Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Carboxylic Acid
R-COOH
Aliphatic Acids: Alkyl group (c chain) bonded to the COOH
seen with fatty acids
Aromatic Acids: have aryl group (ex benzenen) attached to the cooh
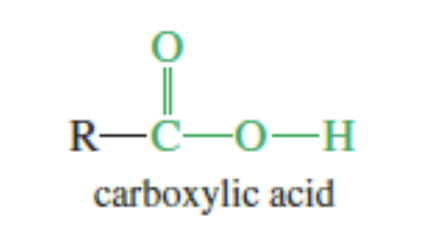
Aliphatc Acids
Carboxylic acid group that has a long chain carbon (alkyl group) attached to the COOH
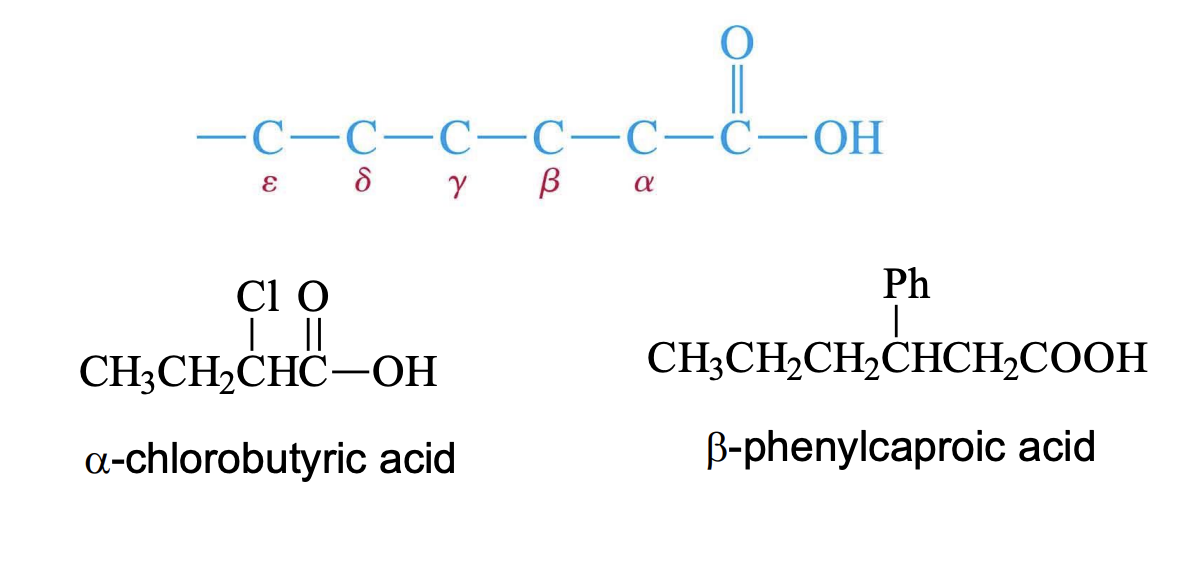
Carboxylic acid IUPAC
Alkane or Alkene —> Alkoic aicd
the cooh’s carbon becomes the 1st numbered C

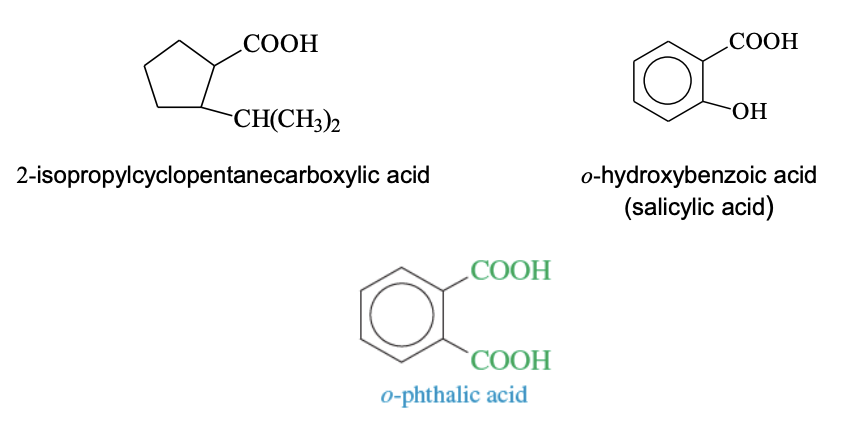
Cylclic Acids
Aryl ring attached to a COOH group
Cycloalkanes + COOH —> cycloalkanecarboxylic acids
Aromatic Acids + COOH —> benzoic acid
Benxoid compounds + 2 COOH —> phthalic acid
Dicarboxylic Acids
