Pregnancy & Human Development
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
how long is the secondary ooctye viable after ovulation
12-24 hrs
when the sperm's chromosomes combine with those of
an ovum to form a fertilized egg (zygote)
fertilzation
enzyme of sperm cell surface that digests the granulosa cells of the corona radiata (arround oocyte)
hyaluronidase
enzymes from what digest holes into the zona pellucida
acrosome
binding of sperm to oocyte membrane causes what reaction?
cortical reaction = Ca2+ surge within oocyte --> granules reasease ZIPs & hardening of zona pellucida --> destruction of sperm-binding receptor = prevent polyspermy
Zonal inhibiting proteins
ZIPs - prevent polypermy
sperm contents to enter the oocyte via .....
sperm and oocyte plasma membranes fusion
The Ca2+ surge from sperm entry triggers completion of
meiosis II
is a zygote diploid or haploid?
Diploid because it contains TWO haploid sets of chromosomes from maternal and paternal family lines
When does implantation happen?
6-7 days after ovulation
what adheres to a site on the endometrium to signal the implantation site?
trophoblast
Implantation is completed by
12th day after ovulation
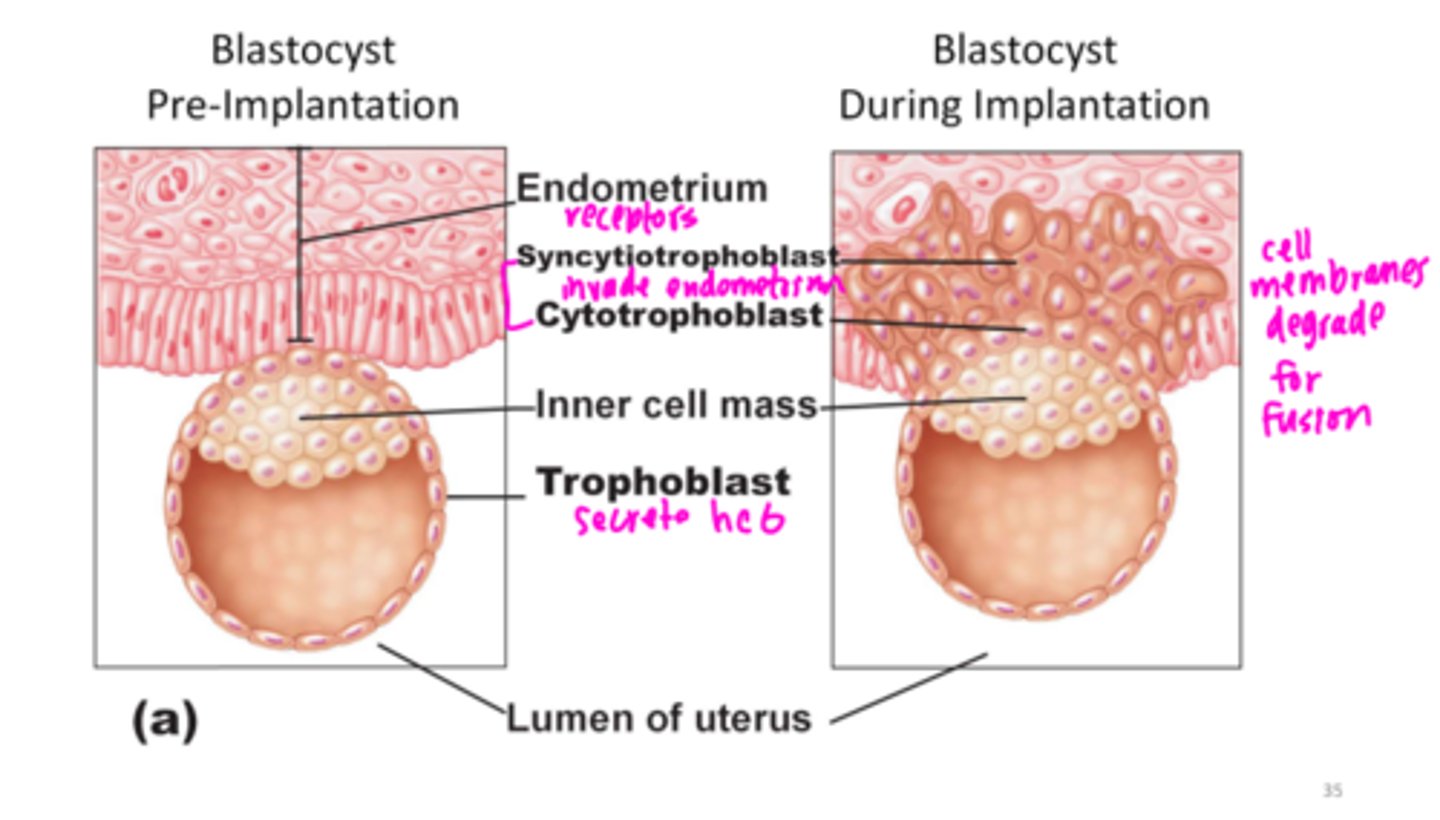
secreted by trophoblast cells that causes the corpus luteum to continue releasing progesterone and estrogen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG secretion declines when
placenta begins to secrete its own progesterone and estrogen (end of 2nd month)
what prevents polyspermy by destroying the sperm receptors?
