PT7130- Physiologic Monitors and Support
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Safety; confidence; manueverability
Therapists need to be aware of different types of monitors/equipment.
- _________________________
- Alarms
- Patient _______________________
- Portability and _________________________
- Interpretation
Telemetry
Monitored at a distant site; continuous monitoring of HR and rhyhtm and RR via ECG.
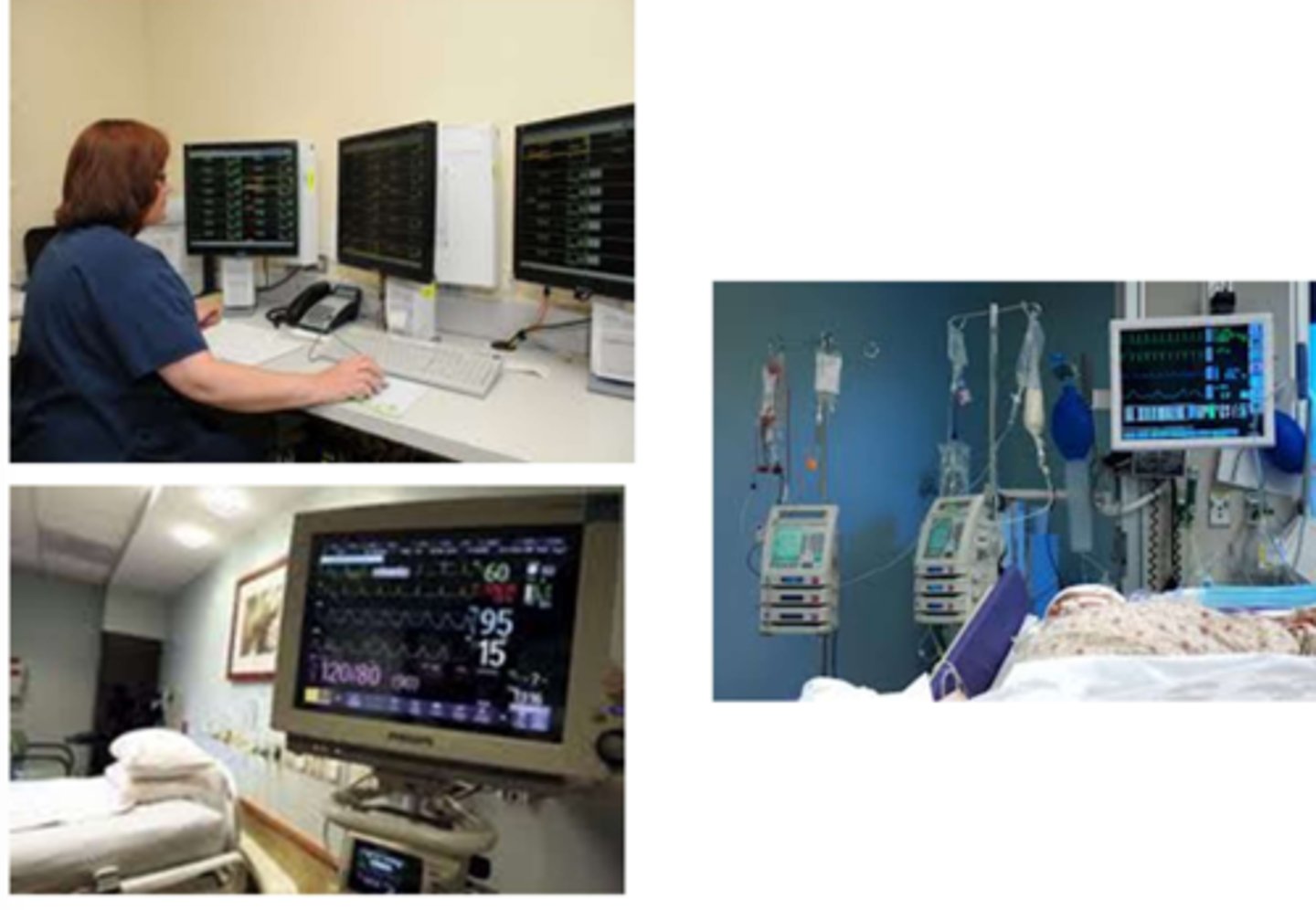
RN; parameters; portable
Specific units will be designated with telemetry.
Therapy Considerations:
- Notify _________________ re: therapy times
- Utilize information before, during, and after activity
- Stay within ______________________ of reception
- _____________________ → unlimited activity
Hemodynamic monitoring
Utilization of invasive lines into the heart, arterial, or venous system to monitor: Fluid and electrolyte balance, blood pressure and blood flow
Cardiovascular system
Purpose of Hemodynamic Monitoring:
Correct assessment of the ________________________ and its response to tissue O2 demands.
Pulmonary artery catheter, arterial line, central venous line
What are some examples of hemodynamic monitoring?
Pulmonary artery catheter (Swans-Ganz)
Measures intra-cardiac pressures.
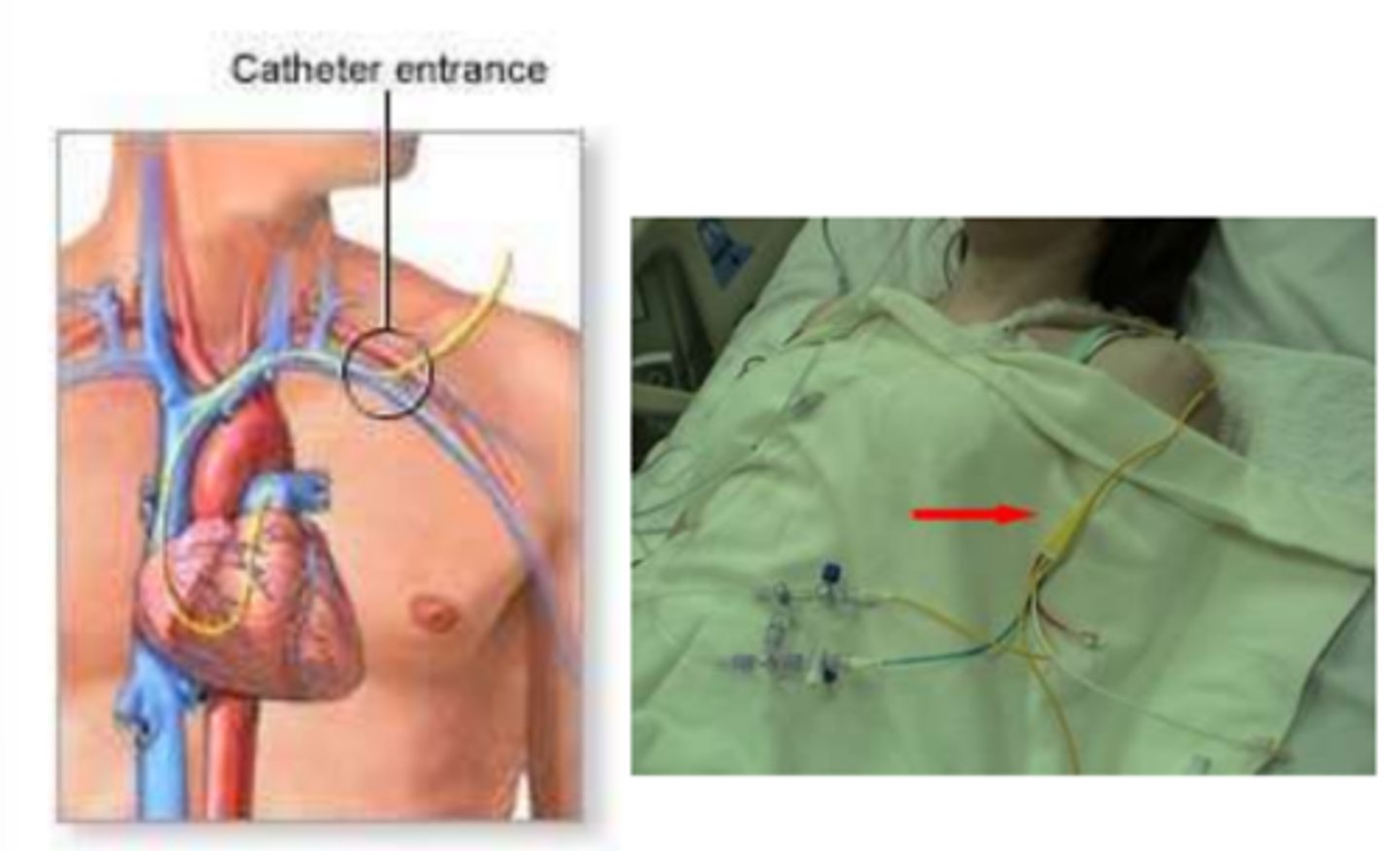
Subclavian or internal jugular veins
What is insertion site of pulmonary artery catheter (Swanz-Ganz)?
Right side of the heart into pulmonary artery
What is the path of pulmonary artery catheter?
Bedrest; head/neck/upper extremity
Patients /c pulmonary artery catheter (Swanz-Ganz) are typically on _________________________ after insertion. Avoid ________________________ movements that can disrupt the PAC insertion site.
10-15 mmHg
Normal PAP?
>25 mmHg
Pulmonary HTN PAP?
