GO!3 (Translation)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Codons
three nucleotide sequences in RNA that are read to code for a specific protein
Reading frame
the way the codons are read, heavily critical to the proteins created, so the reading frame set has lots of impact.
How many reading grams can we have
3, shift let, shift right and the middle
tRNA
translator RNA that reads codons and brings the correct amino acid there (read & bring in)
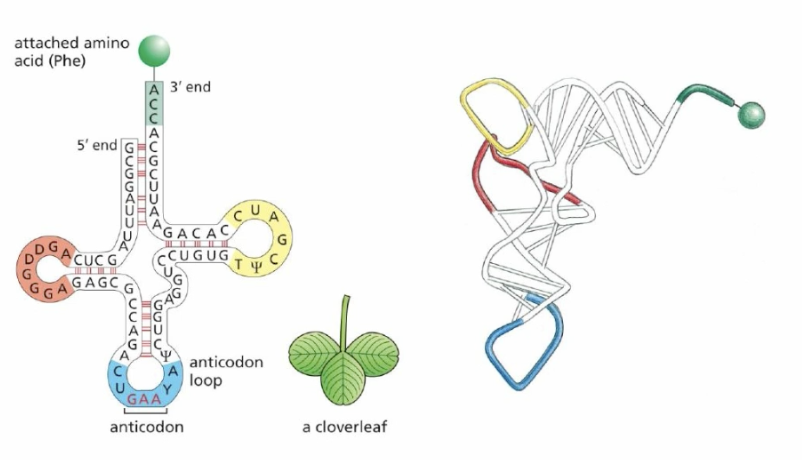
tRNA’s structure (important bits)
Folded RNA
Anticodon loop
Attached amino acid at the 3’ end covalently
Clover shape
Functional RNA
RNA that is not translated into a protein
Anticodon
part of the tRNA that comp base pairs with the specific codon within the mRNA while inside the Ribosome
Amino Acid on tRNA
added to the 3’ end covalently and is the amino acid of the codon in the RNA sequence
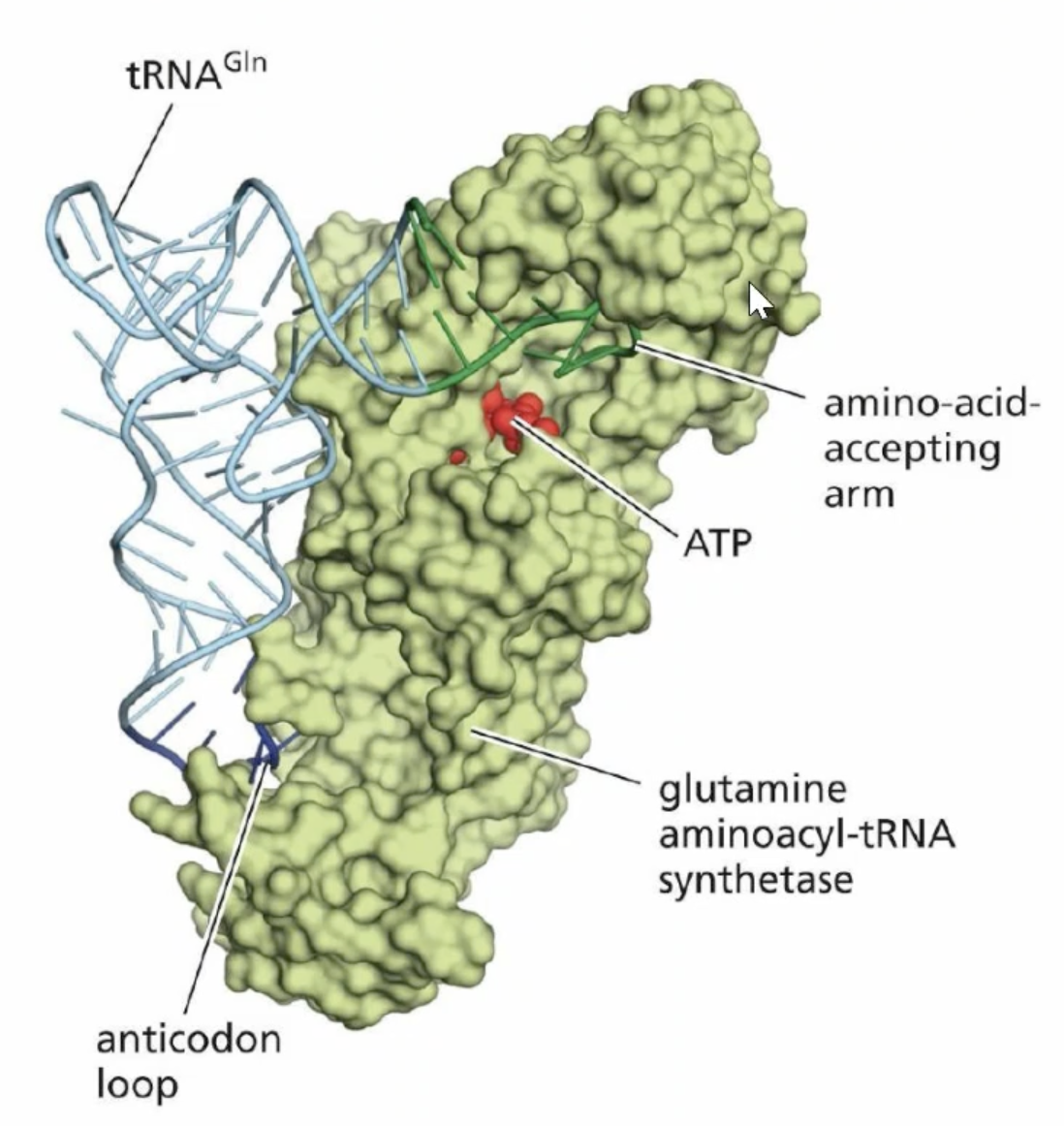