Aliphatic acids (acids with long carbon chain) + 2 COOh groups on its ends = Dicarboxylic Acid
IUPAC numbering started from the coxy group closests to the long carbon chains substituent
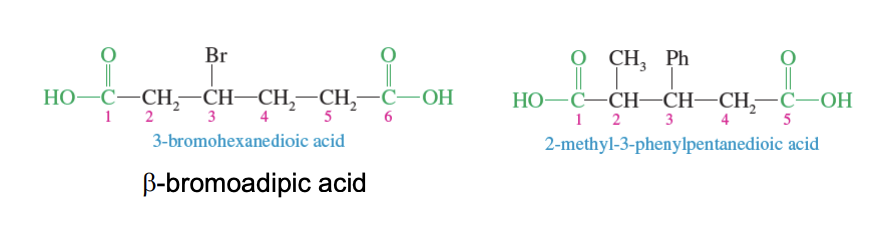
Carboxyl Structure + Resonance forms
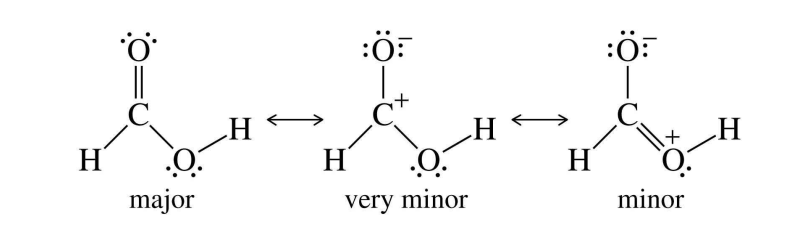
bond angles are 120 with SP2 carbon hybridized (SP2 = carbon bonded to 3 groups)
Carboxy Boiling Pt
Higher than OH (h-bonds similar)
able to do dimer formation —> high bp
Carboxyl Groups BP order
Phthalic (dicarboxy) > Aromatic COOh > Long chain aliphatic COOh > short chain COOH
Carboxylic Acids Melting Points
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
Shorter carbon chain —> Low melting Point
Longer carbon cahin —> melting point increases
Longer carbon alkyl chains —> pack togeter strong IMFs —> higher melting poimt —> SOLDIFIES AFTER C8
