lab evaluation of hemostasis
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
what are the reserve organs of platelets?
spleen
lung
liver
bone
where are platelets formed?
bone marrow
if you are looking at a PLT graph it resembles a "ski slope" what does this indicate?
healthy animal
what does it indicate if the PLT slope is flattened/ lumpy?
platelets are clumped
what does it indicate if the PLT has an upward increase?
large platelets are present
what is the clinical approach if you are given a result of thrombocytopenia?
Is the thrombocytopenia true?
Is it psuedo due to clumping?
Check the tube for clots, can rotate in hand for macroscopic view or look at the blood smear for clumps for microscopic view
If no clumps or clots present than patient has true decrease in platelet concentration
You have accurate thrombocytopenia
what do you advise if platelet clumps are in the body of the smear and feathered edge?
Understand that analyzer for platelet concentrations is a minimum (lowest amount of platelets it could count)
Understand that platelet estimation number is not always possible due to clumping
Consider redrawing the sample if you need a number estimate (maybe first sample was a bad draw or had errors)
what is the healthy platelet count for a dog/cat?
8-10/hpf
about 1 platelet/30 RBCs
how do you calculate platelet concentration?
(# of platelets) * 15000
what is the formula for estimate of [platelet]?
number of platelets / hpf field
how many fields should be counted to calculate a platelet average? then what do you do?
count 10 fields, calculate an average
multiply by 15000/uL
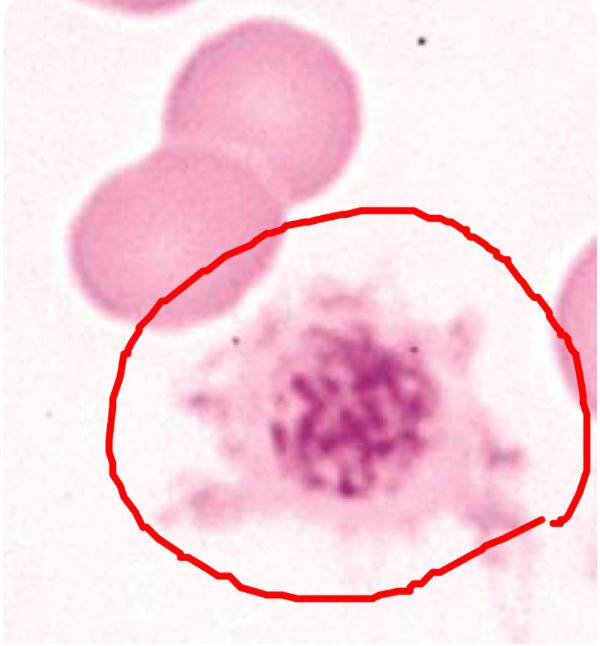
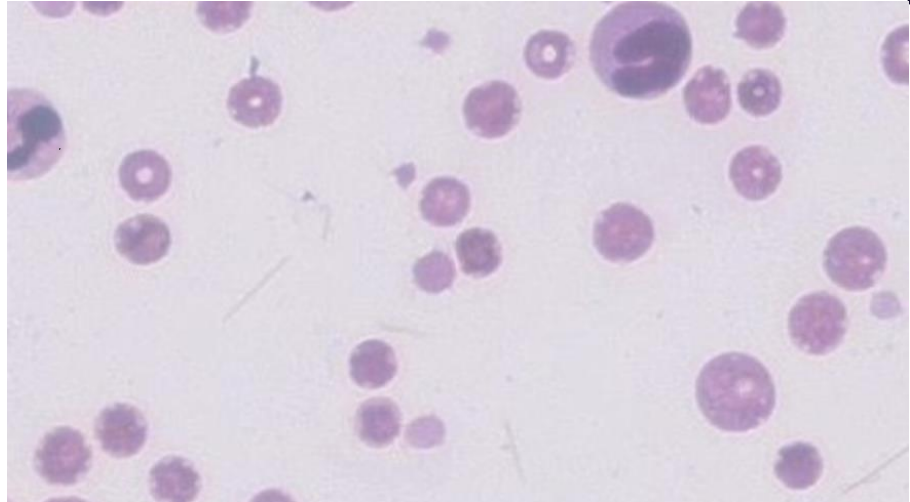
what does the circled image indicate?