ZIPs
the corpus luteum is formed at the site of
ovulation
time since the first day of the last menstruation
gestational age
approximately two weeks shorter than gestational age
fertilzation age
pregnancy truly begins at
implantation
time from the last menstrual period until birth
gestation period
what cell process is happening to the zygote right after fertilzation
cell division
zygote daughter cells are called
blastomeres
solid ball of 16 or more cells
morula
At day 3 or 4, the embryo is called a
blastocyte
fluid accumulation in interal cavity & lose zona pellucida
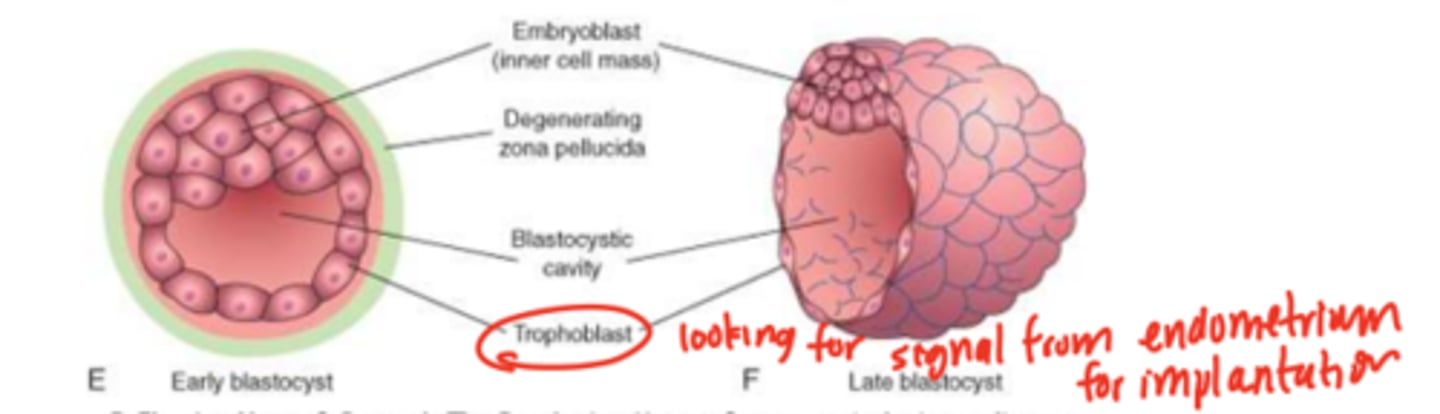
A fluid-filled hollow sphere composed of trophoblast cells and an inner cell mass.
blastocyst
why do trophoblast cells display immunsuppresive factors?
so that implantation and development can proceed without maternal immune rejection.