Complicated; unstable; pulmonary HTN
Indications for Pulmonary Artery Catheter (Swanz-Ganz):
- ______________________ MI
- ______________________ angina
- Severe LVHF
- ________________________
- Sepsis
- Hemorrhage
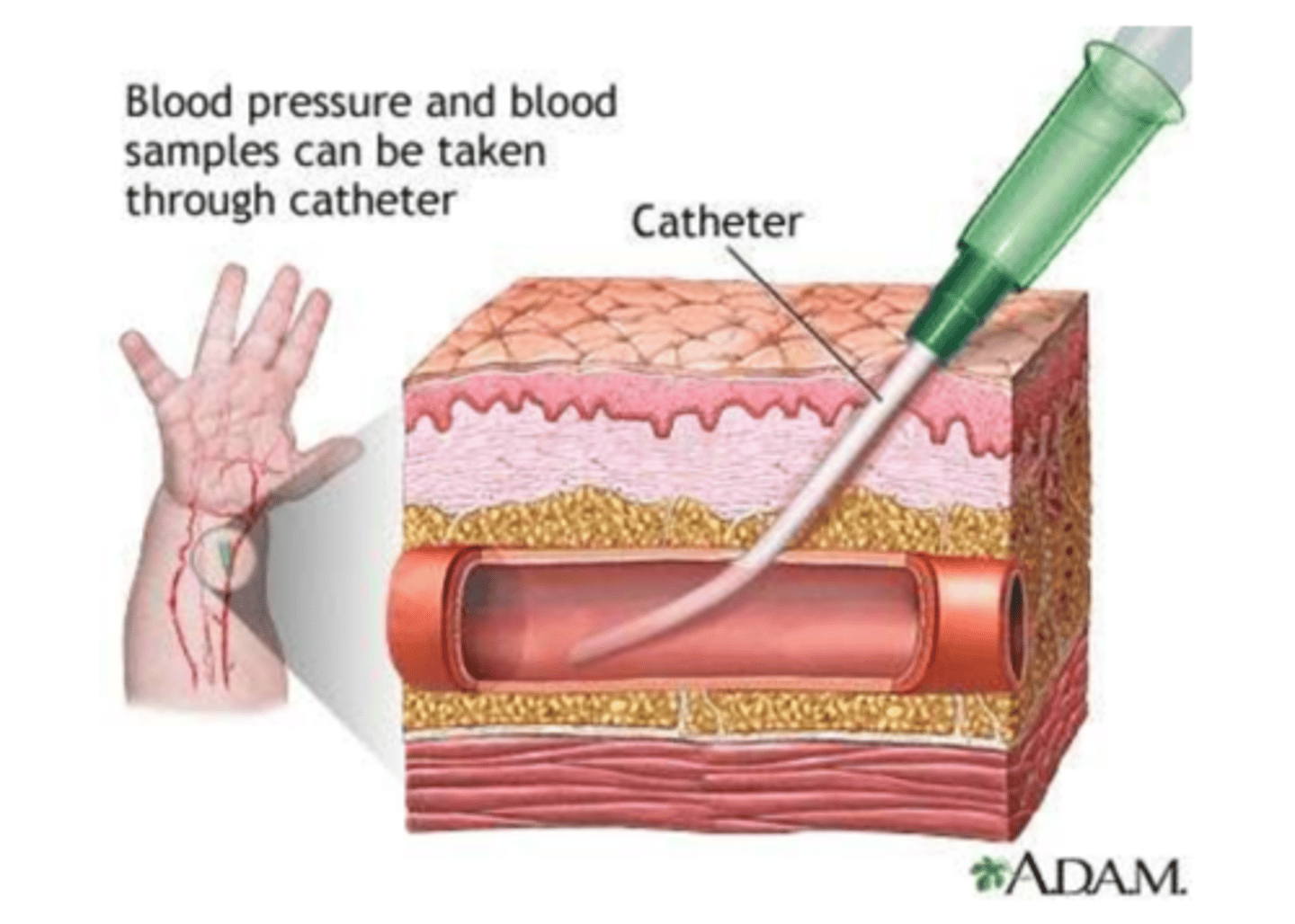
Arterial line
Continuous blood pressure monitoring, repeated arterial blood samples, deliver medication.
Aortic root (less common), brachial artery, radial artery, femoral artery
Where are arterial lines placed?
Pressure; 60-80°; 60-90 minutes; wrist splint
PT Implications of Arterial Line:
- If displaced, apply immediate and direct __________________________
- Femoral: Hip flexion past ________________________ contraindicated for femoral arterial line. After removal, bedrest for _________________________
- Radial: May see _________________________
110; 60-110; 0.6; sitting
Proposed Activity Guidelines - Femoral Lines:
- Safety: Able to follow commands
- Hemodynamically stable:
→ Resting HR <______________ bpm
→ MAP __________________ mmHg
→ FiO2 <_________________
- Types of femoral lines:
→ Central venous catheters
→ Dialysis catheters
→ Arterial catheters
- Inspection: Before and after sessions (document that line was in place)
- Mobility Activities:
→ Transfers to EOB
→ _____________________ EOB with or without assist
→ Standing at bedside
→ Transfer to stretcher chair or regular chair
→ Ambulation
→ No repeated hip flexion
- 210 PT sessions, 630 mobility activities, NO ADVERSE EVENTS
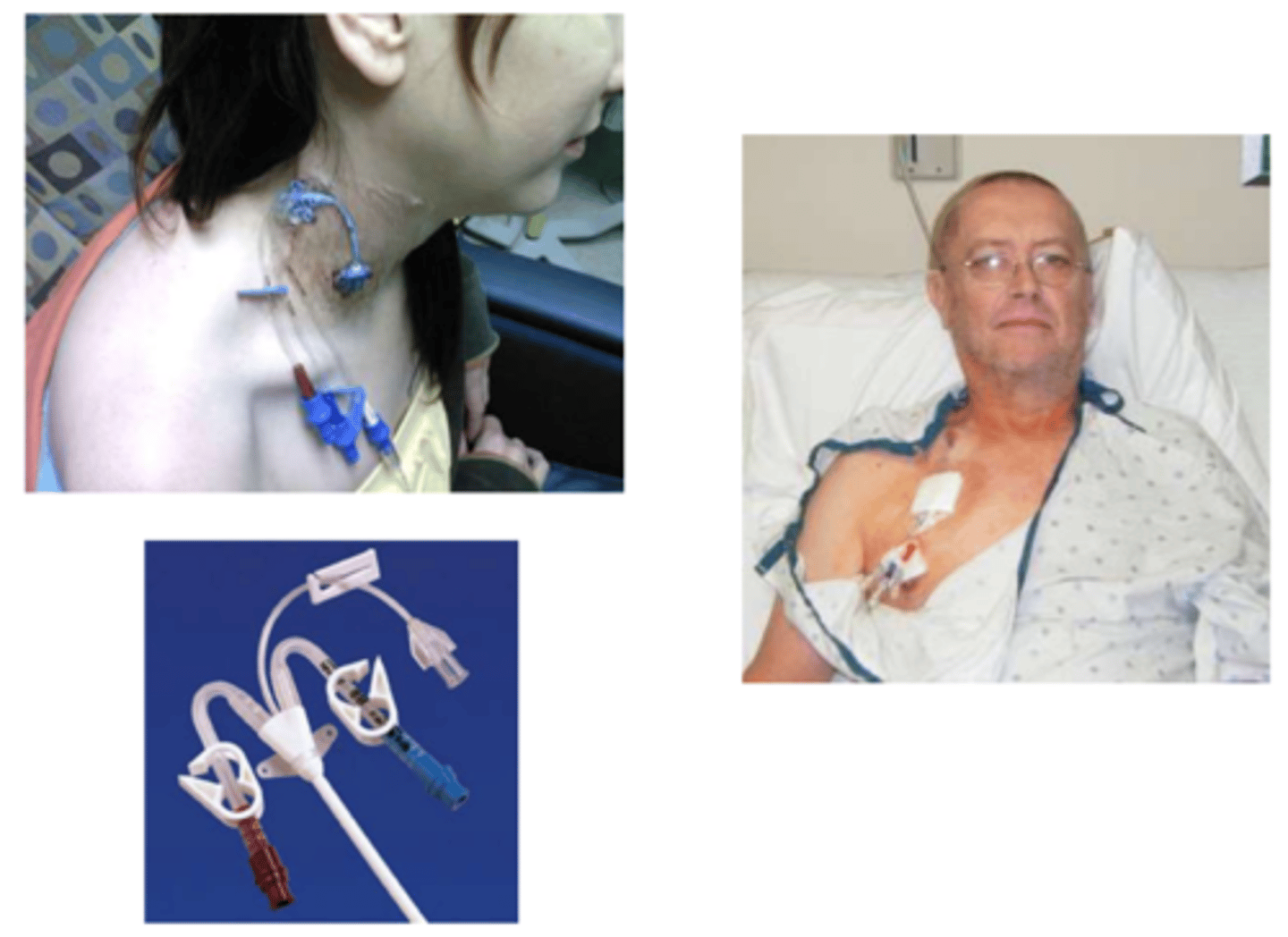
Central venous line
Used for (1) total parenteral nutrition (TPN), (2) repeated blood sampling, (3) administration drugs or fluid → Triple lumen CVL
Critical care
Central venous line is usually short-term use (2-4 weeks) but can be months; often for ____________________________ (ICU patients).
Subclavian, jugular, basilic or femoral vein
Where is central (venous) line inserted?
Superior vena cava
Where does central (venous) line terminate?
Central venous pressure (RAP)
Central (venous) line measures __________________________.
BP; x-ray; bedrest
Clinical Implications of Central (Venous) Line:
- No ______________________ on that UE
- Reduces risk of vein irritation
- ______________________ for placement → unlimited mobility
- ______________________ until cleared
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Contains all daily caloric/nutritional needs including lipids, amino acids, glucose, vitamins and dietary minerals; delivered intravenously. Made specifically for each patient, according to dietary needs. → Skips digestion, bypasses GI tract (especially useful if dysfunctional).
Vascular access port (VAP)
Port-A-Cath, Medi-Port, Pass-port, Infuse-A-Port
Subclavian or jugular veins
Where is VAP placed?
Superior vena cava
Where does VAP terminate?