activated platelet
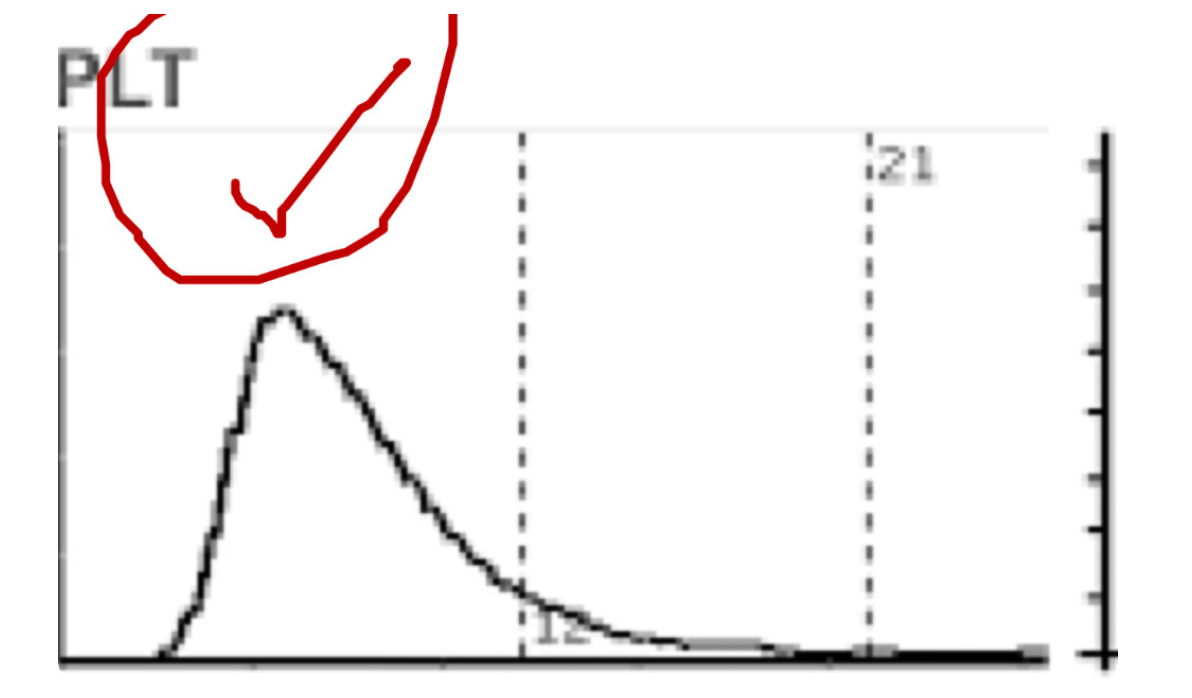
what does this platelet curve indicate?