the inner cell mass of a blastocyst will become
embryo and chorion, yolk-sac, and amniotic sac
adheres to a site on the endometrium with the
proper receptors and chemical signals
trophoblast
two distinct layers formed by the trophoblast
• Cytotrophoblast: inner layer of cells
• Syncytiotrophoblast: cells in the outer later
Which layer formed by the trophoblast have the contents that invade and digest the endometrium allowing the blastocyst to burrow into the endometrial lining
Syncytiotrophoblast
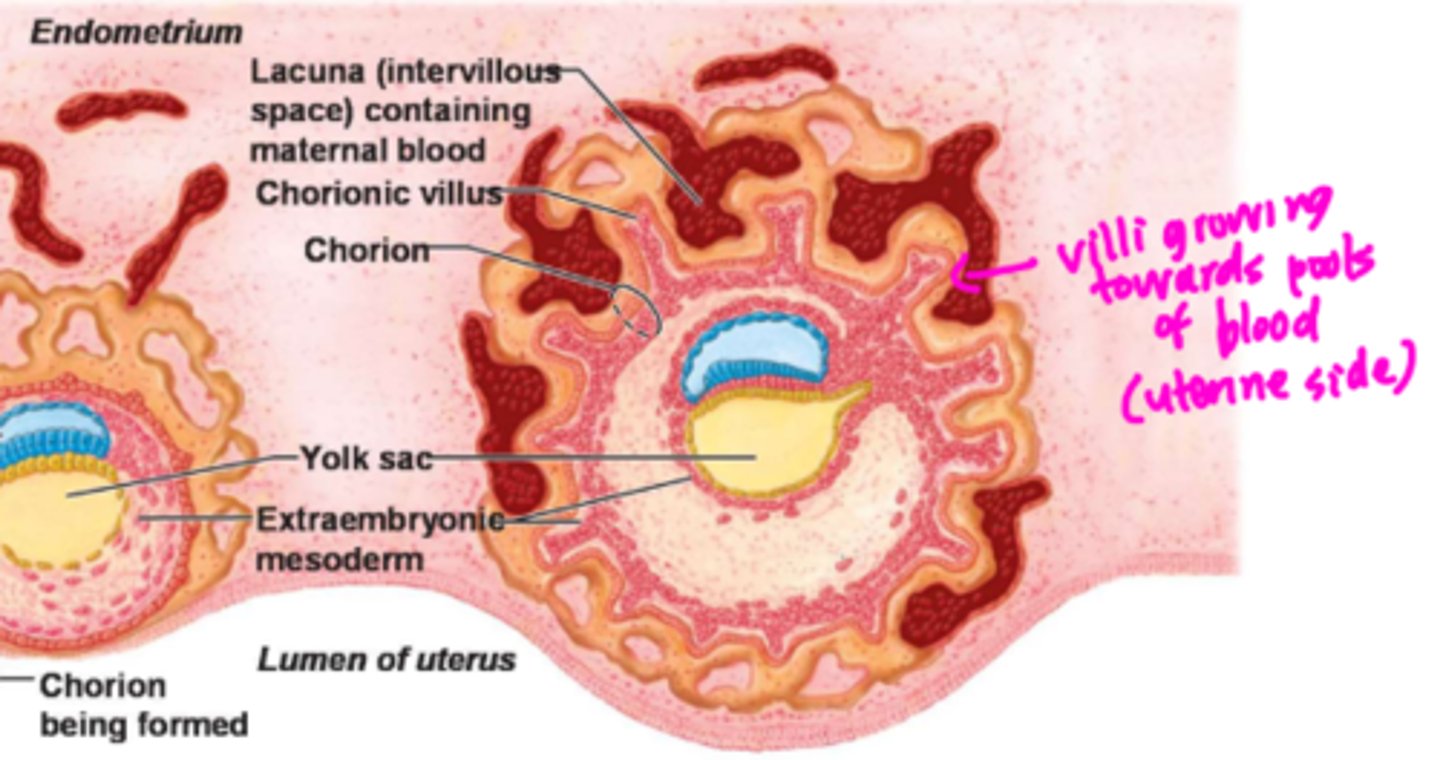
endometrium cells grown around
blastocyst
the ______ forms from embryonic and uterine
tissues after implantation
placenta