Aminoacyl- RNA synthetase
specific enzyme for each tRNA that adds the amino acid to the 3’ end of the tRNA
Aminoacyl- RNA synthetase function
recognize and bind to the specific tRNA molecule for their cognate amino acid.
leaves a high energy bond that drives polypeptide chain formation
TOP hat Question: The anti-codon is 5’ UAA’ 3 what is the codon
5’ UUA 3’
Relationship between anti-codon and codon
the anti-codon and codon complementary base pair attaching the tRNA to the specific segment RNA is corresponds to.

Genetic Code is Degenerate
multiple codons encode for the same amino acid
How is genetic code degenerate
A single tRNA recognizing more than one codon due to expanded base paring WOBBLE
more than one tRNA for an amino acid
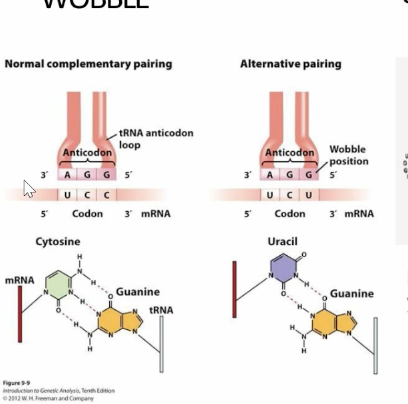
Wobble
tRNA with nearly perfect anti-codons but the third nucleotide is incorrect, creating a wobbly, short-lived bond that still does the job.
