular sclerosis
No bacteria can be found in the dentin as long as the enamel surface is macroscopically intact
What zones appear when caries reach the DEJ
Zone of demineralization
Dead tracts
Sclerotic zone
Normal, but affected dentin
Tertiary dentin
How do caries appear on x-rays?
Less dense, more transparent areas
How does the tooth add minerals to itself?
From the inside out
What happens when the dentin is exposed?
Tooth experiences sensitivities
What happens when the zone of penetration reached the pulp?
Irreversible pulpal inflammation
This happens when enzymes continue to destroy the dentin after the enamel surface has been broken down and plaque is persistently demineralizing
What parts of the tooth are more vulnerable to demineralization than the enamel?
Cementum and dentin
Why are older patients more susceptible to exposed root caries?
Gingival recession exposes more root surface
Lower salivary flow
Reduced oral hygiene capabilities
All hasten the caries process
What is erosion caused by?
NOT bacteria, but the direct dissolution of enamel and dentin die to acids
What are some factors that affect erosion?
Diet: acidic food and drinks
Stomach acids: acid reflux, vomitng
Environment: poor swimming pool maintenance, frequent exposure to acid vapors in industry
Medications: chewable vitamin C tablets
Brutish: Grinding while sleeping
Indirect factors affecting dental caries
Education
Socioeconomic status
Income
Genetics
Age
Dentist
Direct factors affecting dental caries
Host defense/immunity
Oral hygiene
Saliva
Fluoride/ca2+
What type of diet promotes the development of caries?
One rich in readily fermentable carbohydrates
How many tsp of sugar do Americans consume daily?
22.7
How many lbs of high fructose corn syrup do Americans consume yearly?
51
2 most carcinogenic dietary sugars
Sucrose
Glucose
2 least carcinogenic sugars
Sorbitol
Mannitol
What sugar is still carcinogenic, just not as much as sucrose and glucose?
Starch
What dietary sugar has been shown to be proactive against tooth decay?
Xylitol
How many grams of sugar is 1 tsp?
4
How many grams of sugar in a packet?
2.6
Is all water neutral?
No, some popular brands add acid for a fresher flavor
Some also make them more alkaline
Are all mouthwashes above the critical pH?
No
What drinks should you be drinking?
Fluoridated tap water
Alkaline water
Fruit and herb infused water, which contains much less sugar than fruit juices, is low calorie, and inexpensive
What should you avoid in your diet?
Retentive carbohydrates
What does xylitol gum do?
Increases salivary benefits after eating
What other food components may play a protective role?
Proteins
Fats
Preservatives