Finger-like projections from the growing embryo that allow for nutrient and waste exchange
chorionic villi made by the trophoblast
part of the endometrium outside of the chorionic villi
Decidua basalis
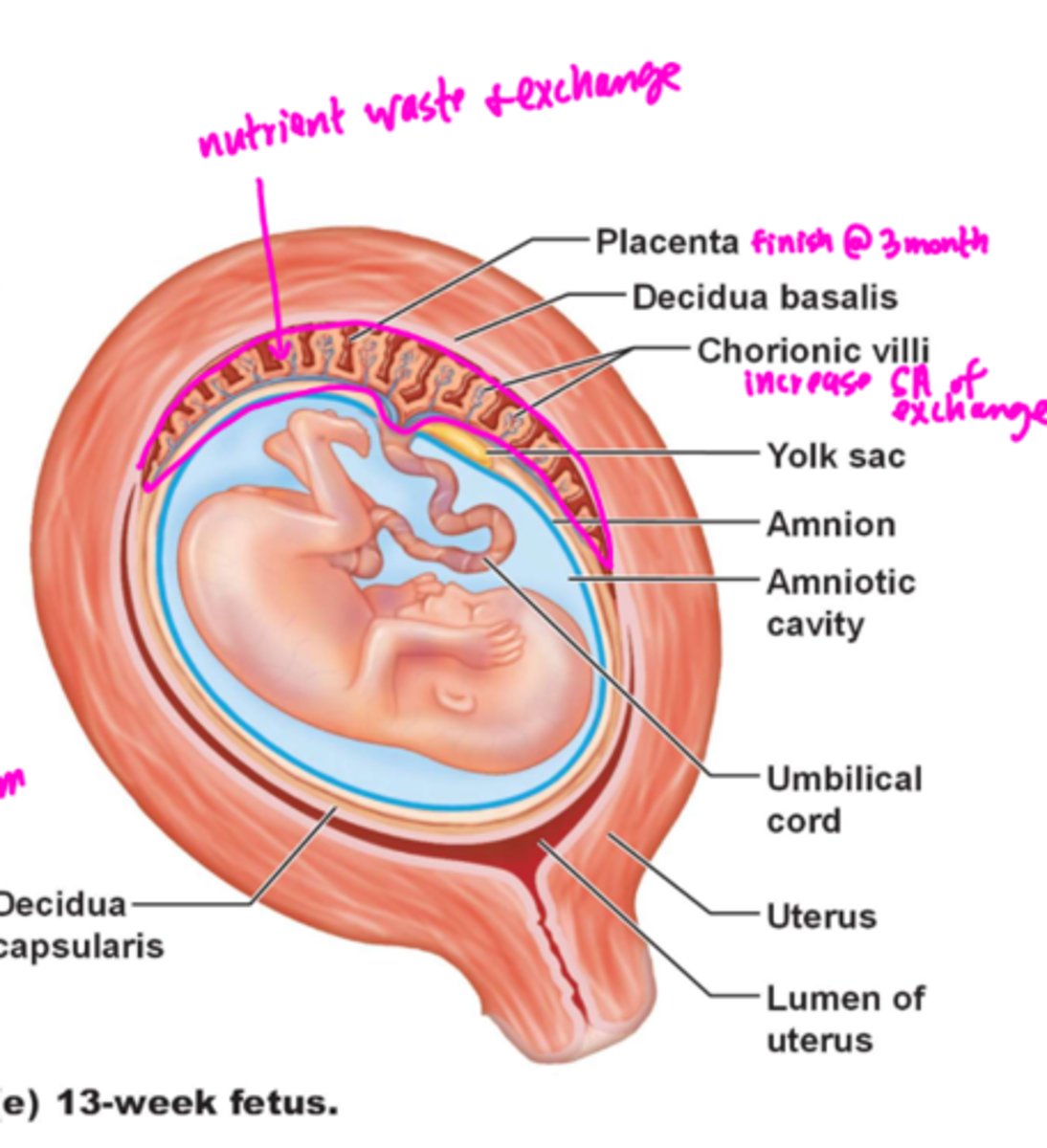
chorionic villi and decidua basalis together
Placenta
Is fully formed and functional by the end of the third month
placenta
Do uterine and embryonic blood supplies intermix?
no
a fetus with a gestational age of 25 would have the fertilization age of
23 weeks (2 weeks after last menstruation)
order of zygote formation
zygote --> morula --> blastocyst
Which fetal cells digest uterine cells?
syncytiotrophoblasts
During implantation the ICM develops into a __________ that develops into the _________.