Longer c chain = stronger packing = strong imfs = high MP (solid at c8)
Carboxylic Acids Melting Point Regarding = bonds
More cis double bonds = more bending = less tightly packed = lower melting point
lower melting pt = lower temp needed for the carboxylic acid to turn from solid to liquid
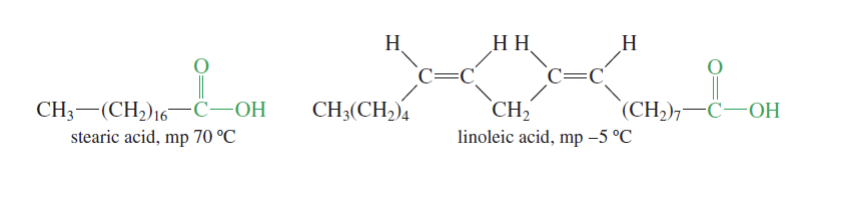
Carboxylic Acids Solubility
Longer carbon chaines subsistuted COOH = Lower water solubility
longer chains = less soluble in water (BUT MORE SOLUBLE IN OH)
shorter chains = more soluble in water = less soluble in OH
All carboxylic acids able to dissolve (are soluble) in nonpolar solvents —> dissolves as a dimer
nonpolar solvents = ex chlorofom
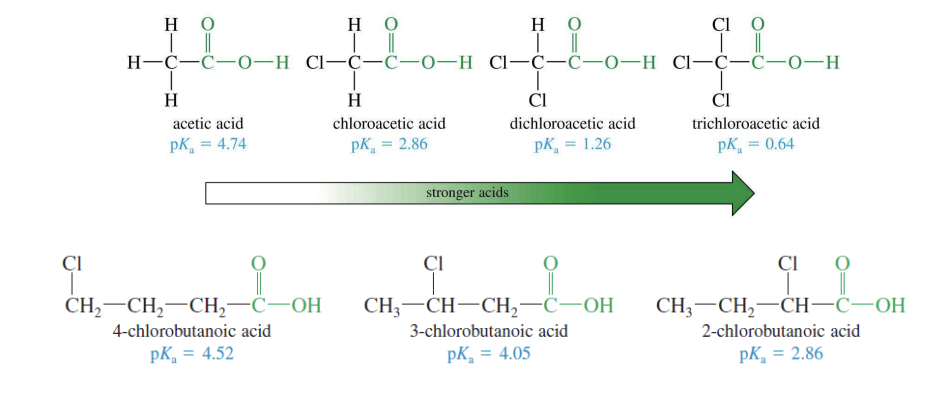