animal is in health
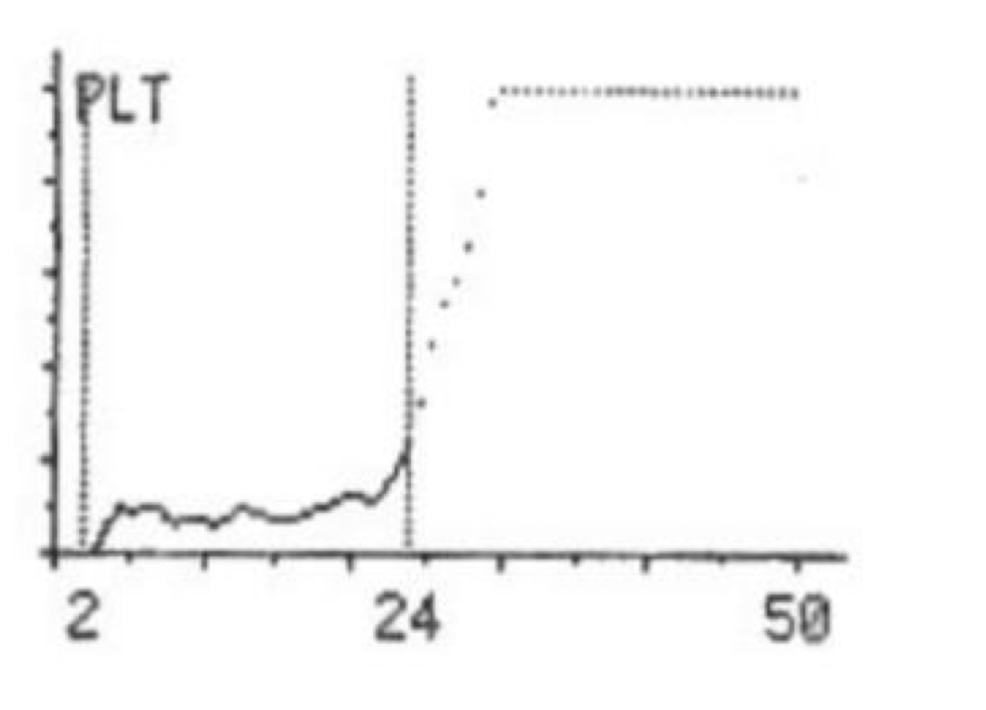
what does this platelet curve indicate?
platelet clumping
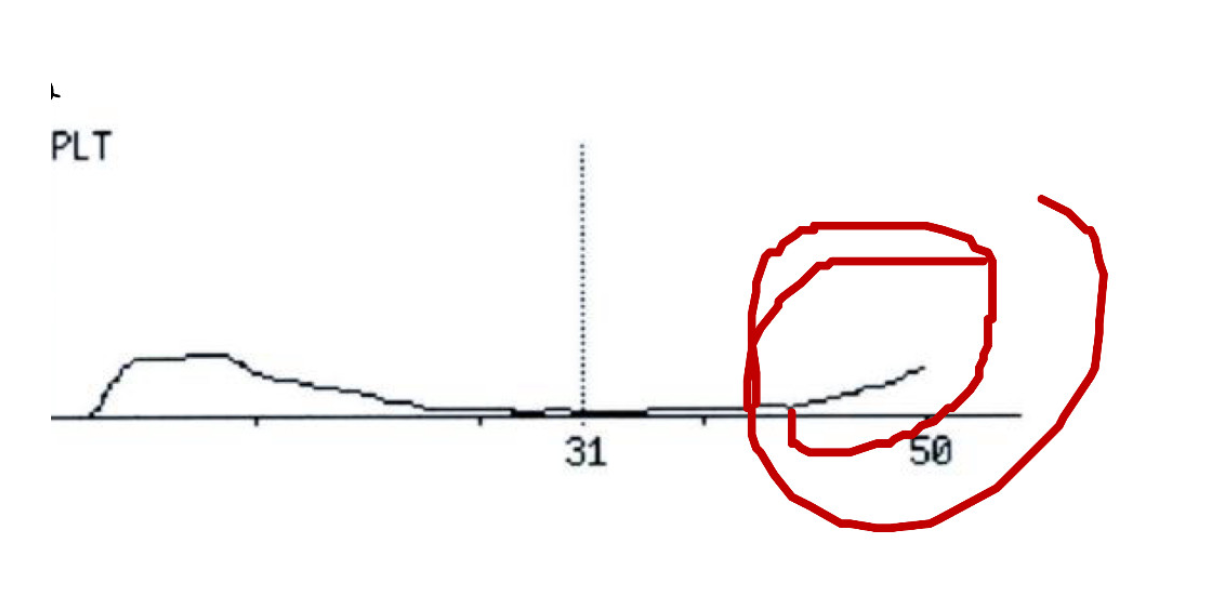
what does this platelet curve indicate?