Ribosome Definition and function
huge protein and RNA complex that decodes the the RNA with its EPA pockets
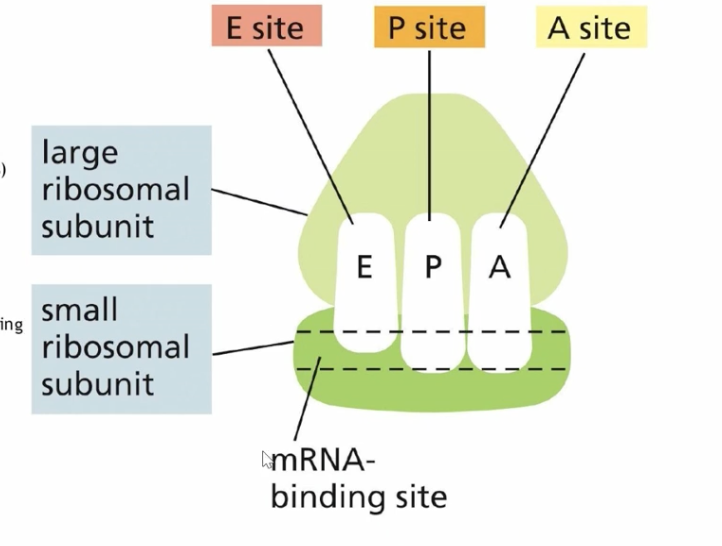
RIbosome anatomy
a ribosome with a large and small subunit that form the 3 pockets EPA
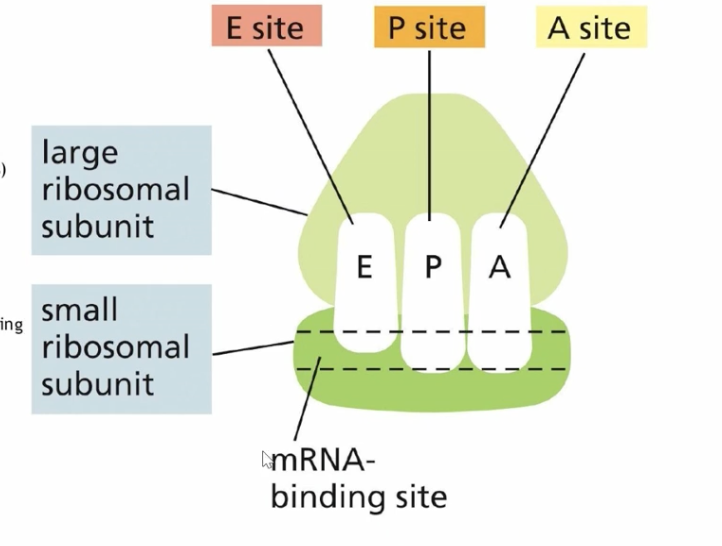
EPA
exit site, peptide site(pass), and aminoacyl site (add) , which are pockets formed inside the ribosome when the large and small subunit come together.
E site (exit site)
the site where the tRNA is ejected
Peptidyl site (pass site)
where the bond between the amino acid and tRNA are broken and the amino acid is bonded to the amino acid in the aminoacyl site
Amioacyl site (add)
where new tRNA holding another amino acid situates itself for bonding with the amino acid in the p site
C terminus
the side in which proteins are added
N terminus
the side that comes out of the ribosome first and never has addition to that side
Hey! go back to the slides and walk through the different steps of translation !
fine
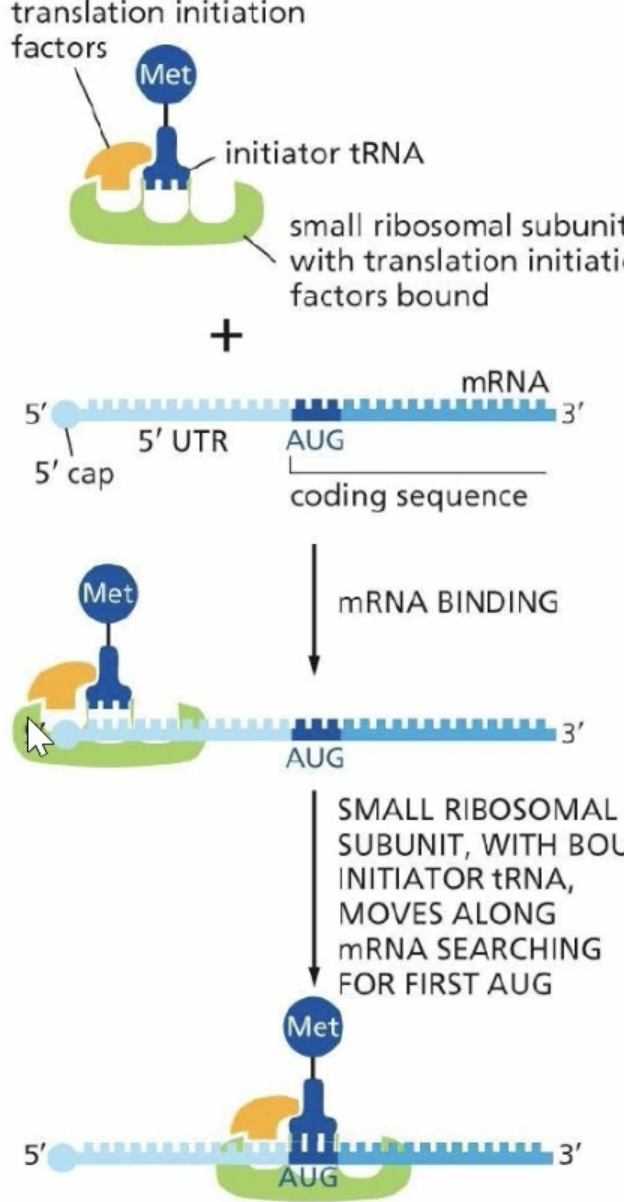
Eukaryotic Translation Initiation