Carboxylic Acid Acidity
The longer the carbon R chain is = less acid
LC c chain = less acidic, shrot c chain = more acidic
Less acidic = high pka value, low ka
more acidic = low pka, high ka
RCOOH + h2o = RCOO- + h30+

RCOOH is more acidic than OH
this is due to RCOOH allowing for resonance stablaizaiton with the c’s neg charge being shared with the O’s
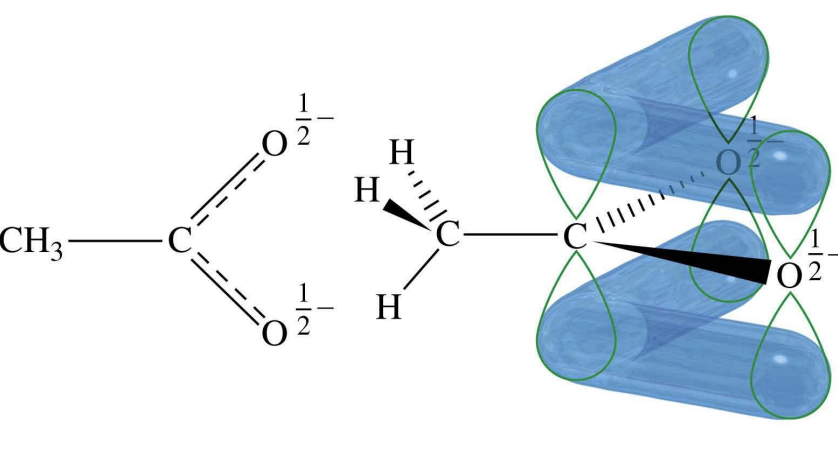
Carboxylic acid substituent effect on acidity
The closer the COOH is to the substituent of the carbon chain = acidity increases
substituent groups pull the RCOOH’s electrons away = making it more acidic (with stronger effect seen when in closer proximity)
Acid Salts IUPAC
start by naming the cation
the acid name = acetate
id —> ate
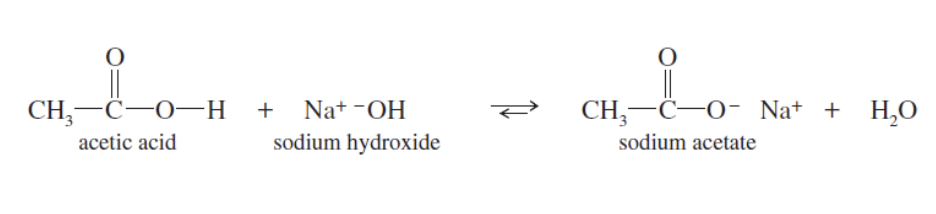