6 months
VAP is for long term use >______________________ → Chemotherapy, TPN, other intermittent infusion therapy
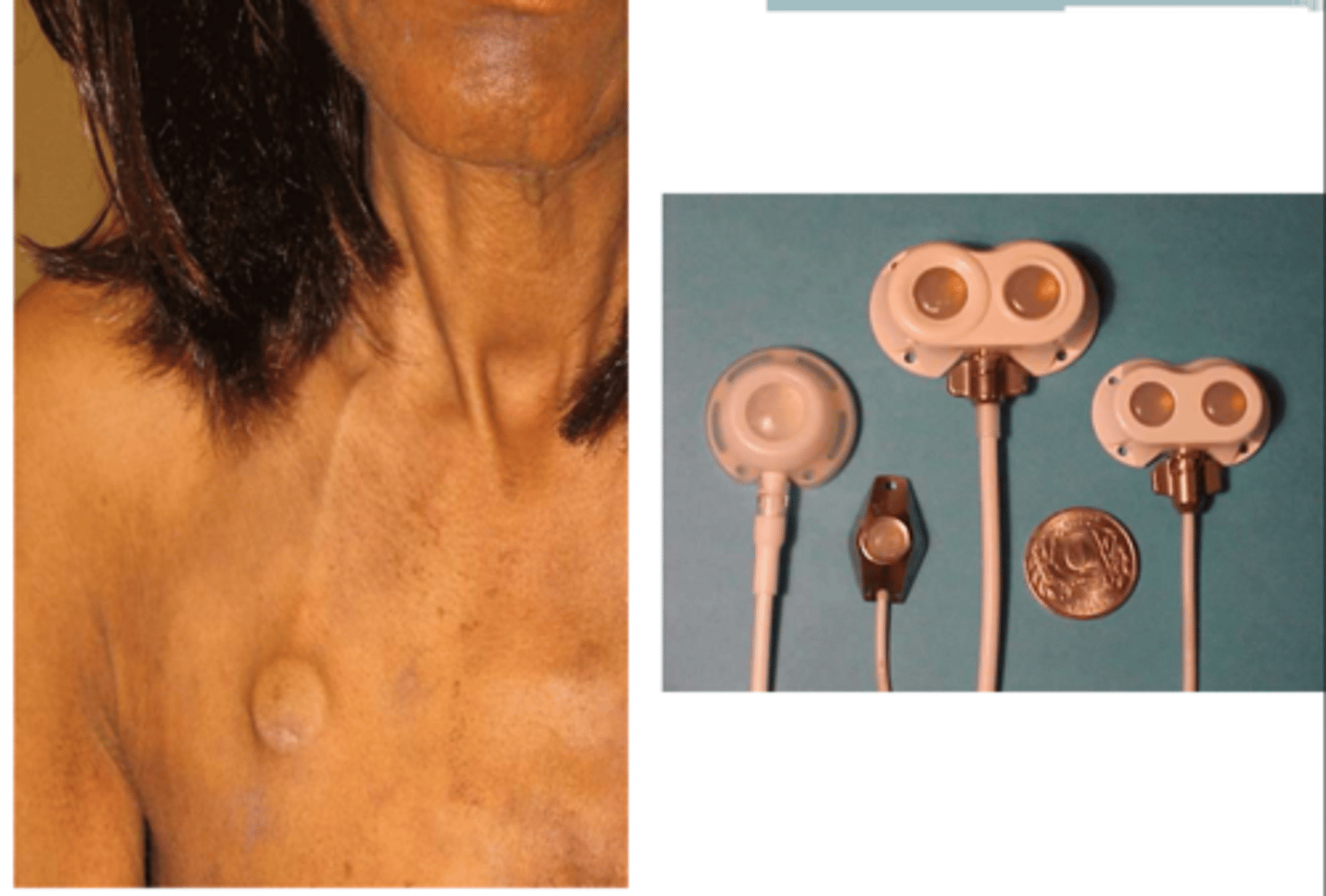
No; protrusion
Clinical Implications of VAP:
- Once healed and cleared by MD, ___________________ activity restriction
- Can bath, swim, exercise without limitation
- Slight ________________________ underneath the skin
- Can go home with a VAP
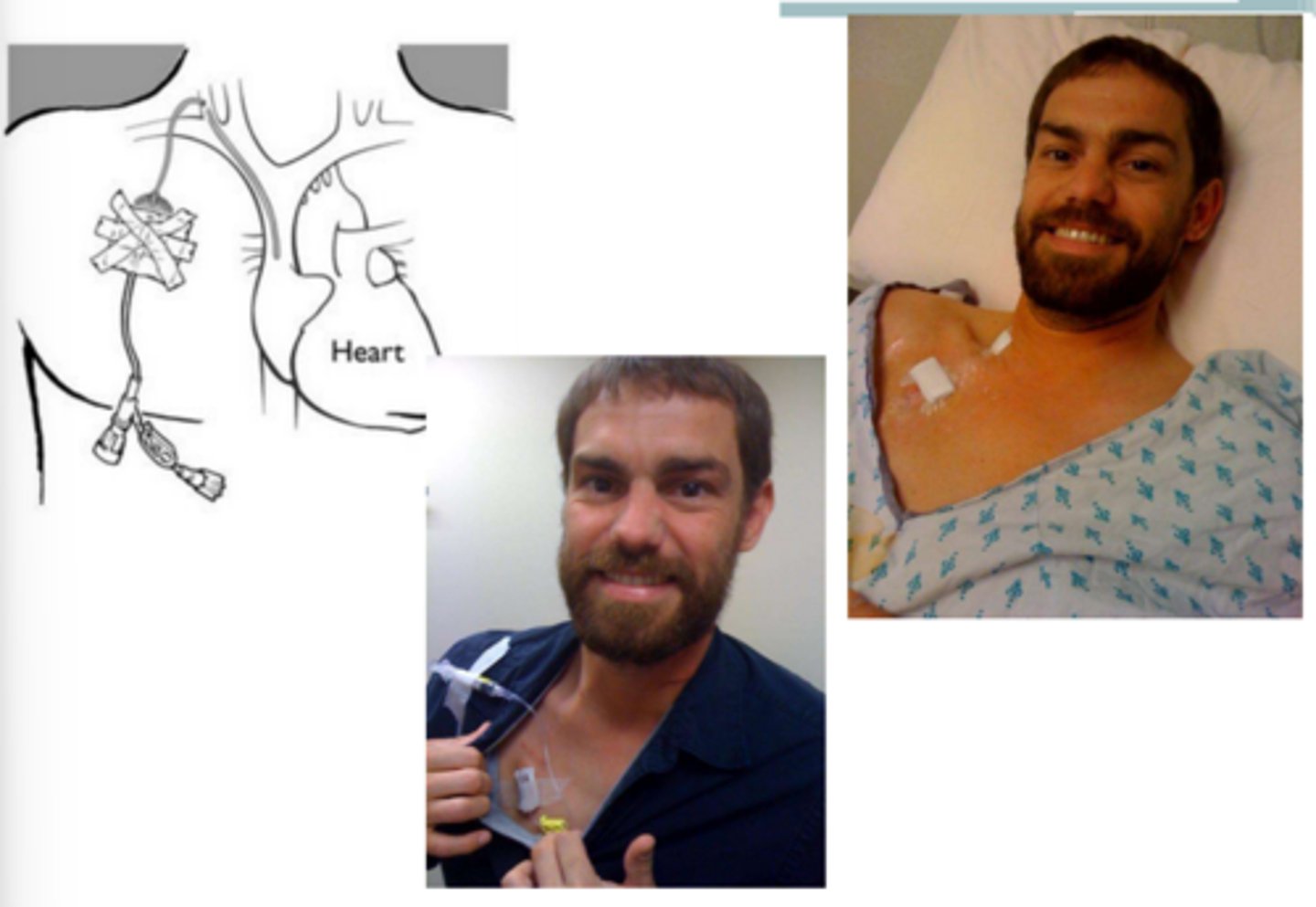
Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)
Similar to central line, different origin insertion site.
Superior vena cava
Where does PICC line terminate?
ROM; pressure; crutches; x-ray
Clinical Implications of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC):
- Repeated _______________________ at the joints of catheter insertion should be limited and/or contraindicated to prevent dislodgement and venous damage.
- If dislodged, apply immediate ______________________ and call for assistance.
- Avoid using _________________________ → Use walker
- May need _______________________ confirmation after placement.
1 week-6 months
Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line is used for midterm >_________________________ and long-term antibiotics.