large platelets have formed
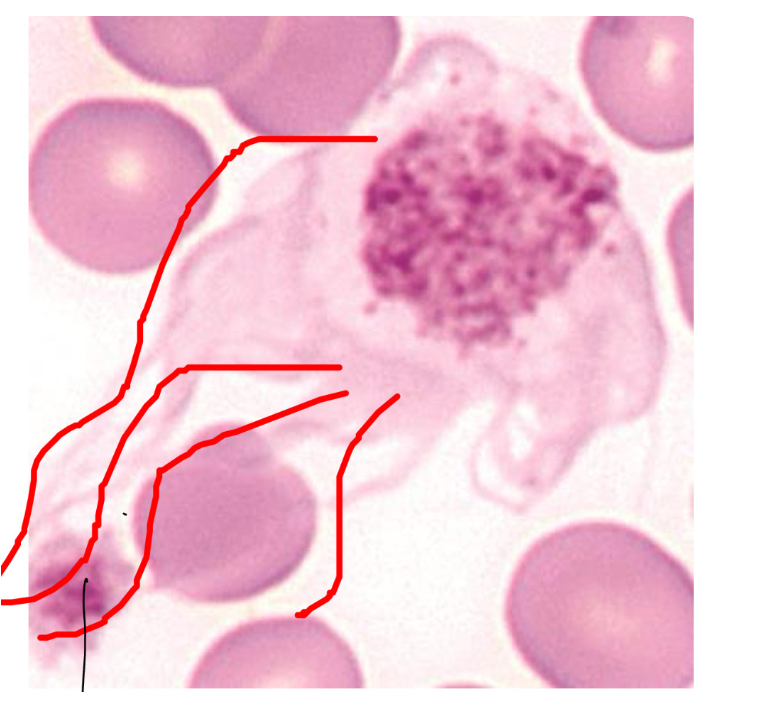
what is outlined in the image and what is the function?
cytoplasmic projections of the activated platelet
function: helps activate other platelets
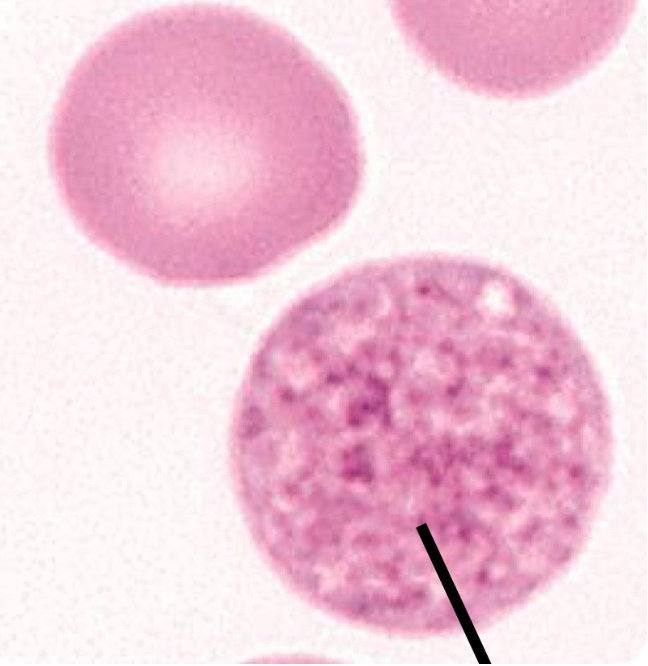
what is depicted in the image? what is its function?