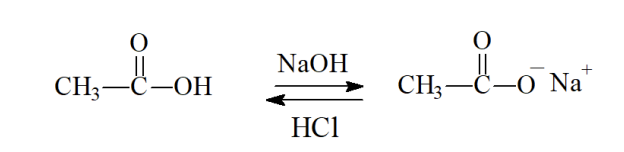
Carboxylic Acid Salts
Carboxylic —> NaOh —> Converts to Slat
Salt —> HCl —> REconverts back to carboxylic acid
Properties of the Acid Salts
The salts are solids (high MP) with no order
soluble in water slats contain Na, K, Li and NH4
Insoluble in waters contain metal ions: Ca
Acid salts are solids with high mp (& no order)
salts w/ Na, K, Li, and NH4 are soluble in water
Metalic ion salts are insoluble in water (ie. Ca)
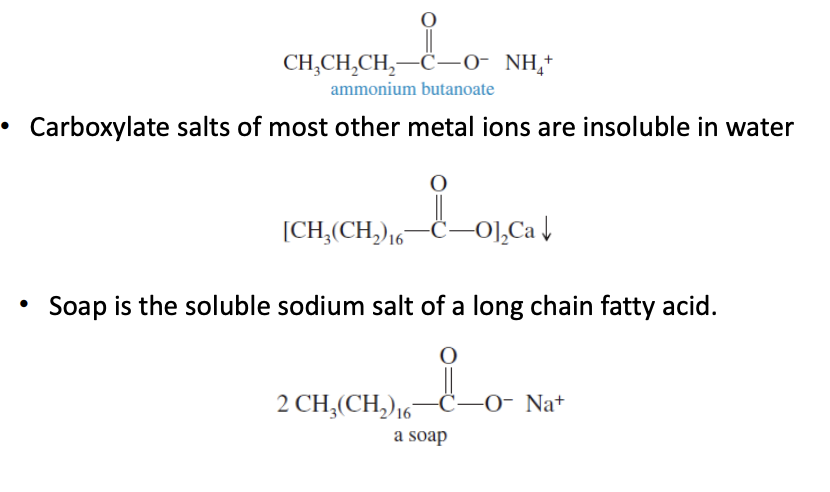
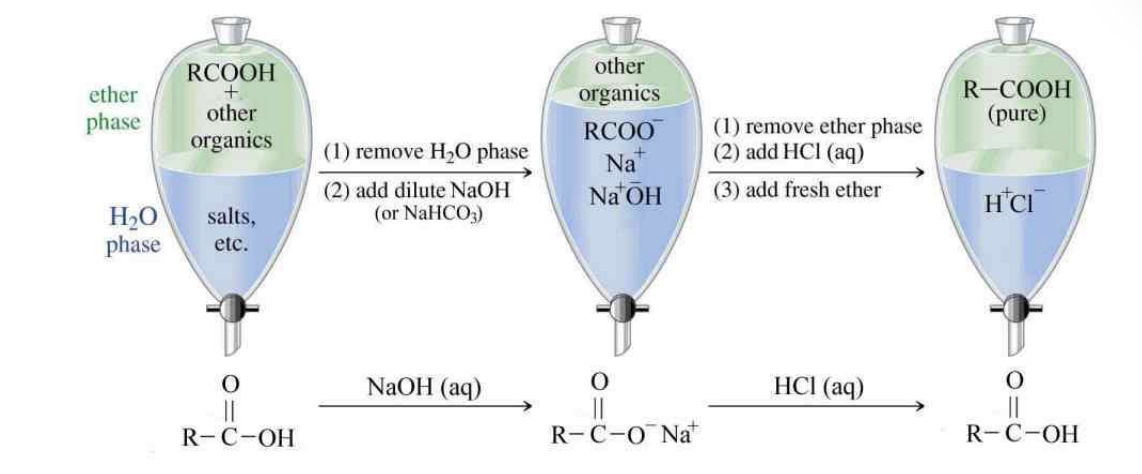
Acid Purification
Same thing as creating acid salt and converting back to carbozyilic acid
RCOH —> NaOH —> RCOO- —> HCL —> RCOOH
Some important acds
Acetic acid : Ch3COOH
Fatty acids: just long carcbon chained COOHs
Benzoic Ring: Benzne + Oh (formed from toule + KMnO4/H2O/Heat)