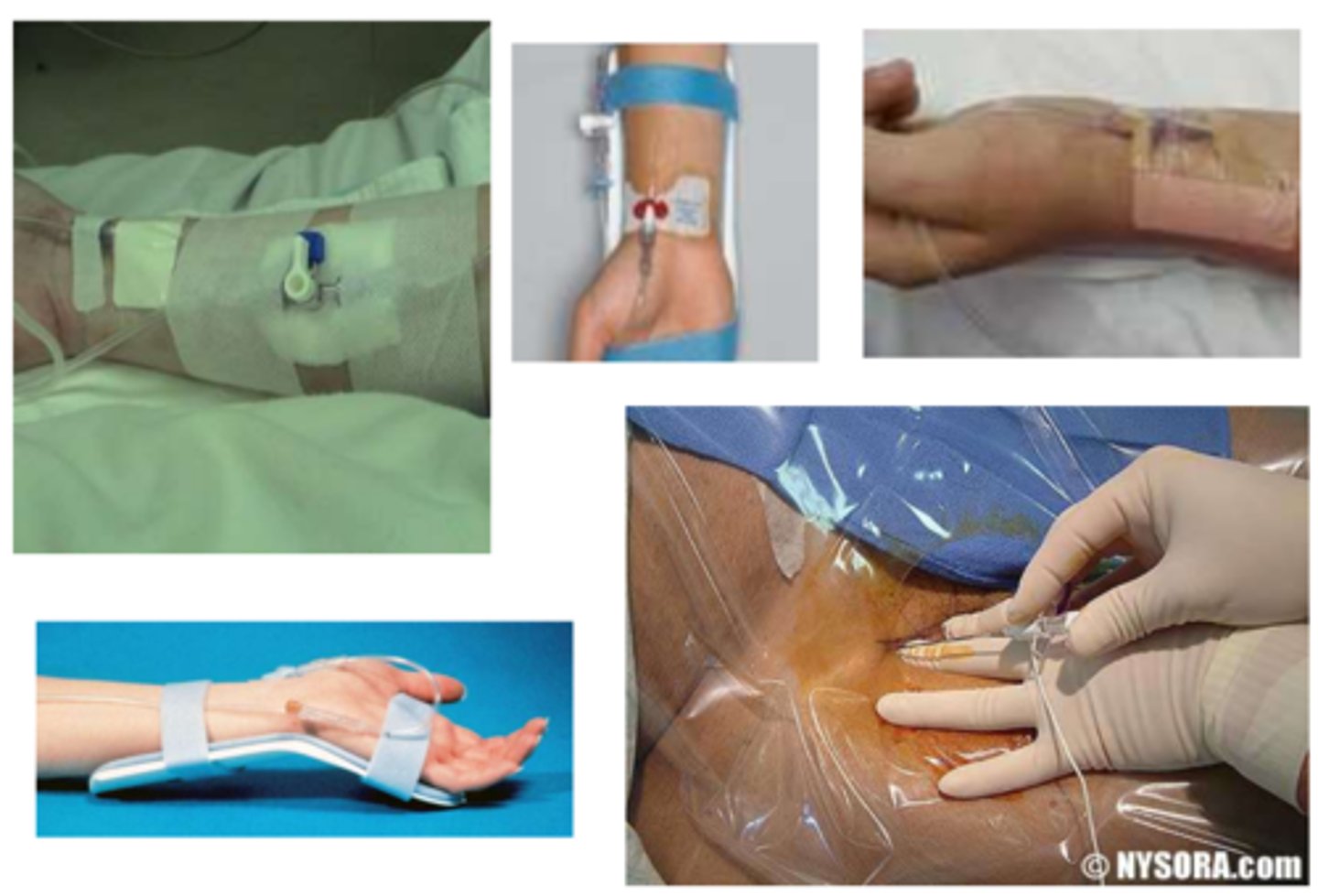
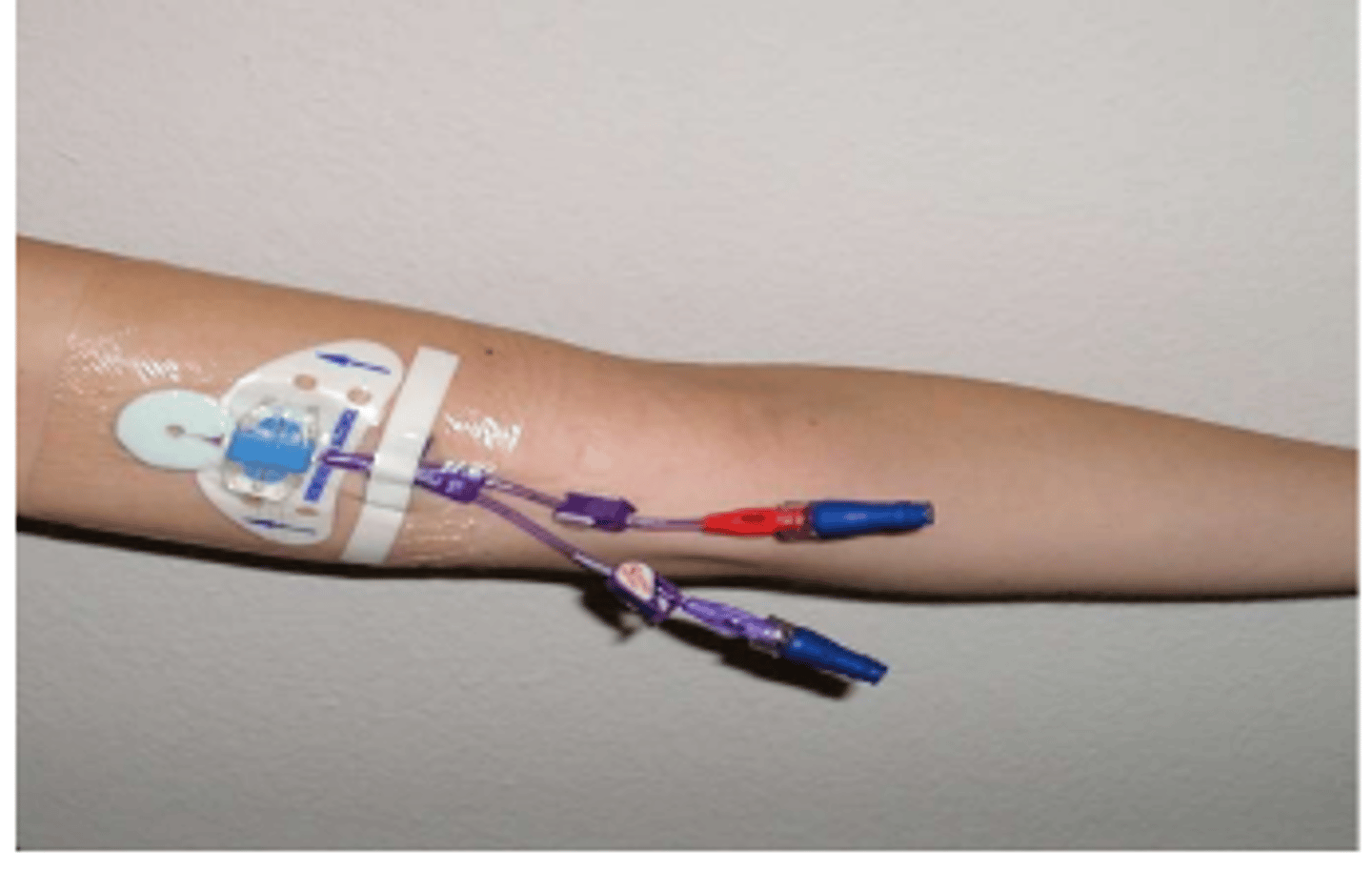
Peripheral IV lines
Temporary access for delivery of medications, fluids, electrolytes, nutrients, or blood product; rarely used for blood draw.
Superficial veins
Peripheral IV lines are placed in _______________________ and quick access.
Blood pressures; kinks
PT Implications of Peripheral IV Lines:
- No ___________________ (to avoid infiltrate of IV fluid into affected UE)
- Avoid ________________________ or occlusions when mobilizing
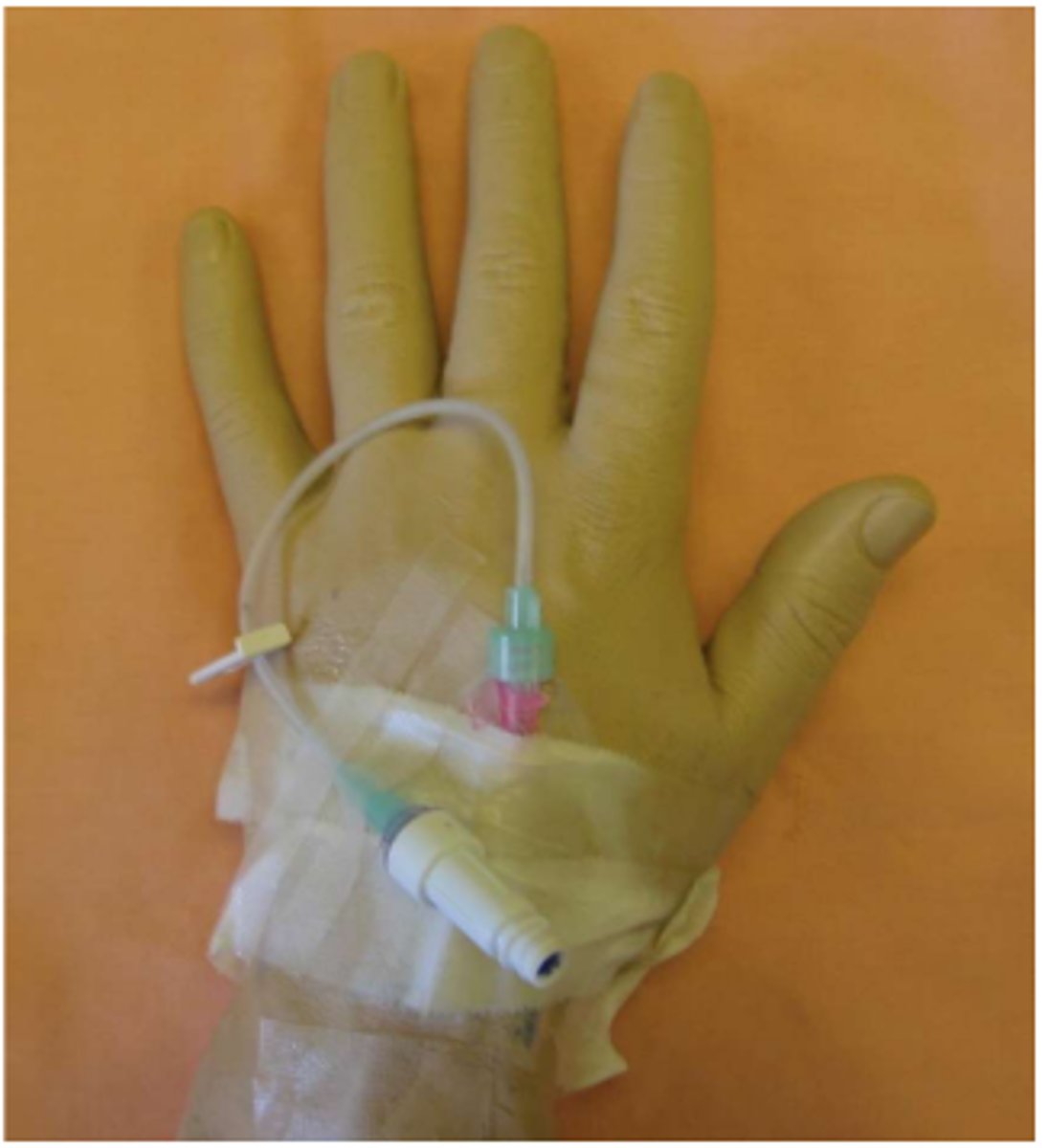
HEP-Lock (saline-lock)
There is a mechanism for the IV to be detached from the pt. Flush with heparin/saline after access.
Elbow, wrist, and foot
Where can peripheral IV lines be located?
Unlimited; infection; limit
If placed at elbow or wrist, ________________________ mobility. If placed at foot, large risk for ________________________, often painful, may ______________________ activity to SPT and exercise.
Pause
If IV lines in both arms, ______________________ flow delivery to take BP in less acute UE then re-establish flow when done. Check /c nursing first!
IV fluid infilatrate
What does the image show?
IV line with HEP-Lock
What does the image show?
IV line without HEP-Lock
What does the image show?
Nasogastric tube (NG)
Conduit to stomach to deliver food or suction.
Clamped/disconnected; nauseau; abdominal distension
Therapy Considerations for Nasogastric Tube (NG):
Review orders to determine if NG tube can be _________________________ from suction for therapy. If so, monitor for __________________________ and _________________________.