granules secreted and activated
function: to form platelet plug
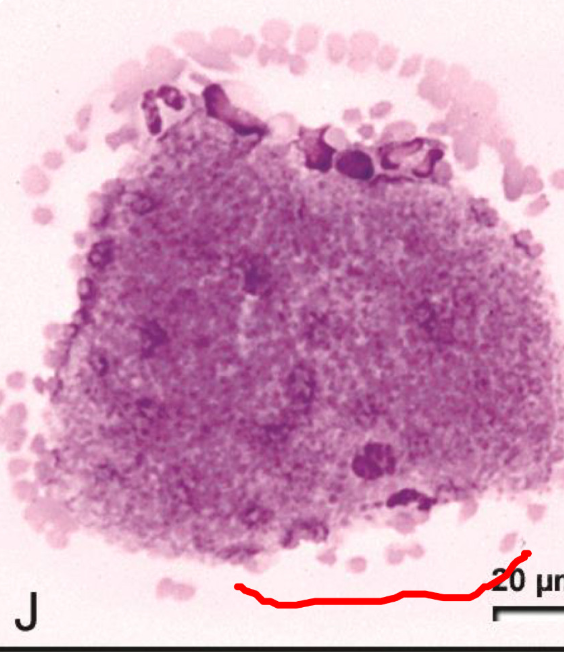
what is occurring in the image?
large thrombocytopenia
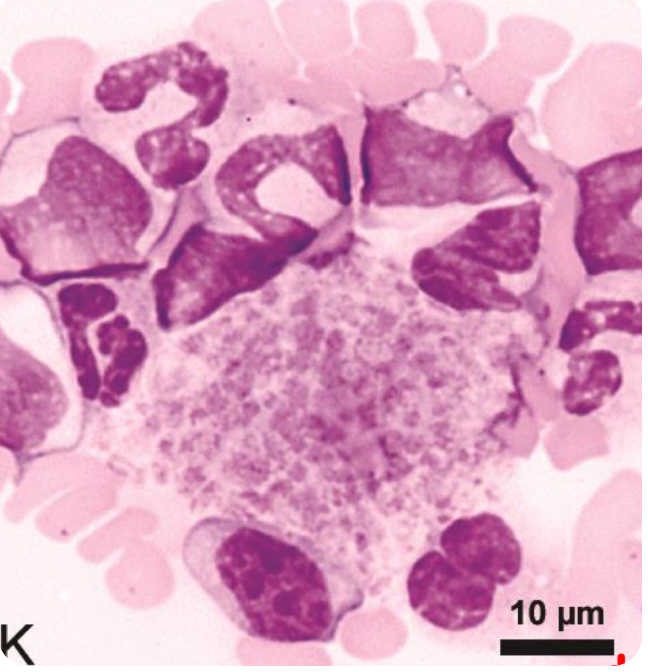
what is occurring in the image?
medium thrombocytopenia
what tests can we conduct to examine primary hemostasis?
BMBT
Plt count
vWF assays
Plt function
what would be occurring in the animal to consider using a test to examine primary hemostasis?
thrombocytopenia
vWF deficiency
abnormal plt function (receptor deficiencies)
what are the causes for psuedothrombocytopenia?
large platelets
platelet clumping
what species are known to have platelets clump?
cat
cow
what are other reasons besides breed specificity why platelets may clump?
delayed transfer of blood from syringe to tube
inadequate mixing
old samples > 5 hours
what specific dog breeds have inherited macrothrombocytopenia?
norfolk terrier
king charles spaniel
what specific species have large platlets?
cats
What answer best matches the image?