flat embryonic disc; embryo
Trophoblast cells and some cells of the embryonic disc form the
extraembryonic membranes
extraembryonic membranes contains:
amnion, yolk sac, allantois
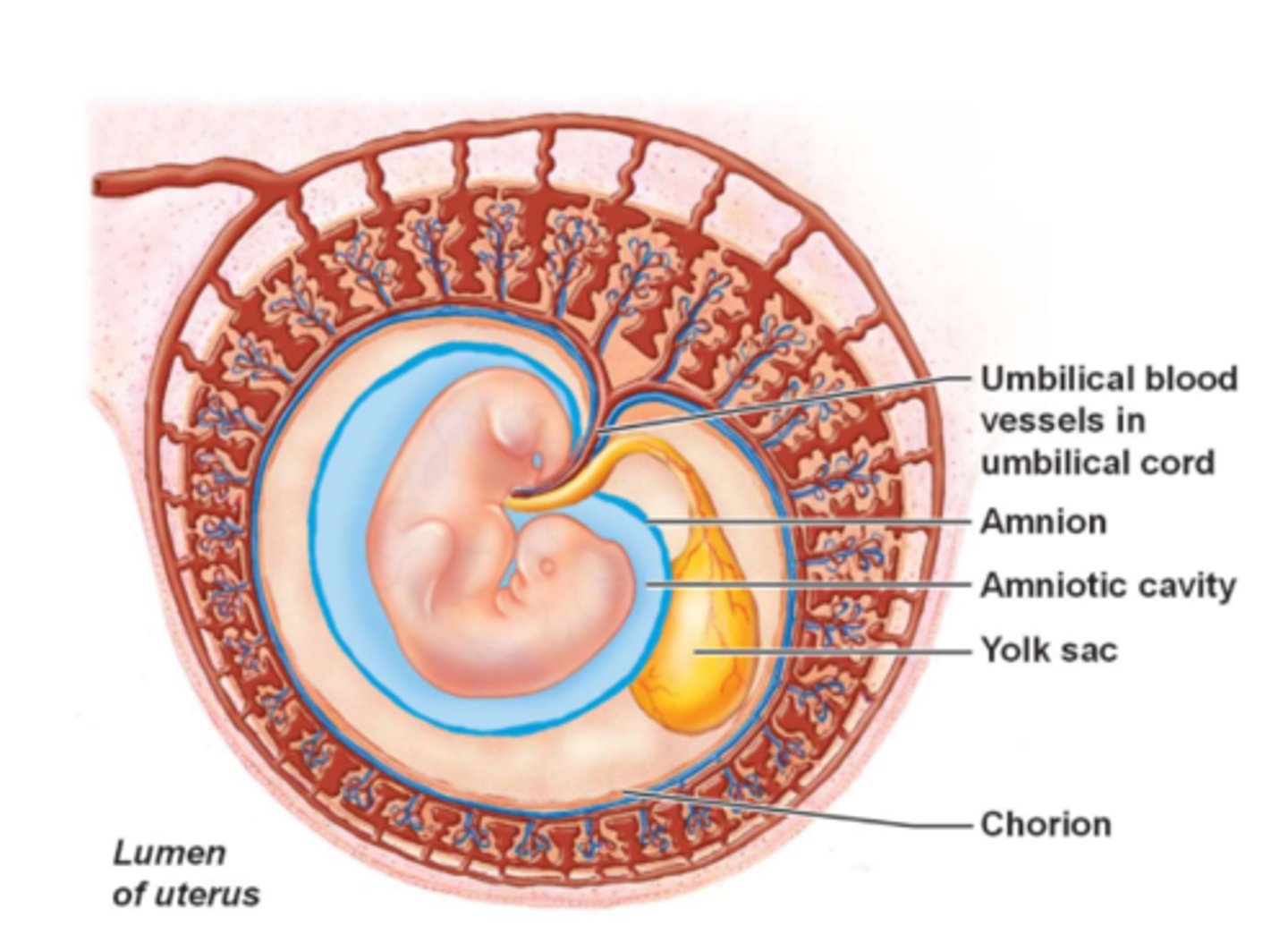
provides a buoyant environment that protects the embryo, contains amniotic fluid
Amnion
source of the earliest blood cells and blood vessels, later forms part of the digestive tube
Yolk sac
structural base for the umbilical cord, becomes part of the urinary bladder
Allantois
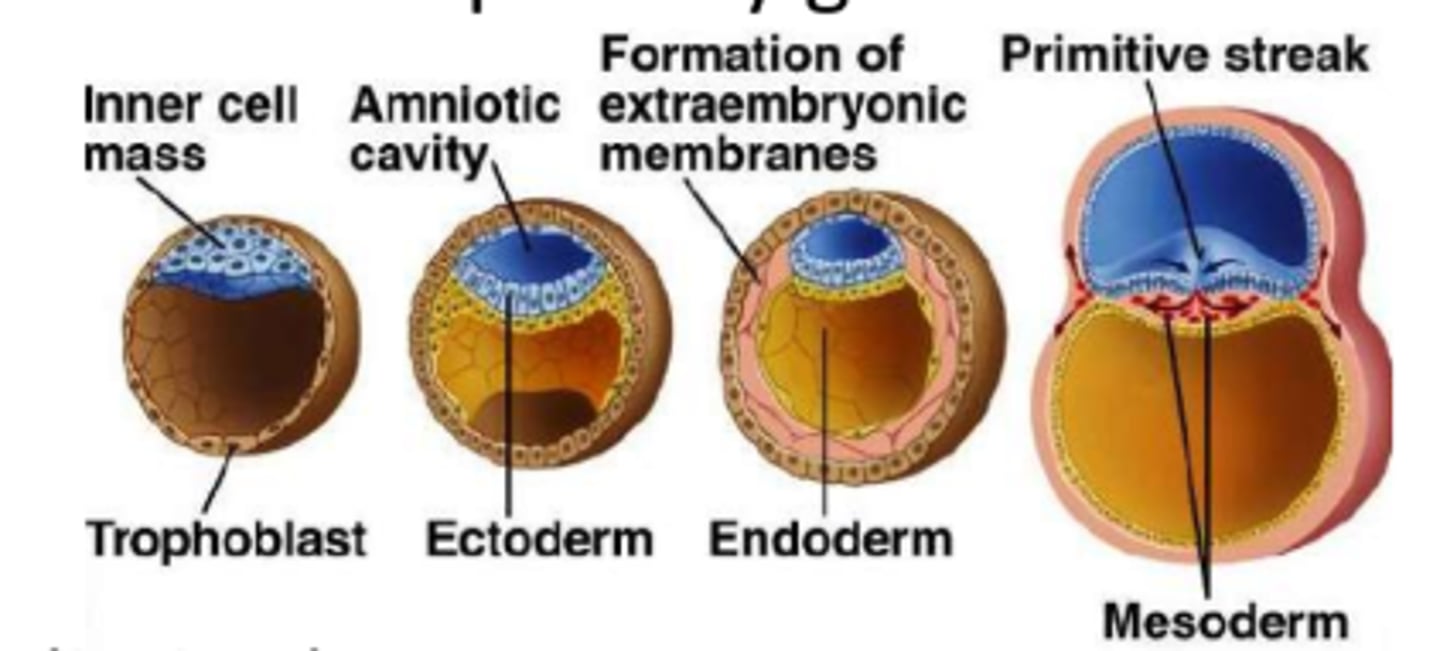
In week ___, the embryonic disc develops into three primary germ layers (gastrula)
3
3 layers of the gastrula will eventually form different tissues
Ectoderm (outer layer)
Mesoderm (middle layer)
Endoderm (inner layer)
nervous system, bones and blood vessels of the head, and skin epidermis develop from which primary germ layer?
ectoderm
epithelial linings & glands of the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital systems develop from which primary germ layer?
endoderm
mesoderm forms
muscle, bone, ligaments, heart, blood vessels, kidney, gonads, serosa, walls of digestive and respiratory organs
formation of body organs and systems
organogenesis
End of embryonic period
week 8 - All organ systems are recognizable (though not functional)
The first major event in organogenesis is ________.
neurulation
Gives rise to brain and spinal cord
Three brain vesicles that are apparent by the end iof the first month
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
In Development of the Nervous System by the end of the second month...