Nasoduodenal, nasojejunal
What are the other types of naso- nutritional support/feeding tubes?
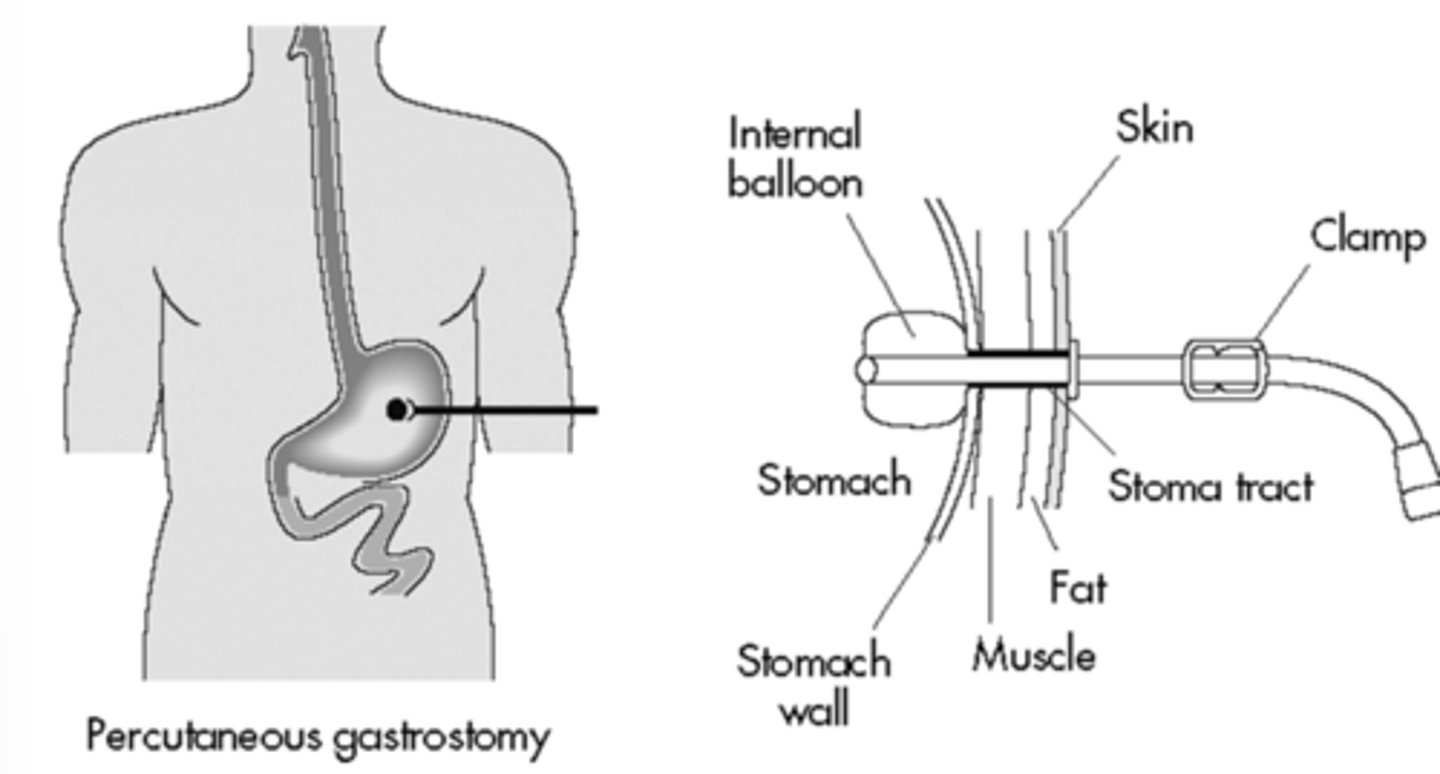
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)/jujunostomy (PEJ)
Establish access to stomach/jejunum directly from skin.
Dysphagia
PEG and PEJ tubes bypass swallowing function for patients /c ________________________.
Hold; head down; 30°
Therapy Considerations for NG, PEG, & PEJ Tubes:
- While running nutritional support, PT to _________________________ or determine if can be temporarily held.
- Avoid _______________________, Trendelenburg position.
- Typically HOB restriction >______________________.
- Ensure feeding tube is properly secured before/during/after session. → Safety pin to gown to avoid discomfort.
Nasogastric suction for bowel rest
Post-op lower GI procedure.
Chest tubes
Large catheter placed in the mediastinum, pericardium, or pleural space to drain fluid or air.
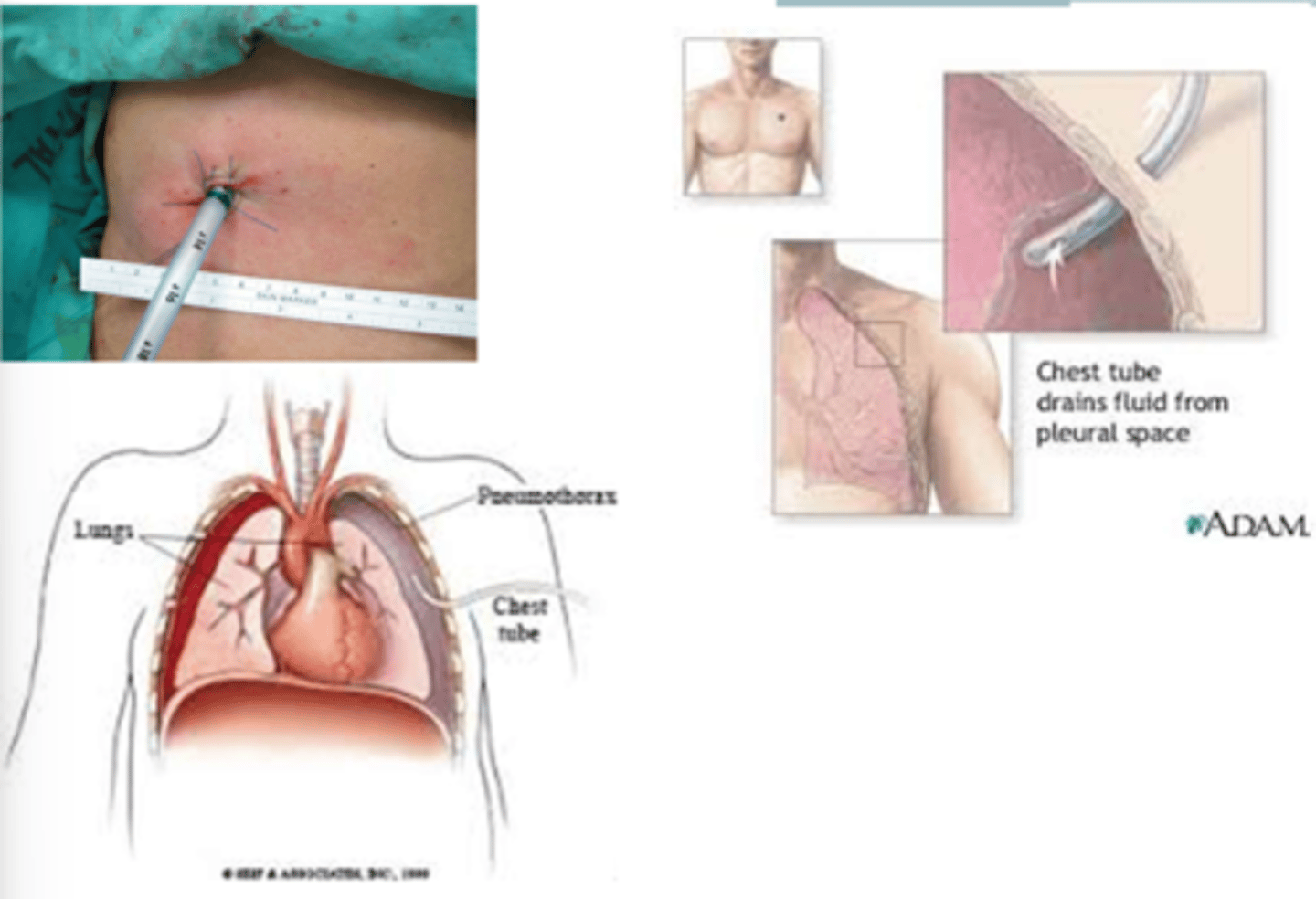
Intercostal space
Chest tubes are typically placed in __________________________.
Chest tube to water seal
Gravity drain; can take off suction. → Creates one-way valve to prevent fluid from being taken back up into lungs.
Chest tube to suction
Suction drain; cannot take off suction.