thrombocytopenia
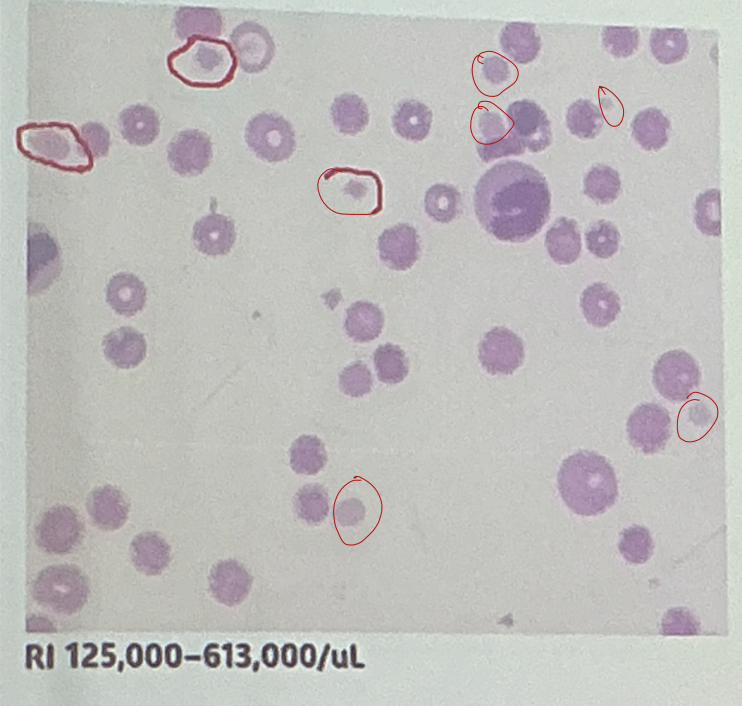
What answer best matches the image?
WRI
what are the causes of thrombocytopenia?
decreased platelet survival
idiopathic or multifactorial
decreased production of platelets
Sequestration (abnormal distribution)
what leads to decreased production of platelets?
bone marrow disease
what specific infections will lead to bone marrow disease?
BVD
canine distemper
parvovirus
what things (general) can lead to bone marrow disease?
drugs
infections
toxins
estrogen, bracken fern poisoning
what are the signs of thrombopoiesis?
LARGE platelets (reactive and immature)
what is the clinical approach if you suspect thrombocytopenia due to marrow disease?
blood smear to see if you can see large platelets
definitive diagnosis via bone marrow aspirate
what pathogenesis is associated with increased destruction of platelets?
Ab-mediated
idiopathic
what pathogenesis is associated with increased activation or consumption of platelets?
vasculitis
DIC
endotoxins
what pathogenesis is associated with sequestration?
endotoxins
what pathogenesis is associated with with multifactorial?
infectious
neoplasia
what is the location and immune cell that corresponds with increased destruction of platelets?
The spleen is the primary location, and macrophages are the immune cells involved in the increased destruction of platelets
what is the pathogenesis of immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT)?
formation of anti-platelet antibodies
macrophages engulf these organisms leading to decreased [plt]
what shape will the platelets take after IMT?
spherocytes due to macrophages taking portions of membrane of platelet
what can be seen with IMHA?
IMT
what is the pathogenesis of consumptive thrombocytopenia? I did this card as more of a process
Damage to endothelium
Platelet activation and aggregation
overconsumption and removal of blood
A dog’s CBC results included a mild leukocytosis, mild
anemia with schizocytosis, keratocytosis, and
thrombocytopenia (100,000/μL; RI 150,000–450,000).
What is the most likely cause of the thrombocytopenia?
Intravascular consumption of platelets
what is the pathogenesis of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
immune-mediated destruction or sequestration
what is the agent for of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
Anaplasma platys
what is the vector for infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
ticks
what is the cyclic aspect of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
peak parasitemia followed by thrombocytopenia
what is important to know about the blood analysis of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
will not always appear on blood smear
what are specific disease names for of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia?
Rickettsial disease
anaplasmosis
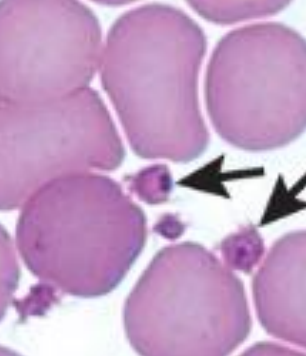
what is this picture showing?
anaplasma platys inclusion bodies
what are the rules of thumb for hemorrhage and thrombocytopenia?