• Cerebral hemispheres cover the top of the brain
• Spontaneous brain waves can be recorded
causes of neural tube defects
improper/no fusion of tube
incomplete closure of neural tube
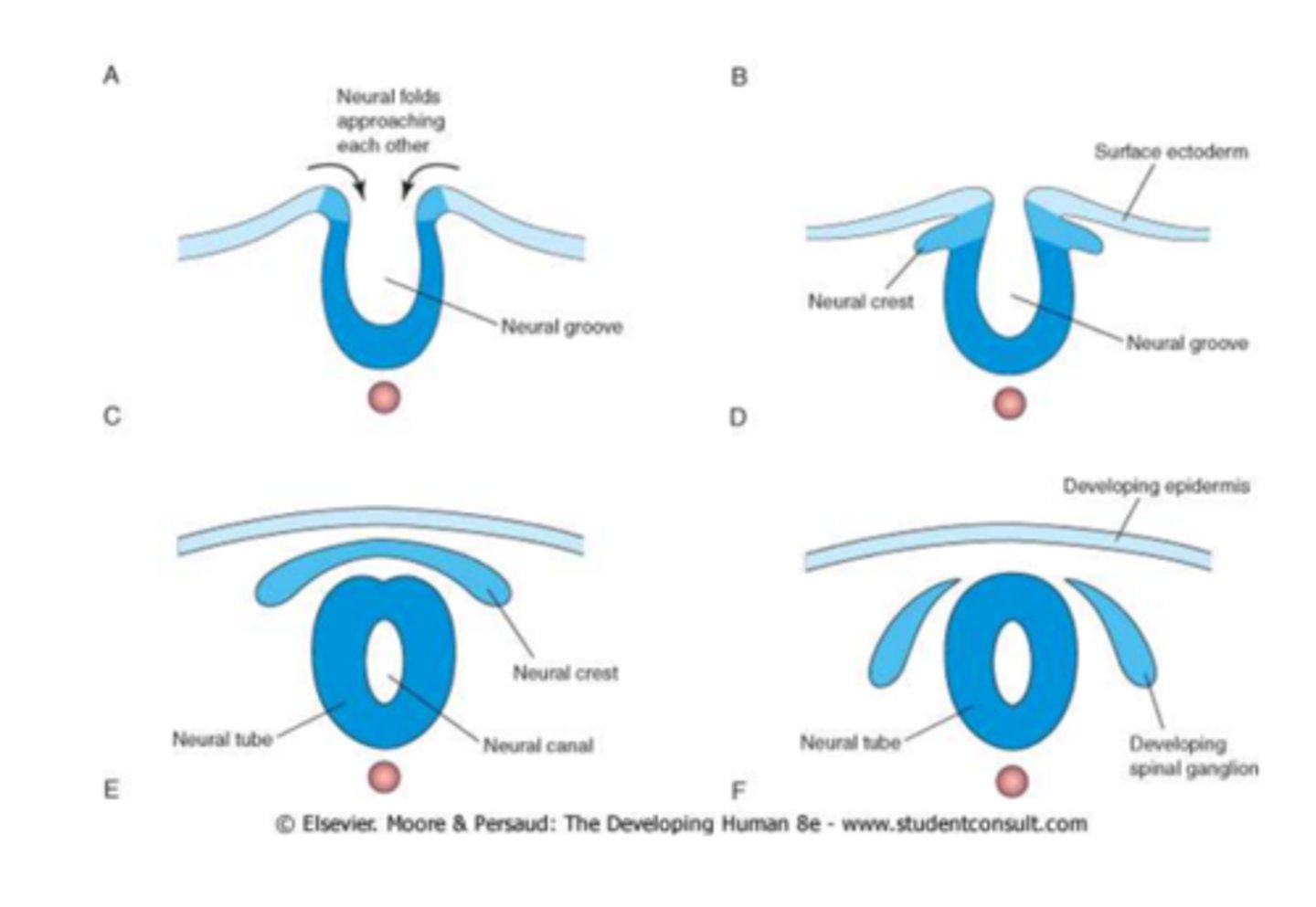
embryonic ecotoderm gives rise to the
skin and nervous system
which structure is encolosed by a tube of endoderm and developed into the primitive gut
yolk sac
after embryonic development is _________ development
fetal
fetal period
9 weeks to birth
by the end of embryonic development (week 8) is the cardiovascular system fully functional?
yes - heart has been pumping blood since week 4
distinguishing body feature of week 8 fetus
head nearly as large as body
when in fetal development does blood cell formation begin in the bone marrow & external genitalia visible
9-12 weeks, month 3
when in fetal development does the face become human (eyes, ears, lips) and body starts outspacing head
13-16 weeks, month 4
when does fetus take fetal position due to rapid growth (lack of space) & kicking happens
17-20 weeks, month 5
when is fetus mostly viable outside except for underdeveloped lungs
21-30 weeks, months 6&7
in the developing fetus, all body systems are present by
week 8 (end of embryonic development)
Any environmental agent that can cause deviations in prenatal development
teratogen
what factor trigger testicular development during gonadal development (week 6-7)
amount of testosterone
drugs that alter sex steroid hormone homeostasis