Tip over; breathing patterns; below; suction
Therapy Considerations for Chest Tubes:
- Do not ______________________ pleuroevac/drainage container
- Watch for kinks in tubing; do not sit on it
- Ensure no pulling/traction on tubing/no kinks
- Monitor ______________________ → Pre-medication prior to exercise may be helpful to encourage deep breathing
- Chest tube should be ________________________ level of insertion
- Portable _______________________ is an option
Pneumothorax; PNA
Indications for Chest Tubes:
- __________________________
- Hemothorax
- Lobectomy
- Severe _______________________
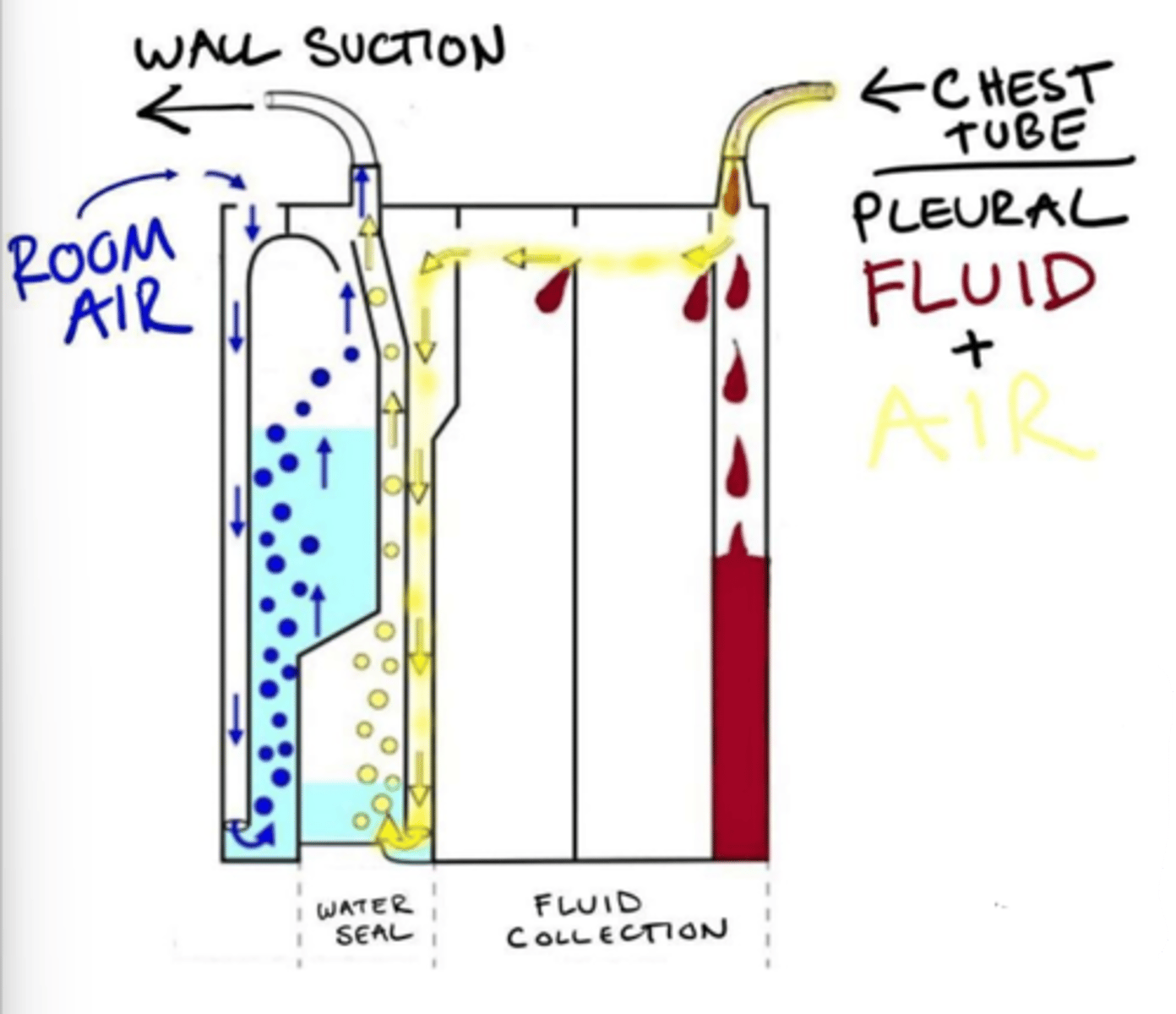
Collection chamber, underwater seal chamber, suction chamber
What are the three chambers of pleurevac container?
Collection chamber
For observation/measurement.
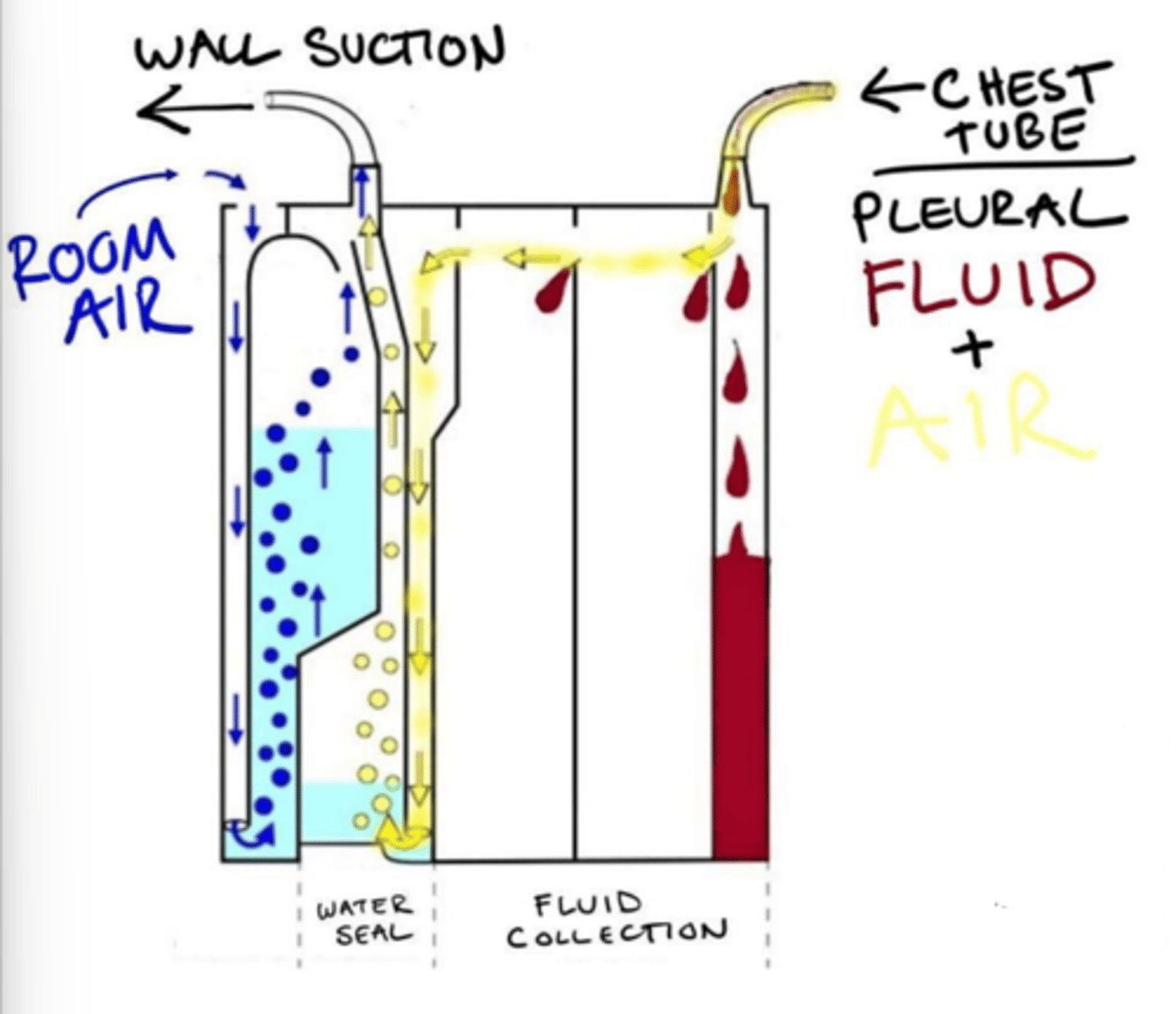
Underwater seal chamber
One-way valve displaces air/fluid from body, prevents backflow into mediastinum.
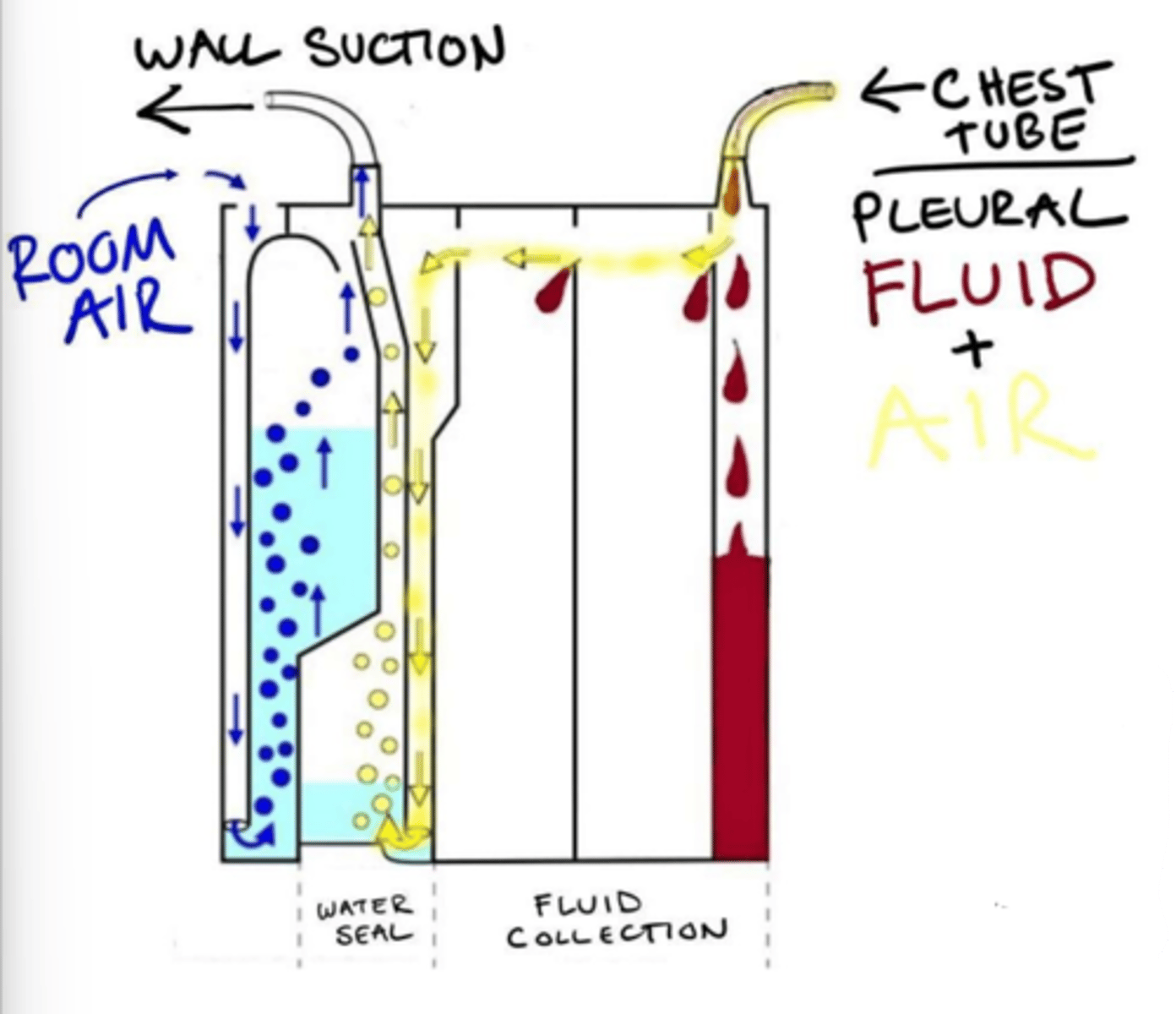
Suction chamber
Applies negative pressure - pulls fluid/air.