MARKED thrombocytopenia causes hemorrhage
hemorrhage does NOT typically mean thrombocytopenia
what must the platelet count be for hemorrhage?
below 20,000
does blood loss cause thrombocytopenia?
usually not, only marked blood loss
how is the severity of hemorrhage reduced in regards to platelets?
shifting platelets from spleen, lung, and possibly liver
thrombocytosis
platelet concentration above reference limit
what is the cause of thrombocytosis?
increased production (clonal or non-clonal)
redistribution (lungs and spleen)
primary thrombocytosis is…
clonal
rare hemic neoplasia
what is the concentration of platelets in primary thrombocytosis?
greater than 2x the URL
extreme thrombocytosis
above 1 million
secondary thrombocytosis
non-clonal
as a reaction to other conditions (reactive thrombocytosis)
what is the concentration of platelets for secondary thrombocytosis?
less than or equal to 2x URL
what are the causes for increased production of platelets (reactive thrombocytosis)?
inflammation
iron deficiency
recovery from thrombocytopenia
what are the causes for redistribution in thrombocytosis?
exercise
epinephrine
severe thrombocytopenia can cause…
spontaneous hemorrhage
what must accompany blood loss for it to cause significant thrombocytopenia?
sever thrombocytopenia
accompanied by anemia
who is the key player in primary hemostasis?
platelets
who is the key player in secondary hemostasis?
coagulation factors
who is the key player in tertiary hemostasis?
plasmin
t-PA
what is the receptor for vWf?
GP1b
what is the receptor for fibrinogen?
GP2b/3a
vWf is involved in…
platelet adhesion
fibrinogen is involved in…
platelet aggregation
platelet granules contain…
ADP
TXA2
bernard soulier syndrome
when there is a deficiency of the Gp1b receptor
von Willebrand disease
deficiency of vWf receptor
adhesion cannot occur despite platelets having receptors
what breed is associated with von Willebrand disease?
doberman pinscher
glanzmann thrombasthenia
deficiency of Gp2b/3a receptor
what breeds of dog are associated with Glanzmann thrombasthenia?
Otterhounds
Great pyranees
what animal besides dog is associated with Glanzmann thrombasthenia?
horses
what coagulation factors are associated with the INTRINSIC pathway?
Factors VIII, IX, XI, and XII
what coagulation factors are associated with the EXTRINSIC pathway?
Factor VII
what coagulation factors are associated with the COMMON pathway?
Factors X,V, and II
what coagulation factors are vitamin K dependent?
Factors II, VII, IX, and X
what anticoagulant is in a blue top tube?
citrate
why is citrate used for PT and PTT?
reversibly binds calcium, preventing clotting without damaging clotting factors
what variables do you need for primary hemostasis to occur?
adequate number of platelets
normal plt function
vWF
what would the differential list be for primary hemostasis?
thrombocytopenia
vWf deficiency
abnormal plt functions
what is an analogy that you can use to remember the coagulation factors of intrinsic pathway?
why pay $12 when you can pay $11.98 at walmart
what are clinical signs for primary hemostasis?
petichiae
mucosal bleeding
bloody urine
epistaxis
what are clinical signs for secondary hemostasis?
hematomas
frank bleeding
hemothorax
hemoabdomen
what are clinical signs of non-specific hemostasis?
ecchymoses
bleeding after blood draw
bleeding following surgery or venipuncture
what tests should you run to confirm that the thrombocytopenia is true?
blood smear
roll tube
PTT is used for
intrinsic and common pathway
PT and OSPT is used for
extrinsic and common pathway
ACT is used for
intrinsic and common pathway
ACT is a good…
screening test
what is the only factor not evaluated in an ACT test?
factor VII
APTT is used to…
confirm since it is a more sensitive test