Adipic Acid: A dicarbozylic acid (cooh on its ends of the carbon chain)
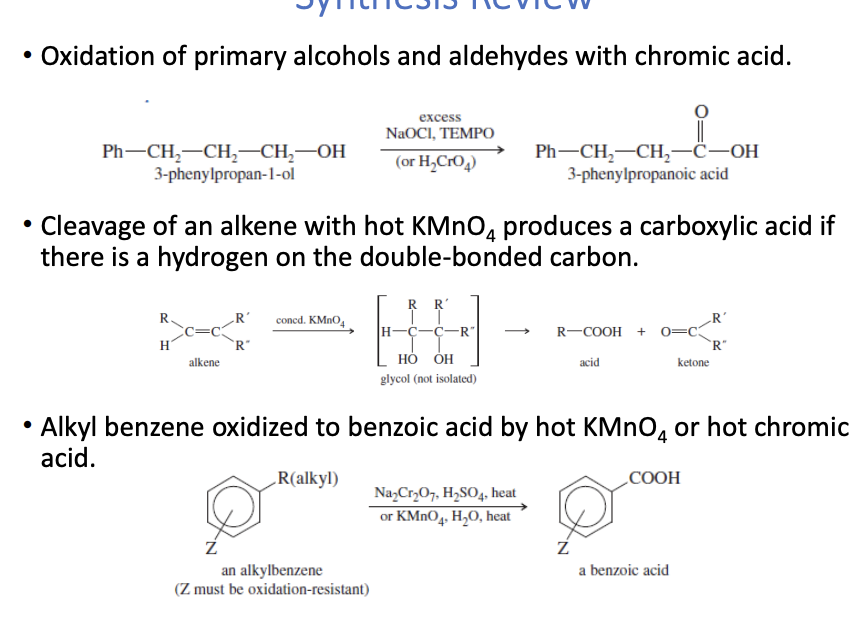
Carboxylic Acid Synthesis
Primary alcohol oxidation to carboxylic acid
uses H2CO7 (chromic acid) + TEMPO + NaOCl
alkene oxidation to carboxylic acid
uses KMnO4
alkyl benzene oxidation to benzoic acid
uses Na2Cr2)7 + H2SO4 or KMnO4 + H20
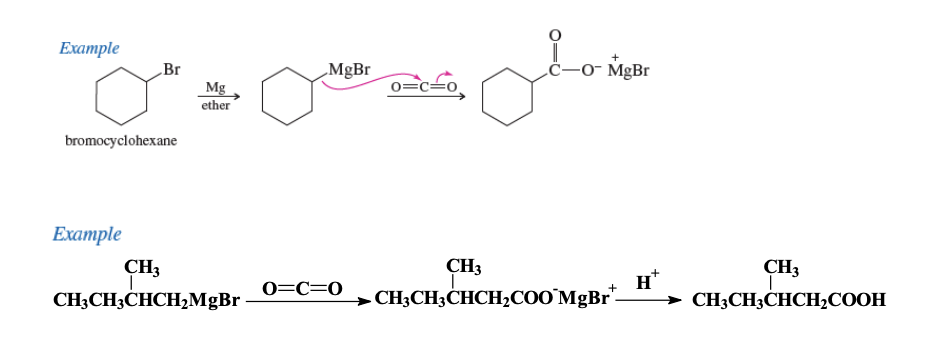
Grignard Synthesis
Grignard Reagent: Mg-X
Benze + x —> Mg + ether —> CO2 —> Carboxylate Salt
Carboxylate salt can change O- to OH through H20 or H+ protonation
GRIGNARD REAGENT + CO2 + H —> CARBOXYLIC ACID
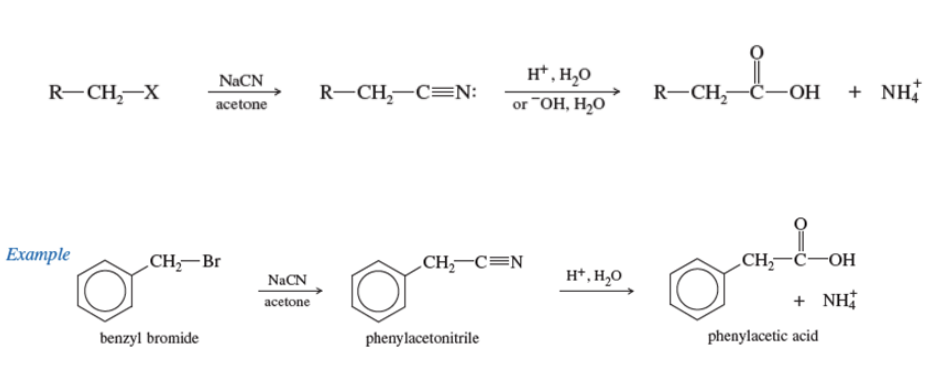
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
NITRILE: C≡N