small ribosomal subunit binds with the tRNA and finds the 5’ cap
After finding the cap it scans 5’ to 3’ for the AUG methionine sequence
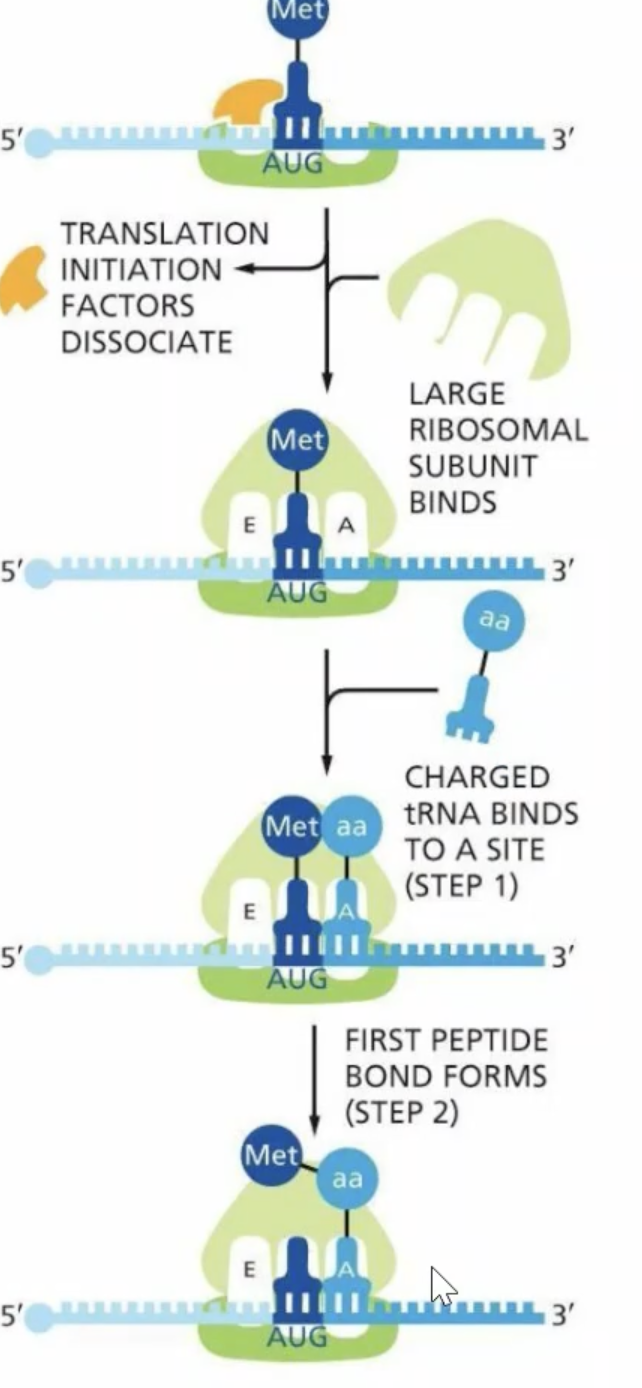
Initiation factors disassociate and th large ribosomal subunit binds, putting methionine in the p-site
another tRNA comes through and goes to the A site
Peptide bond is formed, and EPA stepwise happens
Purpose fo methionine (AUG)
it is always the start codon and let;s the ribosome and tRNA know where to start
Prokaryotic Translation Initiation
Shine- Dalgarno sequence complementary base pairs with the ribosomal RNA (small subunit) and positions the P site over an AUG (meth).
Ribosomal RNA
small subunit of the RNA
Release factor
protein that recognizes stop sequences and catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction, breaking the bond between the tRNA and the growing polypeptide chain causing ribosome to disassociate. (looks like and fits into the p site)
Read Through Mutation
when the stop codon is mutated into a regular codon in turn not having the Ribosome stop, reading throguh and creating longer and wrong protein.