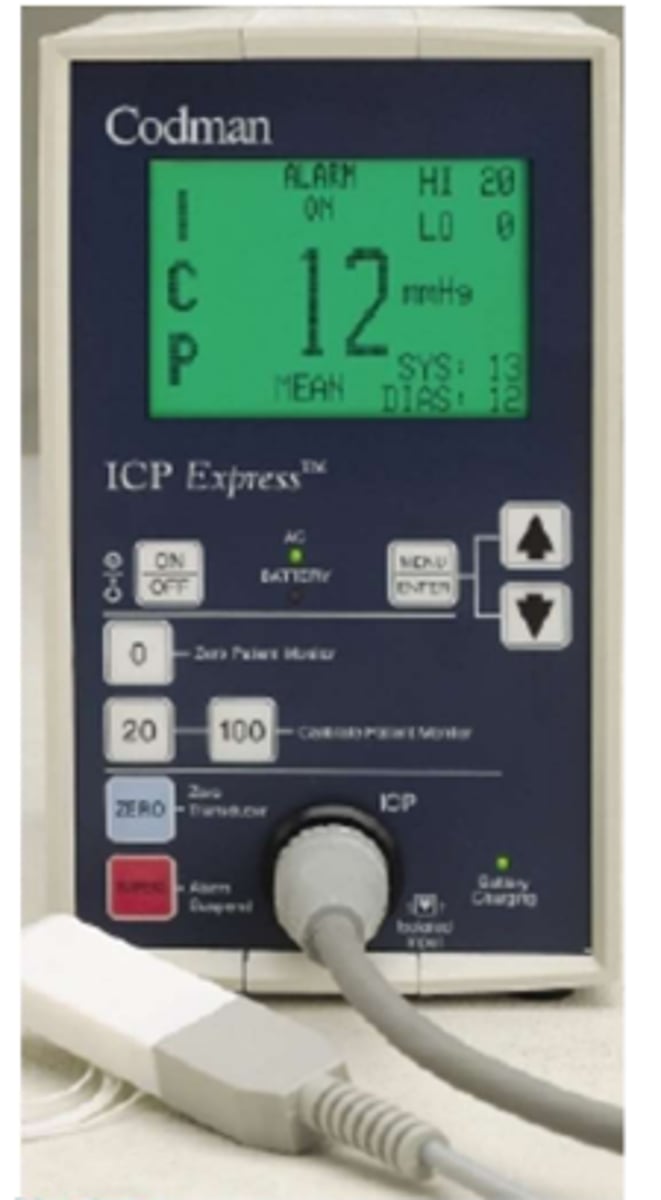
Intracranial pressure monitoring
Early ID of increased ICP prior to the occurrence of cerebral damage, provide access for CSF sampling and/or damage, and to evaluate effectiveness of med/surgical treatment.
7-15 mmHg
Normal intracranial pressure in supine.
10 mmHg
Normal intracranial pressure in standing.
>15 mmHg
Abnormal intracranial pressure.
>20 mmHg
Pathological intracranial pressure.
5 minutes; 30°; flexion; valsalva; ischemia or hypoxia
PT Implications for Intracranial Pressure:
- Momentary elevations in ICP will normally occur, sustained over _______________________ should be reported to an RN
- HOB >______________________ and avoid neck _______________________ - enhance venous drainage
- Avoid _____________________, noxious stimuli, isometric contractions
- Plateau in wave may indicate ______________________
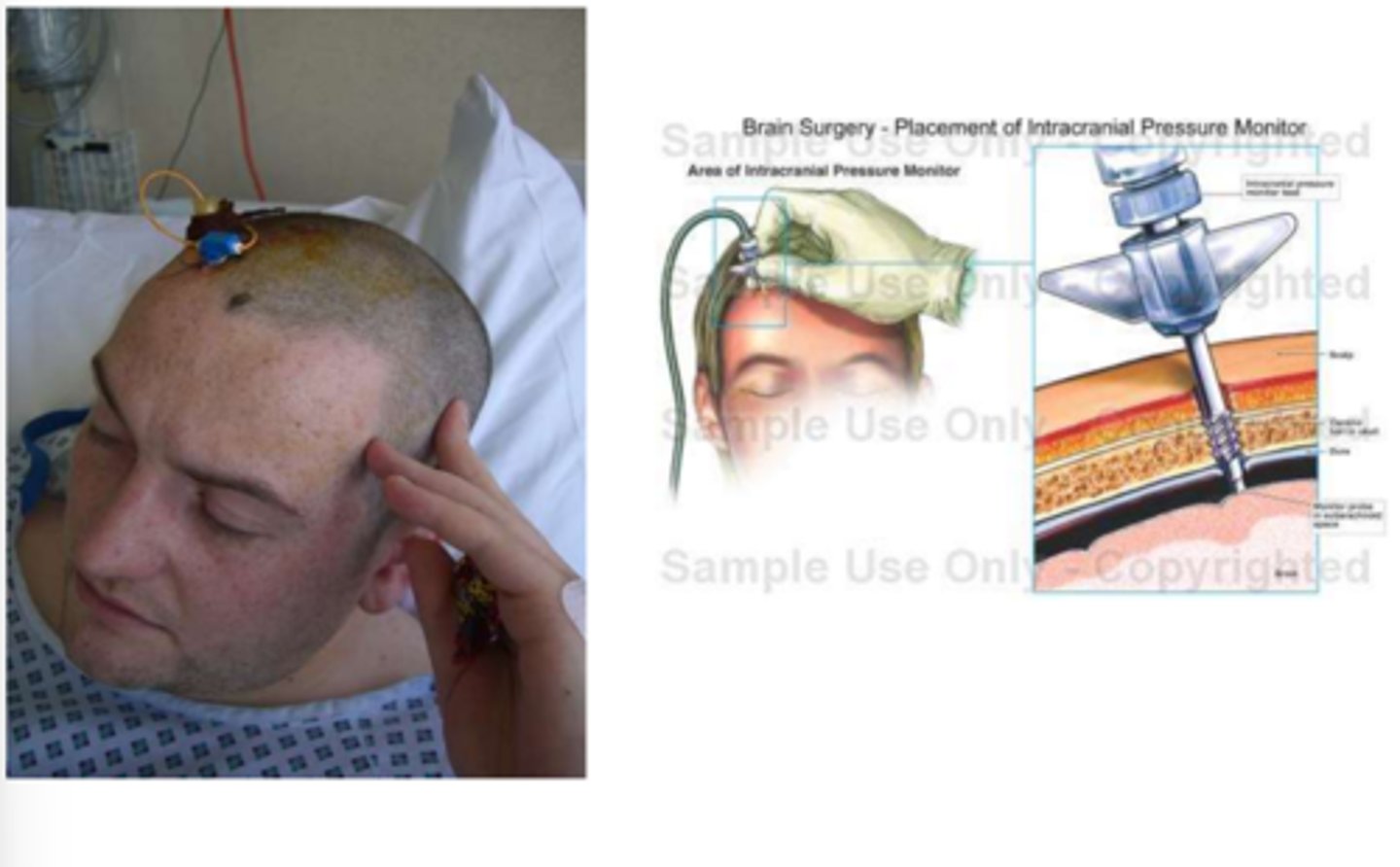
Herniation; oculomotor nerve; upper motor neuron
Signs of Increased ICP:
- Changes in consciousness → _________________________ of BS
- Abnormal pupillary reactions → __________________________ compression
- __________________________ signs → Clonus, babinski, hyperreflexia, rigidity, hemiplegia
- Nausea, vomiting, HA

Lymphedema; AV fistula; mastectomy
Do not take BP on an arterial line, ________________________, ________________________, blood clot, or an extremity ipsilateral to a _________________________. Avoid BP on extremity with a peripheral or central IV line.
Rectal pouch (fecal management system)
- Collects bowel drainage, typically liquid (used for c. diff infections)
- Protects fragile skin
- Infection control purposes
- Use draw sheet for movement to prevent dislodgement
- Keep collection bag below the level of insertion
- Easily dislodged
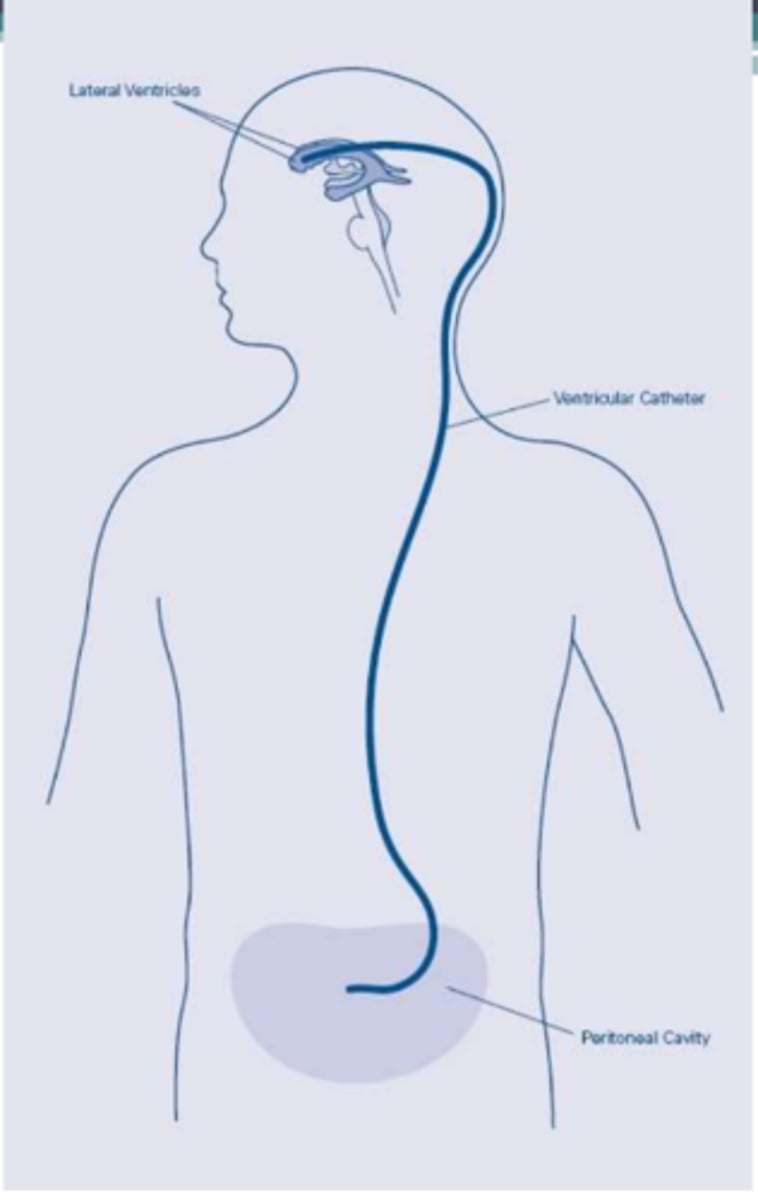
VP shunt
Redirects flow of CSF from brain to peritoneal area where it is absorbed.