R-Ch2-x (primary alkyl group) + CN (nitirle) —> R-Ch2-C≡N (nitrile) —> H+, H20, or -OH, H20 —> carboxylic acid
Acid Derivatives
The group attached to the acyl cabron (RCO) determines what tupe of acid derivative it is
can have substitution of Oh, X. OR, or NH2
NUC ATTACH SUBSTITUTENT ALLOWS FOR THE INTERCONVERSIONS OF THESE DERIVATIES (
acid chloride is most easily interconverted
derivative
cl: acid chloride
OR: ester
NH2: amine
OH: carboxylic acid

Fischer Esterfication
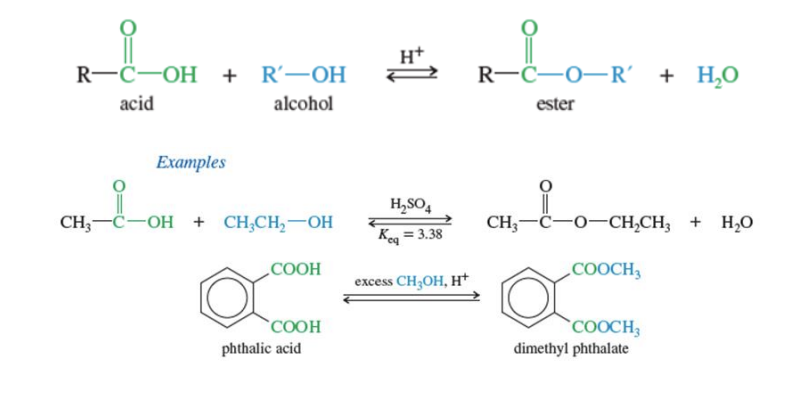
Carboxylic acid + R-OH + H —> produces ester

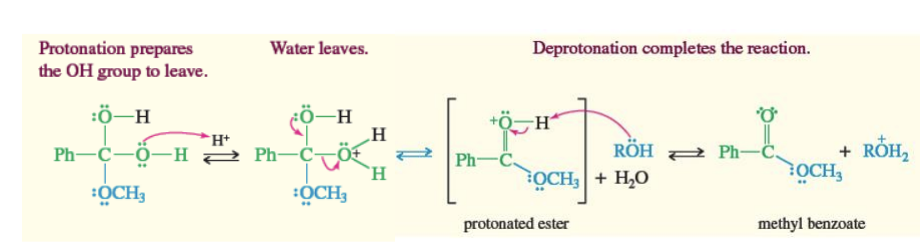
Carboxylic acid + (R-OH)2 + H —> ester hydrate —> H + ROH—> ester
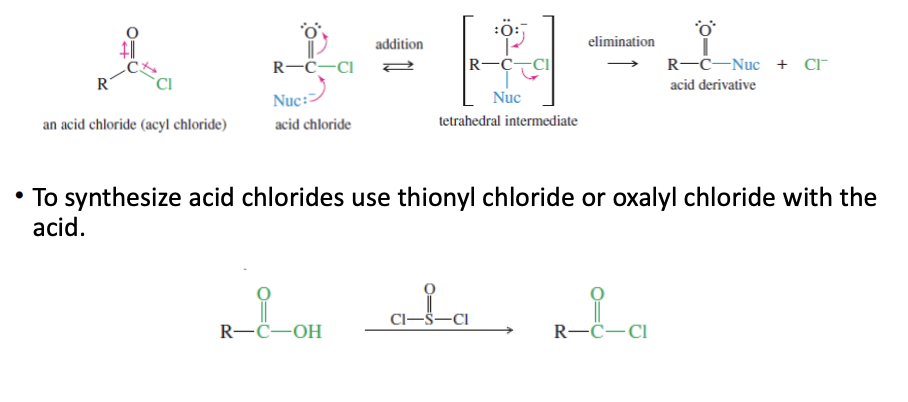
Acid Chloride
good leaving group for nuc attack
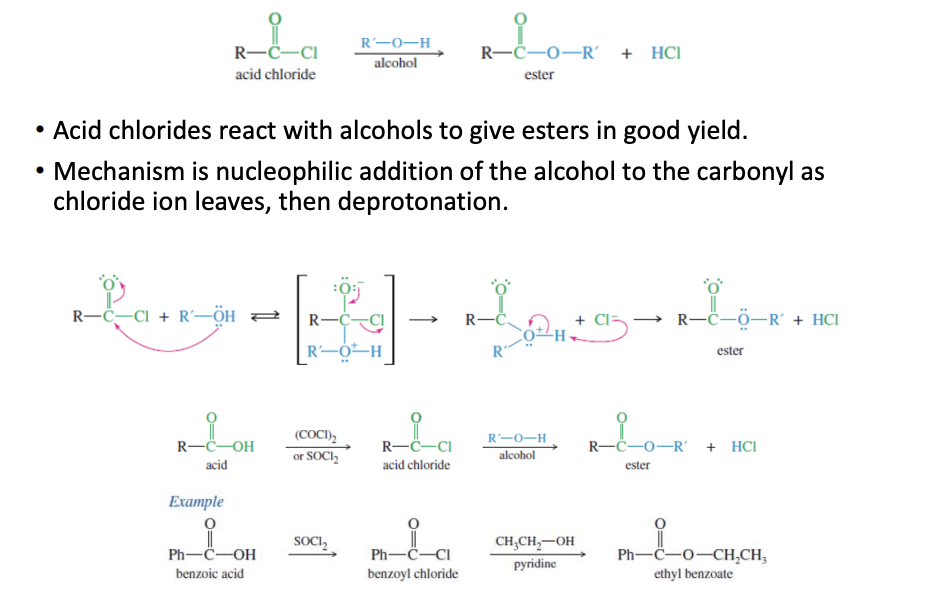
synthesized by carboxylic acid + socl2 —> acid chloride