Polycistronic mRNA
meaning that one mRNA can make multiple polypeptide chains/proteins and only occurs in bacteria!!!
Are polycisitronic proteins related to each other?
NO! they can be vastly different!
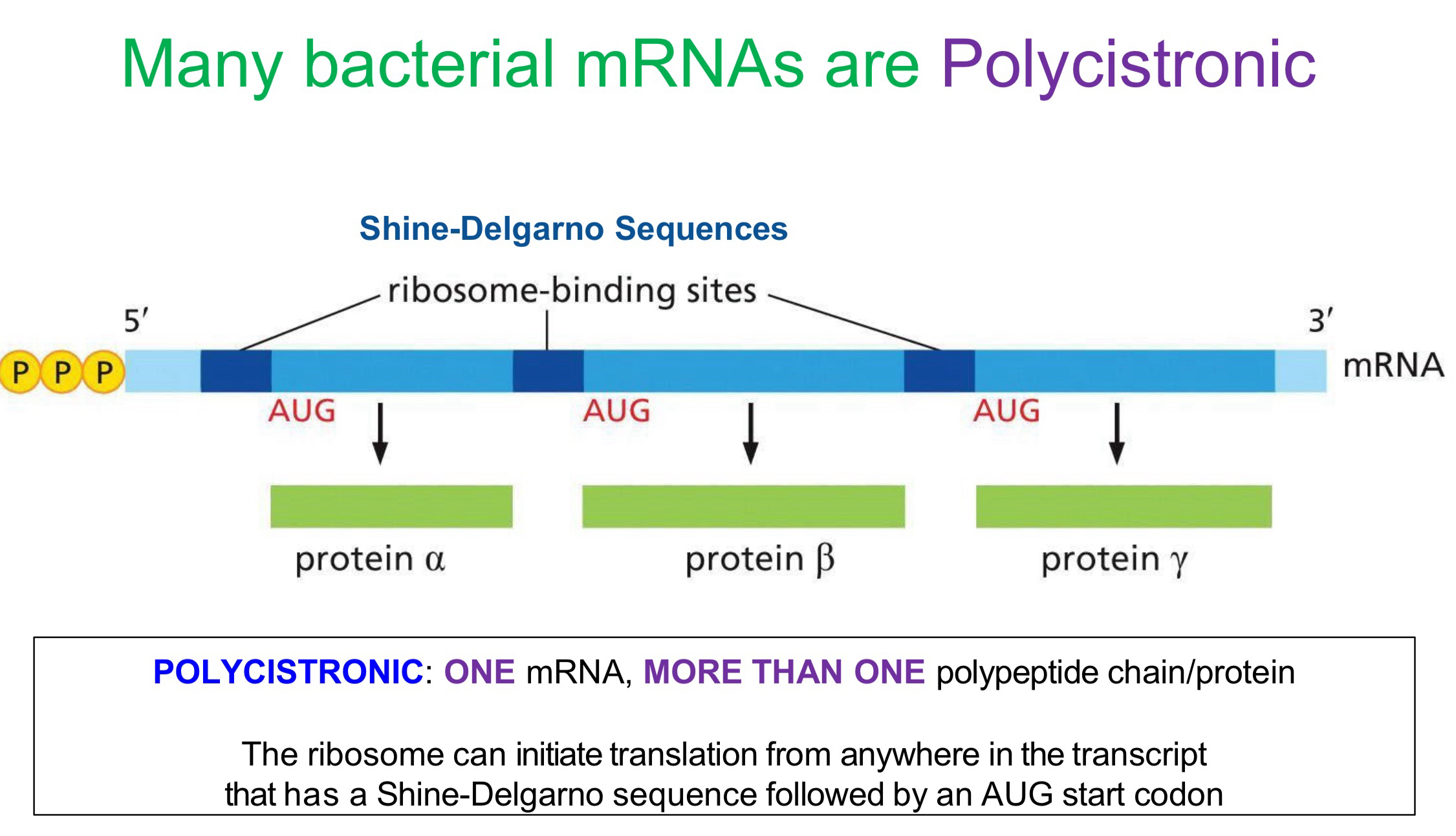
why do bacteria have polycistronic mRNA
they can have multiple shine-dalgarno sequences followed by AUG(meth) sequences anywhere inside the sequence
Monocistronic mRNA