VA shunt
Redirect flow to the atria.
24 hours; pressure; contralateral; blurred
Clinical Implications of VA & VP Shunts:
- Patients undergo general anesthetic
- May be on bedrest for up to ________________________
- Avoid excessive _______________________ over the shunt, palpable under skin behind ear
- Incision areas: Scalp, neck, abdominal regions
- Monitor for signs of increased ICP: Confusion, lethargy, ______________________ paresis, HA, seizure, CN palsy, diplopia, _______________________ vision
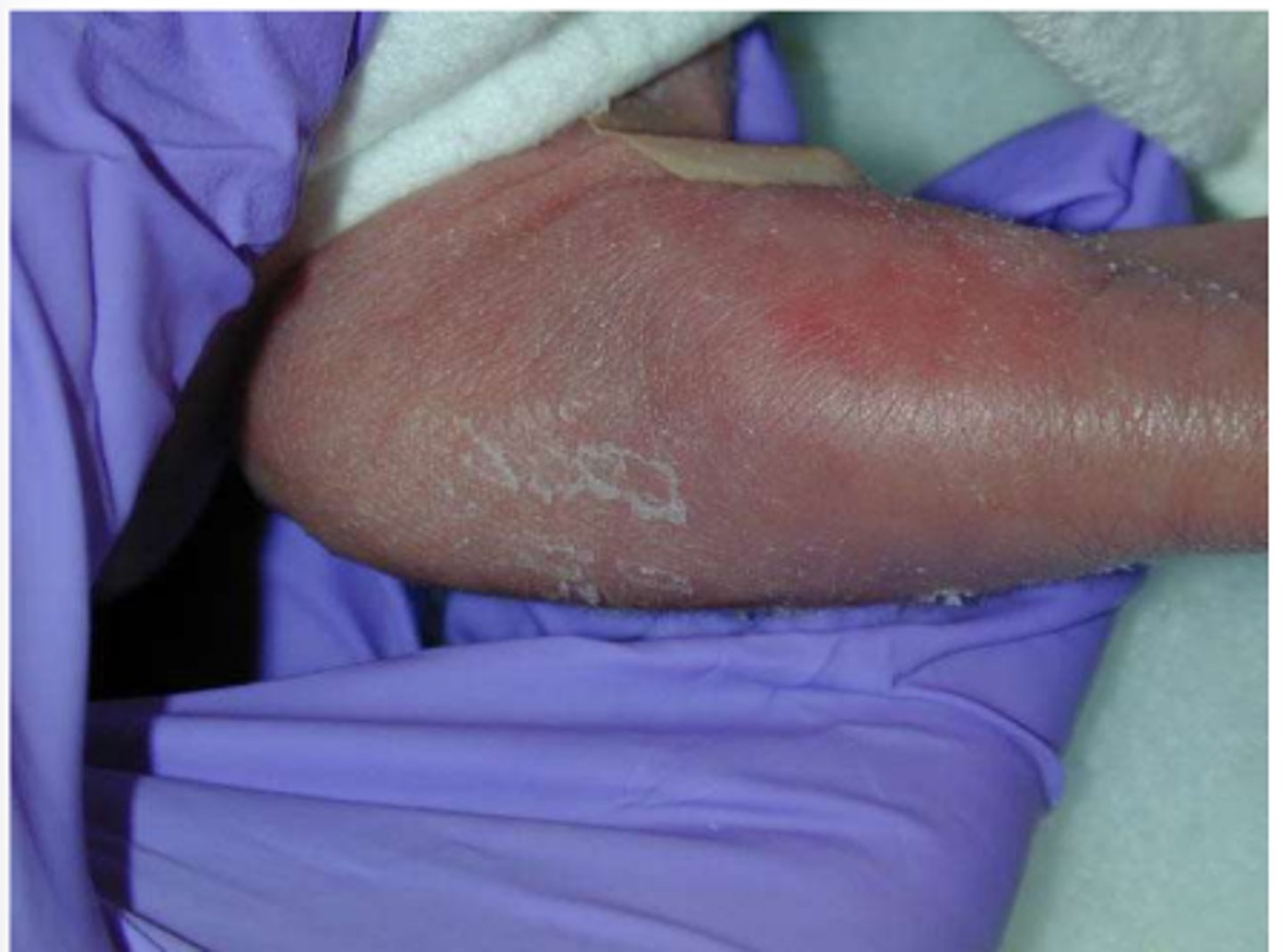
Arteriovenous graft/fistula
Access for hemodialysis; connection between an artery and a vein.
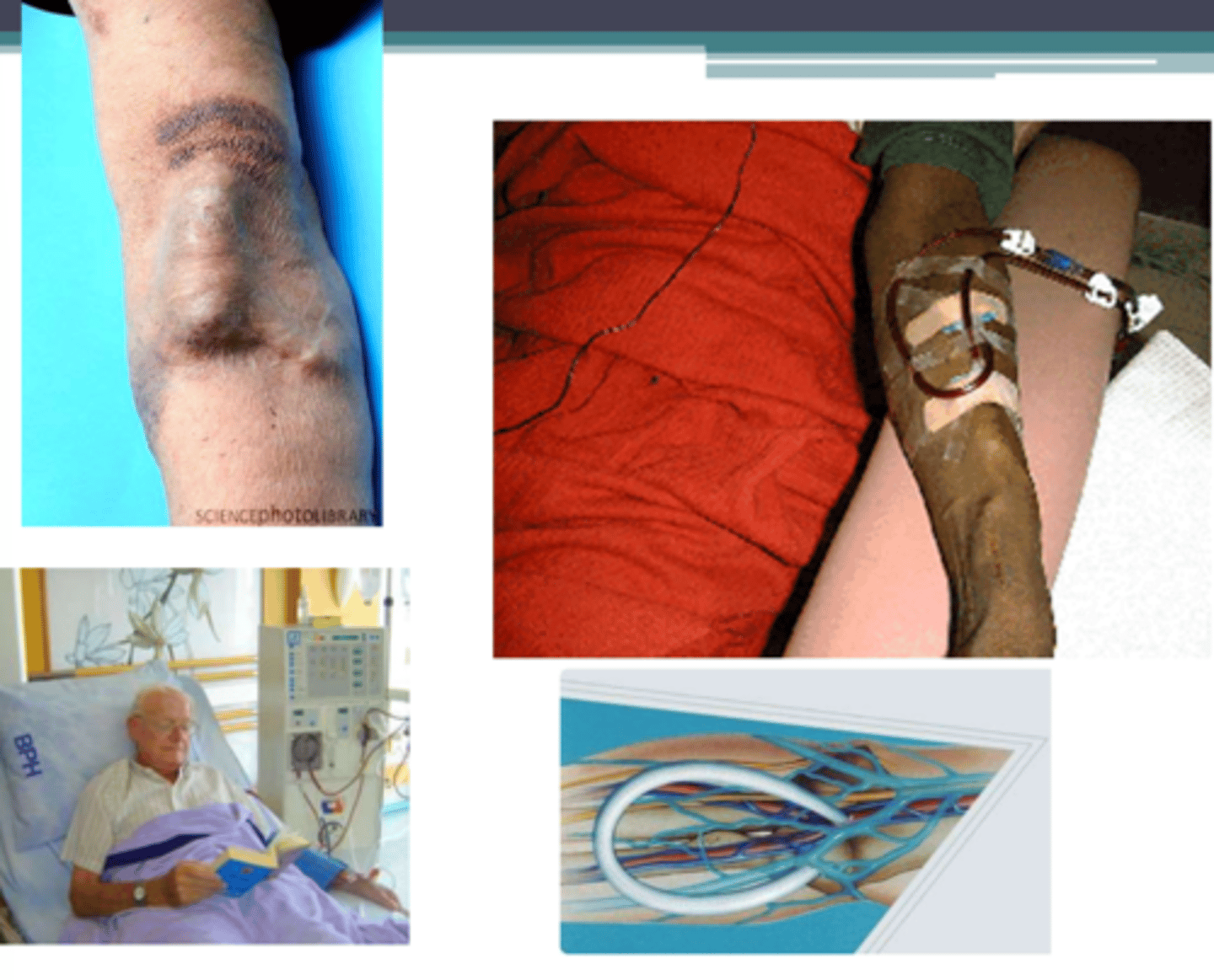
AV fistula
Direct connection between artery and vein, 2-6 months to form after surgery; uses own tissues and is therefore preferred over a graft.
AV graft
Indirect connection between artery and vein, 2-4 weeks until able to be used; most commonly a plastic tube, but donated cadaver arteries or veins can be used.
Clotting; longer
AV fistula resists _______________________ and infection, lasts _______________________.
WB; pressure
Clinical Implications of AV Fistula/Graft:
- Avoid _______________________ on extremity for 24 hours after surgical procedure.
- Avoid _____________________ or constriction over site (bending accessed limb for prolonged periods of time or tight clothing).