Acid Chloride to ester
Carboxylic acid —> socl2 —> acid chloride —> R-OH + Cl —> ester
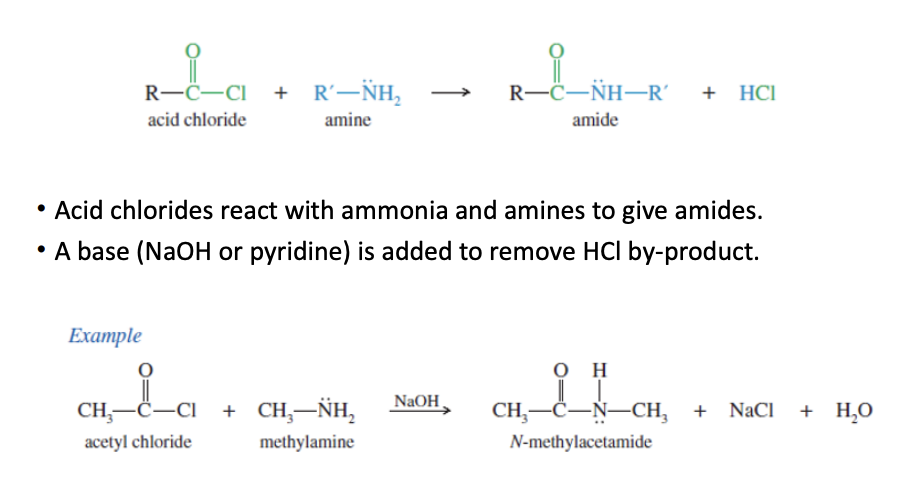
Acid chloride to amide
Acid Chloride + R-NH2 —> cl replaced by NH2-R —> amide
Amide —> NaOH → simpler amide (1 amide becomes 2 amide)
Reuction to primary alcohol
acid + LiAlh/H3O+ —> R-Ch2-Oh
for carboxylic acids
carboxylic acid —> BH3/THF/ H30 —> r-Ch2-Oh

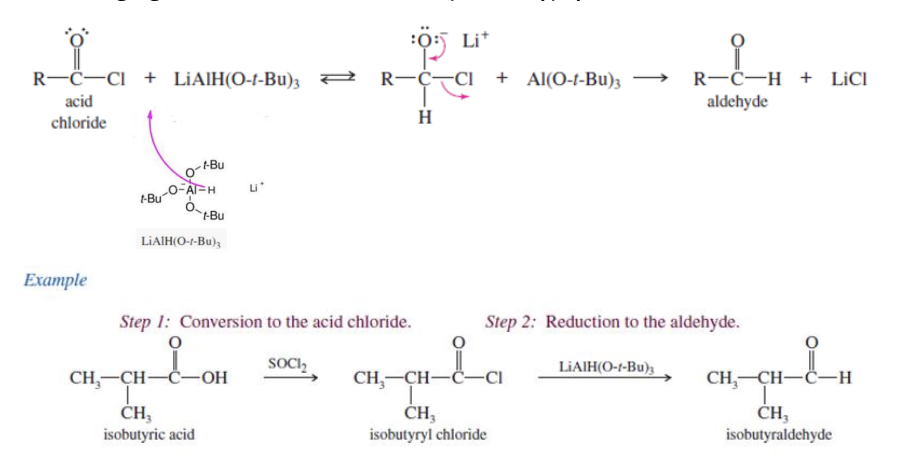
Reduction to form Aldehyde
Redction means using reducing agent
reducing agent in this is LiAlH(O-t-bu)3
acid chlorde + LiAlH(o-t-bu)3 —> aldehyde
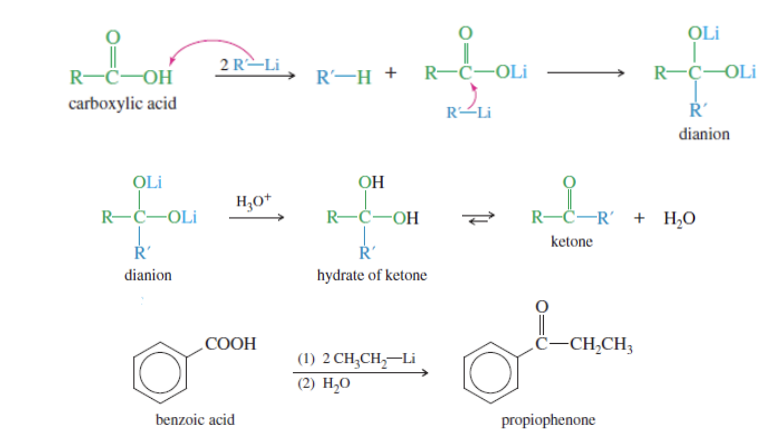
Alkylation to form ketones
Carboxylic acid + Socl2 —> Acid chloride
Acid chloride + 2R-LI + RLI + H3O —> KETONE
USES ORGNAOLITHIUM REAGENTS