one gene, one mRNA, creating ONE proteins and this occurs in eukaryotic cells
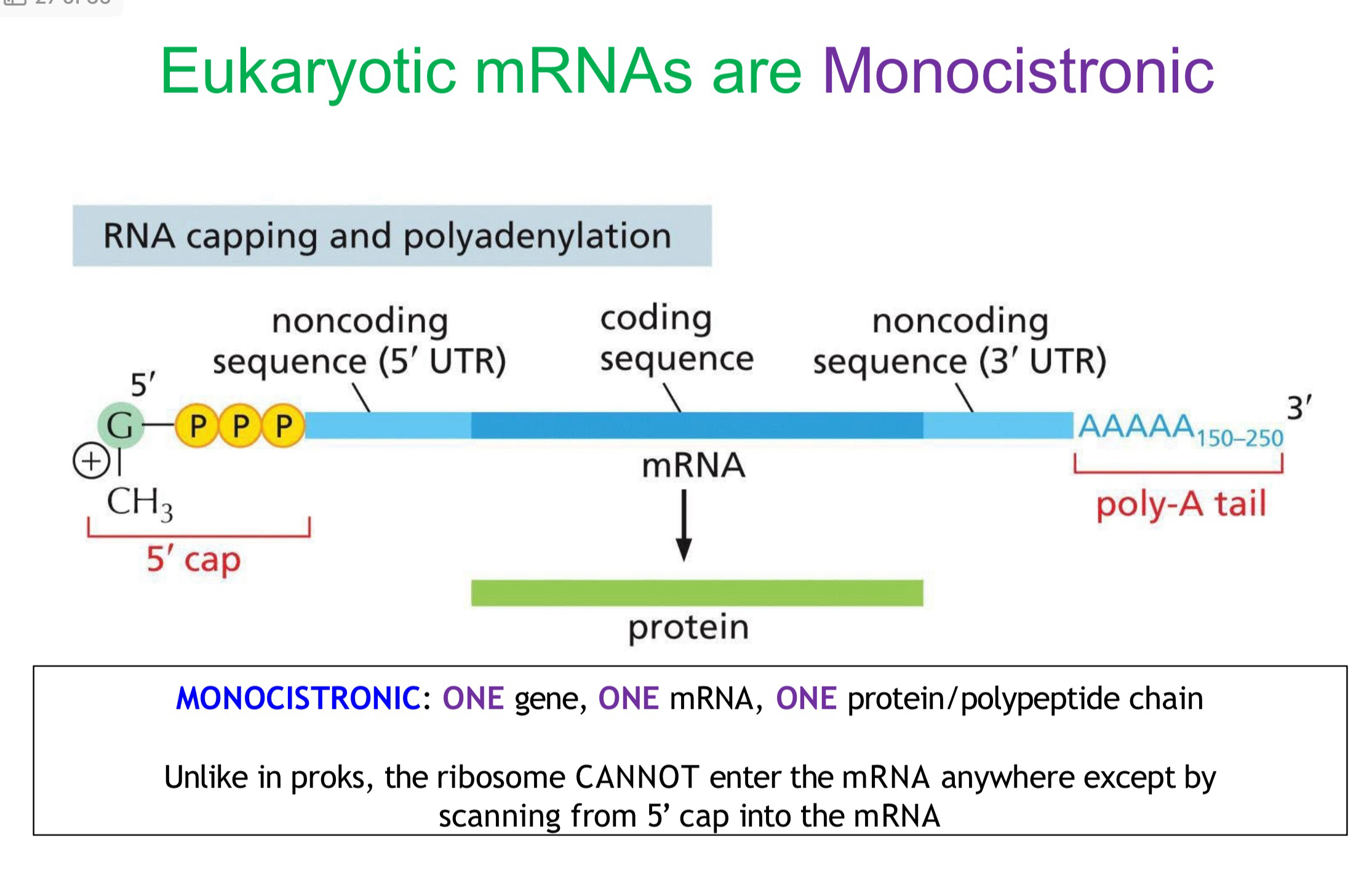
Why do eukaryotes have only monocistronic mRNA
because the tRNA and ribosome can only bond at the 5’ cap and there aren’t multiple 5’ caps within mRNA.
Polysome
many ribosomes binding to a single mRNA and creating lots of protein from one mRNA
Always read RNA
5’ to 3’ since that’s how Ribosome does it